0 引 言
掘进机是煤矿巷道开拓的主要设备,随着快掘系统的深入应用,对井下煤矿巷道掘进的自动化提出了更高要求,掘进机的精确定位定向是其中最为关键的技术[1-2]。要从根本上改变掘进工作面的落后状态,必须解决掘进机的自主精确定位定向问题,提升掘进机的智能化水平。
目前掘进机的定位定向方法主要有激光指向仪、数字全站仪、超宽带、机器视觉、和组合惯导等[3-5]。传统的激光指向仪定位定向依赖于掘进机司机的经验,司机通过激光光斑在断面上位置来调整掘进机截割头掘进,这种掘进定位定向方法存在较大的误差。基于数字全站仪的定位方法已经广泛应用于盾构机形式的掘进机中[6-7],虽然这种方法精度高,但是对于煤矿井下复杂的地理环境,全站仪的视线将可能被挡住,无法实时获得掘进机的位置信息,并且无法检测掘进机的航向。基于超宽带的导向和定位方法采用无线电信号的测距原理对掘进机定位定向,其在一定的范围优势明显,缺点是不适合于井下长距离的掘进机定位定向[8-9]。基于视觉定位方法采用图像处理技术对掘进机的位姿解算,能非接触、实时得到掘进机的定位信息[10],但是容易受井下粉尘影响。捷联惯导系统具有自主性强、环境适应性好的特点,基于捷联惯导的井下设备定位定向方法是目前的研究热点[11-14],但是随着掘进机长时间运行,惯导系统的定位误差会逐渐累积,组合惯导的定位定向方法可以有效抑制纯惯导累积误差。视觉与惯导组合、超宽带与惯导组合等方式在掘进机定位定向应用广泛,但是视觉与惯导组合定位的精度易受煤矿井下低照度、高粉尘等掘进工作面复杂环境影响,超宽带与惯导组合定位的精度难以满足掘进机定位精度要求。
综上所述,以上掘进机的定位定向方法各有其优缺点,针对煤矿井下的复杂环境,结合数字全站仪的定位精度高和光纤惯导自主精确定位定向的优点,提出融合光纤惯导与数字全站仪的掘进机自主定位定向方法,该方法利用卡尔曼滤波算法对两者信息进行融合,实现掘进机的精确定位定向,为实现煤矿掘进机的智能化奠定良好基础。
1 定位定向系统原理
光纤惯导系统主要由陀螺仪和加速度计,以及数学解算平台等构成,它通过二次积分的方式将加速度计测量出的载体的加速度转化为位移,再将它变换到由陀螺仪建立的导航坐标系中,从而得到载体在导航坐标系中的速度、姿态角、位置信息;数字全站仪利用激光反射形成的光点,由内置CCD相机接收,其位置以CCD相机的中心作为参考点来确定[15]。光纤惯导与数字全站仪融合定位定向原理如图1所示,利用煤矿巷道设计的中线上2个地理坐标系下坐标点,数字全站仪根据这两点的坐标建立数字全站仪的坐标系,光纤惯导从而获取掘进机在地理坐标系的位置信息。通过自身的数学解算平台,输出掘进机的位姿信息。采用卡尔曼滤波方法对这两者数据进行融合,实时输出掘进机的精准位姿信息,实现掘进机的精确定位定向。

图1 基于光纤惯导与数字全站仪的组合定位定向原理
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of combined positioning and orientation of strapdown inertial navigation and digital total station
2 定位定向系统误差模型
选取光纤惯导与数字全站仪的系统误差作为定位定向的状态量、位置差值作为量测量,并采用卡尔曼滤波算法对状态量和量测量进行预测,获取二者融合后的位姿。因此,需要对光纤惯导和数字全站仪的误差进行分析与建模。光纤惯导系统误差建模已经有过很多研究[16-19],主要分析数字全站仪的误差来源与数字全站仪的误差建模。
在光纤惯导与数字全站仪的定位定向系统中,数字全站仪的位置误差直接决定了定位定向系统的精度,通过分析数字全站仪的输出位置解算公式,得出数字全站仪的误差,数字全站仪输出位置解算公式如下:
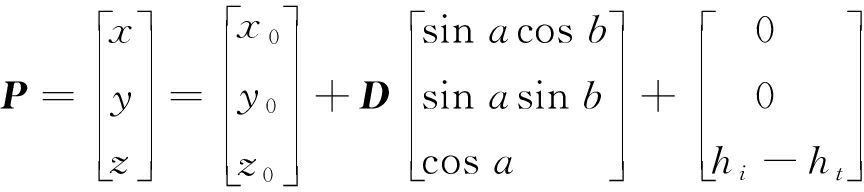
(1)
式中:x0,y0,z0为测站点的N、E、Z坐标(已知);D为斜距;a为目标点与测站点连线与z轴的夹角;b为方位角;hi为仪器高;ht为目标高。
一般测站点、仪器高和目标高为定值,而且目标点与测站点连线与z轴的夹角变化很小,误差可忽略,所以数字全站仪主要误差源为全站仪的斜距距测量误差和方位角误差。
设数字全站仪的两点斜距测量误差为mD,方位角误差δb,则测量误差公式如下:
(2)
式中:δP为数字全站仪测量误差;ρ为弧度化秒因子。
3 定位定向系统融合算法
采用融合光纤惯导与数字全站仪的定位定向算法。首先,建立定位定向的系统状态方程和量测方程;然后,利用卡尔曼滤波器进行滤波处理,由此获取光纤惯导和数字全站仪的融合位姿信息。
3.1 定位定向系统状态方程
光纤惯导与数字全站仪融合的系统状态方程主要包括:捷联惯导的数学平台姿态误差角φE、 φN、 φu,速度误差δE、δN、δu,位置误差δL,陀螺漂移δλ,加速度计误差εE、εN、εu,以及数字全站仪的位置误差∇E、∇N、∇u,如式(3)所示。
(3)
根据上述组合定位定向系统误差模型,可得到融合定位定向状态方程,如式(4)所示:
(4)
式中:F(t)、X(t)、G(t)、W(t)分别为系统状态矩阵、系统的状态、系统噪声系数阵、系统噪声。
3.2 定位定向系统量测方程
选取光纤惯导输出的位置与数字全站仪位置的差值作为量测值,设光纤惯导解算的位置和数字全站仪解算位置分别为xSINS、ySINS、xTS、yTS,则光纤惯导与数字全站仪的量测方程如下式:
Z(t)=H(t)X(t)+V(t)
(5)
式中:![]() 为量测噪声矩阵,其服从期望为0,方差为R的高斯噪声矩阵。
为量测噪声矩阵,其服从期望为0,方差为R的高斯噪声矩阵。
3.3 卡尔曼滤波器设计
根据上述融合定位定向系统的状态方程和量测方程,采用卡尔曼滤波算法将光纤惯导与数字全站仪信息融合,得到准确的定位定向信息,卡尔曼算法流程如下:
1)将上述融合系统的状态量与量测量离散化处理,获得离散型状态方程和量测方程,如式(6)所示:
(6)
式中:A为状态转移矩阵;xk-1,xk分别为k-1和k时刻的状态量;uk为k时刻系统的输入量;wk为过程状态噪声,服从均值为0,方差为Q的正态分布;B为输入增益矩阵;zk为k时刻观测量;H为测量矩阵;vk为量测噪声,服从均值为0,方差为R的正态分布。
2)根据系统上一时刻的状态量预测下一时刻的状态量,公式如下:
(7)
式中:![]() 为第k时刻的状态预测量;uk-1为k-1时刻系统的输入量;
为第k时刻的状态预测量;uk-1为k-1时刻系统的输入量;![]() 为第k-1时刻的状态估计值;Pk-1为k-1时刻估计误差协方差矩阵;
为第k-1时刻的状态估计值;Pk-1为k-1时刻估计误差协方差矩阵;![]() 为预测误差协方差阵。
为预测误差协方差阵。
3)利用数字全站仪和光纤惯导的位置差值作为量测量来校正融合定位定向系统的位置误差,达到融合目的,公式如下:
![]()
![]()
![]()
(8)
其中:![]() 为k时刻的量测估计值;zk为k时刻的量测量真实值;Kk为卡尔曼增益(权重);R为方差,而且R值一般为确定值,与传感器的精度相关。
为k时刻的量测估计值;zk为k时刻的量测量真实值;Kk为卡尔曼增益(权重);R为方差,而且R值一般为确定值,与传感器的精度相关。
4)协方差进行更新,公式如下:
(9)
4 试验验证与分析
搭建如图2所示的光纤惯导与数字全站仪的定位定向试验平台,主要包括光纤惯导,数字全站仪,360°棱镜、协同控制器、开关电源和上位机等。高精度的光纤惯导和数字全站仪主要参数见表1。

图2 定位定向试验平台
Fig.2 Experimental platform of positioning and orientation
表1 光纤惯导与数字全站仪的主要参数
Table 1 Main parameters of fiber optic inertial navigation and digital total station

型号主要参数光纤惯导(MG045)姿态精度≤0.01(°)/h加速度精度≤5×10-5 g航向保持精度≤0.01(°)/h数字全站仪(iX1001)定位精度≤0.01 m
模拟井下掘进的实际情况,取巷道中线上2点,并利用这两点建立数字全站仪的坐标系,此时数字全站仪输出的位置即反映了掘进机在井下掘进巷道坐标系(地理坐标系)的坐标值,从而将光纤惯导的导航坐标系(地理坐标系)与数字全站仪建立的坐标系进行统一。在这次试验中,将这2点连线作为x轴(与巷道中线平行),与之垂直的方向为y轴,建立坐标系o-x-y-z,并以掘进机机身的中线为x1轴,与之垂直的方向为y1,建立载体坐标系o1-x1-y1-z1,掘进机在oxy平面的转动角为航向角,掘进机在oyz平面的转动角为横滚角,掘进机在oxz平面的转动角为俯仰角,如图3所示。棱镜和惯导放在一起,首先进行光纤惯导初始对准,然后掘进机前进,通过无线路由器实时将协同控制器获得的数字全站仪位置发送给惯导系统进行融合,最后输出两者融合的位置和姿态信息。

图3 定位定向坐标系示意
Fig.3 Schematic of positioning and orientation coordinate system
本次试验分为2个部分进行验证:
1)如图2所示,运用光纤惯导静止2 h输出的姿态角变化情况如图4、5、6所示,试验结果表明:航向角、俯仰角和横滚角检测误差小于0.005°,能够提供准确的定向信息。

图4 俯仰角变化
Fig.4 Change of pitch angle

图5 横滚角变化
Fig.5 Change of roll angle

图6 航向角变化
Fig.6 Change of heading angle
2)通过GNSS卫星定位接收机检测得到初始位置为:x0=3 818 661.12 m,y0=592 377.82 m,z0=
346.47 m。融合定位系统中方差R值对融合定位精度影响很大,为验证R值对融合定位精度的影响,将数字全站仪的定位精度的平方作为组合惯导系统的量测量的方差R值。分别采用R=0.12和R=0.012两种方差对掘进机直线行驶进行定位对比试验,其中R=0.012为数字全站仪的定位精度,选取部分采样点进行分析,试验结果分别如图7和图8所示。通过图7与图8的x方向、y方向定位对比可以得出:根据数字全站仪的定位精度确定方差R值后,光纤惯导与数字全站仪融合后的x方向误差在3 cm以内,y方向的误差在2 cm以内,能够实现掘进机精确定位。

图7 x方向位置解算对比
Fig.7 Comparison of position calculation in x direction


图8 y方向位置解算对比
Fig.8 Comparison of position resolution in y direction
通过上述数据分析,基于光纤惯导与数字全站仪的掘进机的定位定向方法,克服了纯惯导定位误差发散和数字全站仪的无法实时获取掘进机位置信息等问题,实现了掘进机的自主精确定位定向。
5 结 论
1)针对掘进机自主定位定向不准确问题,提出了一种基于光纤惯导与数字全站仪组合的自主定位定向方法,该方法发挥了数字全站仪和光纤捷联惯导的各自优势,实现了掘进机的自主定位定向。
2)通过建立光纤惯导与数字全站仪组合定位定向系统的状态方程和量测方程,以及运用卡尔曼滤波器对系统的状态量与量测量进行预测,可以获得惯导与数字全站仪融合后的位姿信息。
3)根据数字全站仪定位精度确定系统量测量的噪声方差R值,可以获得最佳的融合定位定向精度,定位误差小于3 cm,定向误差小于0.005°,能够实现掘进机精确定位定向,对提升掘进工作面的智能化水平奠定了良好基础。
[1] 王步康.煤矿巷道掘进技术与装备的现状及趋势分析[J].煤炭科学技术,2020,48(11):1-11.
WANG Bukang. Current status and trend analysis of coal mine driving technology and equipment[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2020, 48(11):1-11.
[2] 卢新明,闫长青,袁照平. 掘进机精准定位方法与掘进机器人系统[J]. 通信学报,2020,41(2):58-65.
LU Xinming,YAN Changqing,YUAN Zhaoping. Precise positioning method of tunneling machine and tunneling robot system[J]. Journal of Communications,2020,41(2):58-65.
[3] 王国法,刘 峰,庞义辉,等. 煤矿智能化:煤炭工业高质量发展的核心技术支撑[J]. 煤炭学报,2019,44(2):5-13.
WANG Guofa,LIU Feng,PANG Yihui,et al. Coal Mine Intelligence:Core Technology Support for High Quality Development of Coal Industry[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2019,44(2):5-13.
[4] 田 原. 悬臂式掘进机自动定位技术研究与试验[J]. 矿山机械,2019,47(7):6-10.
TIAN Yuan. Research and test of automatic positioning technology of cantileverroadheader[J]. Mining Machinery,2019,47(7):6-10.
[5] 邓国华.基于激光导向器的悬臂式掘进机位置姿态自动测定方法[J].工矿自动化,2009,35(9):20-23.
DENG Guohua.An automatic detecting method for position and posture of boom-type roadheader based on laser guide[J].Industry and Mine Automation.2009,35(9):20-23.
[6] 唐争气,赵俊三,彭国新. 盾构机实时姿态测量和计算方法的研究[J]. 土木工程学报,2007,40(11):101-106.
TANG Zhengqi,ZHAO Junsan,PENG Guoxin. Research on real-time attitude measurement and calculation method of shield machine[J]. Journal of Civil Engineering,2007,40(11):101-106.
[7] 朱信平,李 睿,高 娟,等. 基于全站仪的掘进机机身位姿参数测量方法[J]. 煤炭工程,2011,43(6):121-123.
ZHU Xinping,LI Rui,GAO Juan,et al. Measurement method of body position and attitude parameters of roadheader based on total station[J]. Coal Engineering,2011,43(6):121-123.
[8] 符世琛,李一鸣,杨健健,等. 基于超宽带技术的掘进机自主定位定向方法研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2015,254(11):107-114.
FU Shichen,LI Yiming,YANG Jianjian,et al. Research on autonomous positioning and orientation method of roadheader based on ultra-wideband technology [J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2015,254(11):107-114.
[9] 崔 柳,徐会军,刘治翔,等.基于超宽带定位的掘进机姿态监测仿真与实验研究[J].煤炭学报,2017,42(S1):267-274.
CUI Liu,XU Huijun,LIU Zhixiang,et al.Simulation and experiment on the attitude monitoring of roadheader based on ultra wide band[J].Journal of China Coal Society,2017,42(S1):267-274.
[10] 杜雨馨,刘 停,童敏明,等. 基于机器视觉的悬臂式掘进机机身位姿检测系统[J]. 煤炭学报,2016(11):2897-2906.
DU Yuxin,LIU Ting,TONG Minming,et al. Machine posture detection system of cantilever roadheader based on machine vision[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2016(11):2897-2906.
[11] 薛光辉,张云飞,候称心,等. 基于激光靶向扫描的掘进机位姿测量方法[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2020,48(11):19-25.
XUE Guanghui,ZHANG Yunfei,HOU Chenxin,et al. Measurement of roadheader position and posture based on orientation laser scanning[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2020,48(11):19-25.
[12] 黄 东,杨凌辉,罗 文,等. 基于视觉/惯导的掘进机实时位姿测量方法研究[J]. 激光技术,2017(41):23.
HUANG Dong,YANG Linghui,LUO Wen,et al. Research on real-time position and attitude measurement method of roadheader based on vision/inertial navigation [J]. Laser Technology,2017(41):23.
[13] 冯大龙. 捷联式惯导系统在无人掘进机中的应用[D]. 重庆:重庆大学,2007.
FENG Dalong. Application of strapdown inertial navigation system in unmanned tunneling machine [D]. Chongqing:Chongqing University,2007
[14] GREEN J,HLOPHE K. Underground mine navigation using an integrated IMU/TOF system with unscented Kalman filter[C]// International Conference of Cad/cam,2011.
[15] 马宏伟,姚 阳,薛旭升,等.基于多传感器组合的钻锚机器人机身定位方法研究[J].煤炭科学技术,2021,49(1):278-285.
MA Hongwei,YAO Yang,XUE Xusheng,et al.Research on body positioning method of drill-anchor robot based on multi-sensor combination[J].Coal Science and Technology,2021,49(1):278-285.
[16] 毛玉良,陈家斌,宋春雷,等. 捷联惯导姿态误差模型分析[J]. 中国惯性技术学报,2013,21(2):48-51.
MAO Yuliang,CHEN Jiabin,SONG Chunlei,et al. Analysis of Strapdown Inertial Navigation Attitude Error Model [J]. Chinese Journal of Inertial Technology,2013,21(2):48-51.
[17] 邱宏波,周章华,李 延. 光纤惯导系统高阶误差模型的建立与分析[J]. 中国惯性技术学报,2007,15(5):26-31.
QIU Hongbo,ZHOU Zhanghua,LI Yan. The establishment and analysis of high-order error model of fiber optic strapdown inertial navigation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Inertial Technology,2007,15(5):26-31.
[18] 张小跃,杨功流,张春熹. 捷联惯导/里程计组合导航方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报,2013,21(7):73-77.
ZHANG Xiaoyue,YANG Gongliu,ZHANG Chunxi. Strapdown Inertial Navigation/Odometer Integrated Navigation Method[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,2013,21(7):73-77.
[19] 秦永元. 惯性导航[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2006.
QIN Yongyuan. Inertial navigation[M]. Beijing:Science Press,2006.
[20] 范百兴,谢孟利,杨再华,等. 工业测量全站仪坐标测量精度检定方法[J]. 测绘科学技术学报,2015(3):226-230.
FAN Baixing,XIE Mengli,YANG Zaihua,et al. Verification Method of Coordinate Measuring Precision of Industrial Surveying Total Station [J]. Journal of Surveying and Mapping Science and Technology,2015(3):226-230.
