Study on water loss settlement law of loose aquifer based on distributed optical fiber
-
摘要:
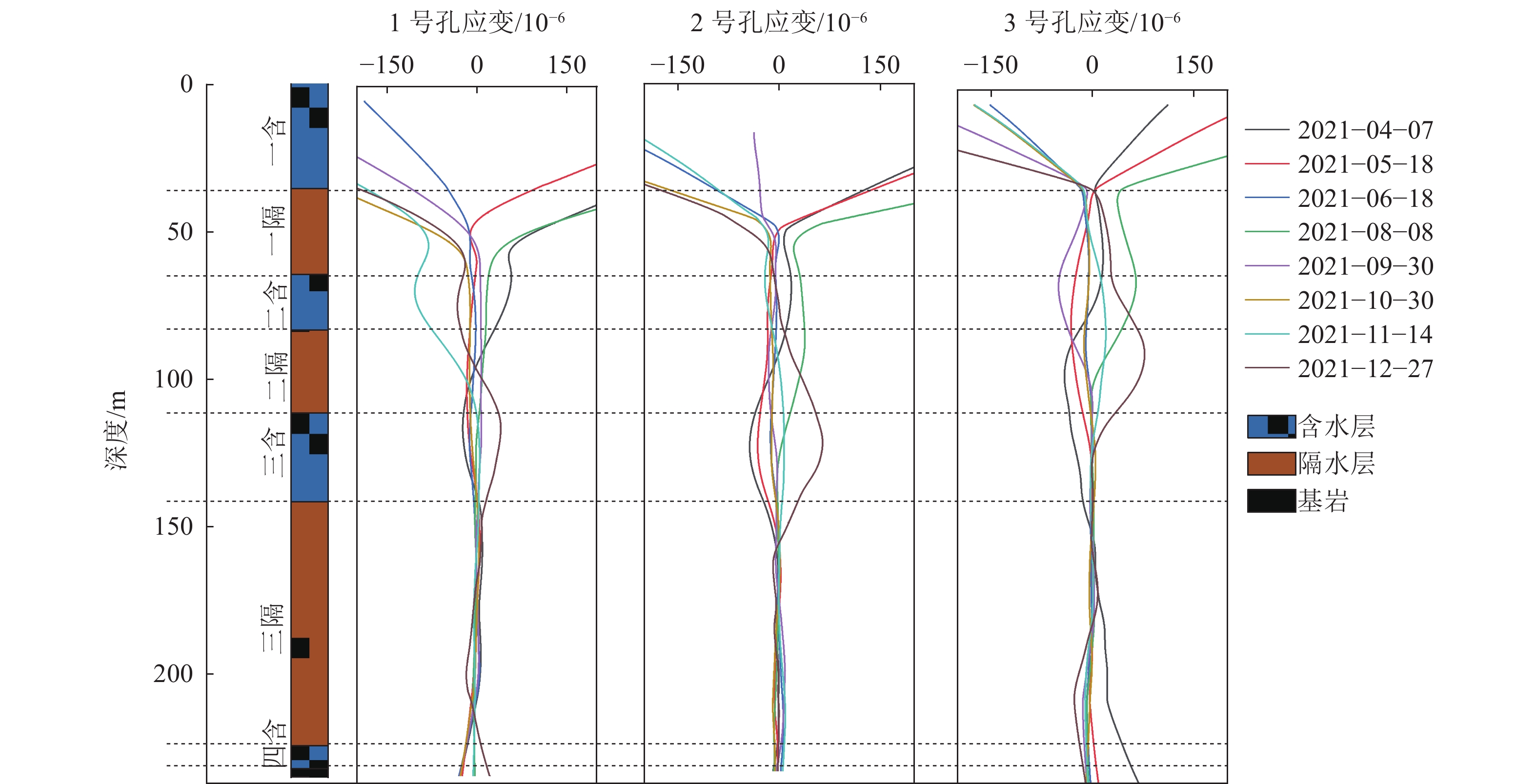
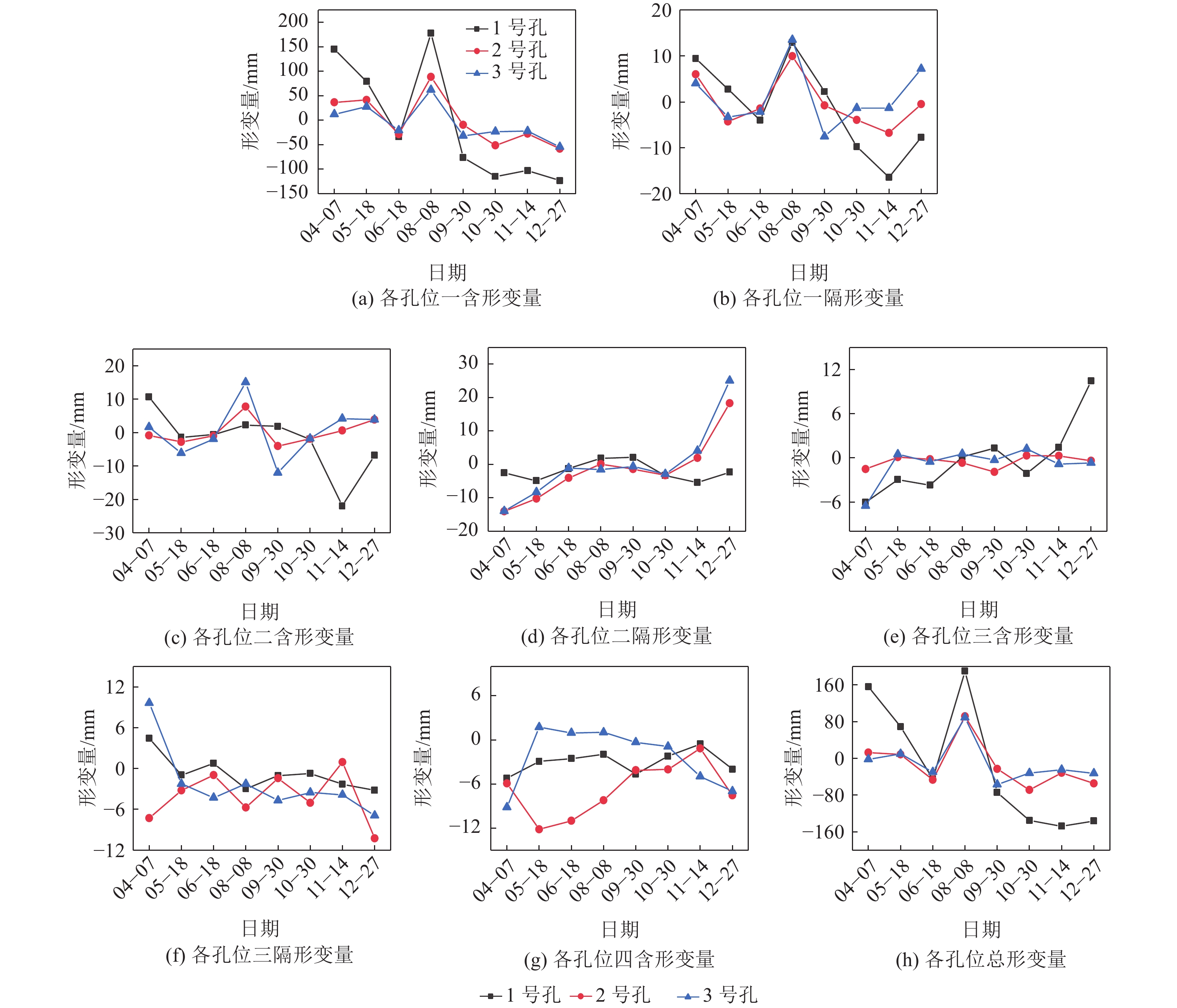
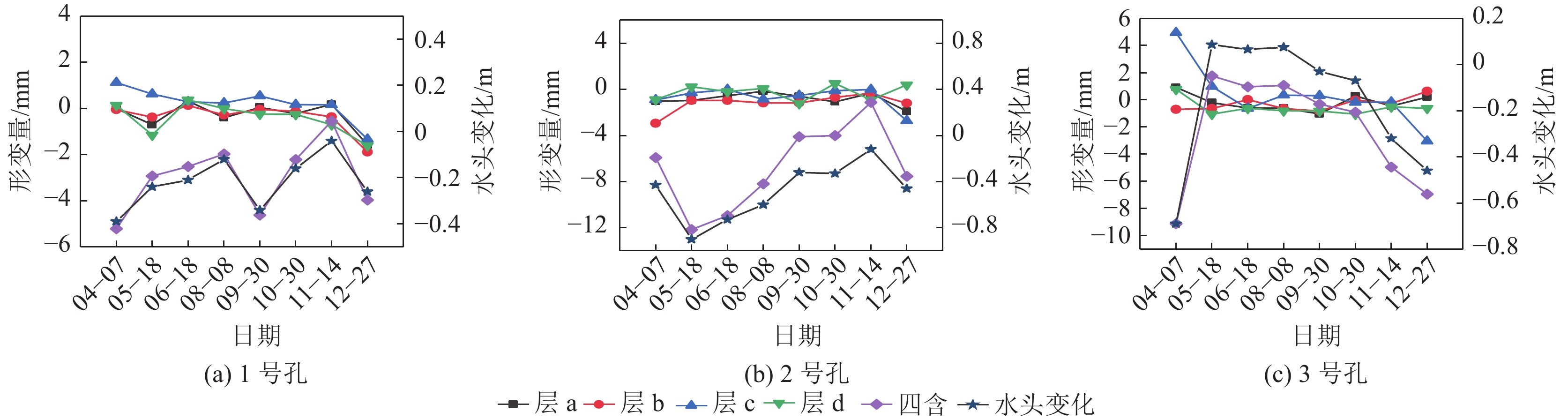
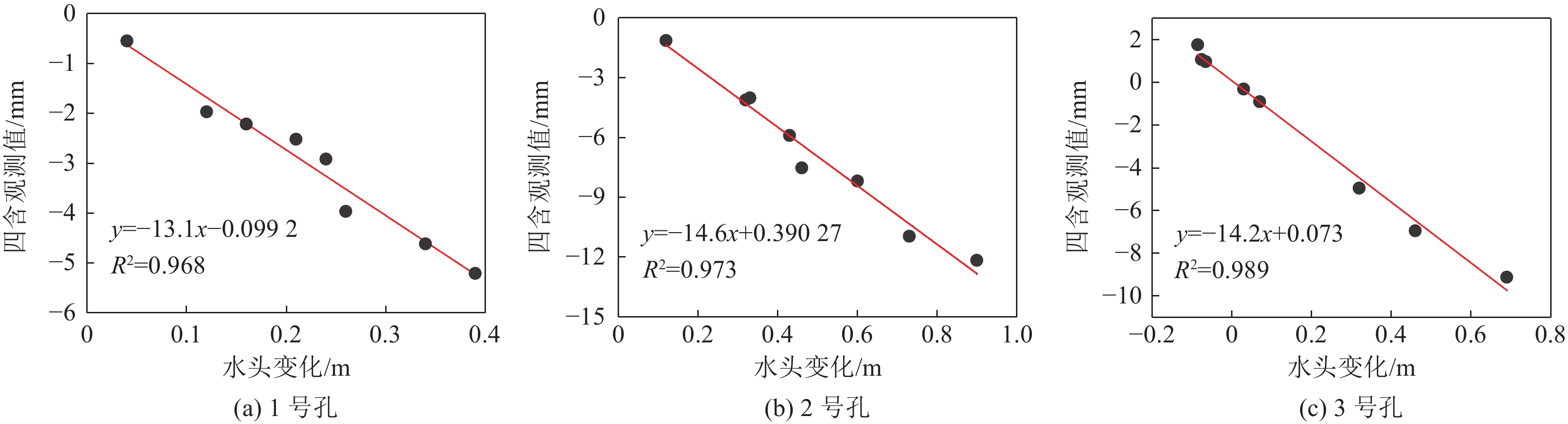
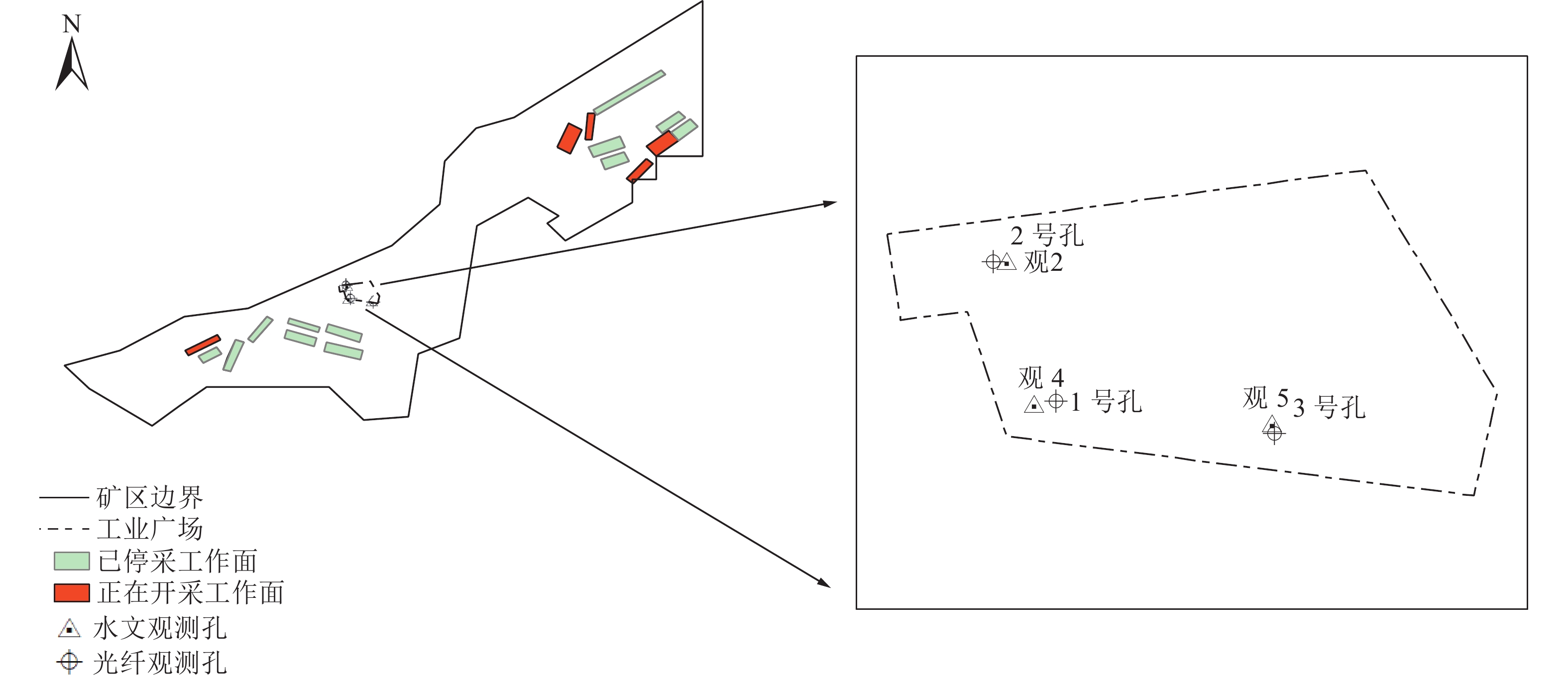
煤矿开采扰动间接引起的地下水散失会使松散层压缩,造成地表沉降,威胁煤矿安全生产。为深入分析此类非采动因素对松散含水层失水沉降的影响,根据已有的地质水文资料将研究区松散层自上而下划分为一含、一隔、二含、二隔、三含、三隔和四含。利用分布式光纤监测技术、水文观测技术和土力学实验对研究区域松散含水层进行全面观测,分析了非采动情形下各层位的形变特征,探究了深层隔水层的黏土弱化规律,明确了深层含水层形变量和该层位水头高度变化之间的关系。结果表明:①四含及上部部分隔水层持续压缩是造成研究区域地表沉降的主要原因。对地层形变贡献最大的两个层位分别为四含和一含,其中一含形变具有季节性特征,春季夏季抬升,秋季冬季沉降,而四含则在观测周期内呈持续沉降态势。②结合布设水文孔、分布式光纤和土力学实验,实现了对目标层位黏土弱化程度的监测,研究区四含上覆黏土层受四含地下水的影响产生黏土弱化,其弱化程度与埋深成反比,与地下水流通性成正比,黏土层弱化将导致含水层顶部隔水层压缩,加剧地表沉降。③四含形变与四含层位水头高度变化的趋势一致,两者呈线性关系,观测结果与理论计算结果相符,表明四含失水是造成四含压缩形变的主要原因。
Abstract:Indirect water loss caused by disturbance from coal mining can cause compression of loose layers and surface subsidence, which poses a threat to coal mine safety. To analyze the effects of such non-mining factors on water loss and subsidence of loose aquifers, the study area was divided into seven layers from top to bottom based on existing geological and hydrological data. Using distributed fiber optic monitoring technology, hydrological observation techniques, and soil mechanics experiments, the loose aquifer in the study area was comprehensively observed and the deformation characteristics of each layer under non-mining conditions were analyzed. The weakening law of the deep aquitard was explored, and the relationship between the deformation of the deep aquifer and the water head height of that layer was determined. The results show that: ① continuous compression of the fourth aquifer and its upper part of the aquitard is the main cause of surface subsidence in the study area. The two layers that contribute the most to the deformation of the strata are the fourth and first aquifers, with the latter showing seasonal deformation characteristics. The fourth aquifer exhibits a continuous subsidence trend during the observation period. ② By combining hydrological boreholes, distributed fiber optic and soil mechanics experiments, monitoring of the degree of clay weakening of the target layer was achieved. The clay layer above the fourth aquifer in the study area is weakened by the impact of the groundwater in the fourth aquifer. The degree of weakening is inversely proportional to the burial depth and directly proportional to the permeability of the groundwater, and the weakening of the clay layer will cause compression of the aquitard at the top of the aquifer and exacerbate surface subsidence. ③ The deformation of the fourth aquifer is consistent with the trend of changes in the water head of the fourth aquifer, and the two are linearly related. The observation results are in agreement with the theoretical calculation results, indicating that water loss from the fourth aquifer is the main cause of its compression deformation.
-
-
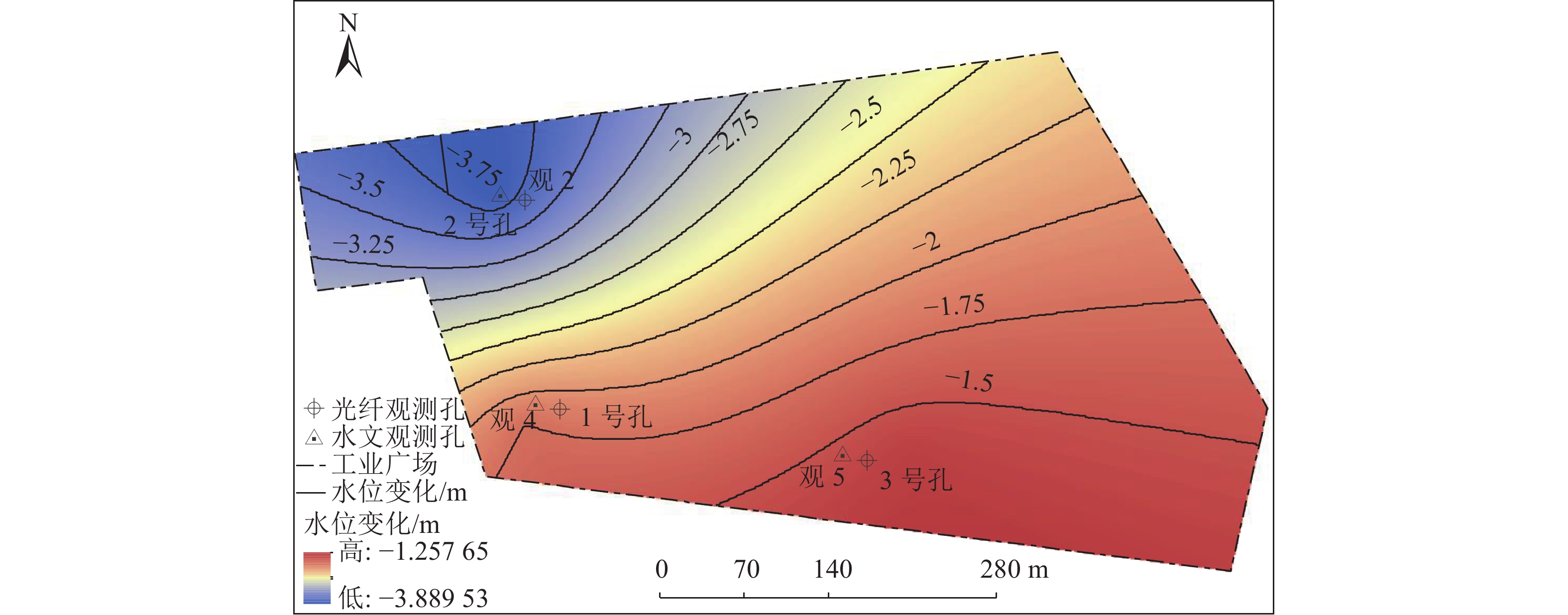
表 1 研究区域地层划分
Table 1 Stratigraphic division of the study area
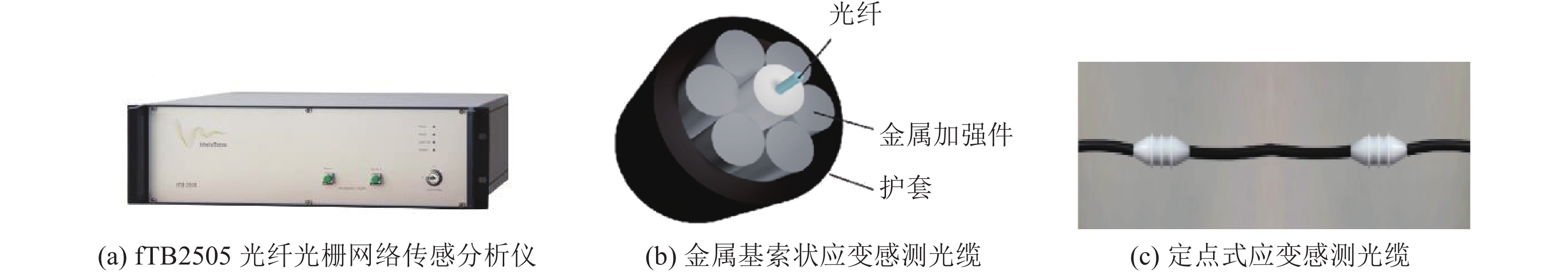
层位 厚度/m 累计深度/m 一含 35.45 35.45 一隔 29.01 64.55 二含 18.85 83.40 二隔 28.05 111.45 三含 30.02 141.65 三隔 82.65 224.30 四含 7.08 232.10 表 2 商用fTB2505型 BOFDA光纤解调仪参数
Table 2 Parameters of commercial fTB2505 BOFDA fiber optic interrogator
参数 取值 参数 取值 最大监测范围/dB >20 最高采样分辨率/m 0.05 光纤类型 单模 应变测试重复性/10−6 $ \leqslant \pm 4 $ 最高空间
分辨率/m0.2 频率扫描范围/GHz 9.9~13.0 应变测试精度/10−6 <2 接口 以太网 应变测试范围/10−6 −30000~
30000光输出接口 E-2000, APC 最大测试量程/km 50 数据输出格式 Binary, ASCII 表 3 各层位土力学试验结果
Table 3 Experimental results of soil mechanics at each layer
层位 埋深/m 平均
含水率/%平均密度/
$({\rm{kg}}·{\rm{c}}{{\rm{m}}}^{-3})$平均初始
孔隙比平均压
缩系数平均压
缩模量三隔 层a 205~210 16.5 2.32 0.36 0.11 10.84 层b 210~213 18.8 2.04 0.58 0.02 5.15 层c 213~216 9.7 2.17 0.37 0.01 10.28 层d 216~220 11.5 2.39 0.26 0.01 10.38 四含 224.5~232.1 16 2.25 0.39 0.02 5.48 -
[1] 刘孝孔,绪瑞华,赵艳鹏,等. 邻近厚松散层既有立井井筒地面注浆地层加固技术[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(7):127−134. doi: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2020-1081 LIU Xiaokong,XU Ruihua,ZHAO Yanpeng,et al. Ground grouting stratum reinforcement technology for existing vertical shafts adjacent to thick loose layers[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(7):127−134. doi: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2020-1081
[2] 程 桦,周瑞鹤,姚直书,等. 厚表土薄基岩凿井突水溃砂井筒破坏治理技术研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2021,49(4):176−185. CHENG Hua,ZHOU Ruihe,YAO Zhishu,et al. Research on wellbore damage control technology for drilling well with thick topsoil and thin bedrock, water inrush and sand burst[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2021,49(4):176−185.
[3] 陈 芳,张劲满,徐良骥,等. 厚松散含水层失水沉降相似模拟实验研究[J]. 工矿自动化,2022,48(1):78−84. CHEN Fang,ZHANG Jinman,XU Liangji,et al. Simulation experiment research on dehydration settlement of thick unconsolidated aquifer[J]. Journal of Mine Automation,2022,48(1):78−84.
[4] 李文平,于双忠. 徐淮矿区深部土体工程地质特性及失水变形机理[J]. 煤炭学报,1997,22(4):21−26. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.1997.04.004 LI Wenping,YU Shuangzhong. Engineering geological characteristics and mechanism of dehydration deformation of deep soil in Xuhuai Mining Area[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,1997,22(4):21−26. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.1997.04.004
[5] 赵仁乐,李红友,侯维华,等. 郭屯矿底部含水层水文地质特征及其失水因素[J]. 煤矿安全,2021,52(6):65−71. ZHAO Renle,LI Hongyou,HOU Weihua,et al. Hydrogeological characteristics and water loss factors of the aquifer at the bottom of Guotun Mine[J]. Safety in Coal Mines,2021,52(6):65−71.
[6] 潘维强,张黎明,丛 宇. 深厚松散地层泄压槽治理井筒破坏判据及其与地下水水位关系[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2021,51(5):1578−1586. PAN Weiqiang,ZHANG Liming,CONG Yu. Criterion for wellbore failure of pressure relief tanks in deep and unconsolidated formation and its relationship with groundwater level[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2021,51(5):1578−1586.
[7] 杜明泽,许延春,姜 鹏. 注水法预防井筒破坏机理及其应用研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2020,48(8):237−245. DU Mingze,XU Yanchun,JIANG Peng. Mechanism and application of water injection to prevent wellbore failure[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2020,48(8):237−245.
[8] GONG Hongkui,MEHMET S Kizil,CHEN Zhongwei,et al. Advances in fibre optic based geotechnical monitoring systems for underground excavations[J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology,2019,29(2):229−238. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmst.2018.06.007
[9] 方新秋,梁敏富,李 爽,等. 智能工作面多参量精准感知与安全决策关键技术[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(1):493−508. FANG Xinqiu,LIANG Minfu,LI Shuang,et al. Key technologies for multi-parameter accurate perception and safety decision-making in intelligent working face[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2020,45(1):493−508.
[10] 刘金瑄,柴 敬,朱 磊,等. 岩层变形检测的光纤光栅多点传感理论与工程应用[J]. 光学学报,2008,28(11):2143−2147. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2239.2008.11.019 LIU Jinxuan,CHAI Jing,ZHU Lei,et al. Fiber bragg grating multipoint sensing theory and engineering application for deformation detection of rock formation[J]. Acta Optica Sinica,2008,28(11):2143−2147. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2239.2008.11.019
[11] 柴 敬,朱 磊,魏世明,等. 松散地层深部沉降变形的光纤Bragg光栅监测[J]. 煤炭学报,2009,34(6):741−746. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2009.06.005 CHAI Jing,ZHU Lei,WEI Shiming,et al. Optical fiber Bragg grating monitoring of deep subsidence deformation in loose strata[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2009,34(6):741−746. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2009.06.005
[12] 柴 敬,董 梁,李 毅,等. 济三矿风井厚松散层沉降变形光纤光栅监测方法[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2010,38(5):13−16. CHAI Jing,DONG Liang,LI Yi,et al. Fiber Bragg grating monitoring method for thick unconsolidated layer settlement deformation in air shaft of Jisan Mine[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2010,38(5):13−16.
[13] 柴 敬,朱 磊,张丁丁,等. 多孔低压注水过程松散层沉降研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2013,38(10):1720−1727. CHAI Jing,ZHU Lei,ZHANG Dingding,et al. Study on settlement of loose layer during porous low pressure water injection[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2013,38(10):1720−1727.
[14] 柴 敬,邱 标,刘金瑄,等. 基于光纤光栅监测的松散地层深部注水试验[J]. 煤炭学报,2012,37(2):200−205. CHAI Jing,QIU Biao,LIU Jinxuan,et al. Deep water injection test in loose formation based on fiber bragg grating monitoring[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2012,37(2):200−205.
[15] 李 超,肖景泽,何 静,等. 北京通州某地浅部松散层压缩变形BOTDR监测分析[J]. 岩土工程技术,2020,34(3):130−134. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.2020.03.002 LI Chao,XIAO Jingze,HE Jing,et al. BOTDR monitoring and analysis of compressive deformation of shallow loose layer in Tongzhou, Beijing[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique,2020,34(3):130−134. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.2020.03.002
[16] 刘苏平,施 斌,张诚成,等. 连云港徐圩地面沉降BOTDR监测与评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(5):158−164. LIU Suping,SHI Bin,ZHANG Chengcheng,et al. BOTDR monitoring and evaluation of land subsidence in Xuwei, Lianyungang[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(5):158−164.
[17] LIU Jin,SONG Zezhuo,LU Yi,et al. Monitoring of vertical deformation response to water draining–recharging conditions using BOFDA-based distributed optical fiber sensors[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2019,78(14):406. doi: 10.1007/s12665-019-8409-7
[18] 何健辉,张进才,陈 勇,等. 基于弱光栅技术的地面沉降自动化监测系统[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(1):146−153. HE Jianhui,ZHANG Jincai,CHEN Yong,et al. Land subsidence automatic monitoring system based on weak grating technology[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(1):146−153.
[19] LIU Pingsu,SHI Bin,GU Kai,et al. Land subsidence monitoring in sinking coastal areas using distributed fiber optic sensing: a case study[J]. Natural Hazards,2020,103(3):3043−3061. doi: 10.1007/s11069-020-04118-1
[20] 吴起帆,吴静红,贾立翔,等. 基于光纤感测技术的盐城陈家港地面沉降精细化过程研究[J]. 苏州科技大学学报(工程技术版),2021,34(2):14−20. WU Qifan,WU Jinghong,JIA Lixiang,et al. Research on the refined process of land subsidence in chenjiagang, yancheng based on optical fiber sensing technology[J]. Journal of Suzhou University of Science and Technology Engineering and Technology edition,2021,34(2):14−20.
[21] 吴静红,施 斌,曹鼎峰,等. 基于DFOS的排灌水条件下土体变形 响应模型试验研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2017,25(6):1455−1464. WU Jinghong,SHI Bin,CAO Dingfeng,et al. Model test research on soil deformation response under irrigation and drainage conditions based on DFOS[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2017,25(6):1455−1464.
[22] 卢 毅,宋泽卓,于 军,等. 基于BOFDA的砂: 黏土互层垂向变形物理模型试验研究[J]. 高校地质学报,2019,25(4):481−486. LU Yi,SONG Zezhuo,YU Jun,et al. Physical model test research on vertical deformation of sand-clay interlayer based on BOFDA[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities,2019,25(4):481−486.
[23] 宋占璞. 基于光纤感测技术的抽水回灌过程砂土变形室内试验研究[J]. 工程勘察,2020,48(8):6−11, 24. SONG Zhanpu. Laboratory experimental research on sand deformation during pumping and recharging based on optical fiber sensing technology[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying,2020,48(8):6−11, 24.
[24] 宋占璞. 基于光纤感测技术的非均质土体变形室内试验研究[J]. 工程勘察,2021,49(3):1−4, 20. SONG Zhanpu. Laboratory experimental research on heterogeneous soil deformation based on optical fiber sensing technology[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying,2021,49(3):1−4, 20.
[25] 张诚成,施 斌,刘苏平,等. 钻孔回填料与直埋式应变传感光缆耦合性研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2018,40(11):1959−1967. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201811001 ZHANG Chengcheng,SHI Bin,LIU Suping,et al. Research on coupling between borehole backfill and direct-buried strain sensing optical cable[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2018,40(11):1959−1967. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201811001
[26] 张诚成,施 斌,朱鸿鹄,等. 地面沉降分布式光纤监测土–缆耦合性分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,2019,41(9):1670−1678. ZHANG Chengcheng,SHI Bin,ZHU Honghu,et al. Analysis of soil-cable coupling for distributed optical fiber monitoring of land subsidence[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2019,41(9):1670−1678.
[27] 何 俊. 膨润土水化膨胀行为简化计算[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版),2006,34(3):299−301. HE Jun. Simplified calculation of hydration and swelling behavior of bentonite[J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences),2006,34(3):299−301.
-
期刊类型引用(15)
1. 范任重. 高应力大采高工作面回采巷道围岩控制技术. 西部探矿工程. 2025(02): 83-87+91 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 闫学忠. 非中空锚索高预应力全长锚固与注浆技术研究. 能源与环保. 2025(01): 279-286 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 涂敏,郭福鑫. “蝶形托板-锚索”匹配性及锚索防剪保护机理研究. 采矿与安全工程学报. 2025(02): 306-316 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 汪占领,刘志文,赵华山,李永元,程利兴. 特厚煤层大巷变形破坏特征及控制技术研究. 煤炭工程. 2024(04): 53-59 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 吴晓宇,周豪,吴晓伟. 近距离下煤层中空注浆锚索注浆前后周边剪应力作用机理. 煤炭工程. 2024(04): 112-118 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 李建志. 开拓大巷变形破坏机理分析及控制措施研究. 西部探矿工程. 2024(09): 134-137 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 吴宁. 注浆锚索主动式超前支护巷道围岩变形控制技术. 煤炭科技. 2024(06): 57-62+66 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 孙长全. 大跨度大空间建筑预应力型钢混凝土组合结构施工技术研究. 粉煤灰综合利用. 2024(06): 115-119 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 傅翔,黄平,陈柏林,彭海游,黄祥超. 坡顶带临空建筑高边坡切脚滑坡抢险加固技术. 山西建筑. 2023(04): 90-92+96 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 赵明洲,方娟,辛程鹏,李回贵. 回采煤巷大厚度泥质层状顶板失稳机理及控制对策. 矿业研究与开发. 2023(04): 75-81 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 李天棚,陈江,张焙炎,谈文州. 近距离煤层重复采动下巷道变形机制及稳定控制技术. 煤炭科技. 2023(04): 182-188 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 路广安. 山寨煤矿高应力巷道底板动态控制方法. 山东煤炭科技. 2023(08): 191-193 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 郭军亮. 强动压巷道柔性锚杆支护方案设计及工业性试验分析. 西部探矿工程. 2023(10): 123-125 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 姚强岭,徐强,何杰,李英虎,刘伟冬. 基于有效锚固层厚度的近距离煤层下伏巷道支护技术数值模拟研究. 能源与环保. 2023(11): 1-6 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 王坤. 杜儿坪矿73907胶带巷超前支护技术研究与应用. 煤. 2023(12): 44-48+60 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(6)



 下载:
下载: