0 引 言
近年来,大采高综合机械化采煤工艺在厚煤层开采中得到了广泛的应用[1]。大采高工作面工作强度大,产煤效率高,同时产尘强度也大。尘源主要来自于截割煤尘、移架煤尘和冲击煤尘[2]。为了保障采煤工作面安全高效地开采,目前大采高工作面多采用采煤机内外喷雾、液压支架顶部喷雾、行人空间移架降架喷雾、煤尘注水等综合防尘措施,大幅降低了采煤工作面的粉尘质量浓度[3-8]。然而对于可吸入煤尘,其降尘效果仍不是很理想[9-10]。为此许多学者对采煤工作面粉尘的运移规律、分布特征以及降尘措施等进行了深入研究,并取得了许多研究成果。徐青云等[11]采用FLUENT软件建立数值模型,对移架及截割两个产尘工序进行了模拟分析,研究了多尘源影响下的大采高综采工作面风流-粉尘的分布规律。许圣东[12]、陈芳[13]以神东补连塔煤矿8 m大采高综采工作面为依据,考虑开采空间设备的阻碍作用,运用CFD模拟方法建立模型,分析了大采高综采工作面风流及呼吸性粉尘的分布特征。苏士龙等[14]在大采高工作面布置测点进行了粉尘质量浓度实测,得到了大采高工作面PM10和PM5粉尘分布特征。孔阳等[15]采用FLUENT软件对综采工作面粉尘弥散规律进行模拟分析,发现综采工作面风流存在“两区一带”的规律,并确定了粉尘重点防护区。崔向飞等[16]分别在神东补连塔煤矿7 m大采高综采工作面的人行道、中心工作面、煤壁处布置测点,对风速、粉尘质量浓度进行了测量,并对大采高工作面除尘措施进行了改造,取得了较好的应用效果。杜善周等[17]采用CFD软件模拟了大采高综采工作面的粉尘分布特征,同时在采煤机上加装机载除尘器,模拟分析了机载除尘器对工作面粉尘的净化效果。目前,关于大采高工作面粉尘分布规律及降尘措施的研究,已取得了较多的研究成果[18]。然而对于大采高综采工作面截割可吸入煤尘的分布特征及降尘措施研究较少。而从职业危害的角度考虑[19],PM10为可吸入粉尘,粒径小于等于10 μm,进入人体后可沉积在上呼吸道;PM5为呼吸性粉尘,粒径小于等于5 μm,可到达呼吸道深处及肺泡区,对人体危害极大。而PM2.5可深入肺泡,一旦进入人体很难再通过呼吸排除,是造成尘肺病的根本原因。
为此,笔者以山西临汾某矿大采高综采工作面为例,在前后滚筒附近设置测点,分别监测顺风和逆风情况下采煤机前后滚筒附近截割产生的PM10,PM5和PM2.5,分析截割可吸入煤尘的分布特征,同时通过在进风巷安装表面活性剂添加装置,为采煤工作面提供添加了表面活性剂的降尘用水,以提高截割煤尘的降尘效率,取得了较好的应用效果。
1 大采高综采工作面概况
山西临汾某矿2103工作面所采煤层为2号煤层,煤层整体向北西倾斜,倾角-2°~6°,一般为2°。煤层局部节理发育,普氏硬度为1.6,属稳定煤层。煤厚为5.38~7.08 m,平均为6.03 m。工作面采用走向长壁后退综合机械化一次采全高的采煤方法,采用MG900/2300-WD型采煤机落煤,截深为0.8 m。工作面采高为6.0 m,滚筒直径为3.2 m。采煤机牵引速度为1.14~1.53 m/min。工作面共布置139台支架,最大支护高度为6.5 m,最小支护高度为2.9 m。工作面采用一进一回“U”型通风方式,平均风速为1.2 m/s。目前工作面所采用的防尘措施有:巷道净化水幕、捕尘网、转载点喷雾、采煤机内外喷雾、支架喷雾、巷道洒水、粉尘清扫、个体防护等。
2 大采高综采工作面截割煤尘测点布置
为研究大采高综采工作面截割煤尘分布特征,分别在采煤机前后滚筒附近布置煤尘监测点,测量顺风情况下和逆风情况下大采高综采工作面PM10,PM5,PM2.5的粉尘质量浓度,测点布置如图1所示。测量时采煤机运行至工作面中部,即前后两滚筒分别在65号和75号支架附近,测点布置沿风流风向依次布置,因此在顺风情况下,测点1位于采煤机后滚筒附近,测点2位于采煤机前滚筒附近;逆风时,测点1位于采煤机前滚筒附近,测点2位于采煤机后滚筒附近。测量仪器选用SidePak AM520i型个体暴露粉尘仪。该仪器可实时显示并记录PM10、PM5、PM2.5质量浓度。
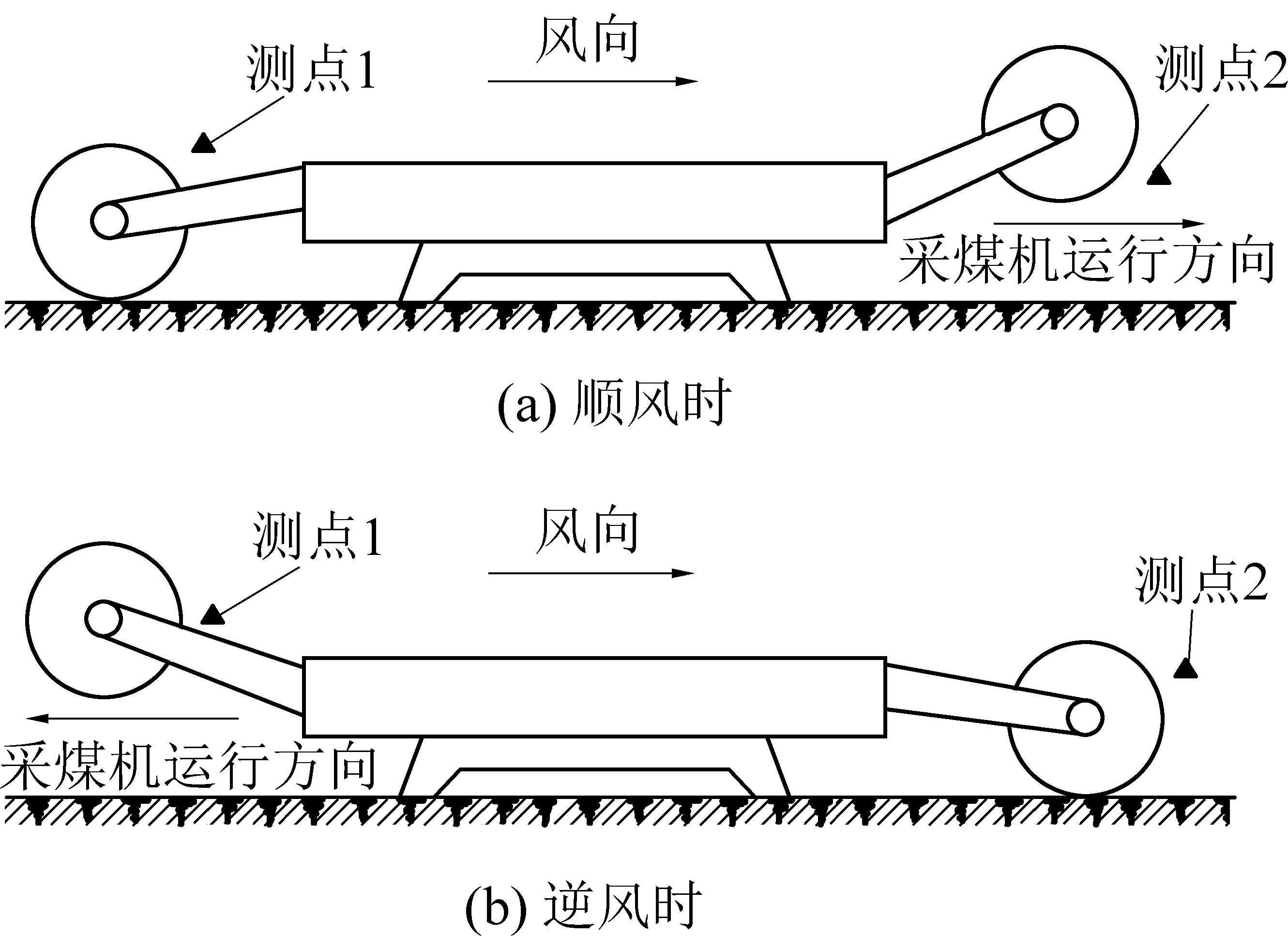
图1 采煤机截割煤尘监测点布置
Fig.1 Position of coal dust monitoring points for
cutting process of shearer
3 截割可吸入煤尘分布特征分析
为保障粉尘监测数据的可靠性,将SidePak AM520i型个体暴露粉尘仪放置于测点位置,静置1 min,待数据稳定后开始监测。监测时间为1 min,每秒记录一次数据,共60组数据,将监测数据绘制成曲线,如图2—图4所示。
由图2可以看出,顺风时,测点1(后滚筒)实时监测的PM10粉尘质量浓度在411~813 mg/m3范围内波动,均值为561 mg/m3;测点2(前滚筒)的PM10粉尘质量浓度在83~1 113 mg/m3波动,均值为609 mg/m3;逆风时,测点1(前滚筒)实时监测的PM10粉尘质量浓度在331~1 079 mg/m3波动,均值为577 mg/m3;测点2(后滚筒)的PM10粉尘质量浓度在154~1 158 mg/m3波动,均值为614 mg/m3。由图3可以看出,顺风时,测点1(后滚筒)实时监测的PM5粉尘质量浓度在324~860 mg/m3波动,均值为489 mg/m3;测点2(前滚筒)的PM5粉尘质量浓度在183~825 mg/m3波动,均值为508 mg/m3;逆风时,测点1(前滚筒)实时监测的PM5粉尘质量浓度在204~833 mg/m3波动,均值为495 mg/m3;测点2(后滚筒)的PM5粉尘质量浓度在240~1 213 mg/m3波动,均值为522 mg/m3。由图4可以看出,顺风时,测点1(后滚筒)实时监测的PM2.5粉尘质量浓度在143~433 mg/m3波动,均值为231 mg/m3;测点2(前滚筒)的PM2.5粉尘质量浓度在185~417 mg/m3波动,均值为245 mg/m3;逆风时,测点1(前滚筒)实时监测的PM2.5粉尘质量浓度在37~595 mg/m3波动,均值为242 mg/m3;测点2(后滚筒)的PM2.5粉尘质量浓度在105~510 mg/m3波动,均值为256 mg/m3。
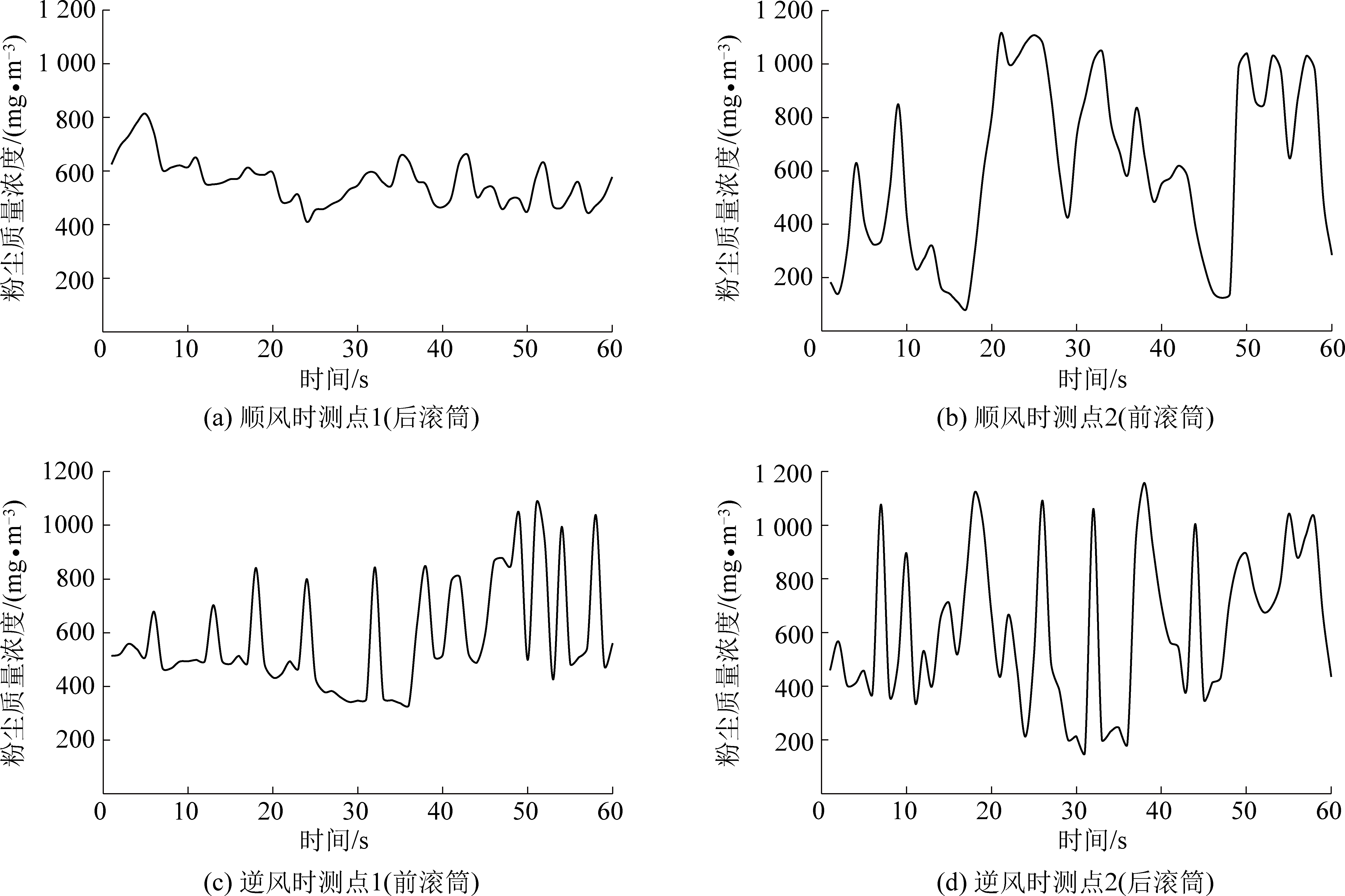
图2 采煤机滚筒处PM10粉尘质量浓度监测曲线
Fig.2 Monitoring curve of PM10 dust concentration at shearer drum

图3 采煤机滚筒处PM5粉尘质量浓度监测曲线
Fig.3 Monitoring curve of PM5 dust concentration at shearer drum

图4 采煤机滚筒处PM2.5粉尘质量浓度监测曲线
Fig.4 Monitoring curve of the PM2.5 dust concentration at the shearer drum
通过对比图2、图3和图4,可以发现:①无论顺风还是逆风,受测点1处割煤、采煤机组空间内落煤的影响,位于下风侧的测点2处的PM10,PM5粉尘质量浓度波动范围更大,其PM10,PM5粉尘质量浓度也大于测点1处的;而对于PM2.5,下风侧测点2处的PM2.5粉尘质量浓度波动范围比测点1处更小,其原因与PM2.5扩散特征有关,微细颗粒的扩散更为均匀,其PM2.5粉尘质量浓度大于测点1处的。②对于测点1,顺风时其位置略高于滚筒,而逆风时其位置略低于滚筒,顺风时影响测点1处PM10,PM5,PM2.5粉尘质量浓度的落煤区域小于逆风时的,故顺风时测点1处的PM10,PM5,PM2.5粉尘质量浓度低于逆风时的。③对于测点2,顺风时其位置略低于滚筒,逆风时其位置略高于滚筒,顺风时影响测点2处PM10,PM5,PM2.5粉尘质量浓度的落煤区域大于逆风时的,然而受上风侧测点1处、以及采煤机组空间内落煤的影响,顺风时测点1位于后滚筒附近,其产尘点位置偏低,而PM10,PM5,PM2.5属于微尘,在静止空气中一般作等速沉降运动[20],PM10,PM5,PM2.5粉尘运移至测点2位置时,其粉尘质量浓度叠加效应不如逆风时明显(逆风时测点1位于前滚筒附近,产尘点位置偏高)。因此逆风时测点2处的PM10,PM5,PM2.5粉尘质量浓度大于顺风时的。
4 截割煤尘表面活性剂降尘
目前该工作面已采取了采煤机内外喷雾、支架喷雾、个体防护等防尘措施,然而对于截割可吸入煤尘的降尘效果并不理想。为进一步降低截割煤尘对工作面环境的影响,在工作面进风巷安装表面活性剂添加装置,该添加装置以风压为动力,可将表面活性剂添加至静压水管,从而为工作面提供降尘用水。表面活性剂选用矿用塵克(C&C)系列除尘剂。
为了确定合理的表面活性剂添加浓度,分别选取了体积分数为0.01%,0.02%,0.03%,0.05%,0.1%,0.15%,0.2%,0.25%,0.3%的矿用尘克(C&C)系列除尘剂进行溶液表面张力测试,溶剂选用矿井水,测试仪器选用JZYW—200B界面张力仪,采用圆环法记录圆环薄膜的拉伸破坏情况,从而计算出液体的表面张力。液滴表面张力越小,其与粉尘接触后,更容易黏结沉降。测试结果如图5所示。
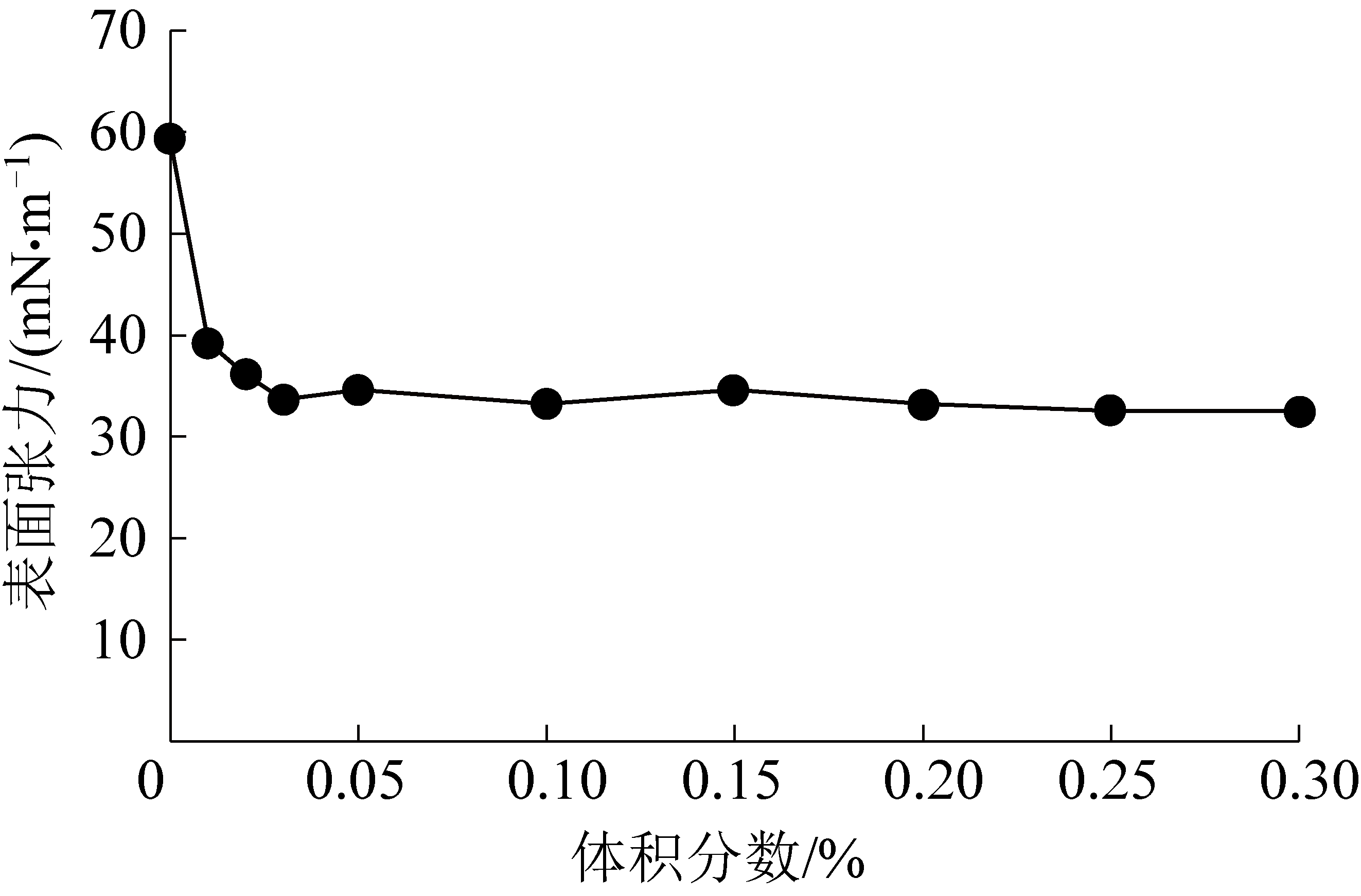
图5 矿用尘克(C&C)系列除尘剂表面张力测试结果图
Fig.5 Surface tension test results of the dust
removal agent of C&C series
由图5可以看出,矿井水的表面张力为59.1 mN/m(标况),随着矿用尘克(C&C)系列除尘剂浓度的增加,溶液表面张力逐渐下降,当溶液体积分数超过0.1%时,其表面张力下降趋势不再明显。浓度为0.1%时矿用尘克(C&C)系列除尘剂溶液表面张力为33.2 mN/m(标况),相比矿井水,其表面张力降低了43.82%。同时考虑矿用成本及现场操作的简便性,最终选用体积分数为0.1%矿用尘克(C&C)系列除尘剂作为大采高工作面的降尘用水。
对所选溶液进行了湿润性试验,测量仪器选用JY-PHb接触角测定仪,将煤样切成块薄片,并且用砂纸进行打磨,使其表面光滑,然后将液滴滴于煤样表面,通过摄影,计算三相界面液滴的接触角,每个样品测量3次,取其平均值。接触角越小表明溶液的湿润性越好,测试结果见表1。同时由表1可以看出,矿用尘克(C&C)系列除尘剂体积分数为0.1%时,接触角为34.27°,相比矿井水,接触角减小了53.86%,具有良好的湿润性。
表1 矿用尘克(C&C)系列除尘剂接触角测试结果
Table 1 Contact angle test results of
dust removal agent of C&C series
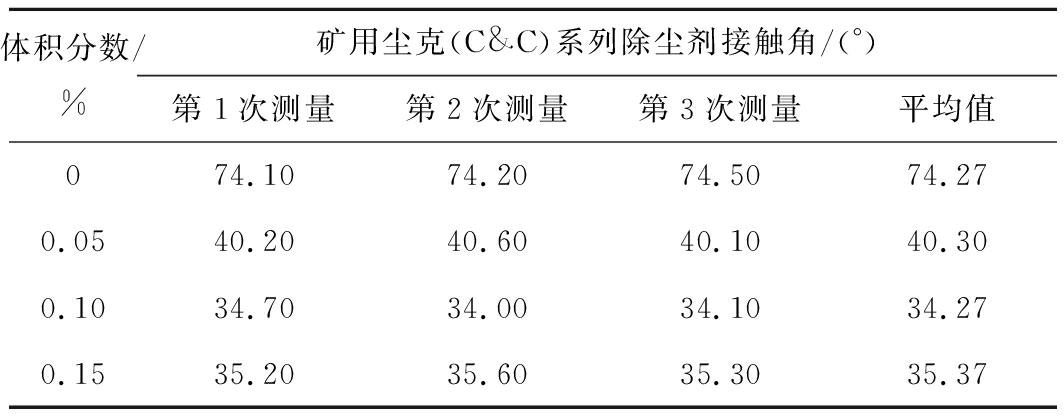
体积分数/%矿用尘克(C&C)系列除尘剂接触角/(°)第1次测量第2次测量第3次测量平均值074.1074.2074.5074.270.0540.2040.6040.1040.300.1034.7034.0034.1034.270.1535.2035.6035.3035.37
通过表面活性剂添加装置将体积分数为0.1%的矿用尘克(C&C)系列除尘剂输送至采煤工作面,用于采煤机内外喷雾,以此改善采煤工作面粉尘环境。根据截割粉尘的分布特征可知,采煤机下风侧滚筒处的粉尘质量浓度更大。因此,在采煤机组下风侧布置粉尘监测点,以此分析降尘效果。通过连续多次监测后发现,表面活性剂采用后截割煤尘可吸入煤尘的降尘效率为48.37%~53.91%,呼吸性粉尘的降尘效率为39.57%~45.11%,取得了较好的降尘效果。
5 结 论
1)采煤机顺风运行时,测点1(上风侧滚筒)处的PM10,PM5,PM2.5的平均粉尘质量浓度分别为561、489、231 mg/m3。测点2(下风侧滚筒)处的PM10,PM5,PM2.5的平均粉尘质量浓度分别为609、508、245 mg/m3;采煤机逆风运行时,测点1(上风侧滚筒)处的PM10,PM5,PM2.5的平均粉尘质量浓度分别为577、495、242 mg/m3;测点2(下风侧滚筒)处的PM10,PM5,PM2.5的平均粉尘质量浓度分别为614、522、256 mg/m3。
2)无论顺风还是逆风,受测点1处割煤、采煤机组空间内落煤的影响,位于下风侧的测点2处的PM10,PM5粉尘质量浓度波动范围更大,其PM10,PM5粉尘质量浓度大于测点1处的;而对于PM2.5,下风侧测点2处的PM2.5粉尘质量浓度波动范围比测点1处更小,其PM2.5粉尘质量浓度大于测点1处的。
3)顺风时测点1处的PM10,PM5,PM2.5粉尘质量浓度低于逆风时的。逆风时测点2处的PM10,PM5,PM2.5粉尘质量浓度大于顺风时的。
4)通过表面张力测试和接触角测试,体积分数为0.1%时矿用尘克(C&C)系列除尘剂溶液表面张力为33.2 mN/m(标况),接触角为34.27°,相比矿井水,其表面张力降低了43.82%,接触角减小了53.86%,具有良好的湿润性。选取浓度为0.1%的矿用尘克(C&C)系列除尘剂,对工作面进行表面活性剂降尘,其截割可吸入煤尘的降尘效率为47.32%~52.81%,呼吸性粉尘的降尘效率为36.55%~43.16%。
[1] 王国法, 庞义辉, 任怀伟, 等. 煤炭安全高效综采理论、技术与装备的创新和实践[J]. 煤炭学报, 2018, 43(4): 903-913.
WANG Guofa, PANG Yihui, REN Huaiwei, et al. Coal safe and efficient mining theory, technology and equipment innovation practice[J].Journal of China Coal Society, 2018, 43(4): 903-913.
[2] 王建国, 周侗柱, 戚斐文, 等. 凉水井矿综采工作面粉尘运移规律数值仿真[J]. 西安科技大学学报, 2020, 40(2):195-203.
WANG Jianguo, ZHOU Tongzhu, QI Feiwen, et al. Numerical simulation of dust movement rules at fully-mechanized mining faces in Liangshuijing coal mine[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Science and Technology, 2020, 40(2):195-203.
[3] 王惠风, 陈殿赋. 基于一组多孔大区域注水技术的工作面粉尘综合治理[J]. 煤矿安全, 2020, 51(11):66-69,73.
WANG Huifeng, CHEN Dianfu. Comprehensive dust management of working face based on a group of porous large area water injection technology[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2020, 51(11):66-69,73.
[4] 马有营, 徐荣萧. 矿用多类型雾化喷嘴雾化参数及其对采掘截割区域降尘效果分析[J]. 工业安全与环保, 2020, 46(11):82-88.
MA Youying, XU Rongxiao. Analysis of atomizing parameters of multi-type atomizing nozzles used in mine and its dedusting effect on cutting area[J]. Industrial Safety and Environmental Protection, 2020, 46(11):82-88.
[5] 翁安琦, 袁树杰, 王晓楠, 等. 煤层注水降尘中表面活性剂复配应用研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(10):90-95.
WENG Anqi, YUAN Shujie, WANG Xiaonan, et al. Study on application of surfactant compound in coal seam water injection for dust reduction[J]. China Safety Science Journal,2020, 30(10):90-95.
[6] 谢建林, 庞杰文, 菅 洁, 等.综采工作面煤层注水降尘试验研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2017, 27(6):151-156.
XIE Jianlin, PANG Jiewen, JIAN Jie, et al. Experimental study on reducing dust at fully mechanized coal mining face by coal seam water injection[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2017, 27(6):151-156.
[7] 王鹏飞, 刘荣华, 汤 梦, 等. 煤矿井下高压喷雾雾化特性及其降尘效果实验研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2015, 40(9): 2124-2130.
WANG Pengfei, LIU Ronghua, TANG Meng, et al. Experimental study on atomization characteristics and dust suppression efficiency of high-pressure spray in underground coal mine[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2015, 40(9): 2124-2130.
[8] 王 亮,廖晓雪,查梦霞,等. 基于主成分分析法的松软煤体煤尘润湿特性研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2020, 48(2): 104-109.
WANG Liang, LIAO Xiaoxue, ZHA Mengxia, et al. Study on wetting characteristics of coal dust in soft coal based on principal component analysis[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2020, 48(2): 104-109.
[9] 王鹏飞, 刘荣华, 桂 哲, 等. 煤矿井下气水喷雾雾化特性及降尘效率理论研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2016, 41(9):2256-2262.
WANG Pengfei, LIU Ronghua, GUI Zhe, et al. Theoretical research on atomization characteristics and dust suppression efficiency of air-water spray in underground coal mine[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2016, 41(9): 2256-2262.
[10] 彭 亚,蒋仲安. 矿井防尘供水管网相似试验模型构建与测点优化[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2020, 48(1): 182-188.
PENG Ya, JIANG Zhongan. Construction of similar test model for mine dust-proof water supply network and optimization of pressure monitoring layout[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2020, 48(1): 182-188.
[11] 徐青云, 白志云, 李锦波. 大采高综采工作面多尘源风流—粉尘分布规律研究[J]. 矿业安全与环保, 2020, 47(5): 56-59.
XU Qingyun, BAI Zhiyun, LI Jinbo. Air flow-dust distribution law of multi-dust sources in fully mechanized working face with large mining height[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection, 2020, 47(5): 56-59.
[12] 许圣东, 李德文, 陈 芳. 8 m大采高综采工作面风流及呼吸尘分布规律数值模拟[J]. 煤矿安全, 2018, 49(12): 160-168.
XU Shengdong, LI Dewen, CHEN Fang. Numerical simulation on distribution laws of air and respirable dust at fully mechanized face with 8 m mining height[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2018, 49(12):160-168.
[13] 陈 芳. 8 m大采高综采工作面风流分布规律数值模拟[J]. 煤矿安全, 2019, 50(11):185-188.
CHEN Fang. Numerical study on airflow distribution law in 8 m large mining height fully-mechanized face[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2019, 50(11):185-188.
[14] 苏士龙, 郝永江. 大采高综采工作面PM5和PM10粉尘分布规律[J]. 煤矿安全, 2020, 51(7):210-214,220.
SU Shilong, HAO Yongjiang. Dust distribution of PM5 and PM10 in large mining height fully-mechanized face[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2020, 51(7):210-214,220.
[15] 孔 阳, 庞浩生, 宋淑郑, 等. 综采工作面粉尘弥散污染规律数值模拟研究[J]. 煤矿安全, 2020, 51(6): 218-222.
KONG Yang, PANG Haosheng, SONG Shuzheng, et al. Numerical simulation study on law of dispersive pollution of dust in fully mechanized mining face[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2020, 51(6): 218-222.
[16] 崔向飞, 薛 娇, 边文辉. 补连塔煤矿7m大采高工作面粉尘分布规律实测及防治技术研究[J]. 中国煤炭, 2017, 43(9):116-120.
CUI Xiangfei, XUE Jiao, BIAN Wenhui. Study on dust distribution measurement and control technology of 7-meter large mining height work face at Bulianta Mine[J]. China Coal, 2017, 43(9):116-120.
[17] 杜善周, 莫金明, 王全龙, 等. 大采高综采工作面粉尘运移分布规律及机载除尘器关键工艺参数研究[J]. 矿业安全与环保, 2020, 47(2):45-51.
DU Shanzhou, MO Jinming, WANG Quanlong, et al. Research on key process parameters of airborne dustcollector based on distribution law of dust movement in fully mechanized working face with large mining height[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection, 2020, 47(2):45-51.
[18] 程卫民,周 刚,陈连军,等.我国煤矿粉尘防治理论与技术20年研究进展及展望[J].煤炭科学技术,2020,48(2):1-20.
CHENG Weimin, ZHOU Gang, CHEN Lianjun, et al. Research progress and prospect of dust control theory and technology in China’s coal mines in the past 20 years[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2020, 48(2):1-20.
[19] 李德文, 隋金君, 刘国庆, 等. 中国煤矿粉尘危害防治技术现状及发展方向[J]. 矿业安全与环保, 2019, 46(6):1-7.
LI Dewen, SUI Jinjun, LIU Guoqing, et al. Technical status and development direction of coal mine dust hazard prevention and control technology in China[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection, 2019, 46(6):1-7.
[20] 中国煤炭工业劳动保护科学技术学会.矿井粉尘防治技术[M]. 北京: 煤炭工业出版社, 2007: 2-3.
