Evaluating method of gas content of coalbed methane based on nuclear magnetic resonance technology
-
摘要:
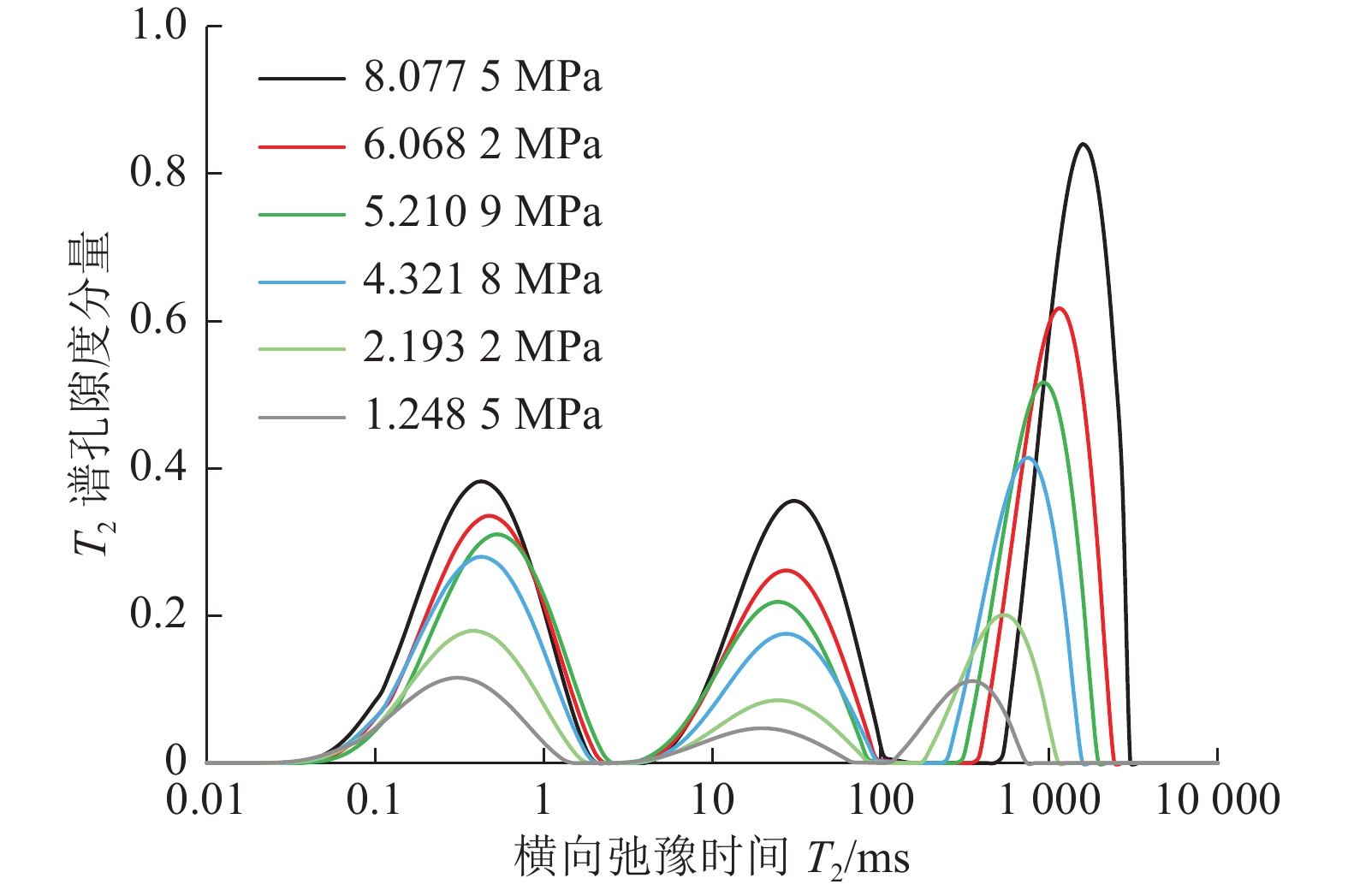
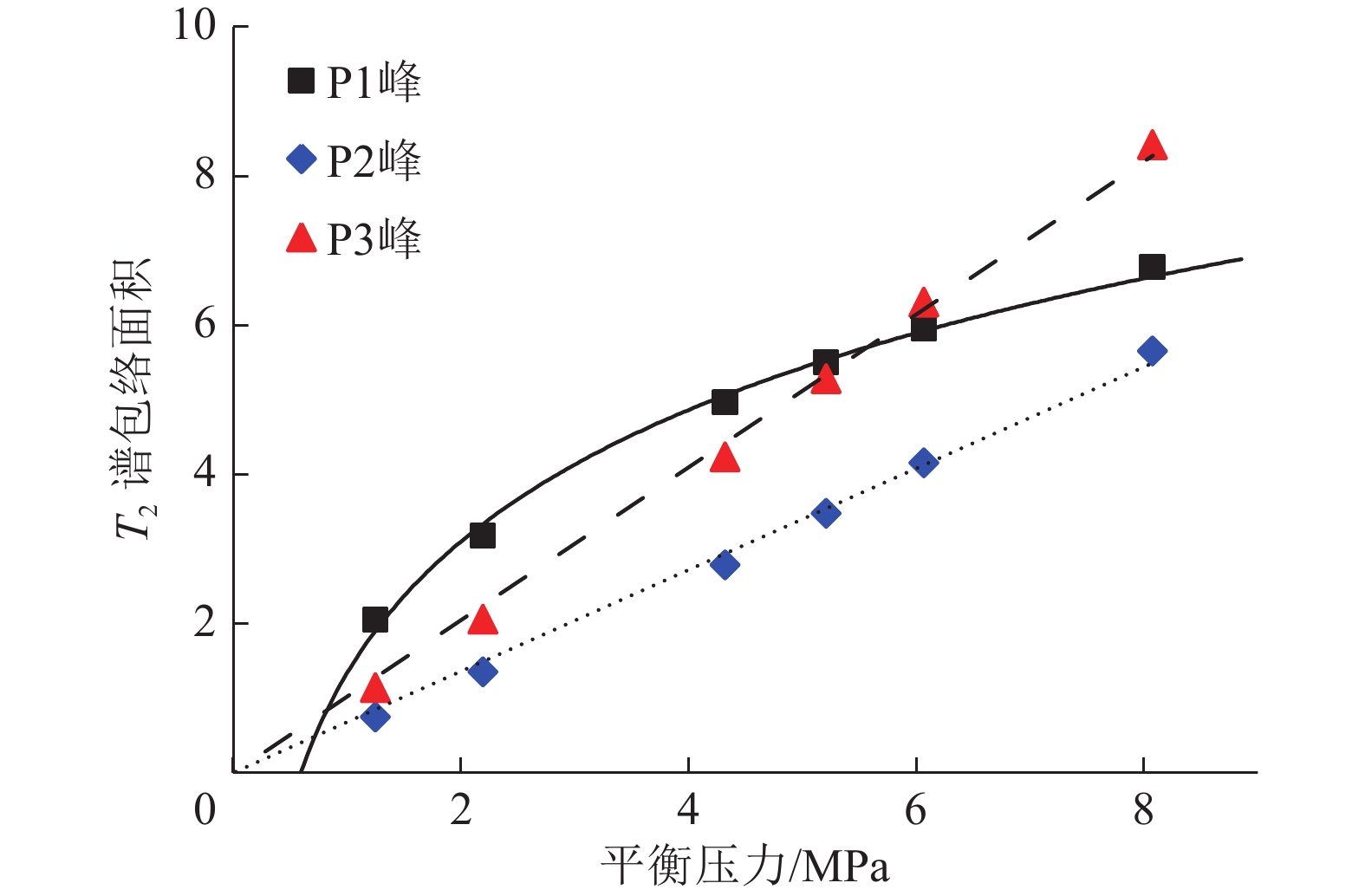
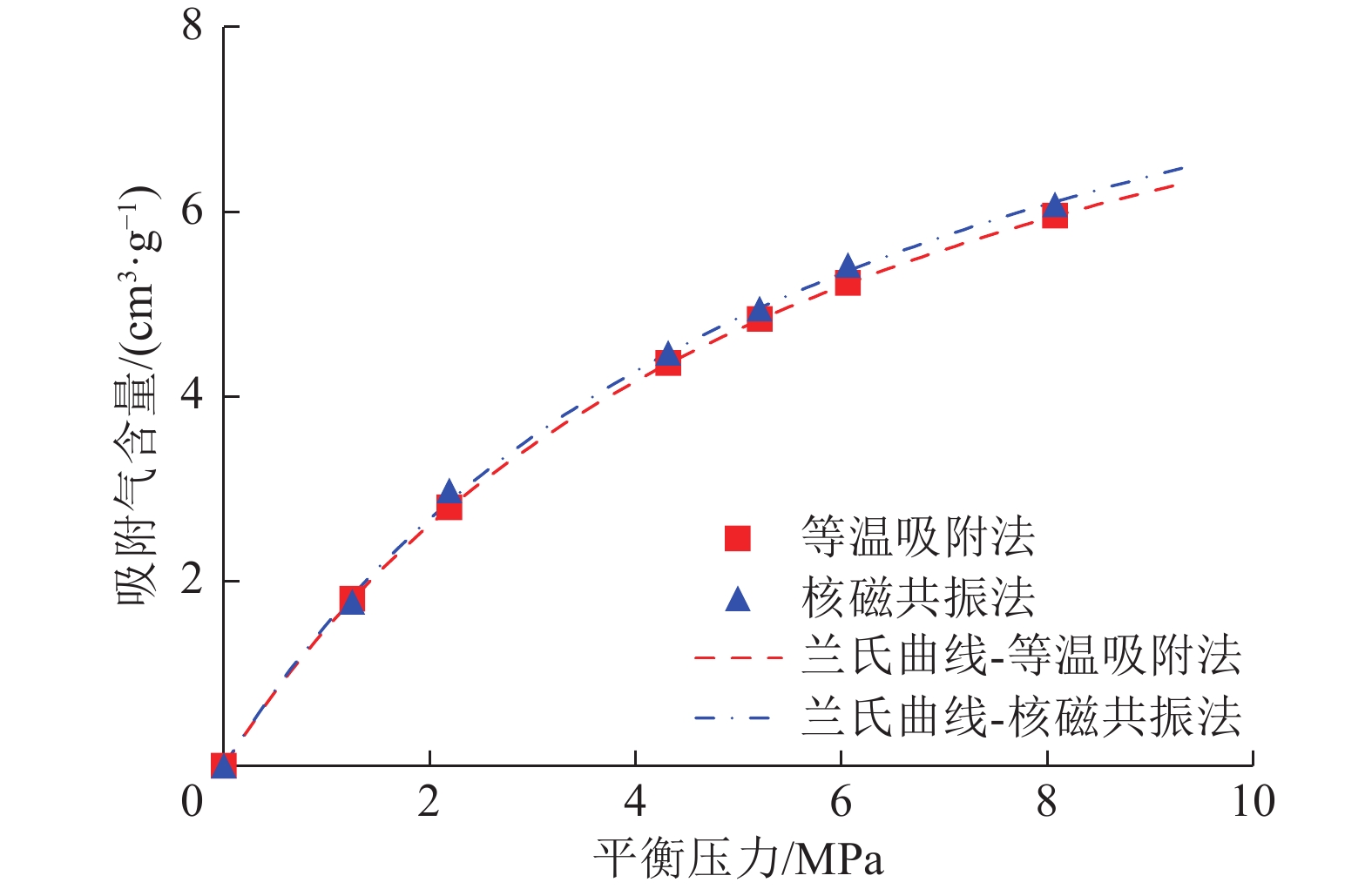
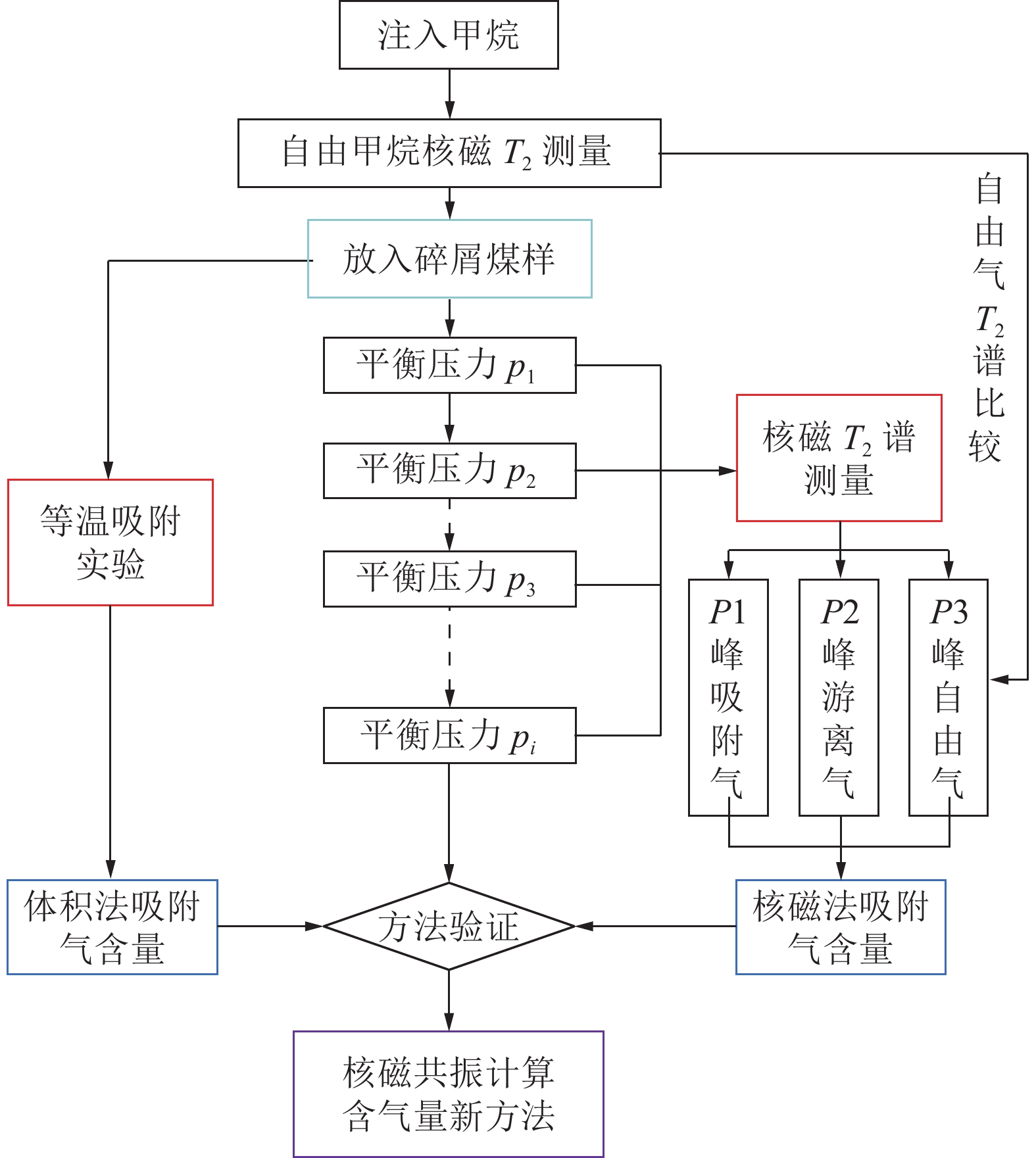
我国煤层气资源储量十分丰富,是良好的天然气后备资源,开发利用煤层气具有多重价值。煤层含气量是评价煤层的关键参数,也是决定煤层气勘探开发选区与产能潜力大小的重要因素,利用测井技术评价含气量可以低成本获得地下煤层气关键参数,准确获得含气量对煤层气勘探开发具有极为重要的影响。为了规避煤层中天然气不同赋存状态导致的密度不同和Langmuir单层吸附模型造成的含气量低估,提出了一种基于核磁共振技术评价煤层含气量的新方法,采用经过校准的核磁共振仪器测量煤层中的核磁共振信号,通过分离煤层中吸附态天然气的核磁共振信号,进而计算单位体积地层中天然气分子的摩尔数,综合体积密度测井换算为标准状态下煤层含气量。为验证方法的有效性,设计开展了实际煤样甲烷等温吸附与核磁共振联测试验,试验结果表明,利用不同的T2(横向弛豫时间)截止值可以区分煤层中不同赋存状态的甲烷气体,基于核磁共振新方法计算的与试验测量的煤层含气量符合很好,证明了新方法的有效性。实际测井资料处理解释结果表明,基于核磁测井新方法比常规测井方法计算煤层含气量更加有效。
-
关键词:
- 煤层气 /
- 核磁共振 /
- T2截止值 /
- 含气量 /
- Langmuir吸附
Abstract:China has abundant coalbed methane (CBM) resources, which is a good reserve of natural gas. The development and utilization of CBM has multiple values. Gas content of coal is the key to evaluate coal seam, and it is also an important factor to determine the exploration and development area and productivity potential of CBM. Using logging data to evaluate gas content is an important means in CBM exploration and development. In order to avoid the density difference caused by different methane states and the underestimation of gas content caused by Langmuir monolayer adsorption model in coal seam, a new method is adopted to separate the NMR signal of adsorbed natural gas in coal seam, calculate the molecules mole number of natural gas in unit volume formation, and convert into the gas content in standard state by density logging. The experimental results of methane isothermal adsorption and NMR show that differentT2 cut-off values can be used to distinguish methane states in coal seam. The adsorpted methane content calculated by using new method based on NMR is in good agreement with the measurement of coal sample, which proves the effectiveness of the method. The actual logging data processing and interpretation results show that the new method based on NMR logging is more effective than the method based on conventional logging in calculating gas content of coal seam.
-
Keywords:
- Coalbed methane /
- nuclear magnetic resonance /
- T2 cutoff /
- gas content /
- Langmui absorption
-
-
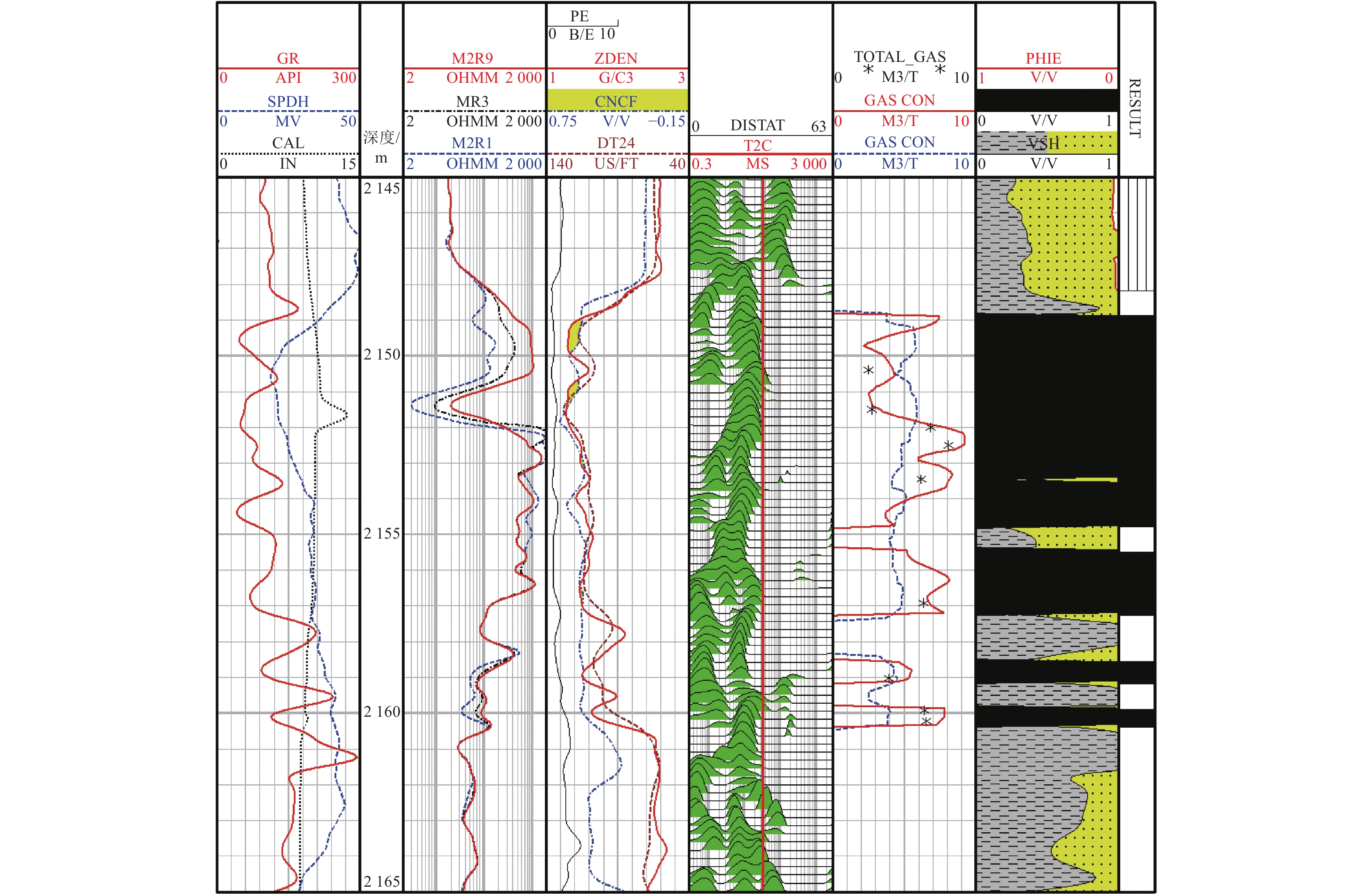
图 5 A井常规测井、核磁测井计算煤层含气量与实际取心分析含气量对比
(注:第1道红色曲线为自然伽马、蓝色曲线为自然电位、黑色曲线为井经;第2道为测量深度;第3道红色、黑色和蓝色曲线分别为深、中、浅阵列感应电阻率;第4道红色曲线为密度、蓝色曲线为中子孔隙度、棕色曲线为纵波时差和黑色曲线为光电俘获截面指数曲线;第5道为核磁共振测井T2谱;第6道红色曲线为核磁法含气量、蓝色曲线为常规法含气量和黑色点为岩心分析含气量)
Figure 5. Comparison of gas content calculated by conventional logging, nuclear magnetic logging and actual coring analysis in A well
表 1 等温吸附试验与核磁共振计算吸附甲烷含量及兰格缪尔方程对比
Table 1 Comparison of adsorbed methane content and Langmuir equation between NMR calculation and experimental measurement
样品号 工业分析/% 平衡压力/
MPa等温吸附法 核磁共振法 吸附气含
量相对
误差/%镜质体
反射率/%水分 挥发分 灰分 固定碳 吸附气
含量/
(cm3·g−1)Langmuir
体积/
(cm3·g−1)Langmuir
压力/
MPa吸附气
含量/
(cm3·g−1)Langmuir
体积/
(cm3·g−1)Langmuir
压力/
MPaSM-17-10 1.15 23.04 43.60 32.21 0 0 10.29 5.88 0 10.56 5.89 0 1.11 1.249 1.80 1.77 1.8 2.193 2.79 2.98 6.7 4.322 4.36 4.47 2.6 5.211 4.83 4.95 2.3 6.068 5.22 5.42 3.7 8.078 5.95 6.08 2.1 SM-14-17 1.10 12.75 34.45 51.70 0 0 13.01 3.98 0 12.89 3.68 0 1.30 2.510 5.03 5.24 3.7 3.608 6.19 6.33 2.1 4.555 6.94 7.19 3.0 5.623 7.62 7.60 0.2 6.573 8.10 8.42 3.4 7.578 8.73 8.88 1.5 8.755 8.94 9.06 1.1 SM-4-29 1.44 25.21 30.57 42.78 0 0 12.13 5.43 0 11.59 5.01 0 1.28 2.316 3.63 3.76 3.8 3.262 4.55 4.45 2.3 4.158 5.26 5.10 3.1 5.419 6.06 6.14 1.3 6.622 6.66 6.77 1.7 7.515 7.04 6.88 2.4 SM-10-40 0.96 10.19 28.24 60.61 0 0 10.29 2.94 0 10.91 3.52 0 1.27 1.355 3.26 3.07 6.0 3.168 5.33 5.11 4.2 5.285 6.60 6.67 1.1 7.298 7.31 7.15 2.3 9.183 7.78 7.98 2.6 11.128 8.16 8.32 2.0 -
[1] 邵龙义,侯海海,唐 跃,等. 中国煤层气勘探开发战略接替区优选[J]. 天然气工业,2015(3):1−11. SHAO Longyi,HOU Haihai,TANG Yue,et al. Optimization of strategic replacement areas for CBM exploration and development in China[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2015(3):1−11.
[2] 张道勇,朱 杰,赵先良,等. 全国煤层气资源动态评价与可利用性分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2018,43(6):1598−1604. ZHANG Daoyong,ZHU Jie,ZHAO Xianliang,et al. Dynamic evaluation and availability analysis of coalbed methane resources in China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2018,43(6):1598−1604.
[3] 张宝生,罗东坤,平 洋. 中国煤层气开发社会效益的评价[J]. 统计与决策,2008(18):53−56. ZHANG Baosheng,LUO Dongkun,PING Yang. Evaluation of social benefits of coalbed methane development in China[J]. Statistics and Decision,2008(18):53−56.
[4] 冯 明,陈 力,徐承科,等. 中国煤层气资源与可持续发展战略[J]. 资源科学,2007,29(3):100−104. FENG Ming,CHEN Li,XU Chengke,et al. China’s coalbed methane resources and sustainable development strategy[J]. Resource Science,2007,29(3):100−104.
[5] 国家能源局. 煤层气(煤矿瓦斯)开发利用“十三五”规划[EB/OL]. http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2016-12/04/content5142853.htm, 2016-11. [6] 宋 岩,柳少波,琚宜文,等. 含气量和渗透率耦合作用对高丰度煤层气富集区的控制[J]. 石油学报,2013,34(3):417−426. SONG Yan,LIU Shaobo,JU Yiwen,et al. Control of high abundance coalbed methane enrichment area by coupling effect of gas content and permeability[J]. Journal of Petroleum,2013,34(3):417−426.
[7] 万金彬,李素娟,黄 科,等. 沁水盆地樊庄区块煤层含气量影响因素分析[J]. 石油天然气学报,2012(9):83−88. WAN Jinbin,LI Sujuan,HUANG Ke,et al. Analysis on influencing factors of coal seam gas content in Fanzhuang block of Qinshui Basin[J]. Journal of Petroleum and Natural Gas,2012(9):83−88.
[8] 孙海涛,舒龙勇,姜在炳,等. 煤矿区煤层气与煤炭协调开发机制模式及发展趋势[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(12):1−13. SUN Haitao,SHU Longyong,JIANG Zaibing,et al. Progress and trend of key technologies of CBM developmentand utilization in China coal mine areas[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(12):1−13.
[9] 连承波,赵永军,李汉林,等. 煤层含气量的主控因素及定量预测[J]. 煤炭学报,2005,30(6):726−729. LIAN Chenbo,ZHAO Yongjun,LI Hanlin,et al. Main controlling factors and quantitative prediction of coal seam gas content[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2005,30(6):726−729.
[10] 曹军涛,赵军龙,王轶平,等. 煤层气含量影响因素及预测方法[J]. 西安石油大学学报:自然科学版,2013(4):28−34. CAO Juntao,ZHAO Junlong,WANG Zhiping,et al. Influencing factors and prediction methods of coalbed methane content[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of petroleum:Natural Science Edition,2013(4):28−34.
[11] 金力钻,冯俊贵,温 渊,等. 基于测井敏感参数的煤层含气量定量评价方法:以鄂东气田三交北区块为例[J]. 石油天然气学报,2015(7):24−29. JIN Lizuan,FENG Jungui,WENG Yuan,et al. Quantitative evaluation method of coal seam gas content based on logging sensitive parameters: Taking Sanjiaobei block of Edong gas field as an example[J]. Journal of Petroleum and Natural Gas,2015(7):24−29.
[12] KIM A G . Estimating methane content of bituminous coalbeds from adsorption data. United States Bureau of Mines Report of Investigations[J]. 1977, 8245, 22.
[13] HAWKINS J M, SCHRAUFNAGEL R A, OL-SZEWSKL A J. Estimating coalbed gas content and sorption isotherm using well log data[J]. SPE, 1992.
[14] AHMED U, JOHNSTON D, COLSON L. An ad-vanced and integrated approach to coal formation evaluation[J]. SPE, 1991.
[15] 李传明,王延斌,韩文龙,等. 基于KIM方程预测沁水盆地柿庄南区块3号煤层含气量[J]. 煤炭技术,2020,39(2):94−96. LI Chuanming,WANG Yanbin,HAN Wenlong,et al. Prediction of 3号 coal seam gas content in Shizhuang south block of Qinshui Basin Based on Kim equation[J]. Coal Technology,2020,39(2):94−96.
[16] MULLEN M J. Coalbed methane resource evaluation from wireline logs in the northeastern San Juan Basin: a case study[J]. SPE, 1989.
[17] 潘和平,黄智辉. 煤层煤质参数测井解释模型[J]. 现代地质,1998,12(3):447−451. PAN Heping,HUANG Zhihui. Logging interpretation model of coal quality parameters in coal seam[J]. Modern Geology,1998,12(3):447−451.
[18] BHANJA A K, SRIVASTAVA O P. A new approach to estimate CBM gas content from well logs[J]. SPE, 2008.
[19] 张作清. 和顺地区煤层气工业组分与含气量计算研究[J]. 测井技术,2013,37(1):99−102. ZHANG Zuoqing. Study on Calculation of industrial components and gas content of coalbed methane in Heshun area[J]. Logging Technology,2013,37(1):99−102.
[20] 陈小军,李鹏飞,李 萍,等. 多元逐步回归分析法在煤层含气量预测中的应用[J]. 煤炭工程,2019,51(2):106−111. CHEN Xiaojun,LI Pengfei,LI Ping,et al. Application of multiple stepwise regression analysis in prediction of coal seam gas content[J]. Coal Engineering,2019,51(2):106−111.
[21] 侯俊胜. 煤层气储层评价的地球物理测井技术[J]. 现代地质,1998(1):130−133. HOU Junsheng. Geophysical logging technology for coalbed methane reservoir evaluation[J]. Modern Geology,1998(1):130−133.
[22] 崔晓松,周 瑞,张 凯. 沁水盆地寿阳西部地区煤层气资源潜力评价[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(7):224−232. CUI Xiaosong,ZHOU Rui,ZHANG Kai. Potential evaluation of coalbed methane resources in western Shouyang County of Qinshui Basin[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(7):224−232.
[23] 向 旻,齐兴华,张峰玮,等. 深度学习在煤层气测井解释中的应用研究[J]. 地质与勘探,2020,56(6):8. XIANG min,QI Xinghua,ZHANG Fengwei,et al. Application of deep learning in CBM logging interpretation[J]. Geology and Exploration,2020,56(6):8.
[24] 黄兆辉. 高阶煤层气储层测井评价方法及其关键问题研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014: 12-18. HUANG Zhaohui. Research on logging evaluation method and key problems of high-order coalbed methane reservoir[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2014: 12-18.
[25] PAPAIOANNOU A, KAUSIK R. Methane storage in nanoporous media as observed via high-field NMR relaxometry[J]. Physical Review Applied, 4, 024018.
[26] BRUNAUER S, EMMETT P H, TELLER E. Adsorp-tion of gases in multimolecular layers[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 60(2), 309–319.
[27] 杨 明,柳 磊,刘佳佳,等. 中阶煤孔隙结构的氮吸附−压汞−核磁共振联合表征研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2021,49(5):67−74. YANG Ming,LIU Lei,LIU Jiajia,et al. Study on joint charac-terization of pore structure of middle-rank coal by ni-trogen adsorption-mercury intrusion-NMR[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2021,49(5):67−74.
[28] Rylander,Erik,Westacott,et al. A Novel Determination of Total Gas-In-Place (TGIP) for Gas Shale From Magnetic Resonance Logs[J]. Petrophysics,2017,58(3):232−241.
[29] 许 江,李奇贤,彭守建,等. 叠置含气系统煤层气开采物理模拟试验方法研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2021,49(1):225−233. XU Jiang,LI Qixian,PENG Shoujian,et al. Study on physical simulation test method of coalbed methane production in superimposed gas-bearing system[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2021,49(1):225−233.
[30] 姚艳斌,刘大锰. 基于核磁共振弛豫谱的煤储层岩石物理与流体表征[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2016(6):14−22. YAO Yanbin,LIU Dameng. Petrophysics and fluid characterization of coal reservoir based on NMR relaxation spectrum[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2016(6):14−22.
[31] 肖立志. 中国复杂油气藏核磁共振测井理论与方法[M]. 科学出版社, 2012. XIAO Lizhi. Theory and method of nuclear magnetic resonance logging for complex reservoirs in China [M]. Science Press, 2012.
[32] 潘新志,叶建平,孙新阳,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地神府地区中低阶煤层气勘探潜力分析[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2015,43(9):65−70. PAN Xinzhi,YE Jianping,SUN Xinyang,et al. Analysis on exploration potential of middle and low rank coalbed methane in Shenfu area of Ordos Basin[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2015,43(9):65−70.



 下载:
下载: