Analysis of mechanical properties, permeability and fracturing mechanism of coal samples at different fracturing time of liquid nitrogen
-
摘要:
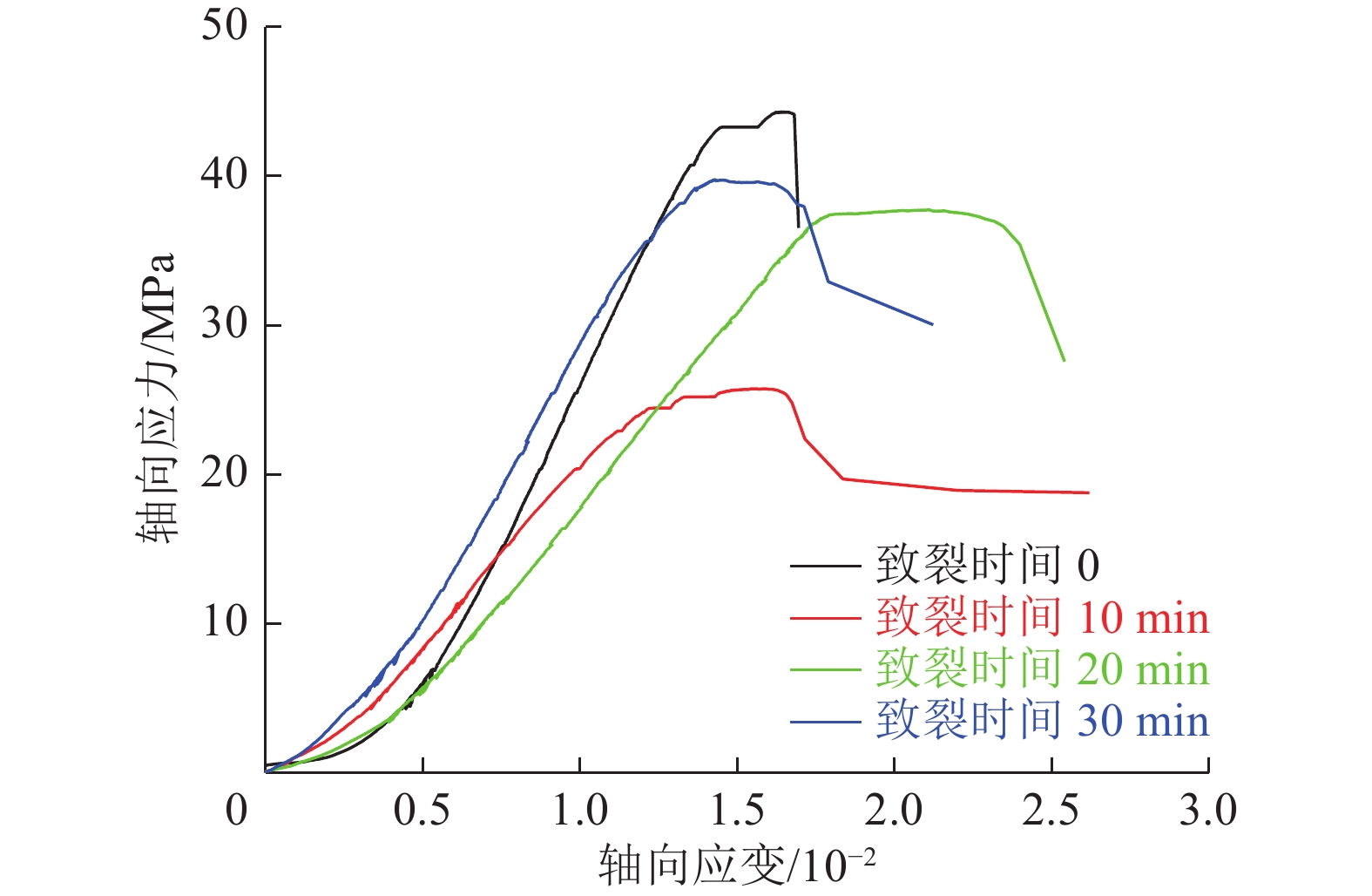
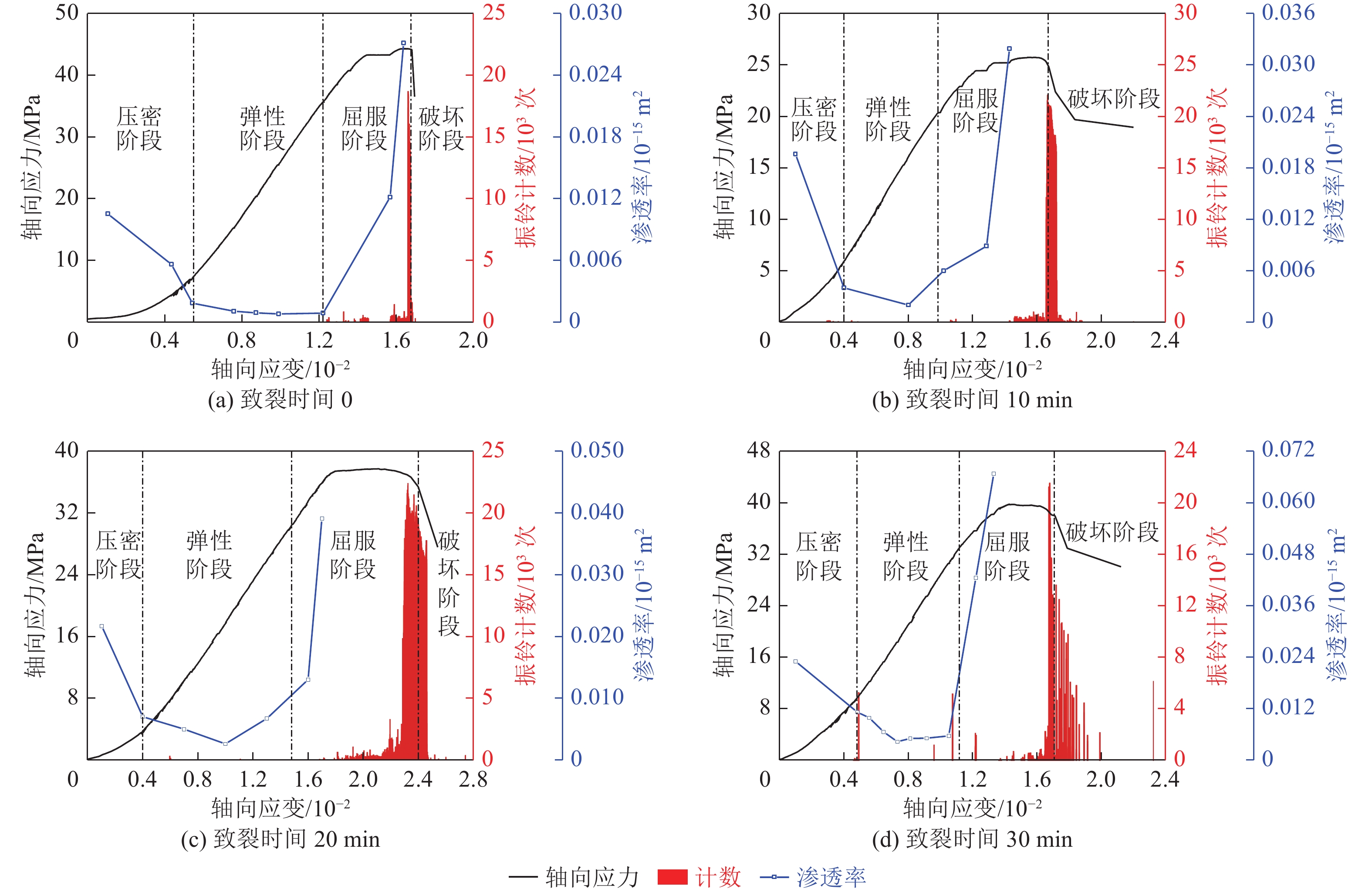
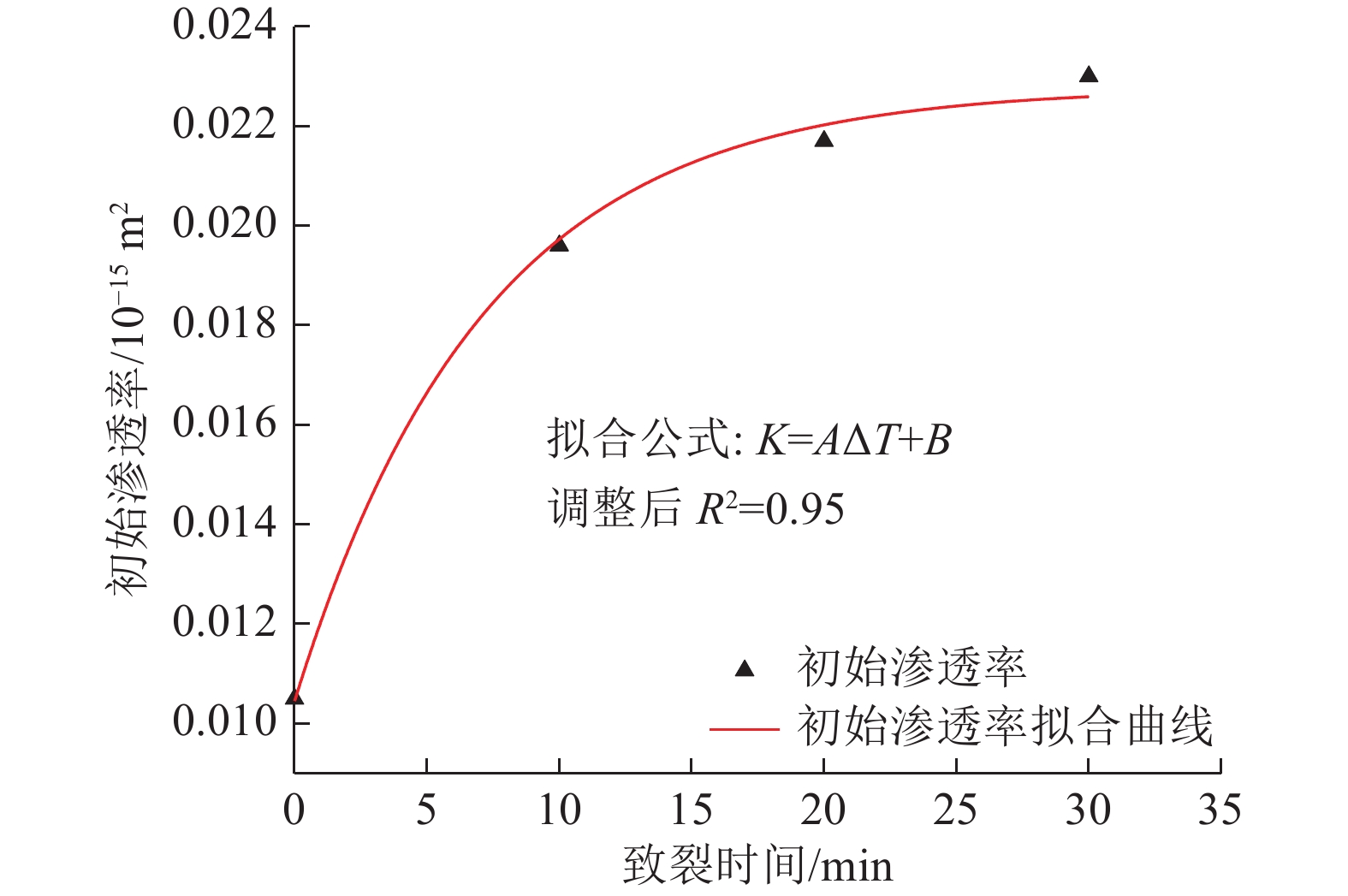
为研究液氮致裂时间对煤样的力学性能和渗透率的影响,利用自主研发的WYS-800三轴瓦斯渗流试验装置及声发射检测系统,对4组不同液氮致裂时间处理的煤样分别进行三轴力学渗流试验并采集声发射信号,对三轴力学渗流试验中各组煤样的力学性能、渗透率的变化进行了分析,描述了声发射信号的特征;根据沸腾换热理论、一维圆柱导热理论、热应力理论分析了致裂机理,计算了不同致裂时间下产生的热应力,通过数据拟合揭示了平均温度降、平均热应力、初始渗透率与致裂时间的关系。研究结果表明:①液氮致裂时间对煤样的力学性能产生不同影响,抗压强度和弹性模量随致裂时间的增加呈现先减小后增大的趋势,泊松比则呈现先增大后减小的趋势,煤样三轴加载时轴向应力-轴向应变曲线的阶段性演化具有明显差异,与力学参数的改变相关。②不同液氮致裂时间煤样在三轴加载过程中的渗透率均呈U型变化,煤样的初始渗透率、最小渗透率、试验测得最大渗透率随致裂时间的增加而增大,致裂30 min时增幅分别为119.05%、437.5%、146.49%;声发射信号在压密和弹性阶段不活跃,主要产生于屈服阶段和破坏阶段,致裂后煤样的声发射振铃计数峰值产生于破坏点附近,均大于20000次。③煤样与液氮之间的膜态沸腾换热系数为570.4 W/(m2·K),煤样平均温度降与致裂时间相关,对平均热应力和初始渗透率起主导作用,致裂30 min时煤样内部产生的平均温度降可达213.63 K,平均热应力可达5.850 MPa。④液氮处理后煤样的初始渗透率与平均温度降之间呈线性关系,与致裂时间呈负指数分布关系。改变参数取值,可推广至其他类似处理的煤样或实际生产评估。
Abstract:In order to study the influence of liquid nitrogen cracking time on mechanical properties and permeability of coal samples, the independently developed WYS-800 triaxial gas seepage test device and acoustic emission detection system were used to conduct triaxial mechanical seepage tests on four groups of coal samples treated with different cracking time and collect acoustic emission signals. The mechanical properties and permeability of coal samples in triaxial mechanical seepage experiment were analyzed, and the characteristics of acoustic emission signals were described. Based on boiling heat transfer theory, one-dimensional cylinder heat conduction theory and thermal stress theory, the cracking mechanism was analyzed, and the thermal stress under different cracking time was calculated. The relationship between average temperature drop, average thermal stress, initial permeability and cracking time was revealed by data fitting. The results show that: ① Liquid nitrogen fracturing time have different influence on the mechanical properties of coal samples, the compressive strength and elastic modulus with the increase of the crack time shows the tendency of increase with the decrease of the first, the poisson's ratio are increased after the first decreases, coal sample triaxial loading when the axial stress and axial strain curve of the periodic evolution has obvious difference, associated with the change of mechanical parameters. ② The permeability of coal samples with different cracking time changes in u-shape during the triaxial loading process. The initial permeability, minimum permeability and maximum permeability increase with the increase of cracking time, and the increase rate is 119.05%, 437.5% and 146.49% when the cracking time is 30min. Acoustic emission signals are not active in compaction and elastic stages, and are mainly generated in yield and failure stages. The peak value of acoustic emission ringing count of coal samples after cracking is generated near the failure point, which is more than 20000 times. ③ The film boiling heat transfer coefficient between the coal sample and liquid nitrogen is 570.4 W/(m2·K). The average temperature drop of the coal sample is related to the cracking time, and the average thermal stress and initial permeability play a leading role. The average temperature drop of the coal sample can reach 213.63 K and the average thermal stress can reach 5.85 MPa after 30 min of cracking. ④ There is a linear relationship between initial permeability and average temperature drop, and a negative exponential relationship between initial permeability and cracking time of coal samples after liquid nitrogen treatment. Changing the parameter value can be extended to other similar coal samples or actual production evaluation.
-
-
表 1 煤样显微组分、工业分析和镜质组反射率参数
Table 1 Coal sample maceral, industrial analysis and vitrinite reflectance parameter
煤样 显微组分体积分数/% 工业分析/% Ro,max/% 煤阶 镜质组 惰质组 壳质组 矿物 Mad Aad Vad FCad 新景矿3号 76.9 20.8 0 2.3 1.74 15.87 8.25 74.14 2.38 高阶煤 表 2 不同致裂时间下的试验方案
Table 2 Experimental scheme under different cracking time
试样编号 液氮致裂
时间/min围压/MPa 瓦斯压力/MPa 加载方式
及速率Y0 0 5 1 力加载0.02 kN/s Y1 10 5 Y2 20 5 Y3 30 5 表 3 不同致裂时间煤样三轴加载下的参数
Table 3 Parameters of coal samples under triaxial loading with different cracking times
试样编号 致裂时
间/min密度/
(g·cm−3)抗压强
度/MPa弹性模
量/MPa泊松比 Y0 0 1.855 44.31 4 279 0.110 Y1 10 1.827 25.73 2 499 0.198 Y2 20 1.873 37.74 2 623 0.351 Y3 30 1.869 39.78 3 645 0.175 表 4 不同致裂时间下煤样的特定渗透率
Table 4 Specific permeability of coal samples at different cracking time
试样编号 致裂时
间/min初始渗透率/
10−15 m2最小渗透率/
10−15 m2试验测得最大
渗透率/10−15 m2Y0 0 0.0 105 0.0 008 0.0 271 Y1 10 0.0 196 0.0 020 0.0 319 Y2 20 0.0 217 0.0 026 0.0 391 Y3 30 0.0 230 0.0 043 0.0 668 -
[1] 孙海涛,舒龙勇,姜在炳,等. 煤矿区煤层气与煤炭协调开发机制模式及发展趋势[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(12):1−13. SUN Haitao,SHU Longyong,JIANG Zaibing,et al. Progress and trend of key technologies of CBM developmentand utilization in China coal mine areas[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(12):1−13.
[2] 王登科,张 平,刘淑敏,等. 温度冲击下煤层内部孔缝结构演化特征试验研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2018,43(12):3395−3403. WANG Dengke,ZHANG Ping,LIU Shumin,et al. Experimental study on evolutionary characteristics of pore-fissure structure in coal seam under temperature impact[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2018,43(12):3395−3403.
[3] 唐世斌,罗 江,唐春安. 低温诱发岩石破裂的理论与数值模拟研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2018,37(7):1596−1607. TANG Shibin,LUO Jiang,TANG Chunan. Theoretical and numerical study on the cryogenic fracturing in rock[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2018,37(7):1596−1607.
[4] 田苗苗,张 磊,薛俊华,等. 液氮致裂煤体技术研究现状及展望[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(7):191−198. TIAN Miaomiao,ZHANG Lei,XUE Junhua,et al. Study and prospection of liquid nitrogen fracturing coal technology[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(7):191−198.
[5] AKHONDZADEH H,KESHAVARZ A,AWAN F U R,et al. Liquid nitrogen fracturing efficiency as a function of coal rank: A multi-scale tomographic study[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering,2021,95:104177.
[6] 卢 硕,张 磊,薛俊华,等. 液氮溶浸作用对不同煤阶煤样渗流特性的影响[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(5):1835−1844. LU Shuo,ZHANG Lei,XUE Junhua,et al. Influence of liquid nitrogen immersion on seepage characteristics of different rank coal samples[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2020,45(5):1835−1844.
[7] LI B, ZONG C, HUANG L, et al. Study on the influence of liquid nitrogen cold soaking on the temperature variations and seepage characteristics of coal samples with different moisture contents[J]. Geofluids, 2021: 8924016.
[8] ZHAO D,WANG Q,LI D,et al. Experimental study on infiltration and freezethaw damage of water-bearing coal samples with cryogenic liquid nitrogen[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering,2018,60:24−31. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2018.09.027
[9] 陈 帅. 液氮致裂烟煤裂隙结构演变及渗流特性试验研究 [D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2020. CHEN Shuai. Characterization of bituminous coal fracture structure and permeability evolution by liquid nitrogen fracturing[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2020.
[10] 张春会,耿 哲,徐 刚,等. 液氮冻融循环作用下饱水煤样力学特性试验研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2020,48(10):218−224. ZHANG Chunhui,GENG Zhe,XU Gang,et al. Experimental study on mechanical properties of saturated coal samples subjected to freezing-thawing cycles of liquid nitrogen[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2020,48(10):218−224.
[11] 张路路,李 波,张 强,等. 液氮冷浸煤岩孔隙损伤和渗透率演化特性研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2018,37(S2):3938−3946. ZHANG Lulu,LI Bo,ZHANG Qiang,et al. Study on pore damage and permeability evolution properties of coal rock caused by liquid nitrogen soaking[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2018,37(S2):3938−3946.
[12] 张 磊,陈 帅,薛俊华,等. 液氮致裂烟煤渗透率及其应力敏感性研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2020,37(2):401−408. ZHANG Lei,CHEN Shuai,XUE Junhua,et al. Permeability of bituminous coal and its stress sensitivity under liquid nitrogen fracturing[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2020,37(2):401−408.
[13] 孟召平,章 朋,田永东,等. 围压下煤储层应力-应变、渗透性与声发射试验分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(7):2544−2551. MENG Zhaoping,ZHANG Peng,TIAN Yongdong,et al. Experimental analysis of stress-strain, permeability and acoustic emission of coal reservoir under different confining pressures[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2020,45(7):2544−2551.
[14] 王 浩. 低温致裂煤体力学演化与数值模拟研究 [D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2021. WANG Hao. Research on mechanical evolution and numerical simulation of low temperature fracturing coal[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2021.
[15] 魏建平,孙刘涛,王登科,等. 温度冲击作用下煤的渗透率变化规律与增透机制[J]. 煤炭学报,2017,42(8):1919−1925. WEI Jianping,SUN Liutao,WANG Dengke,et al. Change law of permeability of coal under temperature impact and the mechanism of increasing permeability[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2017,42(8):1919−1925.
[16] 弗兰克P. 英克鲁佩勒, 大卫P. 德维特, 狄奥多尔L. 伯格曼, 等. 传热和传质基本原理[M]. 第6版. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2007. [17] 许建俊,华泽钊,刘宝林,等. 用淬冷法确定饱和液氮中的池沸腾热流密度曲线[J]. 上海理工大学学报,1998,20(2):11−15. XU Jianjun,HUA Zezhao,LIU Baolin,et al. The pool boiling heat flux curve in saturated liquid nitrogen was determined by quenching method[J]. Journal of University of Shanghai for Science and Technology,1998,20(2):11−15.
[18] 顾祥红. 无限长圆柱非稳态导热平均温度坐标位置求解[J]. 大连交通大学学报,2010,31(2):101−103. GU Xianghong. Coordinate position of mean temperature analysis for infinite cylinder under unsteady-state conduction[J]. Journal of Dalian Jiaotong University,2010,31(2):101−103.
[19] 康 健. 岩石热破裂的研究及应用[M]. 大连: 大连理工大学出版社, 2008. [20] 王春霞,张学博,卢方超. 基于核磁共振与应力分析的液氮冷浸致裂煤岩研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报,2019,29(11):156−163. WANG Chunxia,ZHANG Xuebo,LU Fangchao. Study on coal cracking under liquid nitrogen soaking based on nuclear magnetic resonance and stress analysis[J]. China Safety Science Journal,2019,29(11):156−163.




 下载:
下载: