Occurrence law and classification prevention of rock burst in coal mines of Shaanxi Province
-
摘要:
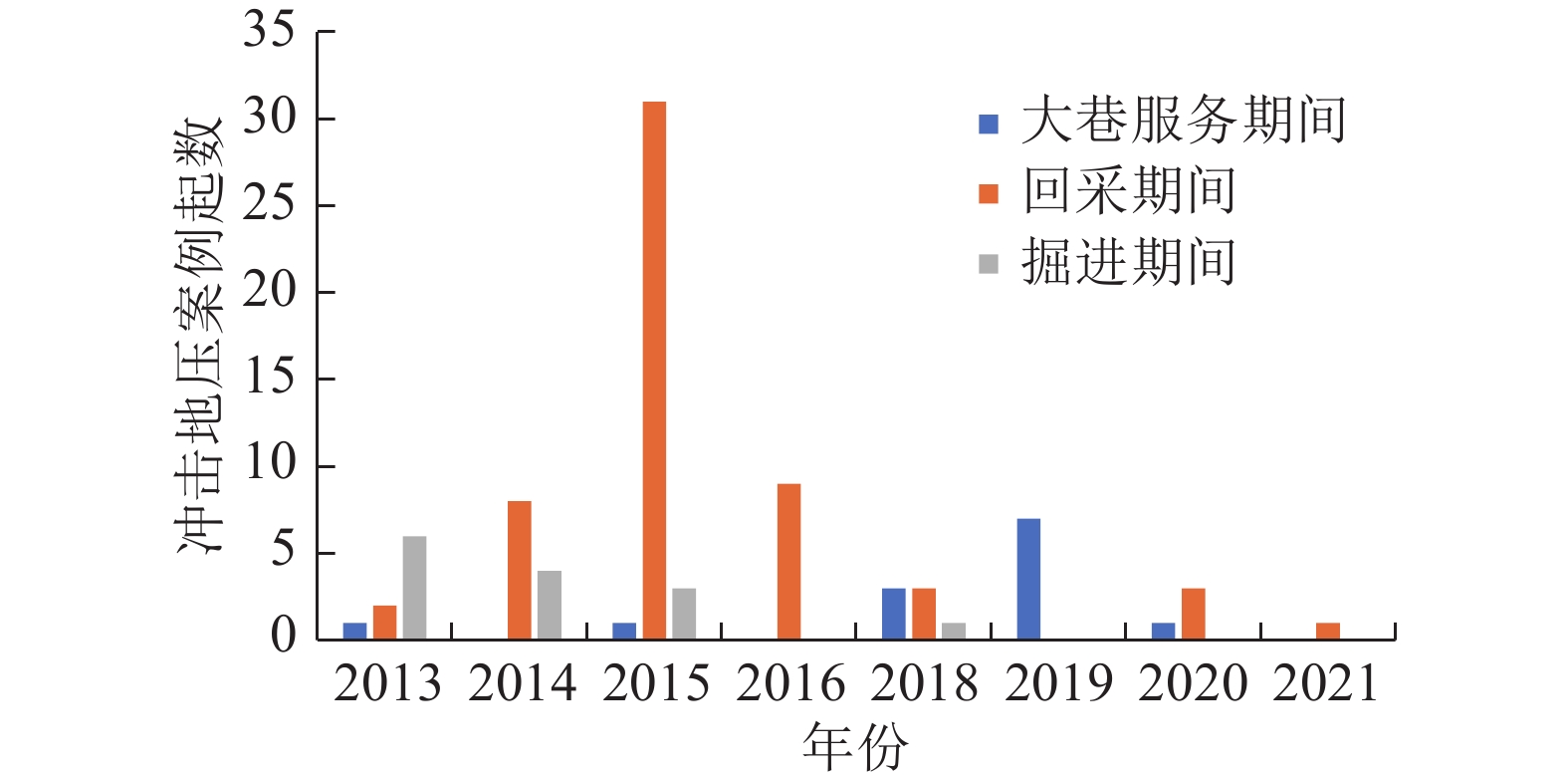
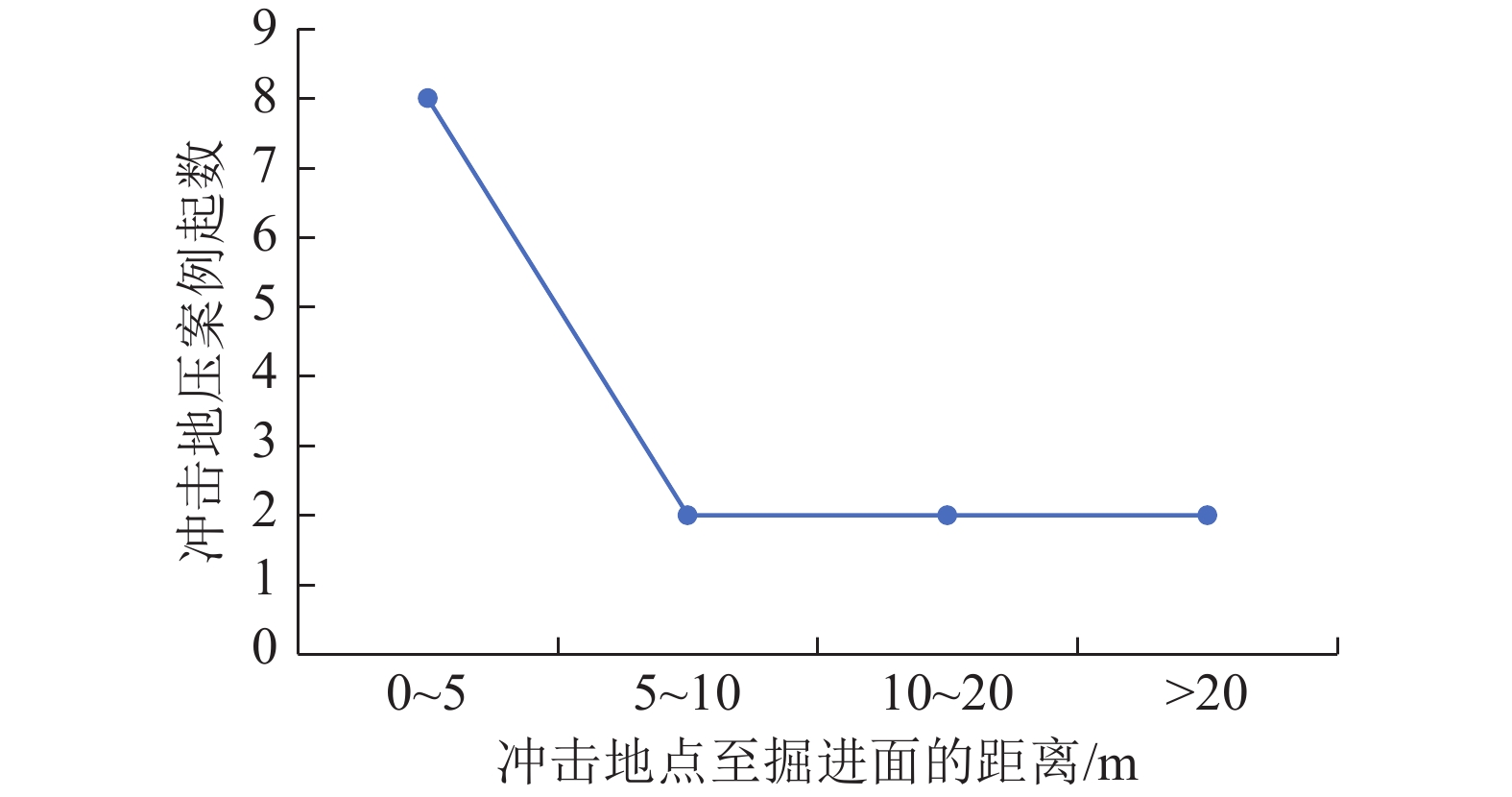
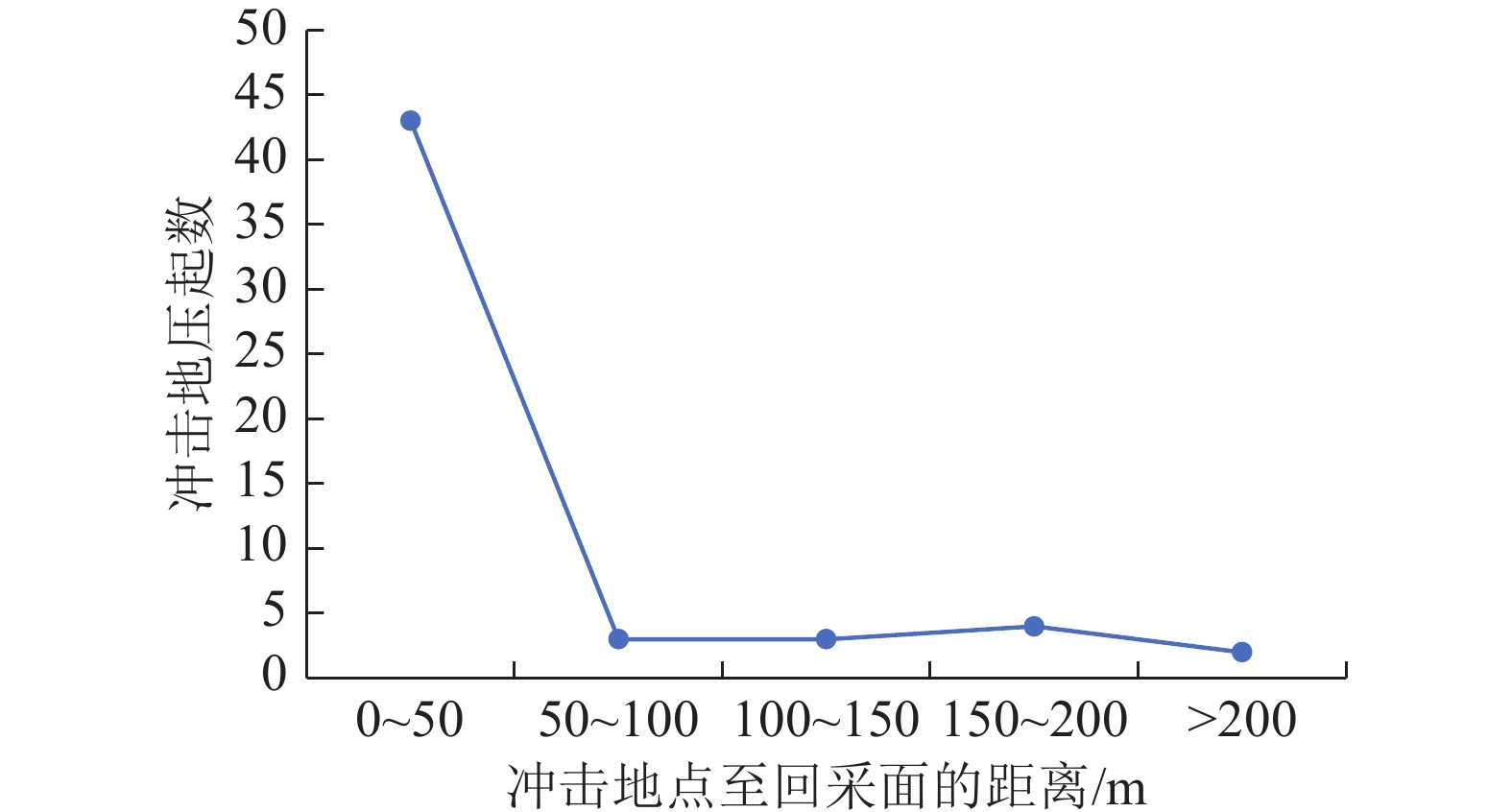
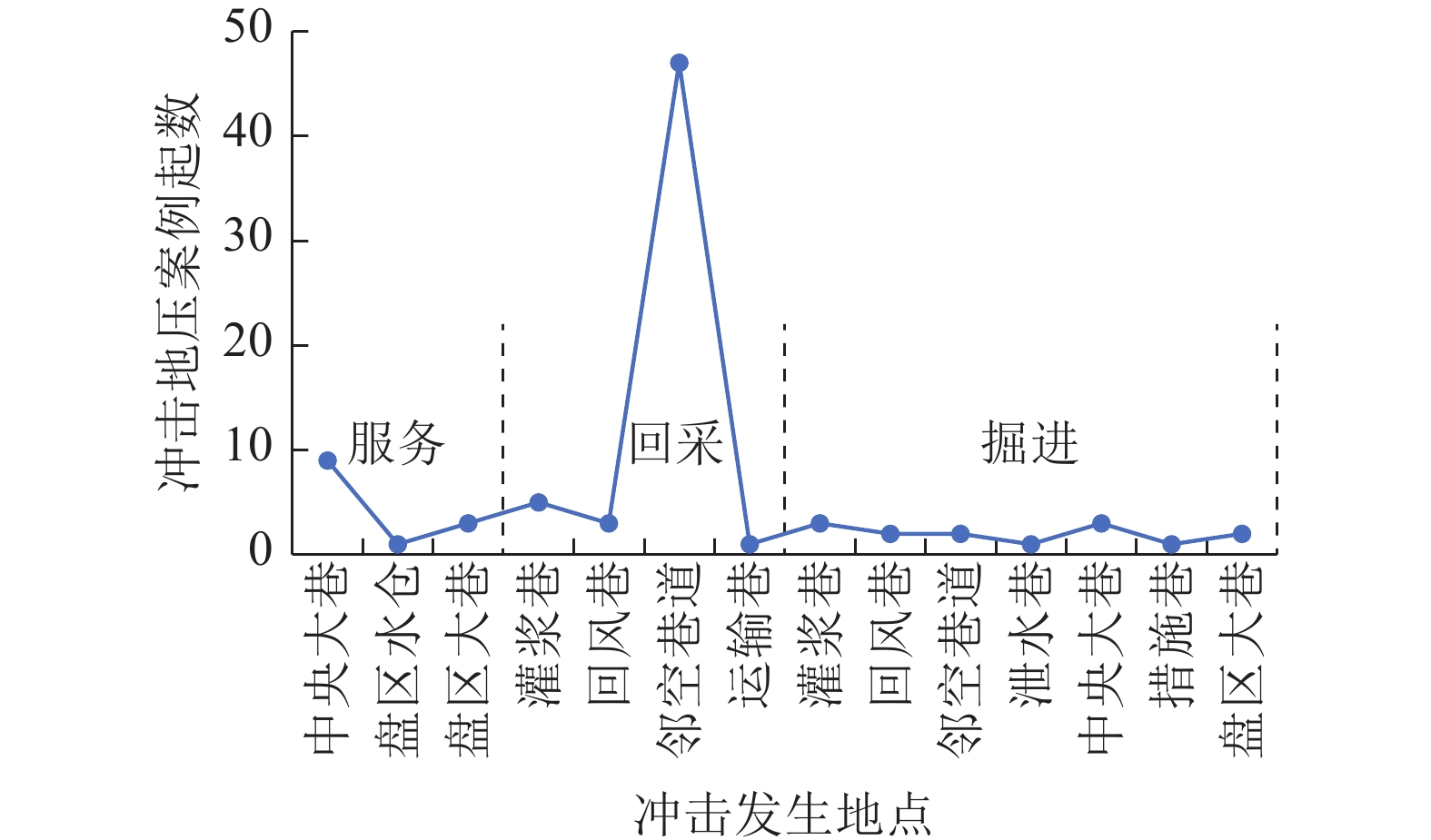
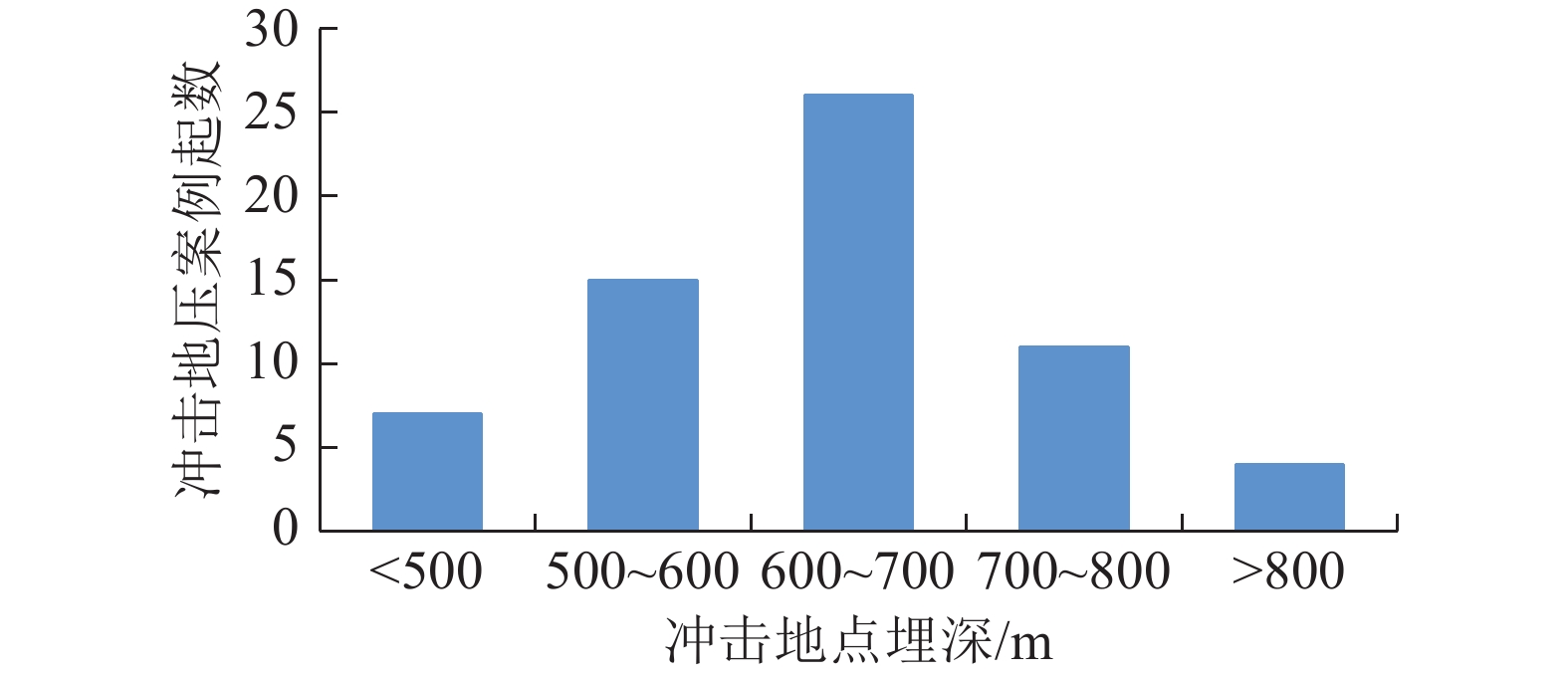
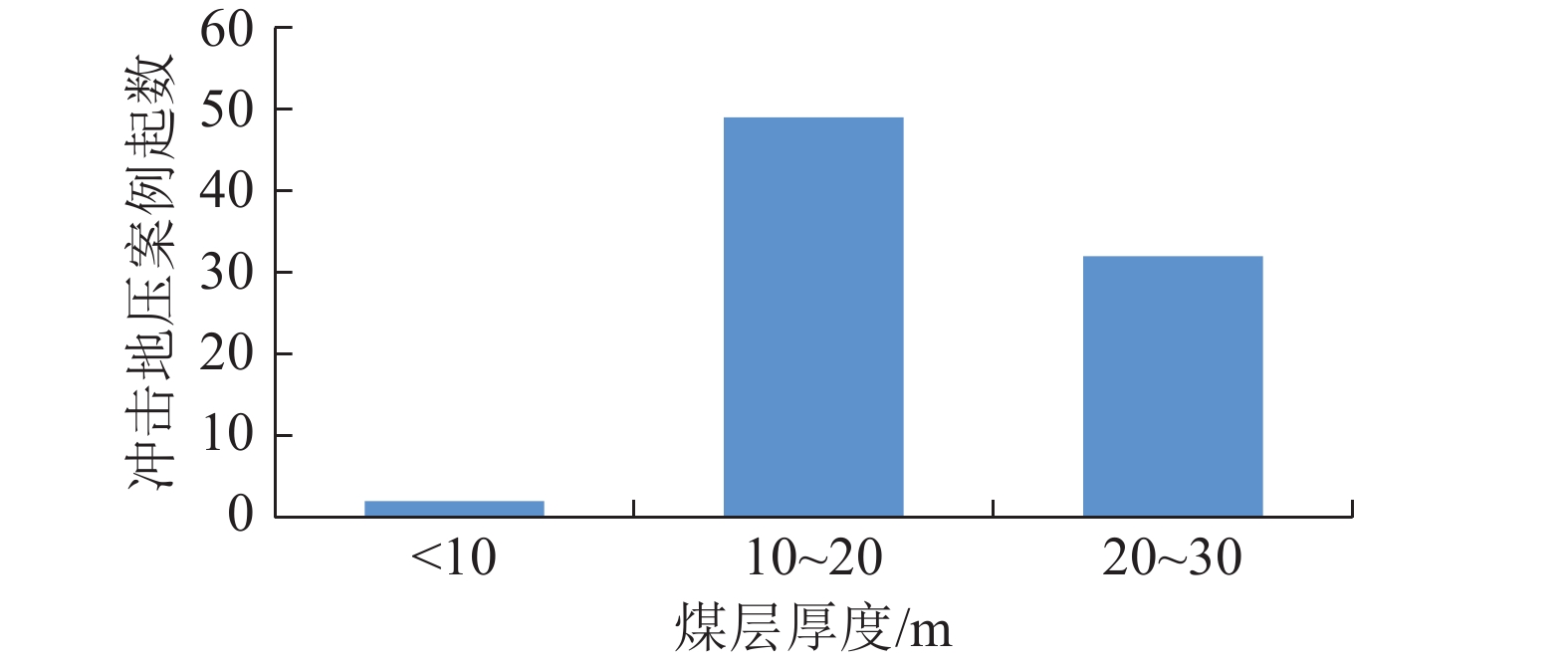
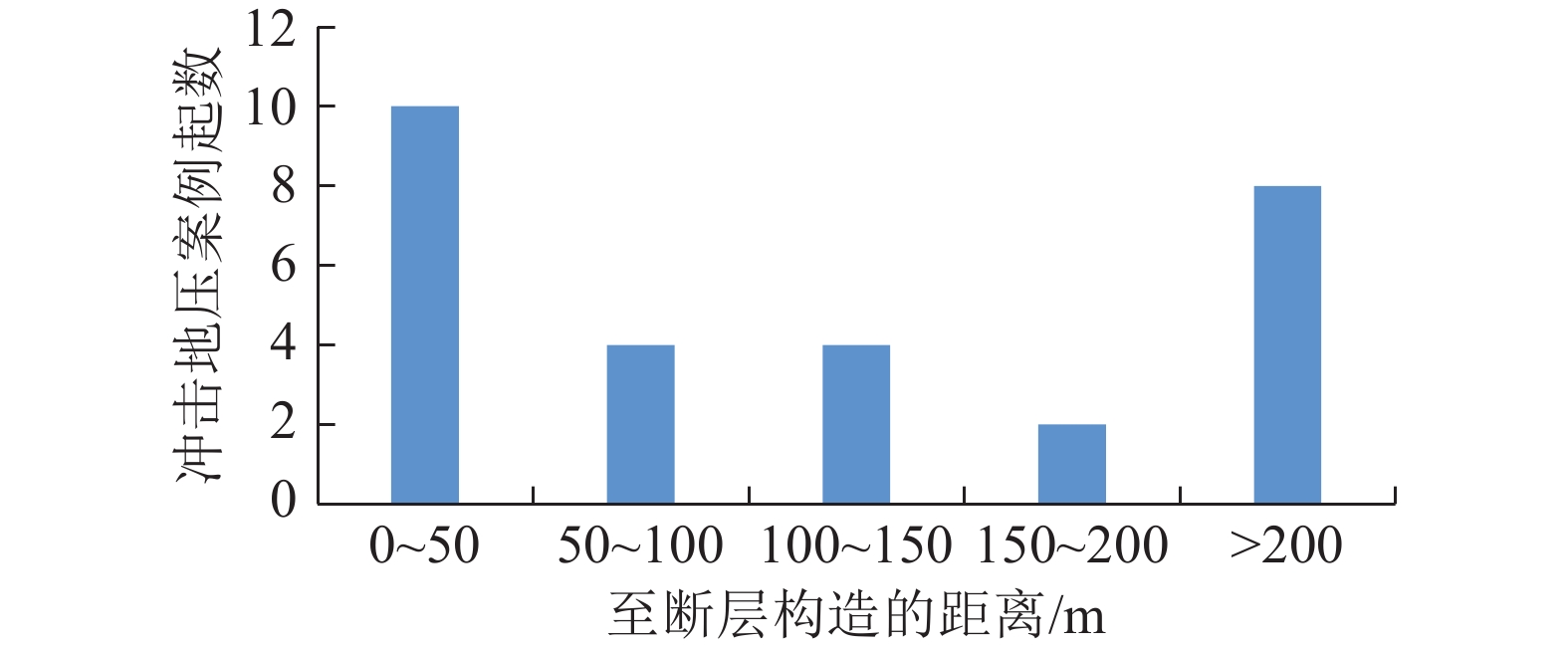
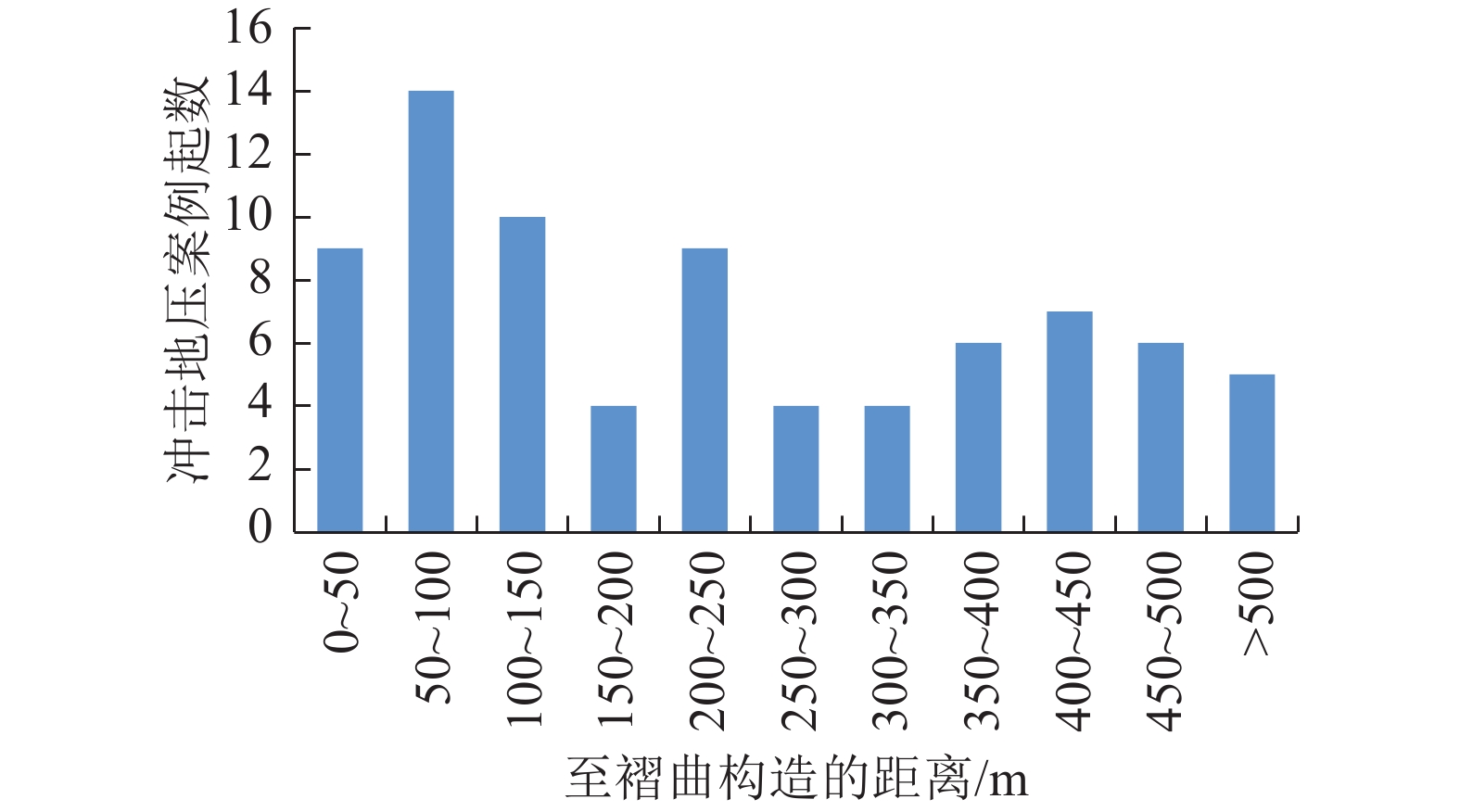
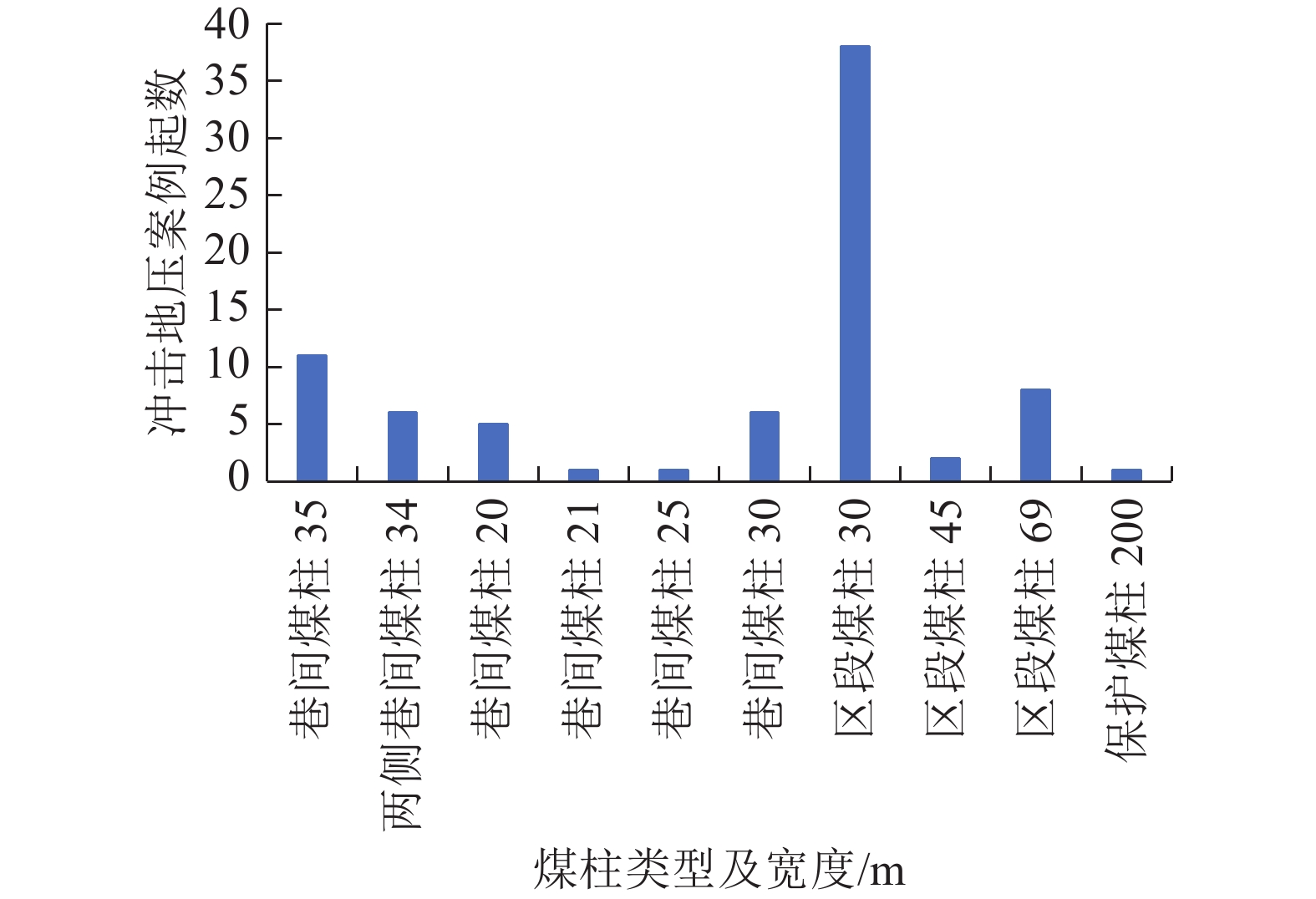
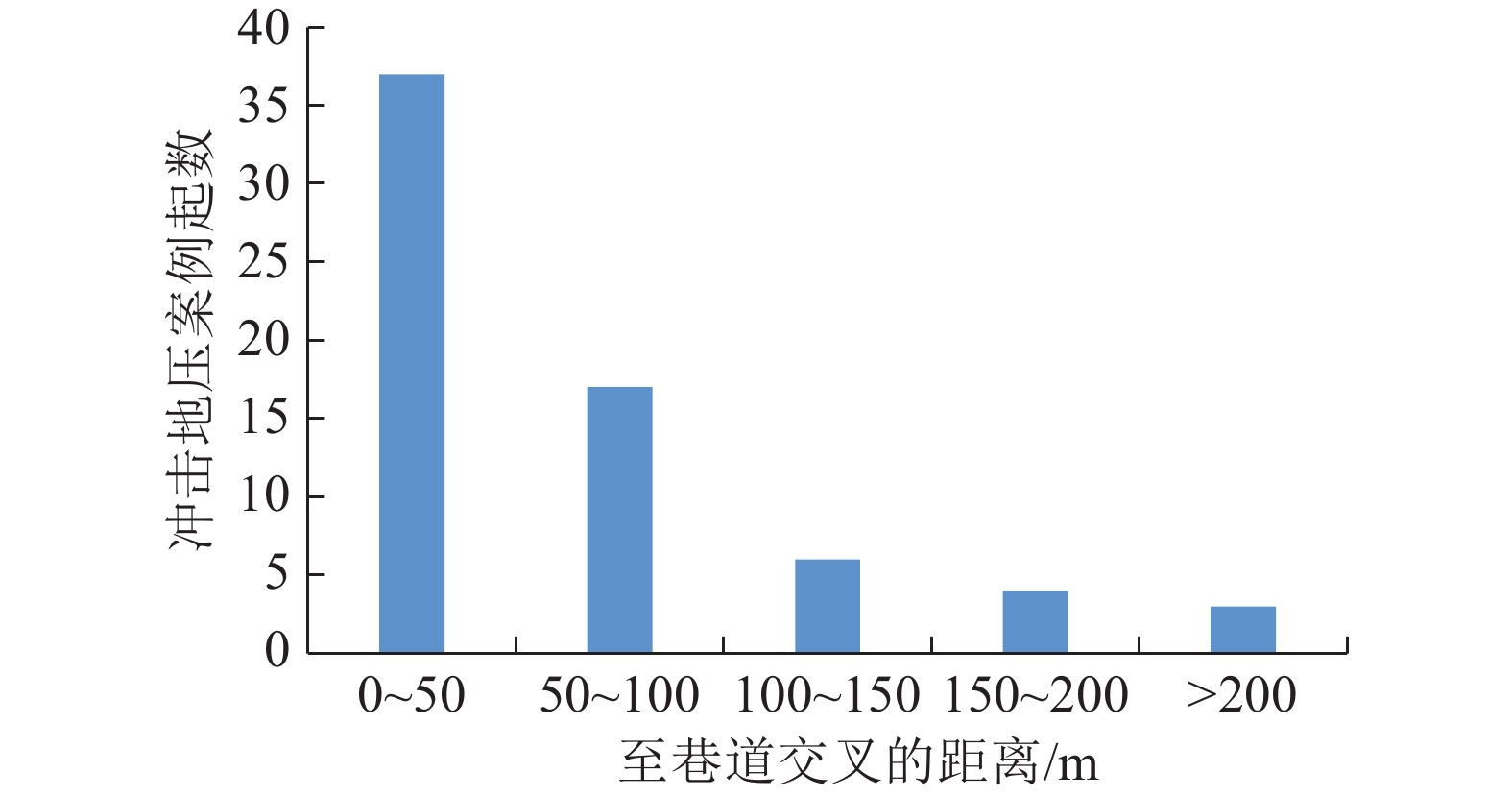
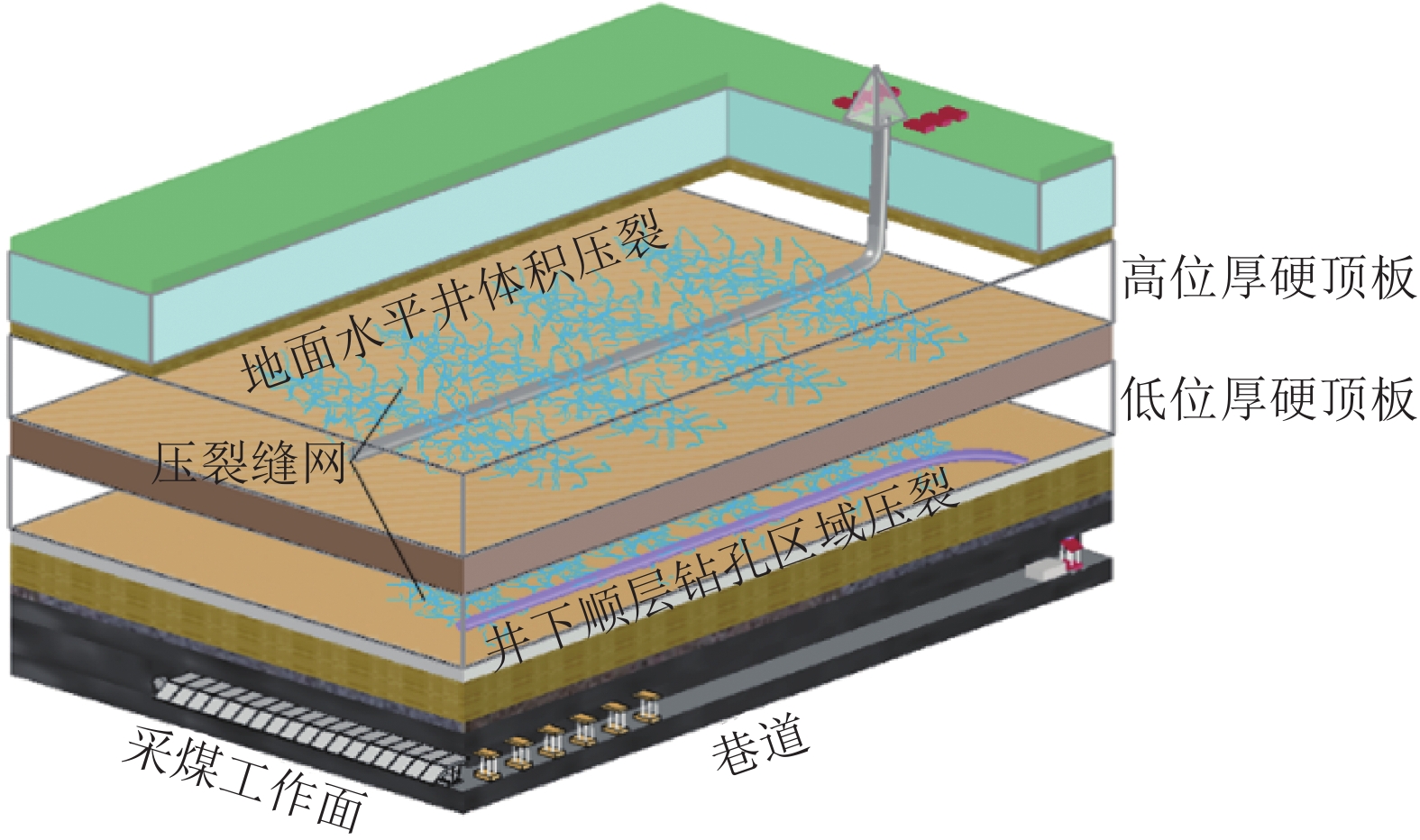
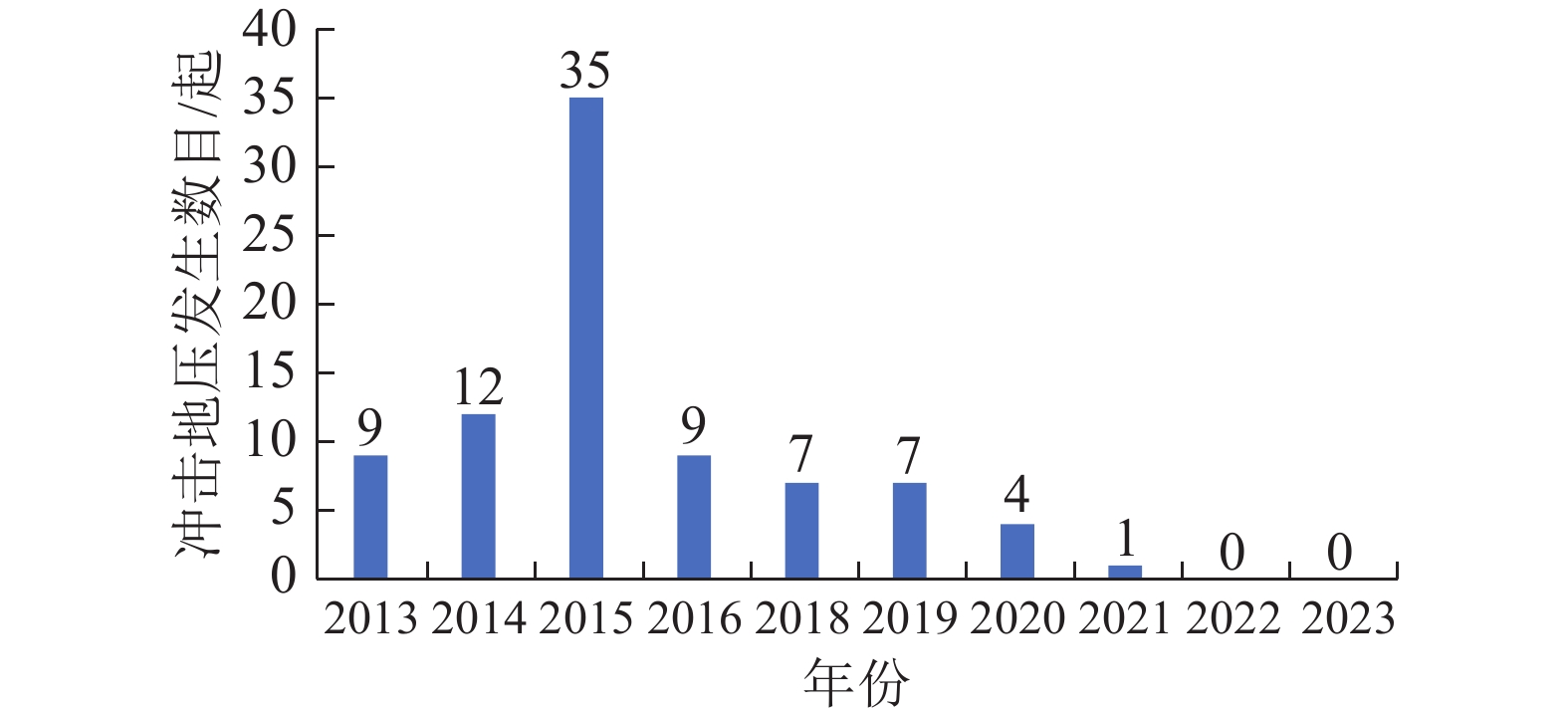
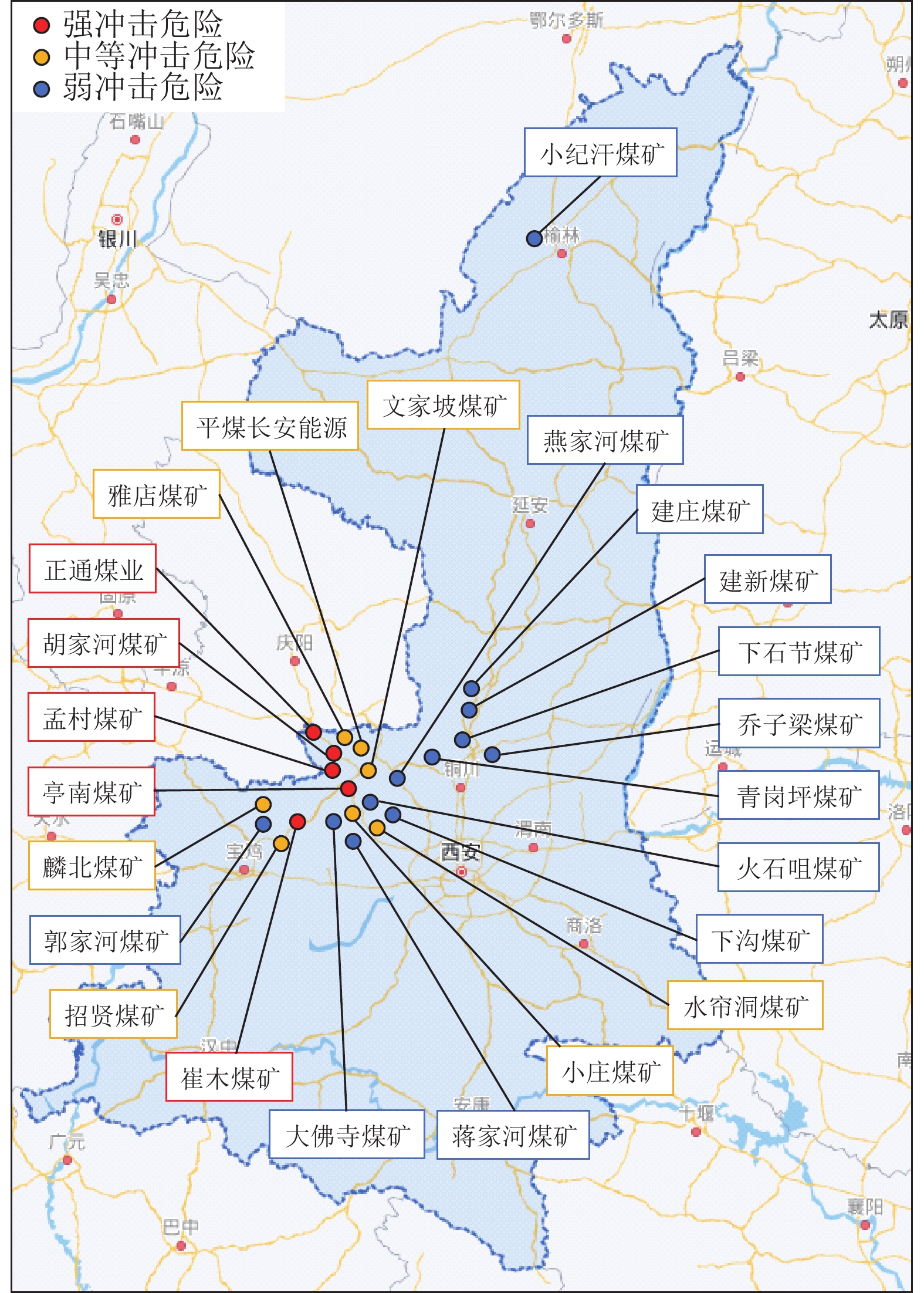
随着煤炭资源开采区域不断向西部以及深部转移,西部地区冲击地压矿井数量呈井喷式增长。陕西省作为煤炭大省,煤炭开发供应规模稳居全国前列,但冲击地压灾害尤为突出,为了有效遏制本地区煤矿冲击地压频繁发生势头,并为类似条件矿区冲击地压防治提供借鉴,通过分析陕西煤矿10年来的24座矿井、85起冲击地压案例,基本厘清了冲击地压发生规律,并开展了基于主控因素的分类防治研究。研究结果表明:陕西省煤矿冲击地压具有灾害矿井集中、灾害程度严重、多灾害叠加影响显著、防治难度大等特点;冲击地压监测技术、防治技术与地方法规建设历程几乎同步,达到了起步晚,起点高,示范效应强的结果;基于冲击地压主控因素,将陕西省冲击地压划分为3大类,分别为:坚硬顶板主导型、地质构造主导型和宽煤柱主导型,并针对主控因素提出弱化坚硬顶板、转移煤柱高集中应力、释放构造应力的防治方法。通过10年来的工程实践,不断优化矿井开采设计,探索煤层厚硬顶板千米顺层钻孔区域压裂新技术,加大防冲卸压技术的落实,冲击地压显现逐年减少,成果显著。
Abstract:With coal resource extraction areas are constantly shifting towards the west and deeper regions, and the number of rock burst mines in the western region is increasing rapidly. As a major coal province, Shaanxi Province has a stable scale of coal development and supply, ranking among the top in the country. However, rock burst disasters are particularly prominent. In order to effectively curb the frequent occurrence of rock burst in local coal mines and provide reference for rock burst prevention and control in areas with similar conditions, the occurrence law of rock burst has been basically clarified by analyzing 24 mines and 85 rock burst cases in Shaanxi coal mines over the past 10 years, and conducted classified prevention and control research based on the main control factors. The research results indicate that coal mine rock burst in Shaanxi Province has the characteristics of concentrated disaster mines, severe disaster severity, significant overlapping effects of multiple disasters, and high difficulty in prevention and control; The monitoring technology and prevention technology of rock burst are almost synchronized with the construction process of local regulations, achieving a late start, high starting point, and demonstration effect;Based on the main controlling factors of rock burst, rock burst in Shaanxi Province is divided into three categories: hard roof dominant type, wide coal pillar dominant type, and geological structure dominant type. In response to the main controlling factors, prevention and control methods for weakening hard roof, transferring high concentrated stress of coal pillar, and releasing structural stress are proposed.Through 10 years of engineering practice, continuous optimization of mine mining design, exploration of new fracturing technologies for drilling areas along the thick and hard roof of coal seams, and increased implementation of anti burst and pressure relief technologies, the occurrence of rock burst has been decreasing year by year, with significant achievements.
-
-
表 1 冲击地压与地应力关系
Table 1 Relationship between impact ground pressure and ground stress
地应力场类型 最大水平主应力/MPa 冲击巷道方位角/(°) 最大水平主应力与冲击巷道夹角/(°) 冲击起数 构造应力主导型 16.5~20.4 144~175 5~36 44 18.0~33.9 59~75 59~75 18 24.9~26.4 130~145 45 2 26.0~38.0 145~171 56~75 14 37.3~38.7 47~57 5~11 5 表 2 冲击地压发生起数与顶板岩性关系统计
Table 2 Statistics of relationship between rock burst occurrence and roof lithology
直接顶岩性
(下→上)直接顶厚度/m
(下→上)基本顶岩性 基本顶厚度/m 冲击起数 泥质粉砂岩 2.7 中粒砂岩
泥质粉砂岩
中粒砂岩
含砾粗砂岩5.7
7.1
2.4
2.110 砂质泥岩 0.6 细粒砂岩
粗砂岩49 1 中粒砂岩 3.5 粉砂岩
粉砂岩
粗粒砂岩18.5
13.2
35.81 泥岩 1.3 粗粒砂岩
细粒砂岩
粗粒砂岩6.8
14.5
20.51 砂质泥岩 3.4 细粒砂岩
粉砂岩
砂岩8.3
12.9
1.82 砂质泥岩 3.4 细粒砂岩
粗粒砂岩
中粒砂岩
粗砂岩
粉砂岩
含砾砂岩
中砂岩7.8
2.4
5.9
17.0
4.0
9.8
7.011 砂质泥岩 12.0 粗粒砂岩
细粒砂岩
粗粒砂岩15.5
2.1
3.42 砂质泥岩 8.5 粉砂岩
细粒砂岩19.3 41 泥岩 0.3 细粒砂岩
粗粒砂岩24.7 2 无 — 粗粒砂岩
含砾粗砂岩
粉砂岩12.2
15.6
5.65 无 — 细砂岩 13.7 6 表 3 陕西省24座冲击地压矿井主控因素
Table 3 Main control factors for 24 rock burst mines in Shaanxi Province
矿井 主采
煤层煤层冲
击倾向顶板冲
击倾向煤层冲
击危险采深/m 顶板岩层 区段煤
柱类型构造发
育程度底煤薄厚 主控因素 辅助因素 陕西彬长胡家河矿业有限公司 4 强 弱 强 578~790 坚硬顶板 宽煤柱 复杂构造 厚底煤 坚硬顶板
复杂构造
宽煤柱大采深、局部巷道密集、大巷煤柱、厚底煤 陕西彬长孟村矿业有限公司 4 强 弱 强 400~900 坚硬顶板 宽煤柱 复杂构造 厚底煤 坚硬顶板
复杂构造
宽煤柱大采深、局部巷道密集、大巷煤柱、厚底煤 陕西正通煤业有限责任公司 4 强 弱 强 820~ 1089 坚硬顶板 窄煤柱 简单构造 厚底煤 坚硬顶板
复杂构造大采深、局部巷道密集、大巷煤柱、厚底煤 陕西长武亭南煤业有限责任公司 4 强 弱
(二盘区强)强 410~730 坚硬顶板 宽煤柱 简单构造 厚底煤 坚硬顶板
宽煤柱大采深、局部巷道密集、大巷煤柱、地质构造、厚底煤 陕西永陇能源开发建设有限责任公司 3 弱 弱 强 650 坚硬顶板 宽煤柱 复杂构造 回采巷道薄底煤
北翼运输大巷厚
底煤坚硬顶板
复杂构造
宽煤柱大采深、煤厚变化、局部巷道密集、局部
厚底煤陕西彬长文家坡矿业有限公司 4 弱 弱 中等 550~809 坚硬顶板 宽煤柱 局部复杂构造 回采巷道薄底煤 坚硬顶板
宽煤柱大采深、煤厚变化、局部巷道密集、局部地质构造 陕西彬长小庄矿业有限公司 4 弱 弱 中等 350~850 坚硬顶板 宽煤柱 局部复杂构造 厚底煤 坚硬顶板
区段宽
煤柱大采深、煤厚变化、局部巷道密集、局部地质构造、厚底煤 陕西金源招贤矿业有限公司 3 弱 弱 中等 400~700 坚硬顶板 宽煤柱 复杂构造 大于1.5 m厚底煤 坚硬顶板
复杂构造
宽煤柱大采深、煤厚变化、局部巷道密集、大于1.5 m厚底煤 陕西麟北煤业开发有限责任公司 2
2-1弱 弱 中等 534~818 坚硬顶板 宽煤柱 复杂构造 薄底煤或不留底煤 坚硬顶板
复杂构造
宽煤柱大采深、局部巷道密集 彬县水帘洞煤炭有限责任公司 4 弱 弱 中等 311~401 坚硬顶板 窄煤柱 局部复杂构造 薄底煤 坚硬顶板 大采深、煤厚变化、局部巷道密集、局部地质构造、孤岛工作面 陕西华彬雅店煤业有限公司 1
4弱 弱 中等 497~892
472~886坚硬顶板 宽煤柱 复杂构造 1煤无底煤
4煤1~4 m底煤坚硬顶板
复杂构造
宽煤柱大采深、孤岛大煤柱、局部巷道密集、4煤厚底煤 平煤长安能源有限公司 — — — 中等 — — — — — — — 陕西华电榆横煤电有限有限责任公司小纪汗煤矿 2 弱 弱 弱 405~445 坚硬顶板 宽煤柱 构造不
发育不留底煤 坚硬顶板
宽煤柱较大采深、区段宽煤柱 陕西煤业集团黄陵建庄矿业有限公司 4-2 弱 弱 弱 407~740 厚硬顶板 窄煤柱 断层构造 薄底煤 坚硬顶板
复杂构造大采深、局部巷道密集、大巷煤柱、孤岛煤柱 陕西建新煤化有限责任公司 4-2 弱 弱 弱 394~818 坚硬砂岩顶板 宽煤柱 简单构造 薄底煤 坚硬顶板
宽煤柱大采深、局部巷道密集、地质构造 陕西陕煤铜川矿业有限公司下石节
煤矿4-2
3-2弱 弱 弱 550~650 坚硬砂岩顶板 宽煤柱 断层构造 不留底煤 坚硬顶板
宽煤柱大采深、局部巷道密集、断层构造 陕西郭家河煤业有限责任公司 3 弱 弱 弱 680~860 坚硬砂岩顶板 宽煤柱 复杂构造 薄底煤 坚硬顶板
复杂构造
宽煤柱大采深、煤厚变化、工作面外错、局部巷道
密集陕西火石咀煤矿有限责任公司 4-2 弱 弱 弱 645~724 顶板较
坚硬宽煤柱 简单构造 薄底煤 无 大采深、煤厚变化、局部巷道密集 彬县煤炭有限责任公司下沟煤矿 4 弱 弱 弱 337~530 厚硬顶板 窄煤柱 小断层、15°~18°
褶曲1~2 m
底煤褶曲构造 采区下山煤柱、局部巷道密集、1~2 m底煤 彬县煤炭有限责任公司蒋家河煤矿 4 弱 弱 弱 440~545 厚层顶板 窄煤柱 构造不
发育不留底煤 坚硬顶板 较大采深、局部巷道密集、煤厚变化 陕西彬长大佛寺矿业有限公司 4
4上弱 弱 弱 265~642
312~725局部坚硬顶板 宽煤柱 局部断层构造 薄底煤 局部坚硬顶板和断层构造、宽煤柱 较大采深、局部巷道密集、煤厚变化、局部厚底煤 旬邑县中达燕家河煤矿有限公司 5
8弱 弱 弱 374~383
295~702坚硬顶板 窄煤柱 断层构造 回采巷道薄底煤
大巷局部厚底煤断层构造
坚硬顶板较大采深、采区下山煤柱、局部巷道密集 陕西旬邑青岗坪矿业有限公司 4 弱 弱 弱 430~510 坚硬砂岩顶板
高位巨厚覆岩宽煤柱 断层构造、褶曲构造 薄底煤,局部1.5 m 坚硬砂岩顶板、宽煤柱 较大采深、断层、褶曲、局部巷道密集、煤厚
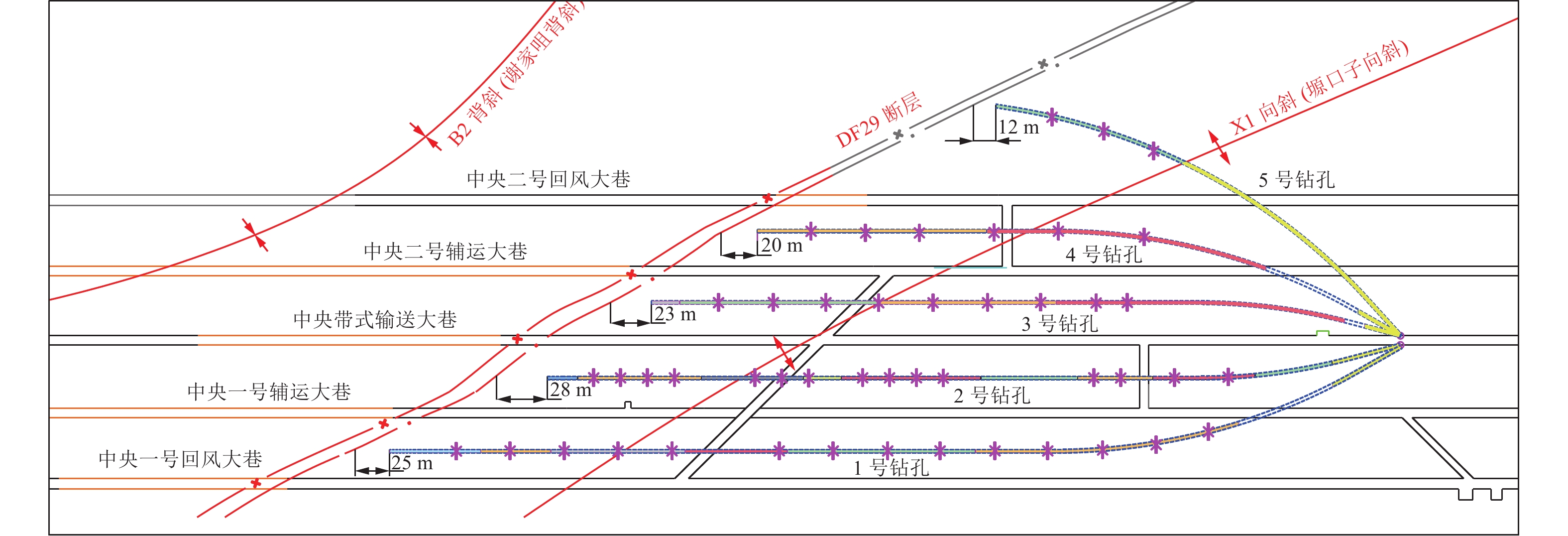
变化注:底煤薄厚以厚度1 m为分界。 -
[1] 潘一山,李忠华,章梦涛. 我国冲击地压分布、类型、机理及防治研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2003,22(11):1844−1851. PAN Yishan,LI Zhonghua,ZHANG Mengtao. Research on the distribution,types,mechanisms,and prevention of rockburst in China[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2003,22(11):1844−1851.
[2] 齐庆新,李一哲,赵善坤,等. 我国煤矿冲击地压发展70年:理论与技术体系的建立与思考[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2019,47(9):1−40. QI Qingxin,LI Yizhe,ZHAO Shankun,et al. 70 years of development of coal mine rock burst in China:establishment and reflection of theoretical and technical systems[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2019,47(9):1−40.
[3] 窦林名,田鑫元,曹安业,等. 我国煤矿冲击地压防治现状与难题[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(1):152−171. DOU Linming,TIAN Xinyuan,CAO Anye,et al. Current situation and difficulties in the prevention and control of coal mine burst in China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(1):152−171.
[4] 姜耀东,赵毅鑫. 我国煤矿冲击地压的研究现状:机制、预警与控制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2015,34(11):2188−2204. JIANG Yaodong,ZHAO Yixin. Research status of coal mine rockburst in China:mechanism,warning and control[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2015,34(11):2188−2204.
[5] 许胜铭,李松营,李德翔,等. 义马煤田冲击地压发生的地质规律[J]. 煤炭学报,2015,40(9):2015−2020. XU Shengming,LI Songying,LI Dexiang,et al. Geological characteristics of rock burst occurrence in Yima coalfield[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2015,40(9):2015−2020.
[6] 窦林名,周坤友,宋士康,等. 煤矿冲击矿压机理、监测预警及防控技术研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2021,29(4):917−932. DOU Linming,ZHOU Kunyou,SONG Shikang,et al. Research on the mechanism,monitoring,early warning and prevention and control technology of coal mine rock burst[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2021,29(4):917−932.
[7] 潘一山,宋义敏,刘 军. 我国煤矿冲击地压防治的格局、变局和新局[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2023,42(9):2081−2095. PAN Yishan,SONG Yimin,LIU Jun. The pattern,changes,and new situation of coal mine rockburst prevention and control in China[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2023,42(9):2081−2095.
[8] 潘俊锋,简军峰,刘少虹,等 . 黄陇侏罗纪煤田冲击地压地质特征与防治 [J]. 煤矿开采,2019,24 (1):110−115. PAN Junfeng,JIAN Junfeng,LIU Shaohong,et al. Geological characteristics and prevention of rock burst in Huanglong Jurassic coal field [J]. Coal Mining,2019,24 (1):110−115.
[9] 刘育晖,张 晔,赵 恒 . 陕西彬长矿区冲击地压防治现状 [J]. 煤矿开采,2017,22 (6):92−95. LIU Yuhui,ZHANG Ye,ZHAO Heng. Current situation of rockburst prevention and control in Binchang mining area,Shaanxi [J]. Coal Mining,2017,22 (6):92−95.
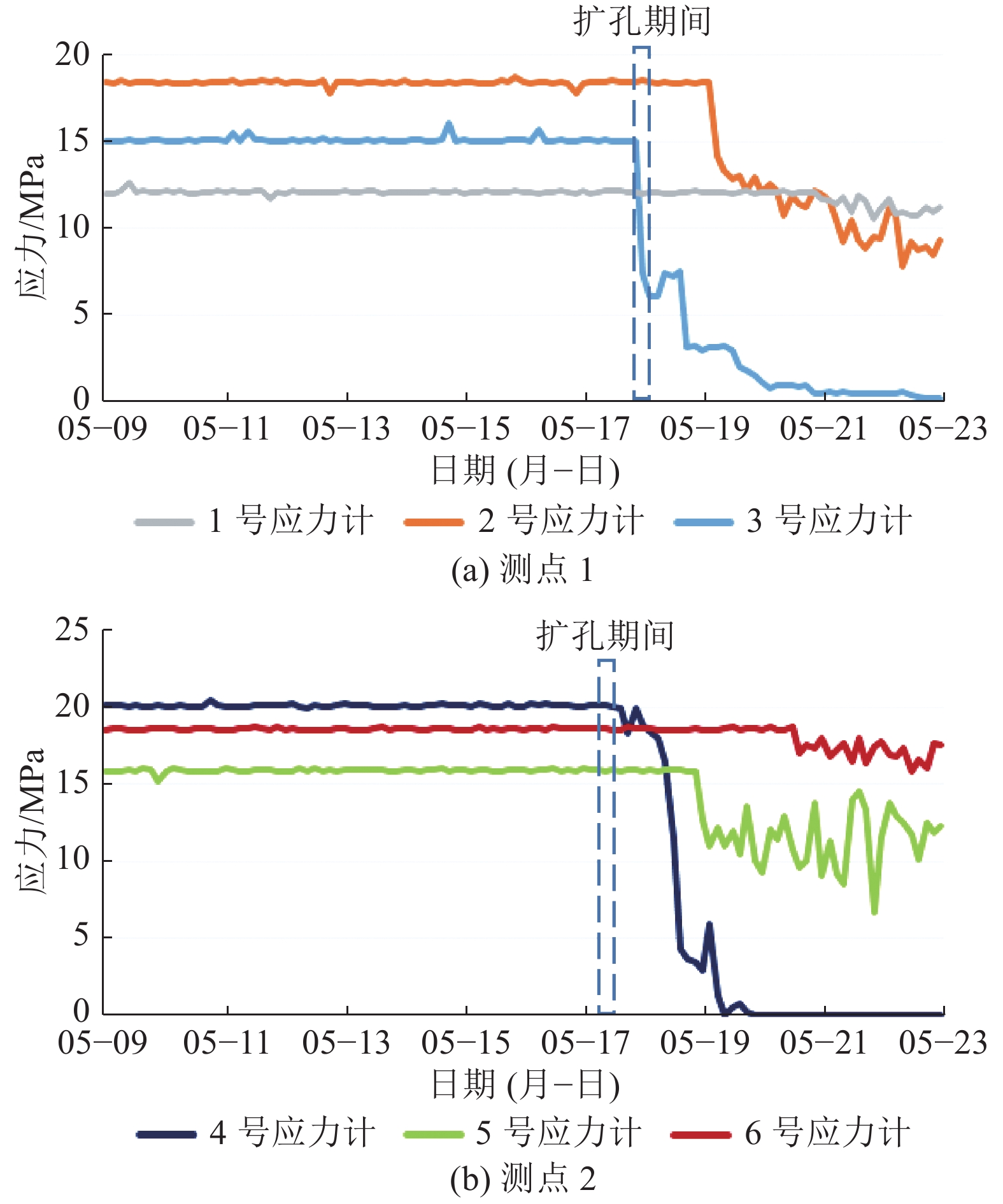
[10] 王元杰,刘 宁,陈法兵,等. 基于井上下微震联合监测技术的地面水平井分段压裂效果分析[J]. 采矿与岩层控制工程学报,2023,5(3):87−97. WANG Yuanjie,LIU Ning,CHEN Fabing,et al. Analysis of segmented fracturing effect in surface horizontal wells based on joint monitoring technology of upper and lower microseisms[J]. Journal of Mining and Rock Formation Control Engineering,2023,5(3):87−97.
[11] 杜涛涛. 冲击地压煤矿井上下微震联合监测技术[J]. 煤矿安全,2022,53(7):92−98. doi: 10.13347/j.cnki.mkaq.2022.07.015 DU Taotao. Joint monitoring technology for upper and lower microseisms in coal mines with impact ground pressure[J]. Safety in Coal Mines,2022,53(7):92−98. doi: 10.13347/j.cnki.mkaq.2022.07.015
[12] 陈 涛. 煤巷底板防冲钻孔释能解危原理及参数优化[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2023,51(5):21−31. CHEN Tao. Principle and parameter optimization of energy release and danger relief for coal roadway floor anti erosion drilling[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2023,51(5):21−31.
[13] 吴学明,马小辉,吕大钊,等. 彬长矿区“井上下”立体防治冲击地压新模式[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2023,51(3):19−26. WU Xueming,MA Xiaohui,LYU Dazhao,et al. A new model for three-dimensional prevention and control of rock burst in the Binchang mining area[J]. Coal Geology and Exploration,2023,51(3):19−26.
[14] 门 鸿,赵华全,窦桂东,等. 特厚煤层地面L型水平井分段压裂技术应用研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2023,54(7):50−58. MEN Hong,ZHAO Huaquan,DOU Guidong,et al. Research on the application of segmented fracturing technology in L-shaped horizontal wells on the surface of ultra-thick coal seams[J]. Safety in Coal Mines,2023,54(7):50−58.
[15] 齐庆新,马世志,孙希奎,等. 煤矿冲击地压源头防治理论与技术架构[J]. 煤炭学报,2023,48(5):1861−1874. QI Qingxin,MA Shizhi,SUN Xikui,et al. Theoretical and technical framework for prevention and control of coal mine rockburst source[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2023,48(5):1861−1874.
[16] 潘俊锋,康红普,闫耀东,等. 顶板“人造解放层”防治冲击地压方法、机理及应用[J]. 煤炭学报,2023,48(2):636−648. PAN Junfeng,KANG Hongpu,YAN Yaodong,et al. Method,mechanism,and application of preventing and controlling rockburst in the “artificial liberated layer” of roof[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2023,48(2):636−648.
[17] 潘俊锋,陆 闯,马小辉,等. 井上下煤层顶板区域压裂防治冲击地压系统及应用[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2023,51(2):106−115. PAN Junfeng,LU Chuang,MA Xiaohui,et al. Fracturing prevention and control of rock burst in the roof area of upper and lower coal seams and its application[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2023,51(2):106−115.
[18] 潘俊锋,刘少虹,高家明,等. 深部巷道冲击地压动静载分源防治理论与技术[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(5):1607−1613. PAN Junfeng,LIU Shaohong,GAO Jiaming,et al. Theory and technology of dynamic and static load source separation prevention and control for deep roadway impact[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2020,45(5):1607−1613.
[19] 潘俊锋,闫耀东,马小辉,等. 考虑时变特性的煤层大巷群冲击地压机理及防治[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(9):3384−3395. PAN Junfeng,YAN Yaodong,MA Xiaohui,et al. Mechanism and prevention of coal seam main roadway group rockburst considering time-varying characteristics[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(9):3384−3395.
-
期刊类型引用(13)
1. 李垂宇,侯俊领,黄童李,黄甫豪,王振亚. 预应力锚杆在拉拔试验过程中的力学分析. 低温建筑技术. 2025(01): 72-74 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘泉声,刘滨,唐彬,康永水,卢海峰,朱元广,黄兴,潘玉丛,邓鹏海,孙磊,唐永志,卢兴利,张程远,余宏淦,李培涛,雷一鸣,贾浩男. 煤矿深部巷道碎胀大变形灾害控制及大变形灾变环境下TBM快速成巷技术. 煤炭学报. 2025(01): 224-244 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 赵能,唐彬,张大欢,胡阳,王逸洋,谢凯. 基于黏聚力模型的螺纹钢锚杆拉拔数值模拟. 煤矿安全. 2024(02): 141-146 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 赵能,陶文斌,沈仁为,胡阳,李宏亮,唐彬. 锚杆拉拔数值模拟试验研究. 福建建材. 2024(01): 10-13 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 杨林,朱训国,夏洪春,杨帅. 拉压复合型锚杆锚固机理的数值及模型试验应用研究. 西安理工大学学报. 2024(01): 132-142 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 段勇信,袁玉福,景小键. 松散软弱围岩巷道锚杆支护失效机理及协同支护研究. 内蒙古煤炭经济. 2024(05): 67-69 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 袁维,王立言,裴子豪,孙瑞峰,王伟. 分级侧向膨胀型锚杆结构力学性能及锚固机理. 地下空间与工程学报. 2024(03): 868-876 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 杜佳敏,何川,汪波,徐国文,陈旭,徐昆杰. 隧道斜向超前系统锚杆支护效果及承载规律. 隧道建设(中英文). 2024(08): 1617-1631 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 郝英豪,韩昌良,刘计寒,杨厚强,白刚,宋凯,杨浩兴,魏民. 强采动巷道破碎顶板全长锚固案例分析. 煤炭技术. 2024(11): 6-11 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 杜志刚,陶亚文,高富强,杜艳强. 玄武岩纤维筋的力学特性与破坏模式试验研究. 矿产勘查. 2023(02): 304-309 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 王想君,李英明,赵光明,孟祥瑞,王艺,程详. 全长锚固锚杆支护软岩巷道围岩承载结构力学响应解析. 煤炭科学技术. 2023(10): 24-34 .  本站查看
本站查看
12. 石垚. 预应力锚杆支护应力场叠加效应试验研究. 能源与环保. 2023(11): 51-60 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. ZHU Zheng-de,SHU Xiao-yun,LI Zhe,TIAN Hong-ming,TIAN Yun. Stress analysis of full-length grouted bolt under shear deformation of anchor interface. Journal of Mountain Science. 2022(11): 3286-3301 .  必应学术
必应学术
其他类型引用(14)



 下载:
下载: