Numerical simulation study on the impact of high intensity mining activities on groundwater
-
摘要:
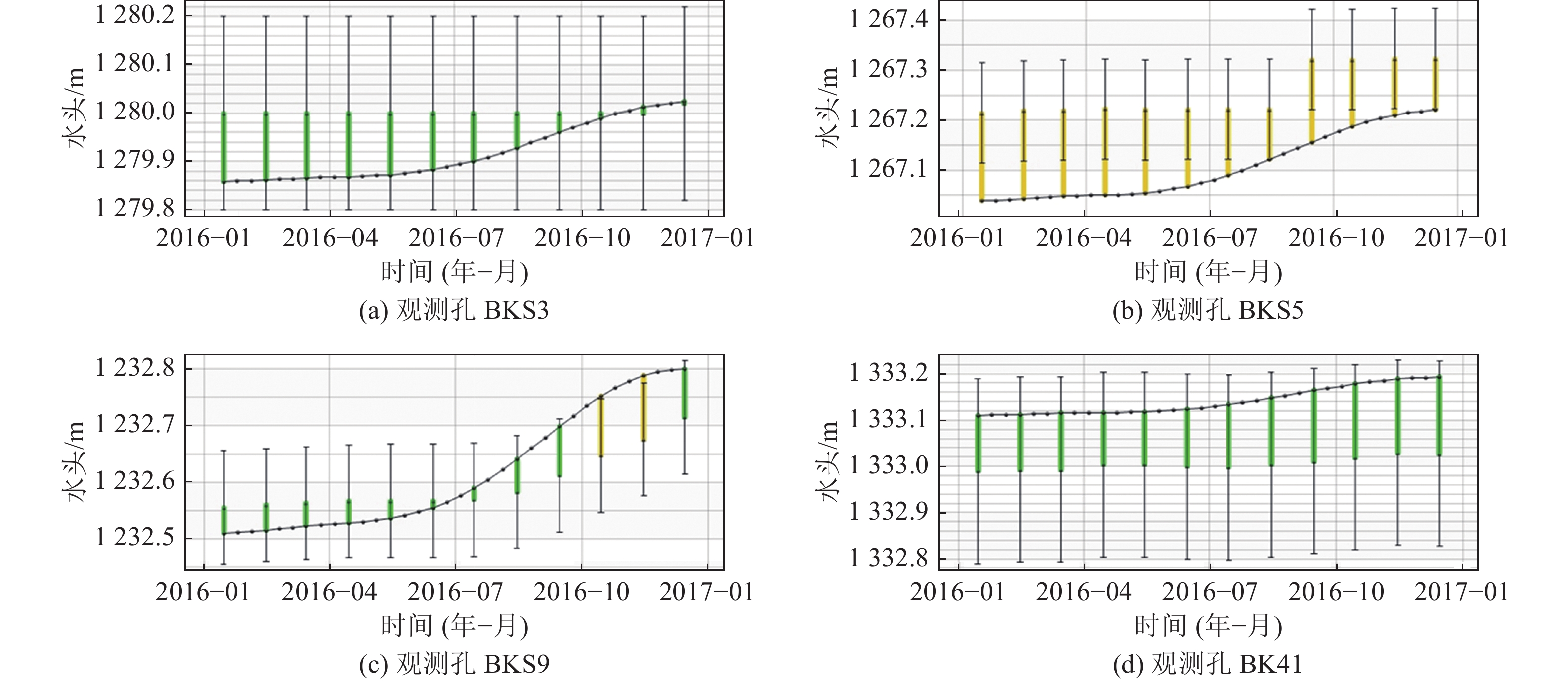
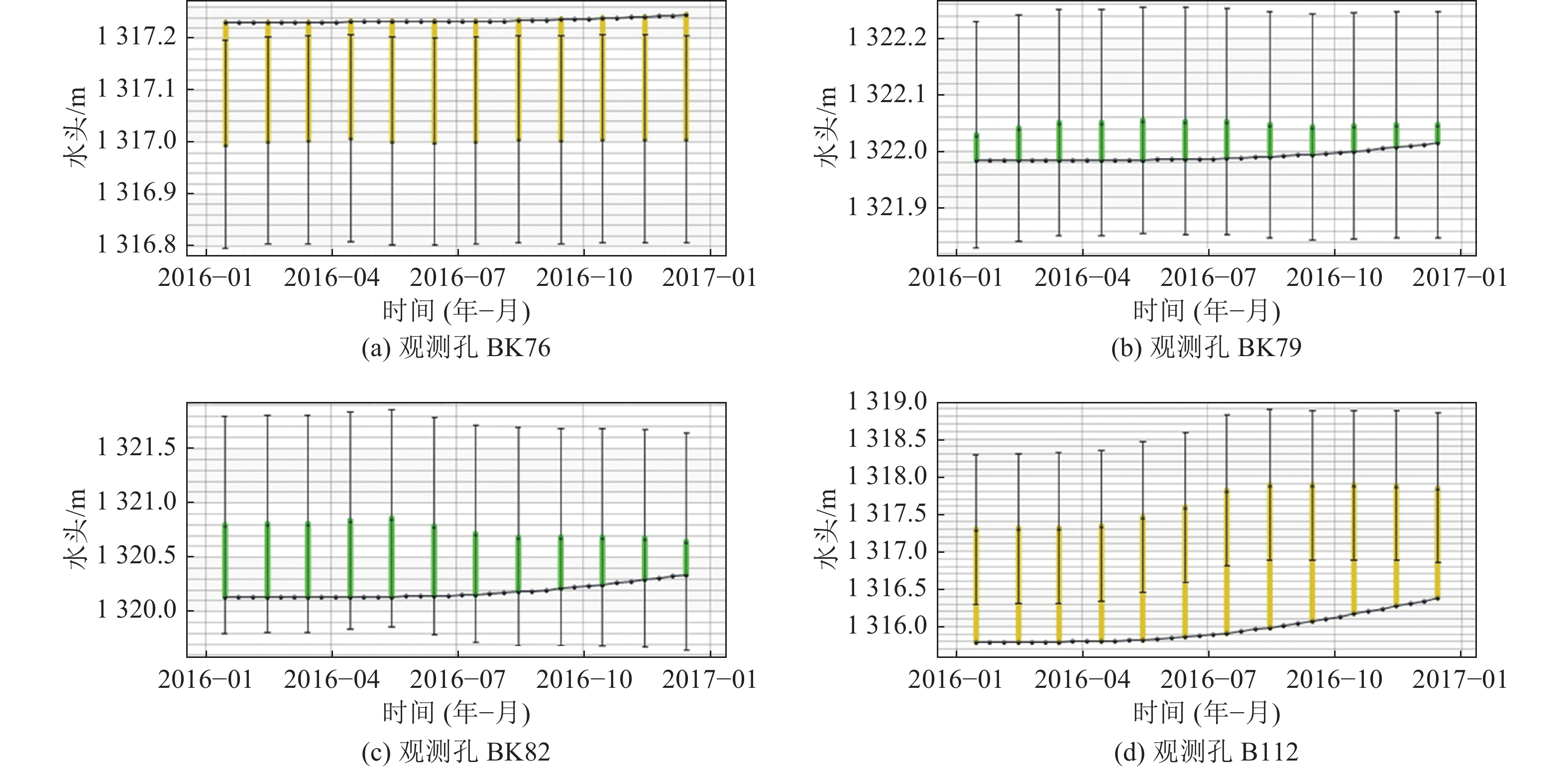
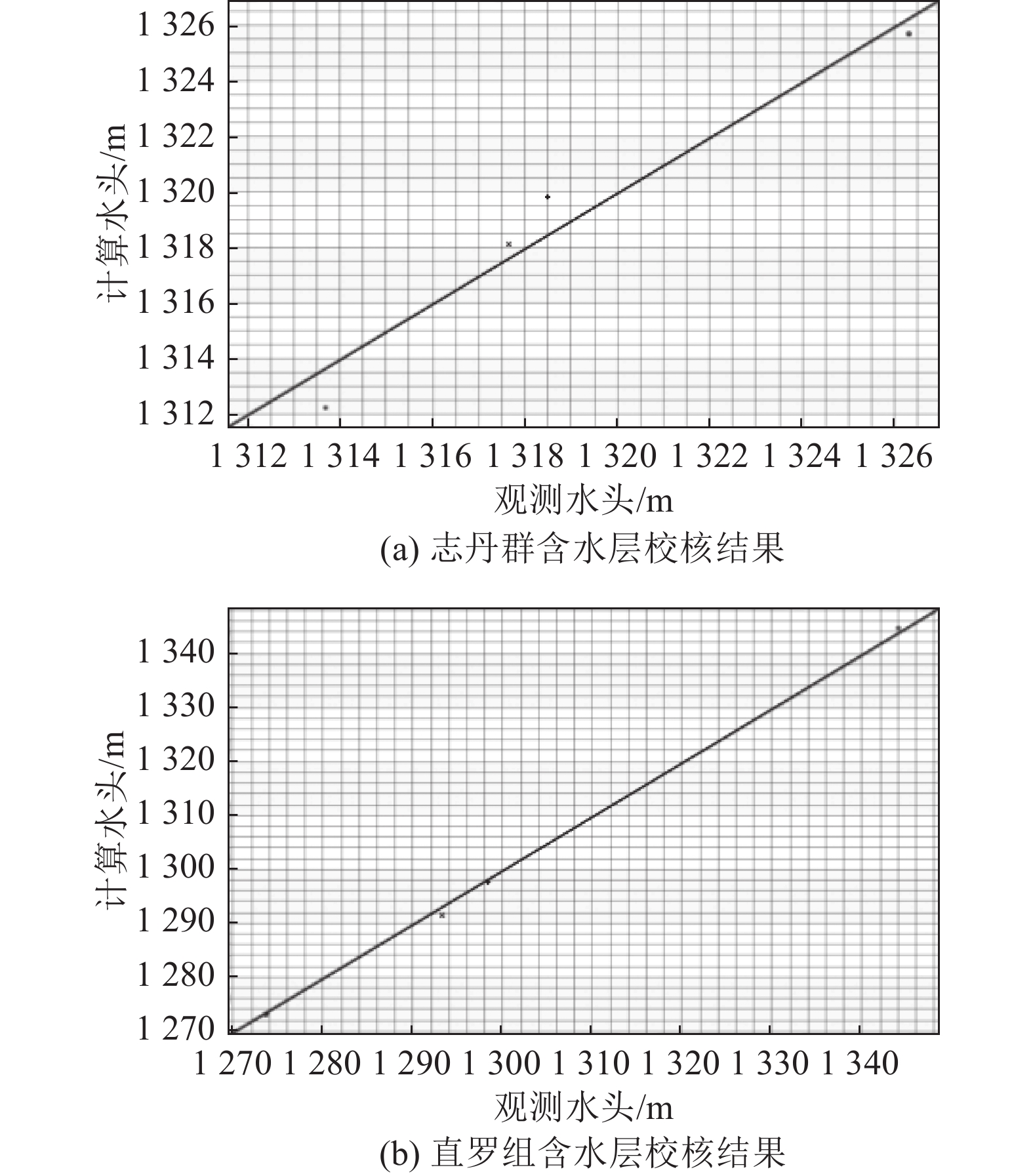
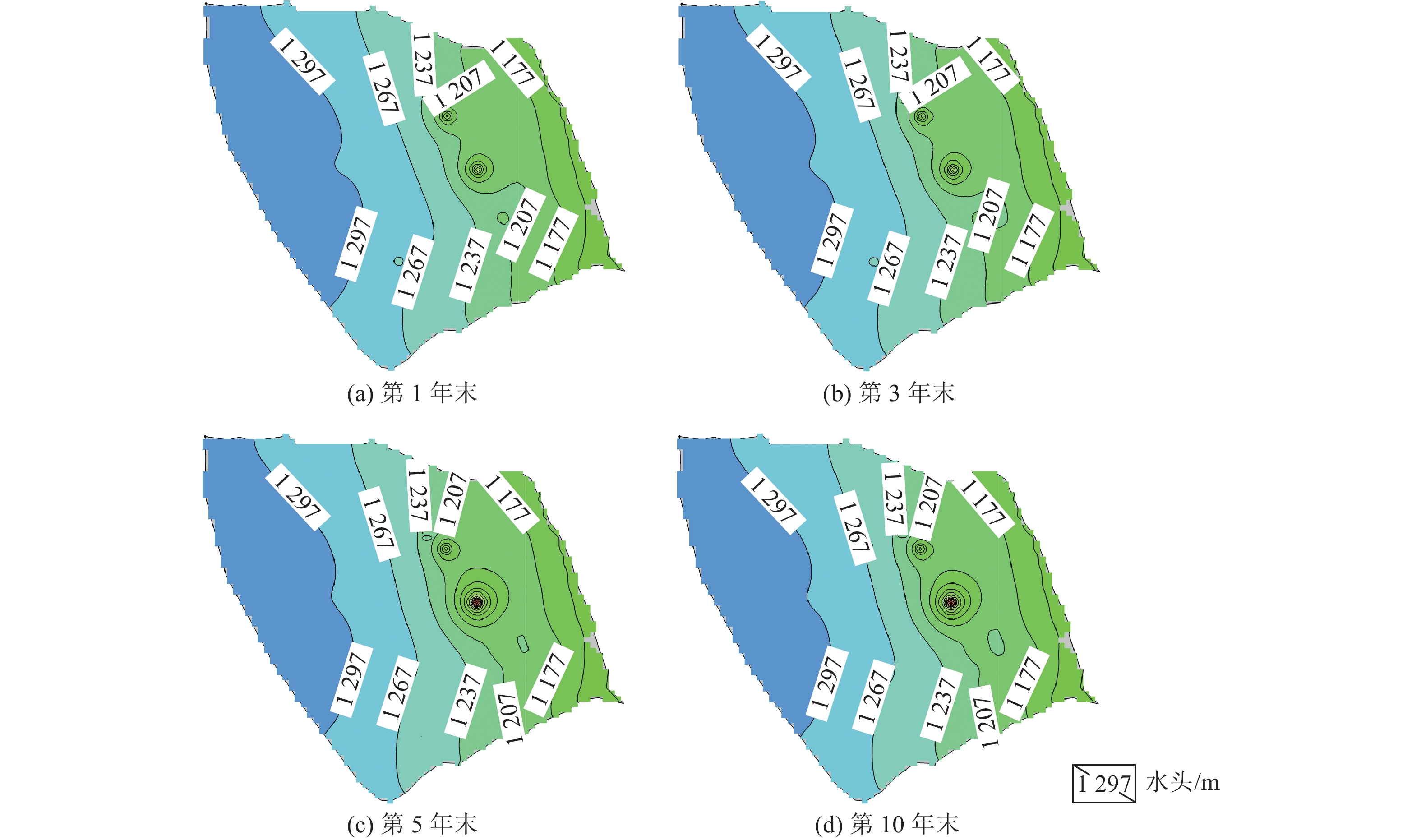
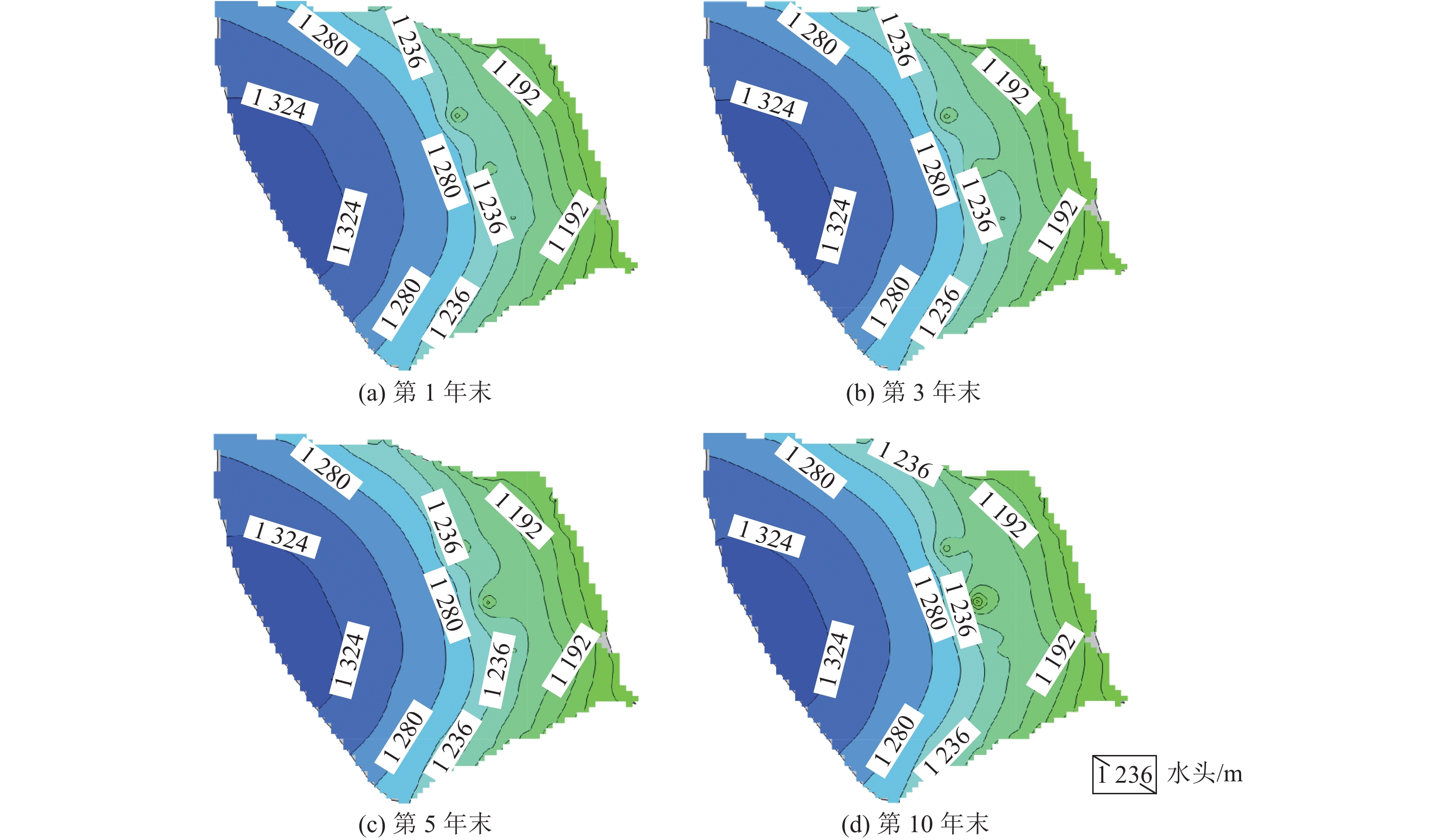
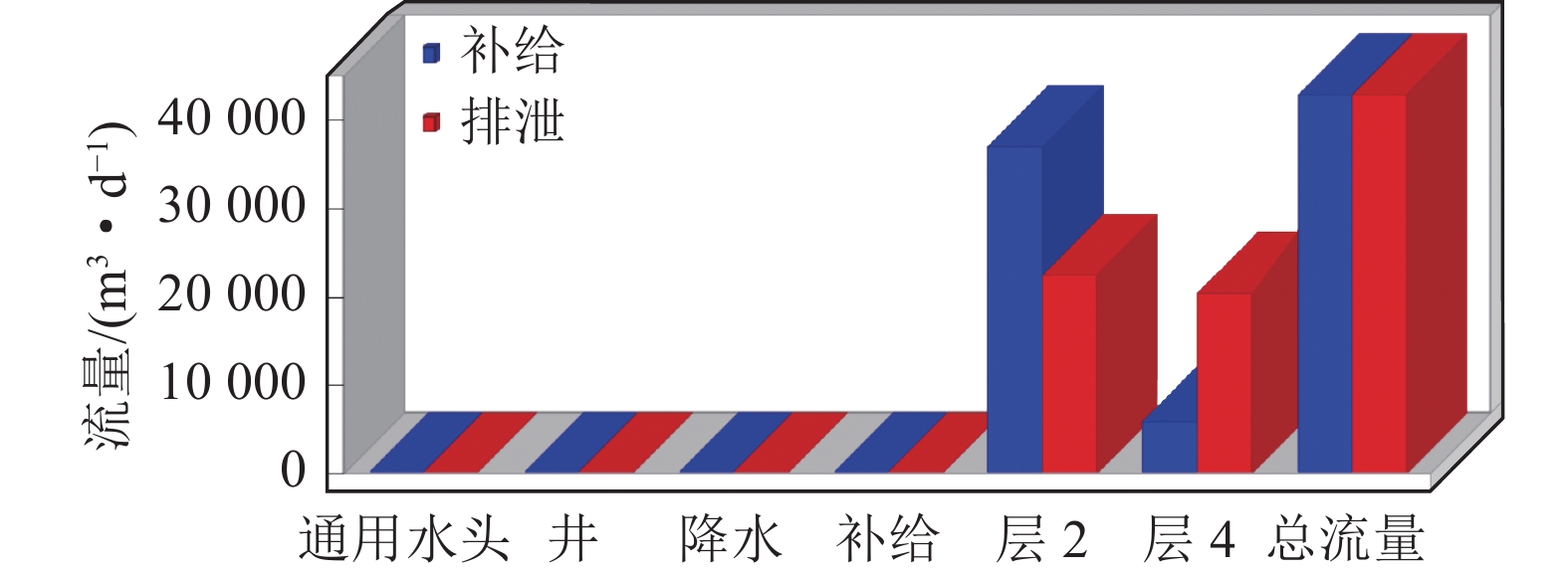
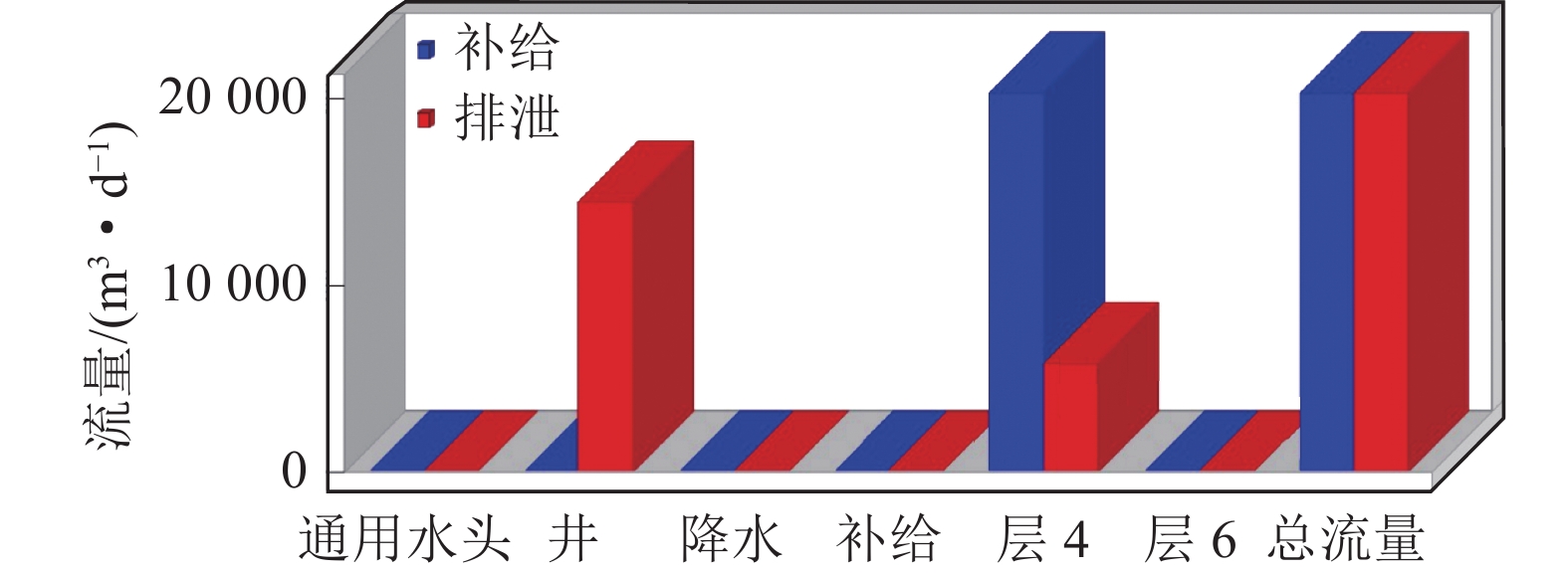
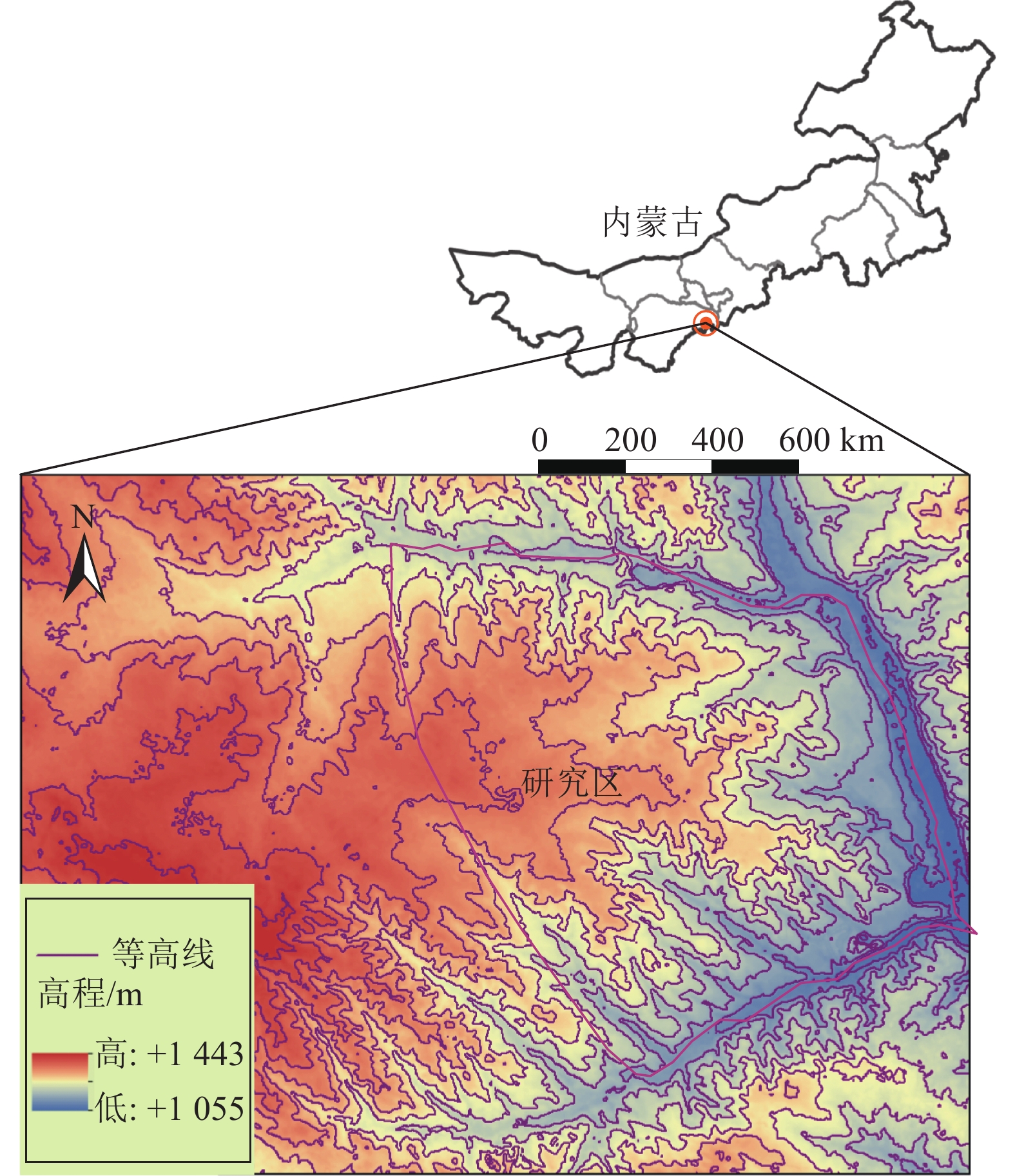
为探究高强度采矿活动对地下水的影响,选取内蒙古神东煤矿区某井田为研究对象,该煤矿为平面上开采面积占比大、空间上开采尺寸大、时间上开采速度快为特点的高强度开采方式。在收集整理相关水文气象、勘测资料的基础上,利用GMS(Groundwater Modeling System)数值模拟软件建立符合研究区水文地质条件的地下水流模型,对研究区未来10年采动影响下的地下水水位及流场进行预测分析,并对地下水水均衡状态进行分析。研究结果表明:高强度采动对直罗组含水层的扰动影响最大,在开采盘区内形成了多个水位降落漏斗,降落漏斗中心水位下降幅度由第1年末的105 m增大到第10年末的351 m,该层地下水整体水位与径流条件均发生改变。高强度采动对志丹群含水层的扰动影响较小,仅在矿井上方局部位置水流场发生改变,10年间,采掘中心处水位由20 m下降至116 m。通过水均衡分析可知,地下水总补给量为357589.74 m3/d,总排泄量为357563.62 m3/d,误差为0.0073%,其中降雨入渗是研究区的主要补给来源,占比51.90%,其次为河流补给,占比45.21%;河流排泄为主要排泄方式,占比达78.24%,其次为潜水蒸发,占比9.82%,矿井排水占比4.52%。志丹群和直罗组含水层补给排泄分别占区域总均衡量的12.0%和5.7%,其中矿井排水量为直罗组含水层的主要排泄方式,占比71.3%。研究结果为保护矿区生产安全与可持续发展提供一定依据。
Abstract:In order to explore the impact of high-intensity mining activities on groundwater, a mine field in Shendong Coal Mine Area of Inner Mongolia is selected as the research object. This mine is characterized by a large proportion of mining area on the plane, a large mining size in space and a fast mining speed in time. Based on the collection of relevant hydrometeorological and survey data, the Groundwater Modeling System numerical simulation software was used to establish a Groundwater flow model in accordance with the hydrogeological conditions of the study area. The Groundwater level and flow field under the influence of mining in the study area in the next 10 years were predicted and analyzed. The equilibrium state of groundwater is also analyzed. The results show that the disturbance of Zhiluo group Aquifer is most affected by high intensity mining, and several water level drop funnels are formed in the mining area. The water level in the center of the drop funnels increases from 105 m at the end of the first year to 351 m at the end of the tenth year, and the overall groundwater level and runoff conditions of this layer are changed. The influence of high intensity mining on the aquifer of Zhidan Group is small, and the water flow field changes only in the local position above the mine. In 10 years, the water level at the mining center decreases from 20 m to 116 m. According to the water balance analysis, the total groundwater recharge is 357 589.74 m3/d, and the total excretion is 357 563.62 m3/d, with an error of 0.0073%. Rainfall infiltration is the main recharge source in the study area, accounting for 51.90%, followed by river recharge, accounting for 45.21%. River drainage was the main way of discharge, accounting for 78.24%, followed by phreatic evaporation, accounting for 9.82%, and mine drainage, accounting for 4.52%. The recharge and discharge of the Zhidan group and Zhiluo group account for 12.0% and 5.7% of the total mean measurement in the region, respectively, and mine drainage is the main discharge mode of the Zhiluo Formation aquifers, accounting for 71.3%. The research results provide some basis for the protection of production safety and sustainable development in mining areas.
-
Keywords:
- coal mining /
- numerical simulation of groundwater /
- groundwater flow field /
- GMS
-
-
表 1 煤炭资源开采强度划分指标
Table 1 Coal resources exploitation intensity classification index
采高/m 开采强度 平面开采比
≥ 60%平面开采比
60% ~ 30%平面开采比
30% ~ 10%平面开采比
≤ 10%≥ 4.50 极高 高 中 低 1.30 ~ 4.50 高 中 中 低 ≤ 1.30 中 低 低 低 表 2 校正后水文地质参数
Table 2 Corrected hydrogeological parameters
分区 各向渗透系数/(m·d−1) 储水率
Ss/m−1给水度
SyKx Ky Kz 第一含水层 3.95 3.95 3.95×10−1 — 3.0×10−2 第一隔水层 2.1×10−3 2.1×10−3 2.1×10−4 5.5×10−5 — 第二含水层 2.3×10−1 2.3×10−1 2.3×10−2 6.4×10−6 — 第二隔水层 5.8×10−3 5.8×10−3 5.8×10−4 7.9×10−7 — 第三含水层 1.5×10−1 1.5×10−1 1.5×10−2 2.0×10−6 — 第三隔水层 2.0×10−4 2.0×10−4 2.0×10−5 4.0×10−8 — 表 3 地下水均衡情况
Table 3 Groundwater balance
水均衡项 类型 水量/(m3·d−1) 类型占水均衡项比例/% 补给项 降雨入渗补给 185591.06 51.90 侧向补给 10332.68 2.89 河流补给 161665.4 45.21 小计 357589.74 100 排泄项 潜水蒸发 35122.67 9.82 侧向排泄 26522.79 7.42 河流排泄 279766.16 78.24 矿井排水 16152 4.52 小计 357563.62 100 均衡差 26.12 误差 0.0073% -
[1] 国家统计局. 中华人民共和国2019年国民经济和社会发展统计公报[N]. 中国信息报, 2020-03-02(002). National bureau of statistics. Statistical bulletin of the people's republic of china on national economic and social development 2019[N]. China Information News, 2020-03-02(002).
[2] 中国能源中长期发展战略研究项目组. 中国能源中长期 (2030、2050)发展战略研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2011. China energy medium - and long-term development strategy research project team. Research on china’s energy medium - and long-term (2030, 2050) development strategy[M]. Beijing: Science Press.
[3] 叶贵钧,张 莱,李文平,等. 陕北榆神府矿区煤炭资源开发主要水工环问题及防治对策[J]. 工程地质学报,2000,8(4):446−455. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2000.04.011 YE Guijun,ZHANG Lai,LI Wenping,et al. The main hydro-engineering-environmental-geological problems arose from the exploitation of coal resource in yu-shen-fu mine area of northern shanxi and their prevention measures[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2000,8(4):446−455. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2000.04.011
[4] 张耀辉,熊祖强,李西凡,等. 复杂水文地质条件下矿井水害综合防治技术研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2021,49(3):167−174. doi: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2021.03.023 ZHANG Yaohui,XIONG Zuqiang,LI Xifan,et al. Study on technology of mine water disater prevention and control in underground mine under complex hydrogeological conditions[J]. Coal science and technology,2021,49(3):167−174. doi: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2021.03.023
[5] 胡振琪,理源源,李根生,等. 碳中和目标下矿区土地复垦与生态修复的机遇与挑战[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2023,51(1):474−483. HU Zhenqi,LI Yuanyuan,LI Gensheng,et al. Opportunities and challenges of land reclamation and ecological restoration in mining areas under carbon neutral target[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2023,51(1):474−483.
[6] 魏建平,温志辉,苑永旺,等. 应力对含瓦斯煤解吸特征影响的试验研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2021,49(5):35−43. WEI Jianping,WEN Zhuihui,YUAN Yongwang,et al. Study on influence of stress on desorption characteristics of coal containing gas[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2021,49(5):35−43.
[7] 刘 伟. 巍山煤矿开采对地下水影响的数值模拟研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2015. LIU Wei. Numerical simulation study about mining influence on groundwater in weishan coal mine[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2015.
[8] MU W,WU Q,XING Y,et al. Using numerical simulation for the prediction of mine dewatering from a karst water system underlying the coal seam in the Yuxian Basin, Northern China[J]. Environmental Earth Ences,2018,77(5):215. doi: 10.1007/s12665-018-7389-3
[9] 沈 冲. 基于GMS的安徽某铁矿矿井涌水量研究[D]. 邯郸: 河北工程大学, 2019. SHEN Chong. A dissertation submitted to hebei university of engineering for the academic degree of master of engineering [D]. Handan: Hebei University of Engineering, 2019.
[10] SHAO Aijun,MENG Qingxin,WANG Shiwen,et al. Prediction of mine inrush water based on BP neural network method[J]. Advanced Materials Research,2014,989−994:1814−1820.
[11] ZHANG Kai,CAO Bin,LIN Gang,et al. Using Multiple methods to predict mine water inflow in the Pingdingshan No. 10 Coal Mine, China[J]. Mine Water and the Environment,2017,36(1):154−160. doi: 10.1007/s10230-015-0381-1
[12] 张凤娥,刘文生. 煤矿开采对地下水流场影响的数值模拟:以神府矿区大柳塔井田为例[J]. 安全与环境学报,2002(4):30−33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6094.2002.04.008 ZHANG Feng’e,LIU Wensheng. A numerical simulation on the influence of underground water flow regime caused by coal mining: a case study in daliuta, shenfu mining area[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment,2002(4):30−33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6094.2002.04.008
[13] 白 晓,边 凯,贾亚琳,等. 基于Modflow和ARIMA模型的峰峰矿区岩溶地下水模拟及预测[J]. 科学技术与工程,2019,19(17):84−90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.17.011 BAI Xiao,BIAN Kai,JIA Yalin,et al. Numerical simulation of karst groundwater and dynamic prediction based on modflow and arima model in fengfeng mining area[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2019,19(17):84−90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.17.011
[14] 李亚娇,张 强,李家科,等. Visual MODFLOW与GMS研究综述[J]. 人民黄河,2021,43(4):89−93,130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2021.04.016 LI Yajiao,ZHANG Qiang,LI Jiake,et al. Overview of research on visual MODFLOW and GMS[J]. Yellow River,2021,43(4):89−93,130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2021.04.016
[15] 王 浩,陆垂裕,秦大庸,等. 地下水数值计算与应用研究进展综述[J]. 地学前缘,2010,17(6):1−12. WANG Lu,LU Chuiyu,QIN Dayong,et al. Advances in method and application of groundwater numerical simulation[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2010,17(6):1−12.
[16] SUN Wenjie, WU Qiang, LIU Honglei, et al. Prediction and assessment of the disturbances of the coal mining in Kailuan to karst groundwater system[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 2015, 89/90: 136−144.
[17] 沈 冲. 基于GMS的安徽某铁矿矿井涌水量研究[D]. 邯郸: 河北工程大学, 2019. SHEN Chong. Study on gushing water volume of an iron mine in anhui province based on GMS[D]. Handan: Hebei University of Engineering, 2019.
[18] 初道忠,赵忠琦. 基于GMS的大庄子矿区矿井最大涌水量预测研究[J]. 山东理工大学学报(自然科学版),2020,34(5):42−46. doi: 10.13367/j.cnki.sdgc.2020.05.009 CHU Daozhong,ZHAO Zhongqi. Prediction of maximum water inflow in dazhuangzi mining area based on GMS[J]. Journal of Shandong University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2020,34(5):42−46. doi: 10.13367/j.cnki.sdgc.2020.05.009
[19] 范立民. 榆神府区煤炭开采强度与地质灾害研究[J]. 中国煤炭,2014,40(5):52−55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-530X.2014.05.014 FAN Limin. On coal mining intentsity and geo-hazard in Yulin-Shenmu-Fugu mine area[J]. China Coal,2014,40(5):52−55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-530X.2014.05.014
[20] 李全友,任印国,程忠良. 地下水数值模拟模型识别和验证方法与标准[J]. 南水北调与水利科技,2012,10(2):30−31. LI Quanyou,REN Yinguo,CHENG Zhongliang. Identifying and verifying method & standard of groundwater numerical model[J]. South-to-north Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology,2012,10(2):30−31.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 王磊,钟浩,范浩,邹鹏,商瑞豪,晋康. 循环荷载下含瓦斯煤力学特性及应变场演化规律研究. 煤炭科学技术. 2024(06): 90-101 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: