Comprehensive treatment technology for wellbore deflection in thick loose bed and thin bedrock formation
-
摘要:
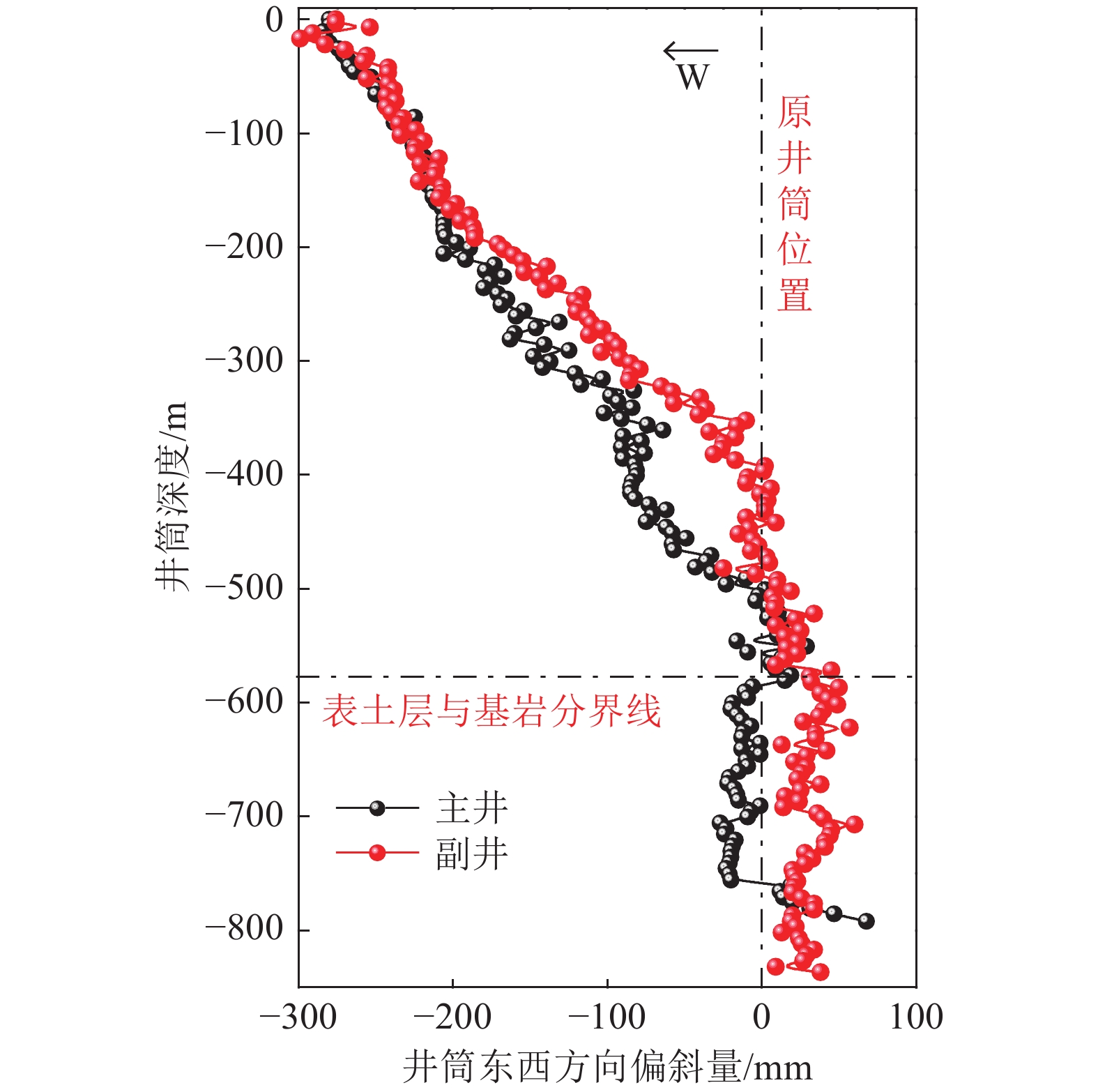
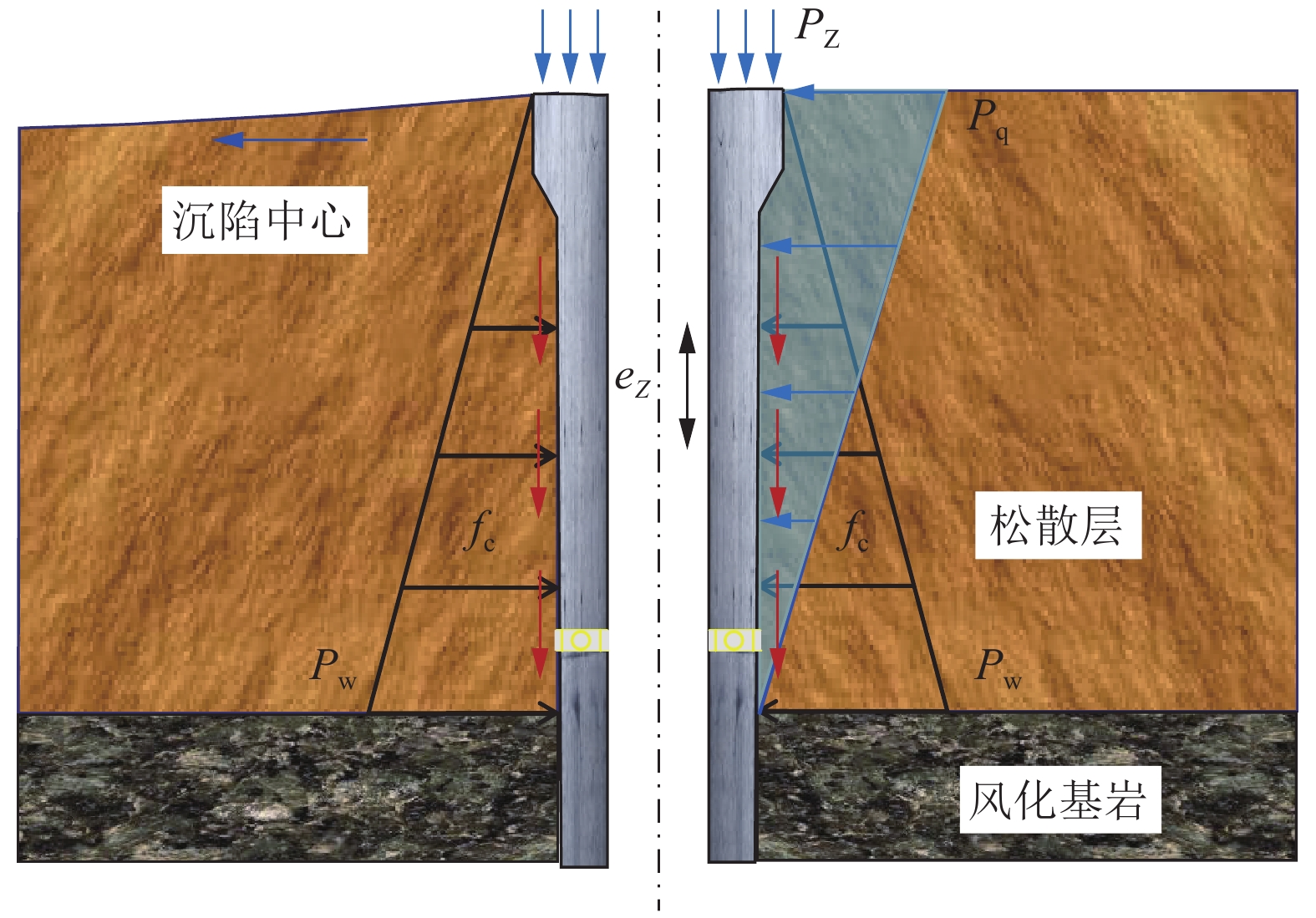
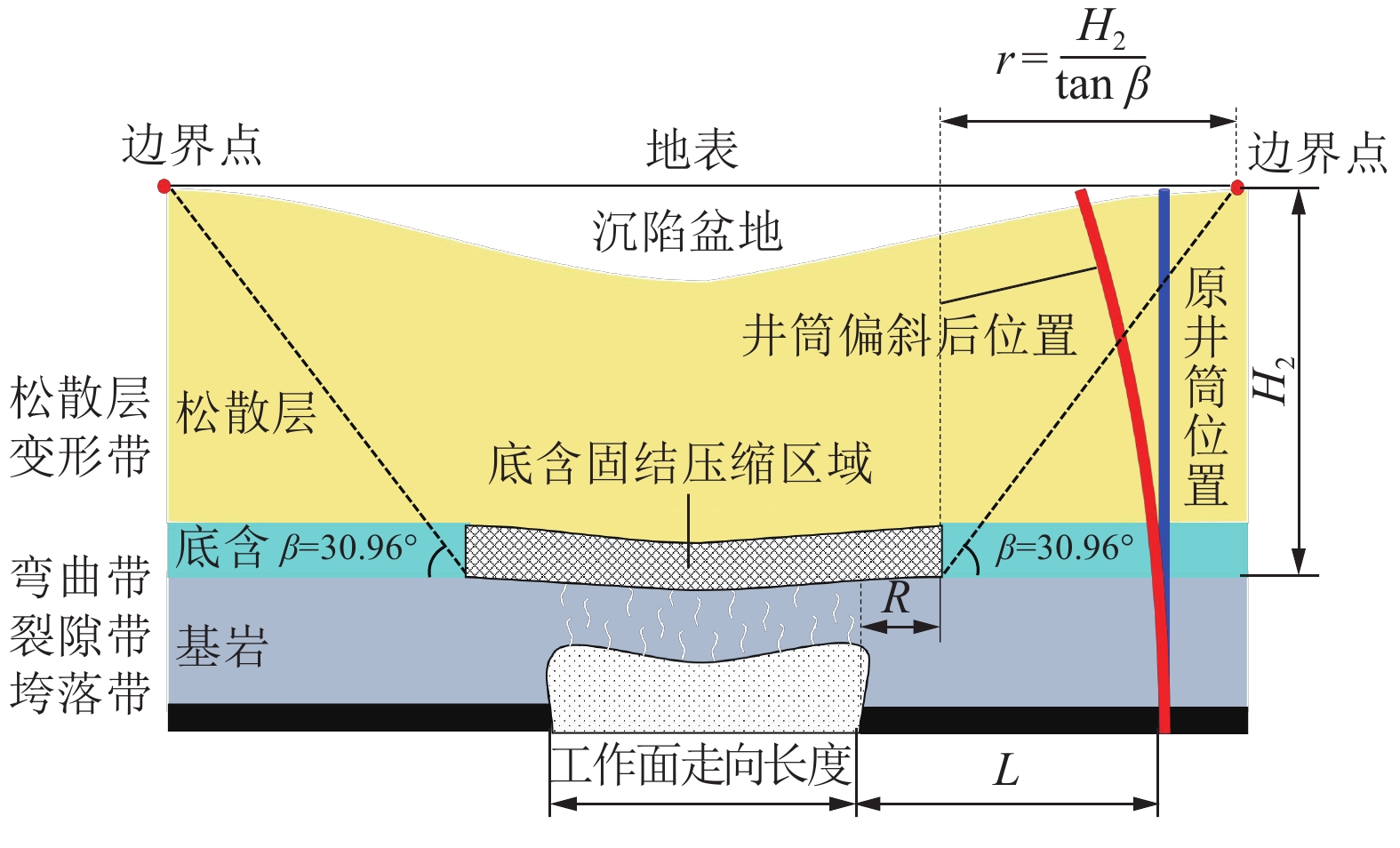
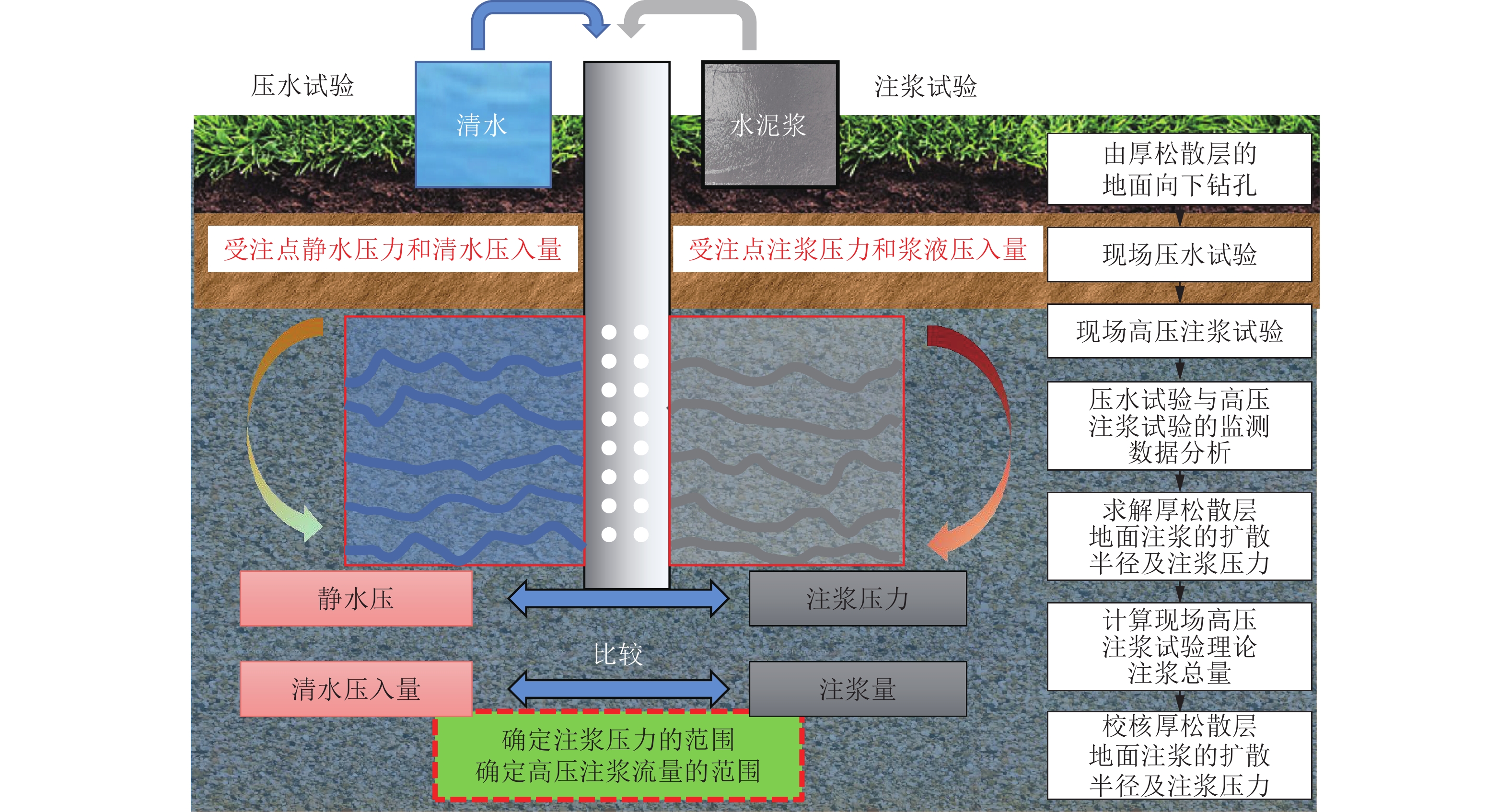
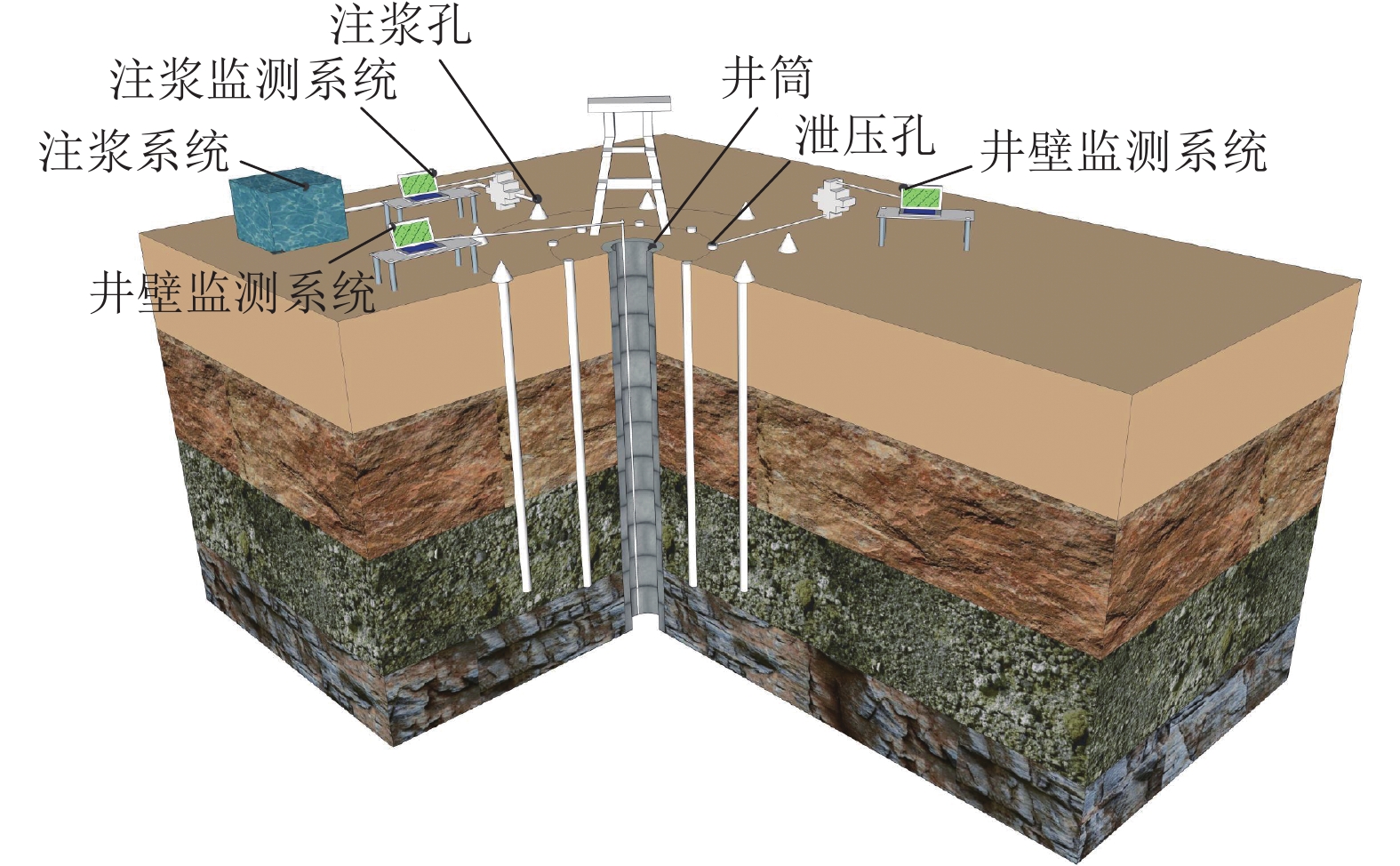
针对厚松散层薄基岩地层井筒偏斜综合治理技术难题,以山东巨野矿区郭屯煤矿偏斜井筒地面注浆治理工程为背景,基于井筒松散层段偏斜与竖向压缩变形共存且向非对称开采工作面方向偏斜的全新破损特征,揭示郭屯煤矿井筒偏斜与竖向压缩变形机理,分析认为该2种特征分别是煤层非对称开采引发的底含非均匀疏水固结沉降叠加作用下地层水平倾覆推力和竖向附加力所致。本着确保安全、不停产治理的原则,制定了在役偏斜井筒不停产地面注浆综合治理方案,研发了系列井筒偏斜综合治理技术:①保护在役井筒“泄压-预警”双控地面高压注浆技术;②厚松散层单孔多层段注浆新型套管与施工工艺;③厚松散层地面注浆参数工程化确定方法;④在役井筒不停产运营下深孔高压注浆治理预警技术。综合监测结果表明:郭屯煤矿主、副、风3个偏斜井筒治理工程注浆过程中严格按照厚松散层薄基岩条件下偏斜井筒不停产综合治理技术进行实施,完成注浆孔钻探工程量31 026.8 m,注浆量达到35 536.66 m3,实现了矿井不停产注浆治理;治理后井筒向北向西不再继续偏移,主井井筒注浆期井口处向北和向西偏斜量分别减小12 mm和18 mm,副井井筒井口处向北和向西分别减小13 mm和41 mm,注浆结束1 a内井筒整体偏斜量仍继续减小并有回正趋势,且井筒周边下沉速率减缓,确保了井筒运营安全。研究成果在郭屯煤矿厚松散层薄基岩地层偏斜井筒地面高压注浆治理工程得到了成功应用,为今后在类似工程中应用提供参考依据和工程经验。
Abstract:Aiming at the technical problems of comprehensive treatment of shaft deflection in thick loose bed and thin bedrock strata, taking the ground grouting treatment engineering of the deflected shaft in Guotun Coal Mine in Juye Mining Area, Shandong Province as the background, new damage characteristics based on the coexistence of deviation and vertical compression deformation of the loose layer section in the shaft and the deviation to the direction of asymmetric mining face, the mechanism of shaft deflection and vertical compression deformation in Guotun Coal Mine is revealed. The analysis shows that the two characteristics are respectively caused by the horizontal overturning thrust and vertical additional force of the stratum under the superposition action of the non-uniform hydrophobic consolidation settlement of the bottom aquifer caused by the asymmetric mining of the coal seam. In line with the principle of ensuring safety and non-stop production treatment, a comprehensive treatment plan for ground grouting of in-service deflected shaft without stopping production has been formulated, and a series of comprehensive treatment technologies for deflected shaft have been developed: ① The dual control ground high-pressure grouting technology of “pressure relief and early warning” for protecting the shaft in service; ② New casing and construction technology for single hole and multi-layer grouting in thick loose layer; ③ Engineering determination method of ground grouting parameters in thick loose layer; ④ Early warning technology of deep hole high-pressure grouting treatment under the condition of continuous production operation of the in-service shaft. The comprehensive monitoring results show that during the grouting process of the main, auxiliary and wind deflected shaft treatment projects of Guotun Coal Mine, the comprehensive treatment technology of continuous production of the deflected shaft under the condition of thick loose bed and thin bedrock was strictly followed, and the drilling quantity of the grouting hole was 31026.8 m, the grouting quantity reached 35536.66 m3, realizing the grouting treatment of the shaft without stopping production. After the treatment, the shaft no longer deviates from north to west, during the grouting period of the main shaft, the deviation from the wellhead to the north and the west decreased by 12 mm and 18 mm respectively, and the deviation from the wellhead of the auxiliary shaft to the north and the west decreased by 13 mm and 41 mm respectively. Within one year after the completion of the grouting, the overall deviation of the shaft continues to decrease and has a positive trend, and the sinking rate around the shaft slows down, which ensures the safety of the shaft operation. The research results have been successfully applied in the ground high-pressure grouting treatment project of the deflected shaft in thick loose bed and thin bedrock strata of Guotun Coal Mine, providing reference and engineering experience for the future application in similar projects.
-
Keywords:
- thick loose layer /
- shaft deflection /
- shaft support /
- non stop production /
- ground grouting /
- pressure relief hole
-
-
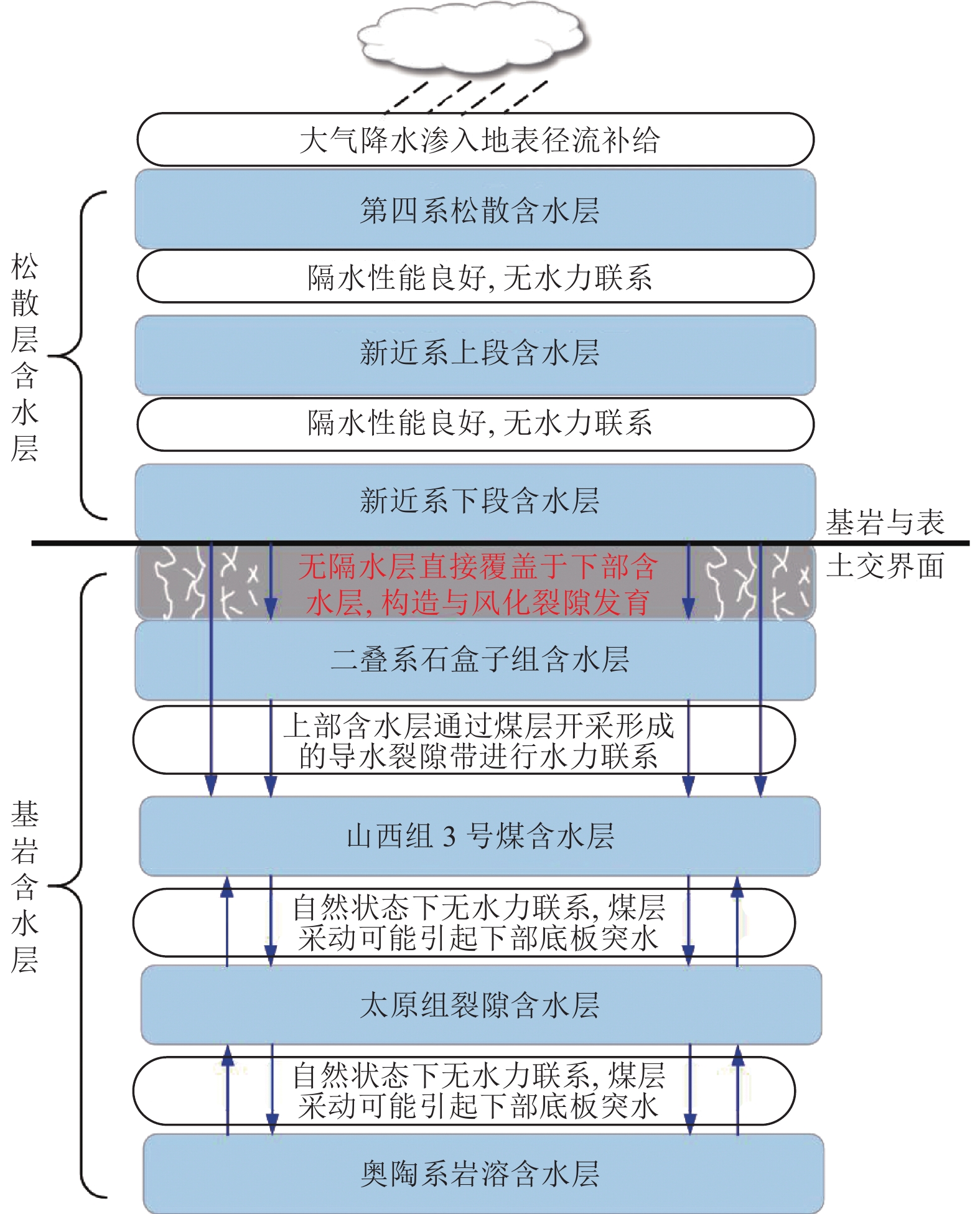
表 1 含、隔水层(组、段)划分
Table 1 Division of aquifer and aquifuge
地层 含隔水层 底板深度/m 厚度/m 检1孔(风) 检2孔(副) 检3孔(主) 检1孔(风) 检2孔(副) 检3孔(主) 第四系 含水层 86.3 85.20 85.60 37.30 37.17 45.75 隔水层 136.2 138.30 136.10 44.80 48.20 45.70 上第三系 上部含水层 332.2 334.30 333.60 73.00 78.10 74.70 中部隔水层 544.8 546.60 542.00 159.70 144.00 149.86 下部含水层 583.1 586.22 587.40 25.50 29.92 37.00 上石盒子组 风氧化带上隔 591.8 613.10 609.80 8.57 26.46 22.06 风氧化带中含 660.3 666.20 660.20 50.73 37.22 36.35 风氧化带下隔 668.9 680.39 674.00 8.46 13.88 13.60 风氧化带下含 上 688.1 698.10 697.40 18.56 17.53 18.12 下 854.0 883.48 874.77 57.18 68.14 49.12 表 2 井筒注浆孔与泄压孔钻孔深度统计
Table 2 Statistics of borehole depth of shaft grouting hole and pressure relief hole
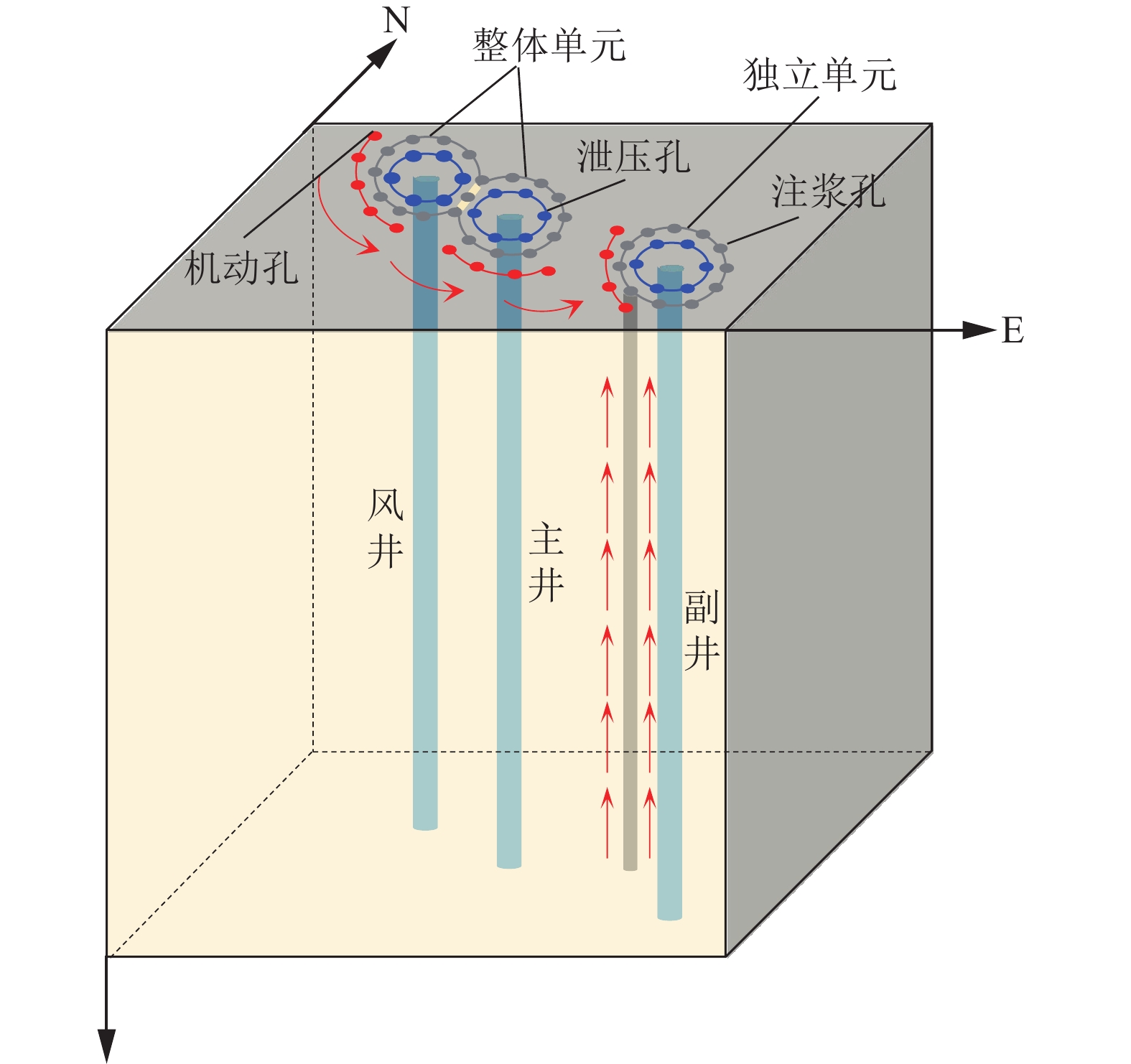
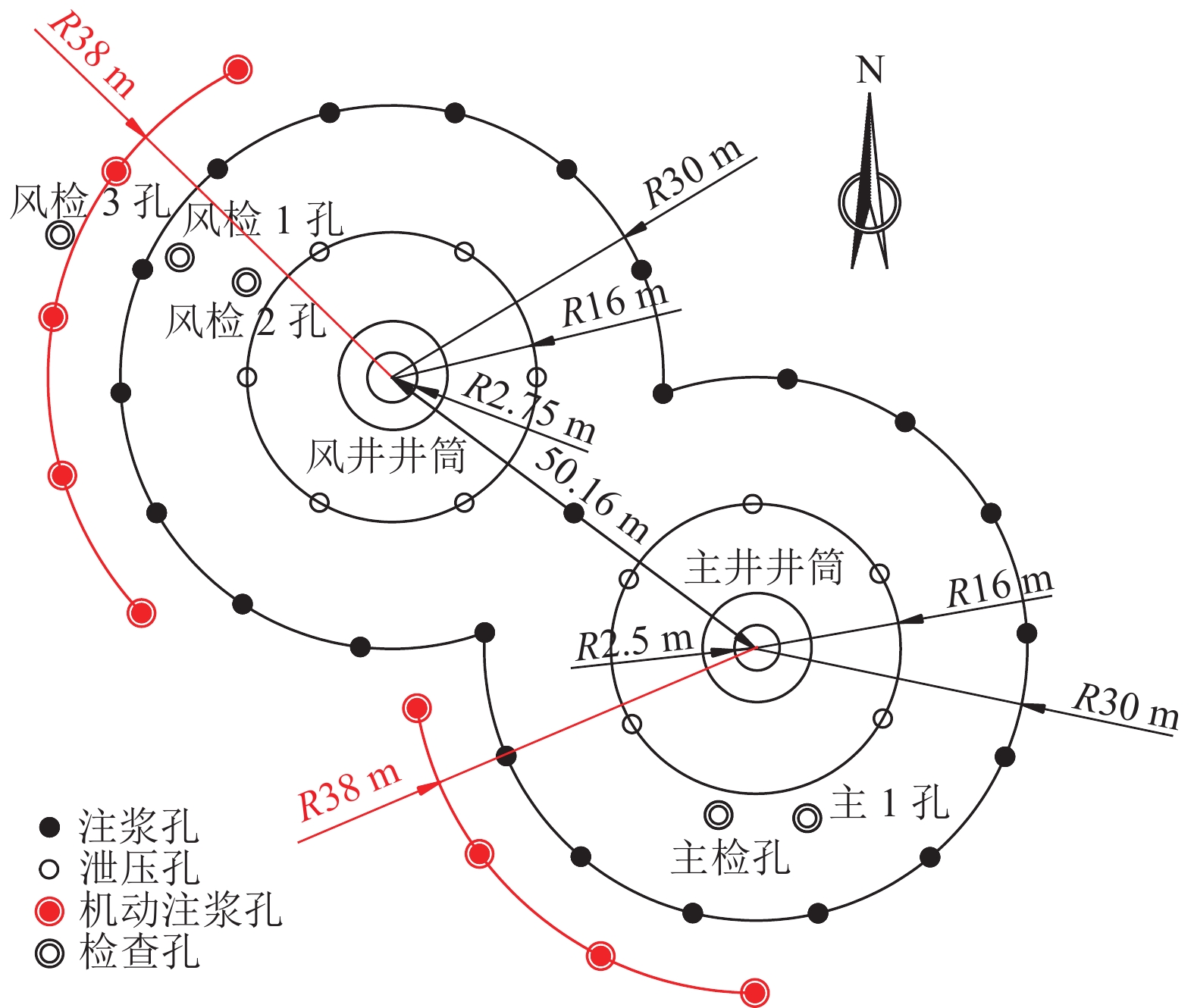
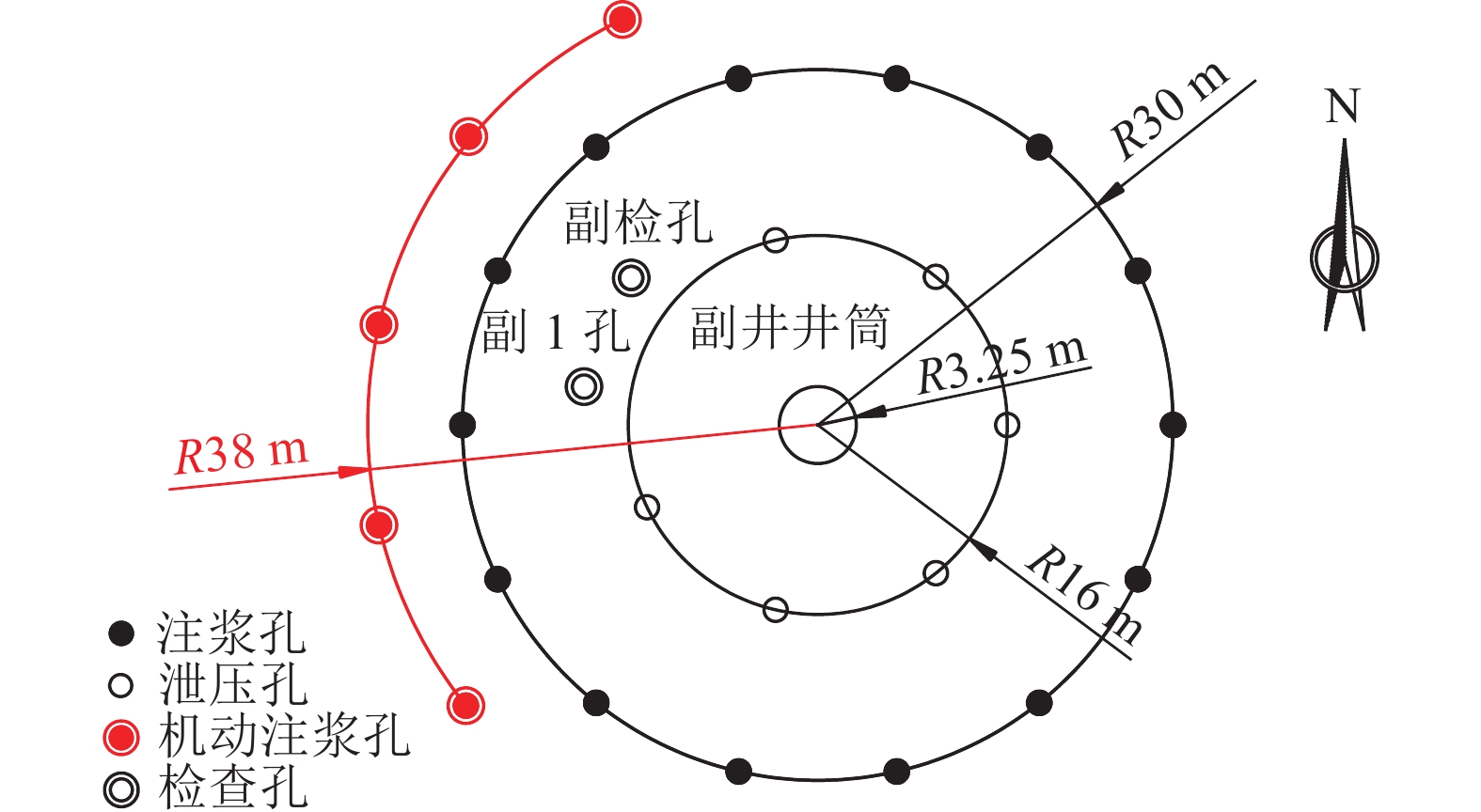
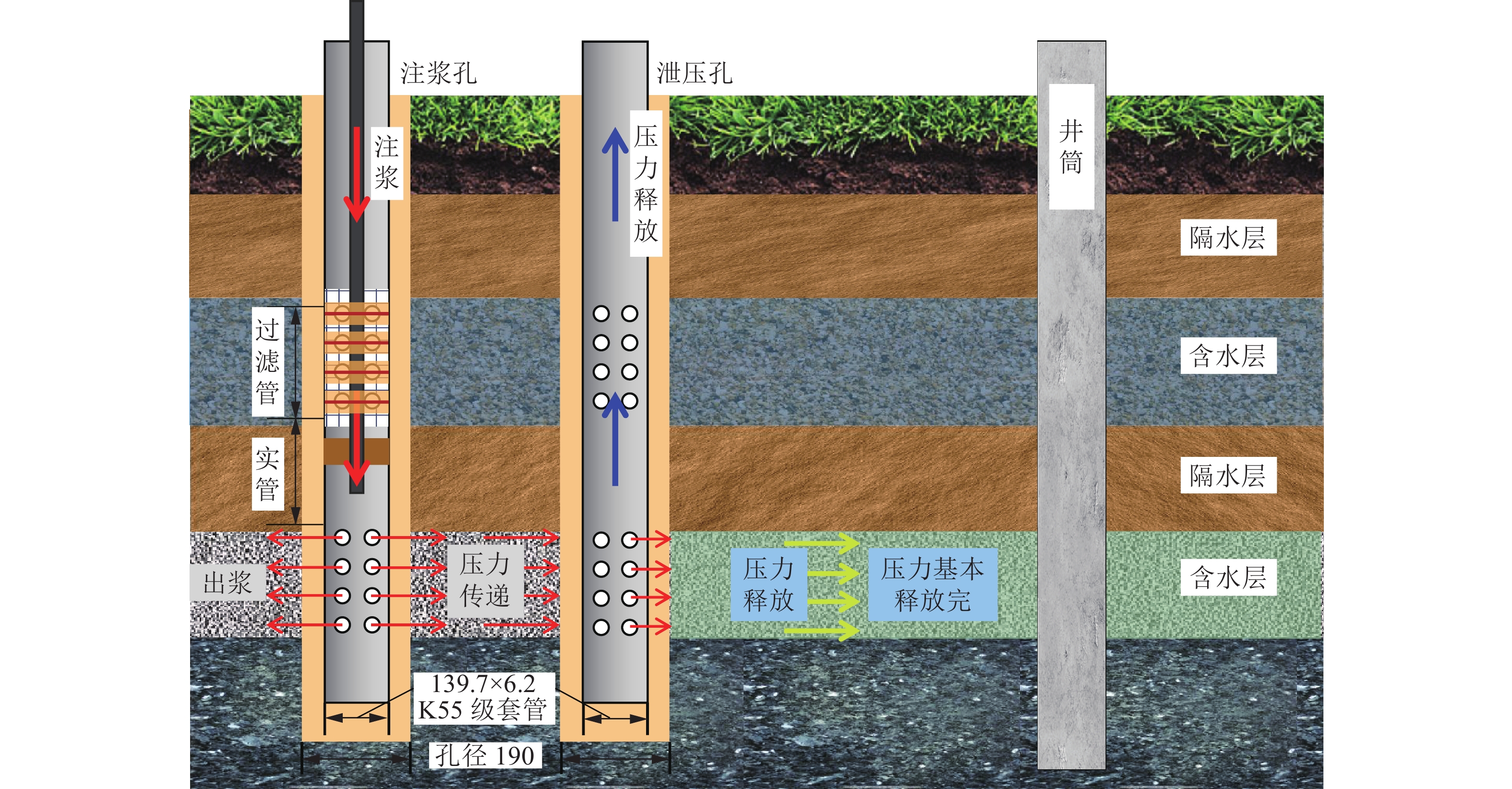
注浆孔深度/m 泄压孔深度/m 主井井筒 副井井筒 风井井筒 主井井筒 副井井筒 风井井筒 576.00 577.00 567.00 580.00 581.00 571.00 表 3 井筒注浆层段划分
Table 3 Statistics of division of shaft grouting sections
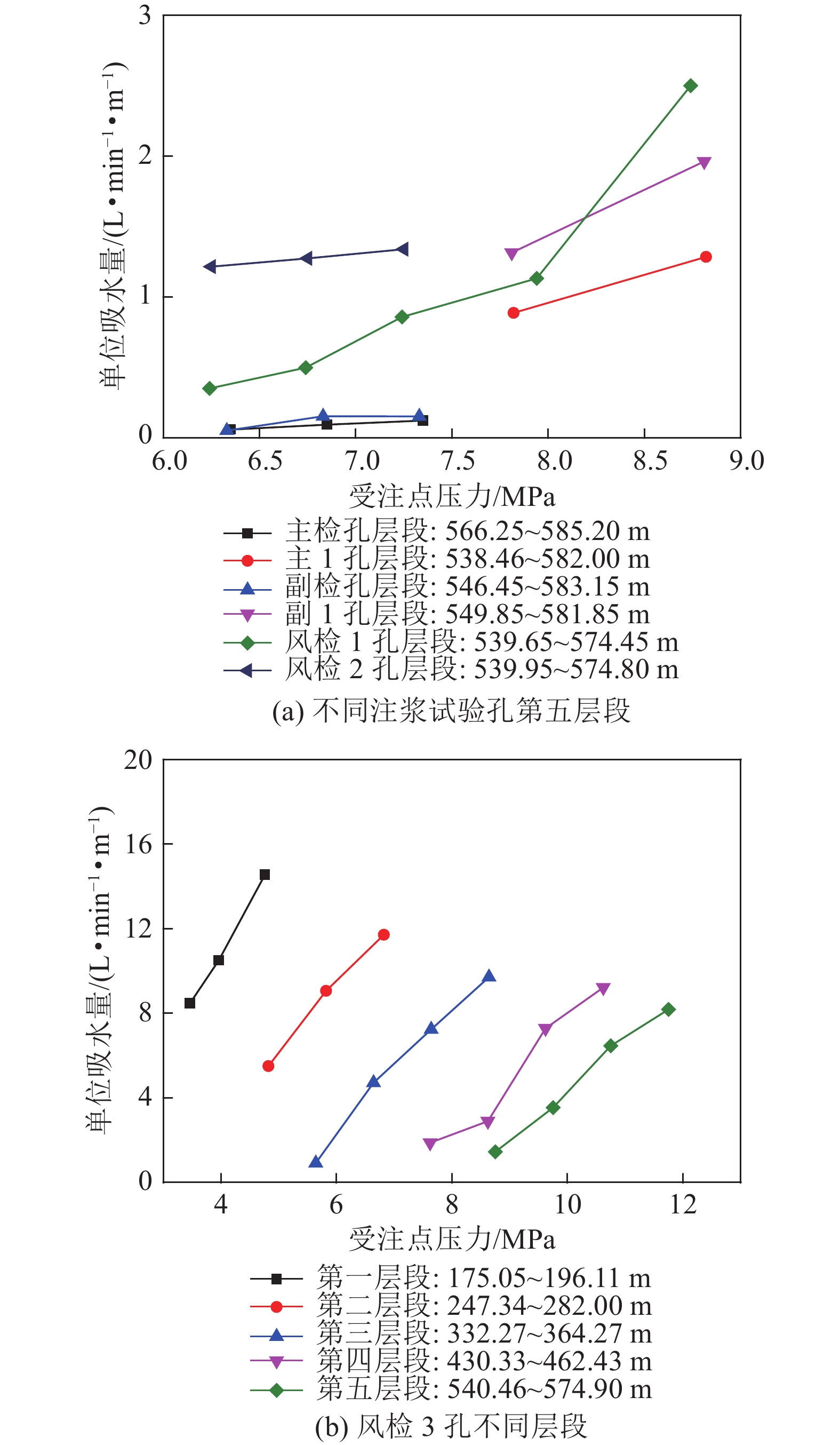
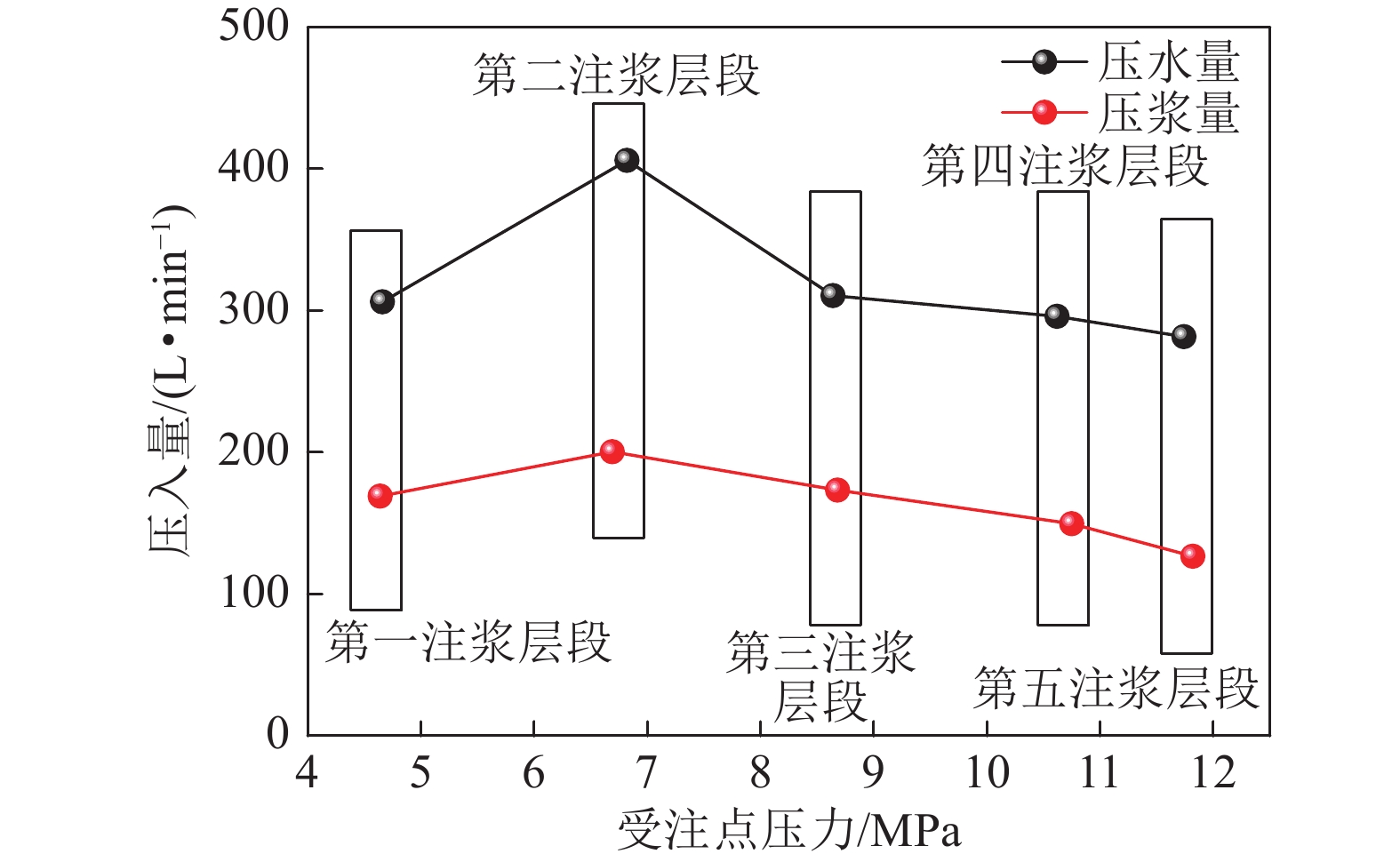
层段 起止深度/m 段长/m 主井井筒 副井井筒 风井井筒 主井井筒 副井井筒 风井井筒 第七段 150~192 150~192 150~192 42 42 42 第六段 219~265 219~265 219~265 46 46 46 第五段 292~319 292~319 292~319 27 27 27 第四段 348~375 348~375 348~375 27 27 27 第三段 405~450 405~450 405~450 45 45 45 第二段 477~510 477~510 477~510 33 33 33 第一段 541~576 541~577 541~567 35 36 26 合计 255 256 246 表 4 风检3孔注浆压力与静水压力的关系
Table 4 The relationship between the grouting pressure and the hydrostatic pressure of 3 holes in the wind test
孔号 注浆层位/m 受注点压力/MPa 注入流量/
(m3·h−1)受注点压力/
静水压力风检3 540.46~574.90 11.82~13.92 7.50 2.1~2.4 430.33~462.43 8.73~13.40 8.75 1.9~2.9 332.27~364.27 7.18~9.99 9.58 2.0~2.7 247.34~282.00 4.89~6.69 9.42 1.7~2.4 175.05~196.11 4.24~4.80 9.69 2.2~2.4 平均 — — — 2.0~2.5 表 5 井筒预警范围
Table 5 Scope of wellbore warning
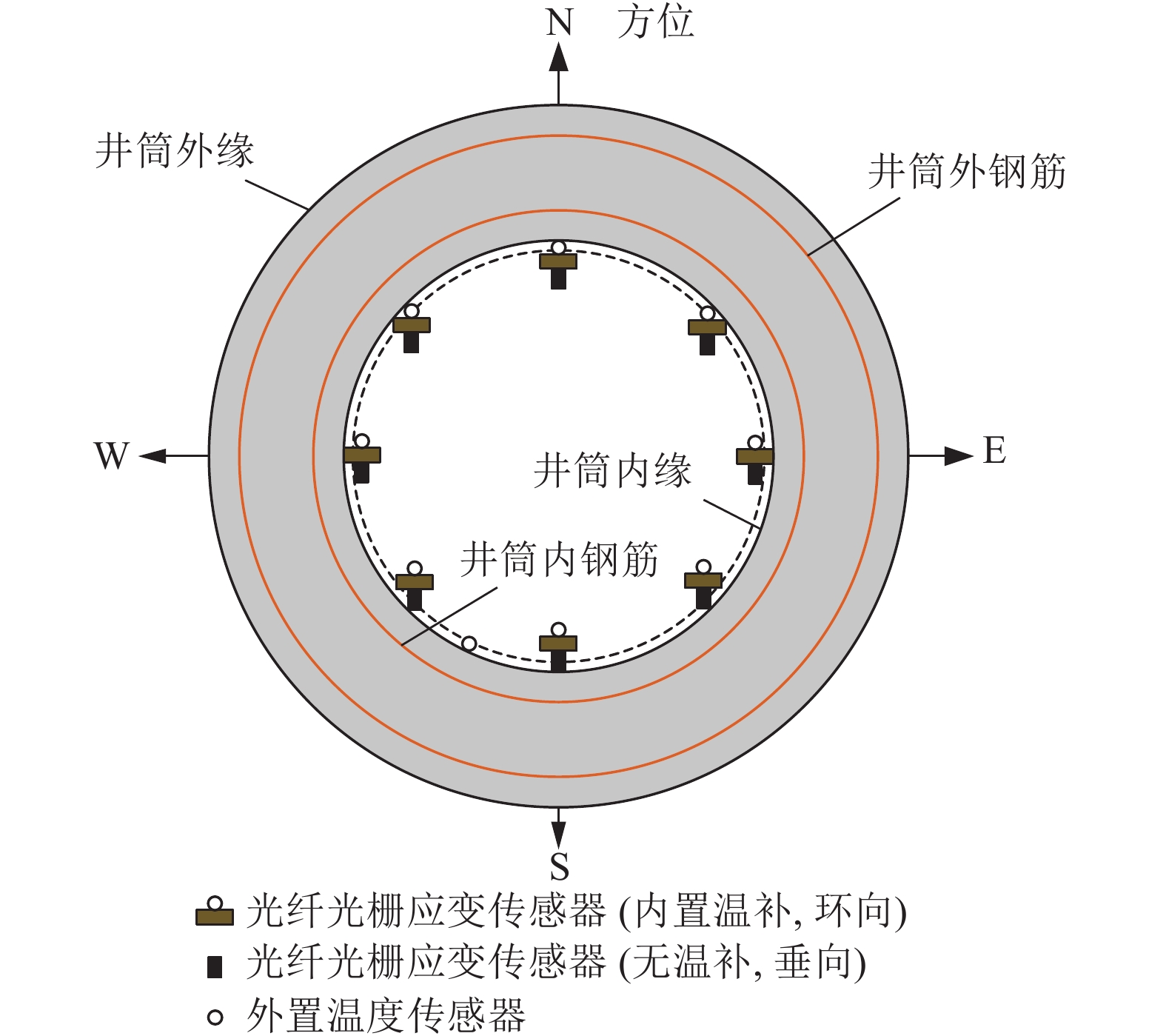
破坏方式 预警 预警方式 预警范围 压 黄 考虑荷载分项系数1.35 $ {\left[ \varepsilon \right]_c} - 1.35{\varepsilon _t} $≤$ \Delta \varepsilon $<$ {\left[ \varepsilon \right]_c} - 1.2{\varepsilon _t} $ 橙 考虑荷载分项系数1.20 $ {\left[ \varepsilon \right]_c} - 1.2{\varepsilon _t} $≤$ \Delta \varepsilon $<$ {\left[ \varepsilon \right]_c} - {\varepsilon _t} $ 红 不考虑荷载分项系数 $ \Delta \varepsilon $≥$ {\left[ \varepsilon \right]_c} - {\varepsilon _t} $ 拉 黄 考虑初始压应变折减1/3 $ - {{{\text{2}}{\varepsilon _t}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{\text{2}}{\varepsilon _t}} {\text{3}}}} \right. } {\text{3}}} $<$ \Delta \varepsilon $≤$ - {{{\varepsilon _t}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{\varepsilon _t}} {\text{3}}}} \right. } {\text{3}}} $ 橙 考虑初始压应变折减2/3 $ - {{{\text{2}}{\varepsilon _t}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{\text{2}}{\varepsilon _t}} {\text{3}}}} \right. } {\text{3}}} - {\left[ \varepsilon \right]_t} $<$ \Delta \varepsilon $≤$ - {{{\text{2}}{\varepsilon _t}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{\text{2}}{\varepsilon _t}} {\text{3}}}} \right. } {\text{3}}} $ 红 考虑初始压应变折减2/3且达到混凝土允许拉应变 $ \Delta \varepsilon $≤$ - {{{\text{2}}{\varepsilon _t}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{\text{2}}{\varepsilon _t}} {\text{3}}}} \right. } {\text{3}}} - {\left[ \varepsilon \right]_t} $ 注: $ {\varepsilon _t} $为注浆前井壁内壁环向应变;$ \Delta \varepsilon $为注浆过程应变变化值,压为正,拉为负。 表 6 注浆工程量统计
Table 6 Statistical of grouting quantities
井筒 设计注浆总量/m3 实际注浆量/m3 误差/% 主井 16 980 10 960.03 35.5 副井 18 270 12 563.17 31.2 风井 13 167 12 013.46 8.7 合计 48 417 35 536.66 26.6 -
[1] 苏 骏,程 桦. 疏水沉降地层中井筒附加力理论分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2000,19(3):310−313. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2000.03.011 SU Jun,CHENG Hua. Analysis on additional forces of shaft with drainage of stratum[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2000,19(3):310−313. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2000.03.011
[2] 程 桦,苏 俊,姚直书. 疏水沉降地层竖向可缩性井壁附加力分布规律研究[J]. 岩土力学,2007,28(3):471−475. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2007.03.008 CHENG Hua,SU Jun,YAO Zhishu. Study on distributing rule of additional force of compressible shaft wall in hydrophobic settlement stratum[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2007,28(3):471−475. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2007.03.008
[3] 何朋立,王在泉. 考虑温度效应的井壁竖向附加力反演分析[J]. 岩土力学,2013(12):3425−3430. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2013.12.025 HE Pengli,WANG Zaiquan. Inverse analysis for vertical additional force of shaft wall considering temperature effect[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2013(12):3425−3430. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2013.12.025
[4] 荣传新,史忠引,程 桦,等. 沉降地层破裂井壁修复治理工程设计原理[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2004,33(7):4−8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2336.2004.07.002 RONG Chuanxin,SHI Zhongyin,CHENG Hua,et al. Design principles of mine shaft failed liner repair and treatment in sedimentation strata[J]. Coal science and Technology,2004,33(7):4−8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2336.2004.07.002
[5] 程 桦,杨俊杰,姚直书,等. 钻井井壁可缩性接头模型试验研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2001,26(6):584−589. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2001.06.005 CHENG Hua,YANG Junjie,YAO Zhishu,et al. Modeling experiments and studies on retractable flanging device for shaft walls[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2001,26(6):584−589. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2001.06.005
[6] 荣传新,程 桦,姚直书. 钻井井壁可缩性接头力学特性研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2003,28(3):270−274. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2003.03.010 RONG Chuanxin,CHENG Hua,YAO Zhishu. Study on compressive joint mechanics characteristic of shaft-boring lining[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2003,28(3):270−274. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2003.03.010
[7] 夏红春,周国庆. 地面注浆加固地层法在治理井壁破裂中的应用[J]. 矿业安全与环保,2008,35(4):25−27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-4495.2008.04.009 XIA Hongchun,ZHOU Guoqing. Application of ground grouting for stratum reinforcement in preventing shaft-wall disruption[J]. Mining Safety and Environmental Protection,2008,35(4):25−27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-4495.2008.04.009
[8] 周国庆,刘雨忠,冯学武,等. 围土注浆缓释和抑制井壁附加力效应及应用[J]. 岩土工程学报,2005,27(7):742−745. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2005.07.003 ZHOU Guoqing,LIU Yuzhong,FENG Xuewu,et al. Application and effect of grouting in surrounding soil on releasing and restraining additional stress of shaft lining[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2005,27(7):742−745. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2005.07.003
[9] 付厚利. 深厚表土层地面注浆加固过程中井壁应变变化规律[J]. 岩土力学,2003,24(S1):21−23. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2003.s1.005 FU Houli. Strain variation regularity of shaft lining during grouting reinforcement process for deep topsoil ground[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2003,24(S1):21−23. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2003.s1.005
[10] 刘全林,程 桦. 立井壁后土层注浆加固机理及注浆参数研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2000,25(5):486−490. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2000.05.009 LIU Quanlin,CHENG Hua. Study on grouting mechanism and parameters in the depths of thick topsoil[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2000,25(5):486−490. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2000.05.009
[11] 姚直书,程 桦,秦 勇,等. 厚表土薄基岩复杂地质条件下马头门修复技术[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2016,45(S2):6−9. YAO Zhishu,CHENG Hua,QIN Yong,et al. Ingate repair technology under complicated geological conditions in thick alluvium and thin bedrock[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2016,45(S2):6−9.
[12] 陈 轲,王增光. 地面注浆堵水技术在矿山建设中的应用[J]. 中国矿山工程,2009,38(1):36−40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-609X.2009.01.011 CHEN Ke,WANG Zengguang. Application of pre-grouting on the ground technology in mine construction[J]. China Mine Engineering,2009,38(1):36−40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-609X.2009.01.011
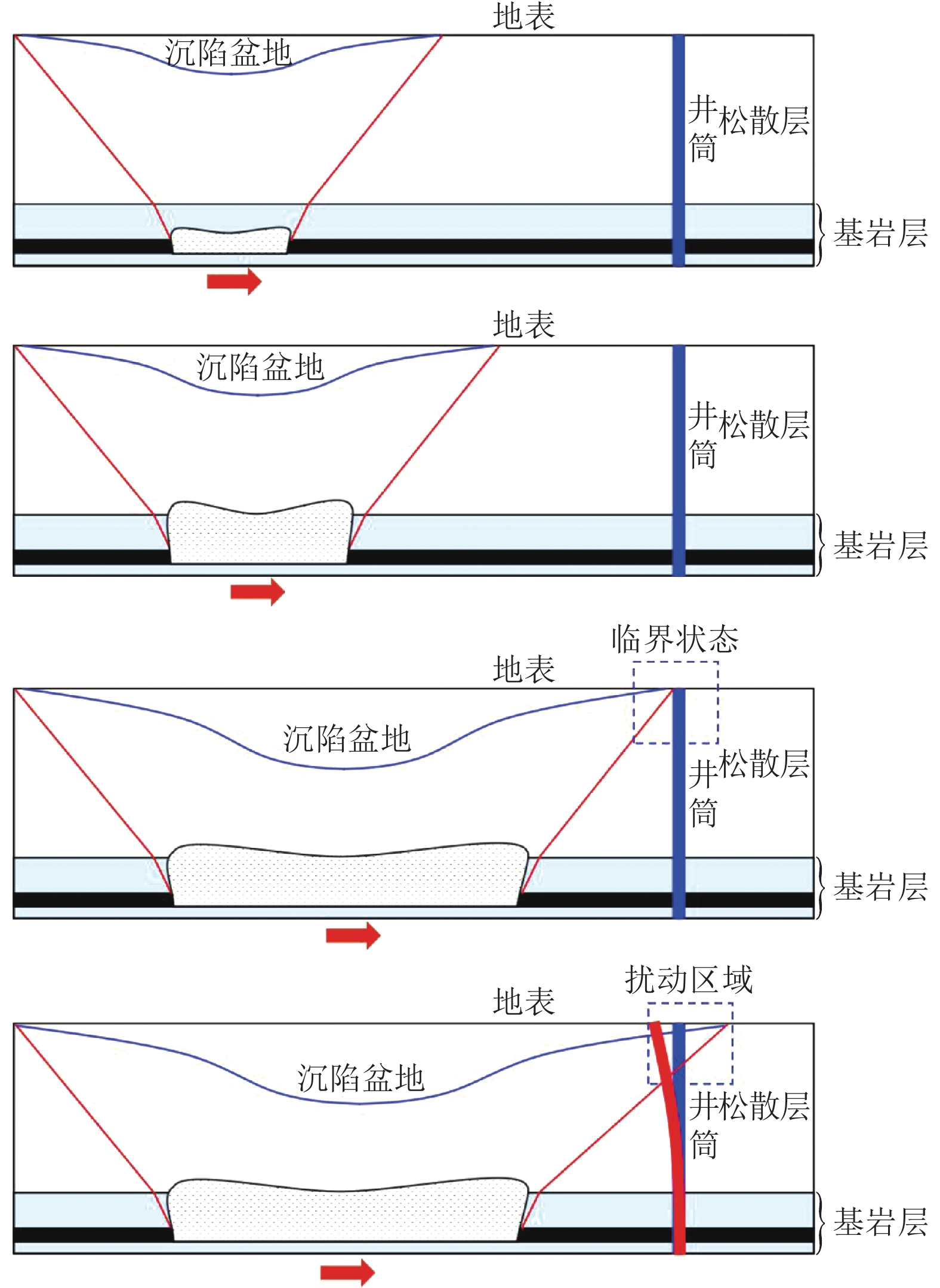
[13] 程 桦,张亮亮,姚直书,等. 厚松散层薄基岩非对称开采井筒偏斜机理[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(1):102−114. CHEN Hua,ZHANG Liangliang,YAO Zhishu,et al. Mechanism of shaft deflection caused by asymmetric mining in thin bedrock and deep loose strata[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(1):102−114.
[14] 刘孝孔,绪瑞华,赵艳鹏,等. 邻近厚松散层既有立井井筒地面注浆地层加固技术[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(7):127−134. LIU Xiaokong,XU Ruihua,ZHAO Yanpeng,et al. Ground grouting stratum reinforcement technology for thick loose layer adjacent to existing shaft[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(7):127−134.
[15] 彭世龙, 程 桦, 姚直书, 等. 厚松散层底含直覆薄基岩开采地表沉陷预计及特征研究[J/OL]. 煤炭学报: 1-13 [2022-10-30]. Doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.w022.067. PENG Shilong, CHENG Hua, YAO Zhishu, et al. Study on prediction and characteristics of surface subsidence in mining when the bottom aquifer of thick loose layer directly covers thin bedrock[J/OL]. Journal of China Coal Society: 1-13 [2022-10-30]. Doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.w022.067.
[16] 彭世龙. 厚表土薄基岩开采地层沉陷规律及其井筒偏斜致因研究[D]. 淮南: 安徽理工大学, 2019. PENG Shilong. Study on stratigraphic subsidence law and cause of shaft deflection in thick topsoil and thin bedrock[D]. Huainan: Anhui University of Science and Technology, 2019.
[17] HAN J,ZOU J,HU C,et al. Deflection mechanism and safety analysis of coal mine shaft in deep soil strata[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering,2019,2019(4):1−11.
[18] HAN J,ZOU J,HU C,et al. Study on size design of shaft protection rock/coal pillars in thick soil and thin rock strata[J]. Energies,2019,12(13):1−17.
[19] 韩继欢,杨权威,杨维好. 深厚松散层薄基岩采动沉陷致裂井壁机理[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2021,38(4):784−790. doi: 10.13545/j.cnki.jmse.2020.0027 HAN Jihuan,YANG Quanwei,YANG Weihao. Mechanism of fracturing in shaft lining caused by mining subsidence in thin bedrock and deep loose strata[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2021,38(4):784−790. doi: 10.13545/j.cnki.jmse.2020.0027
[20] 袁 力,张荣亮,左红飞,等. 新河煤矿井筒偏斜的原因及监测对策[J]. 煤炭科技,2000,3(3):5−7. doi: 10.19896/j.cnki.mtkj.2000.03.003 YUAN Li,ZHANG Rongliang,ZUO Hongfei,et al. Causes and monitoring countermeasures of shaft deflection in Xinhe Coal Mine[J]. Coal Science & Technology Magazine,2000,3(3):5−7. doi: 10.19896/j.cnki.mtkj.2000.03.003
[21] 刘焕新. 张双楼煤矿井筒变形原因分析[J]. 煤炭科技,2017(1):46−48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-3731.2017.01.013 LIU Huanxin. Cause analysis of shaft deformation in coal mine of Zhangshuanglou Coal Mine[J]. Coal Science & Technology,2017(1):46−48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-3731.2017.01.013
[22] 于保华. 大黄山矿井筒偏斜原因分析与治理措施[J]. 矿山测量, 1997 (1): 17-19. YU Baohua. Inclination of the shaft of Dahuangshan Coal Mine cause and countermeasures[J], Mine Surveying, 1997 (1): 17-19.
[23] 国家安全生产监督管理总局. 煤矿安全规程[S]. 北京: 煤炭工业出版社, 2016. [24] 国家安全监管总局, 国家煤矿安监局, 国家能源局, 等. 建筑物、水体、铁路及主要井巷煤柱留设与压煤开采规范[M]. 北京: 煤炭工业出版社, 2017. [25] 李存禄,余大有,翁洪周,等. 厚松散层地面高压注浆参数现场试验确定方法[J]. 煤炭工程,2021,53(1):65−70. LI Cunlu,YU Dayou,WENG Hongzhou,et al. Parameters determination for ground high pressure grouting in thick alluvium through field test[J]. Coal Engineering,2021,53(1):65−70.
[26] 范吉宏,戴德胜,周均民,等. 深厚松散层地面注浆压力与扩散半径确定方法[J]. 建井技术,2020,41(6):18−23. doi: 10.19458/j.cnki.cn11-2456/td.2020.06.004 FAN Jihong,DAI Desheng,ZHOU Junmin,et al. Method to define pressure and diffusion radius of grouting at surface[J]. Mine Construction Technology,2020,41(6):18−23. doi: 10.19458/j.cnki.cn11-2456/td.2020.06.004
[27] 周松柏. 厚表土薄基岩在役冻结井筒偏斜受力状态与注浆治理预警研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽建筑大学, 2018. ZHOU Songbai. Study on the stress state of slant and grouting treatment of thick overburden thin bedrock in service frozen wellbore[D]. Hefei: Anhui University of Science and Technology, 2018.



 下载:
下载: