Optimization analysis of layered materials of composite filling body beside gob-side entry retaining
-
摘要:
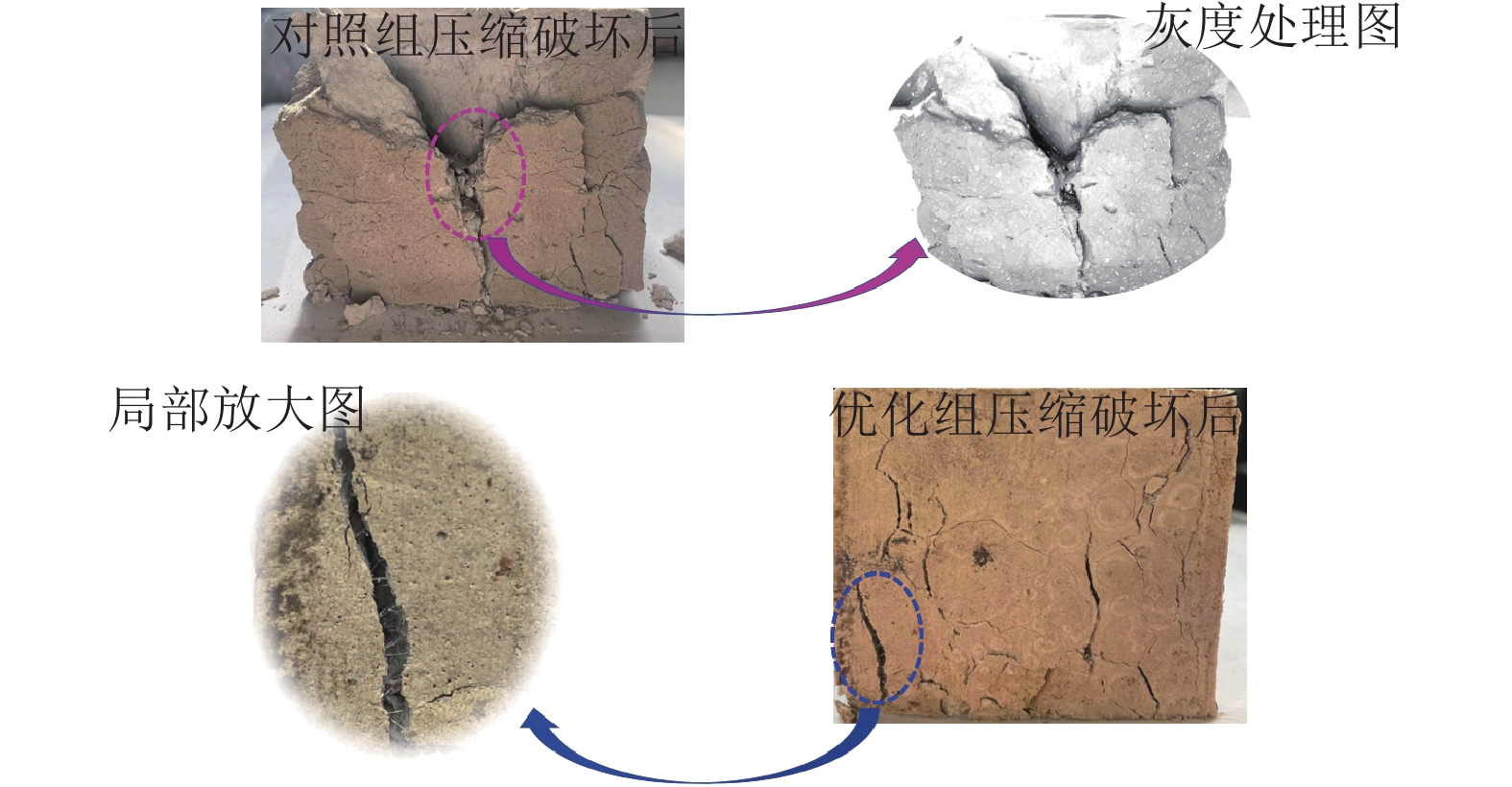
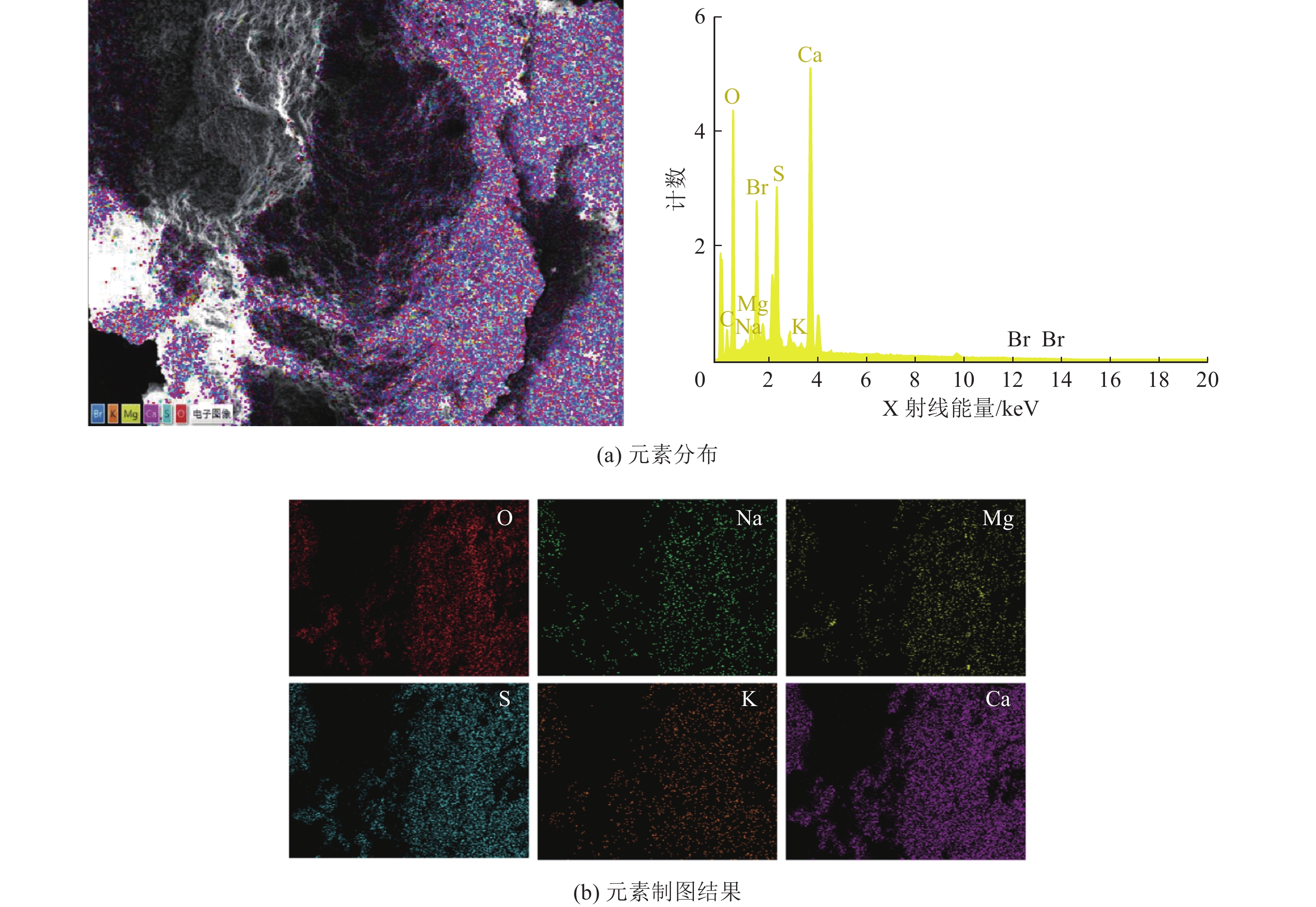
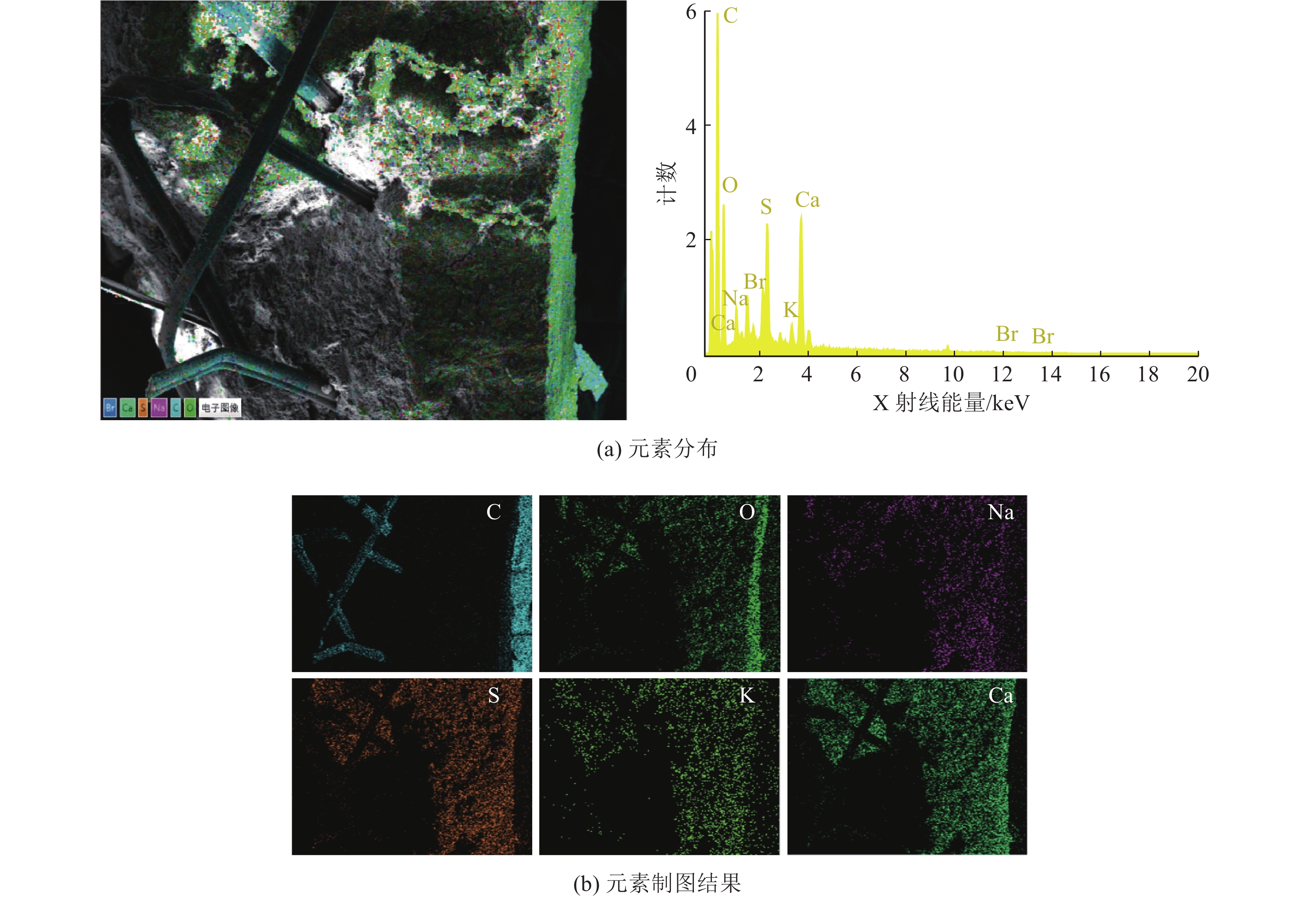
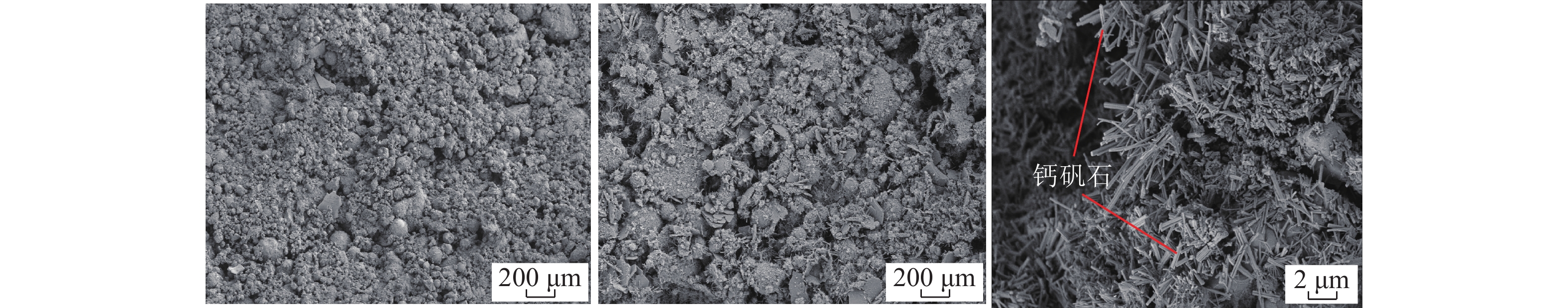
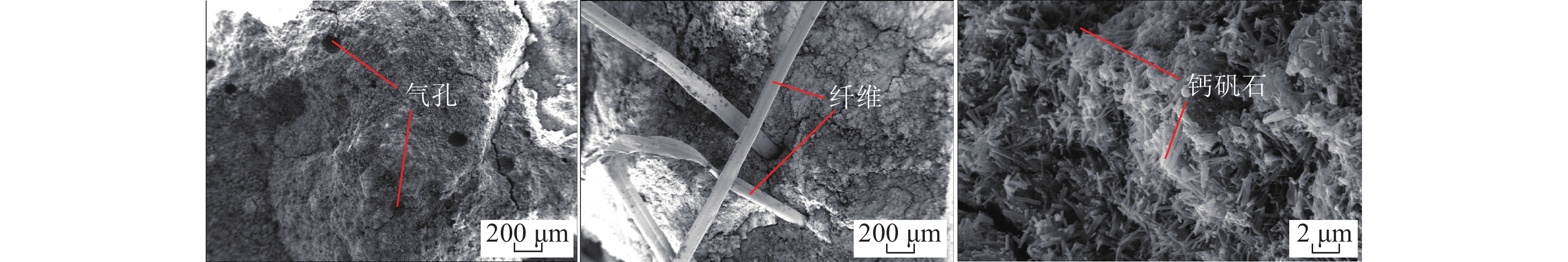
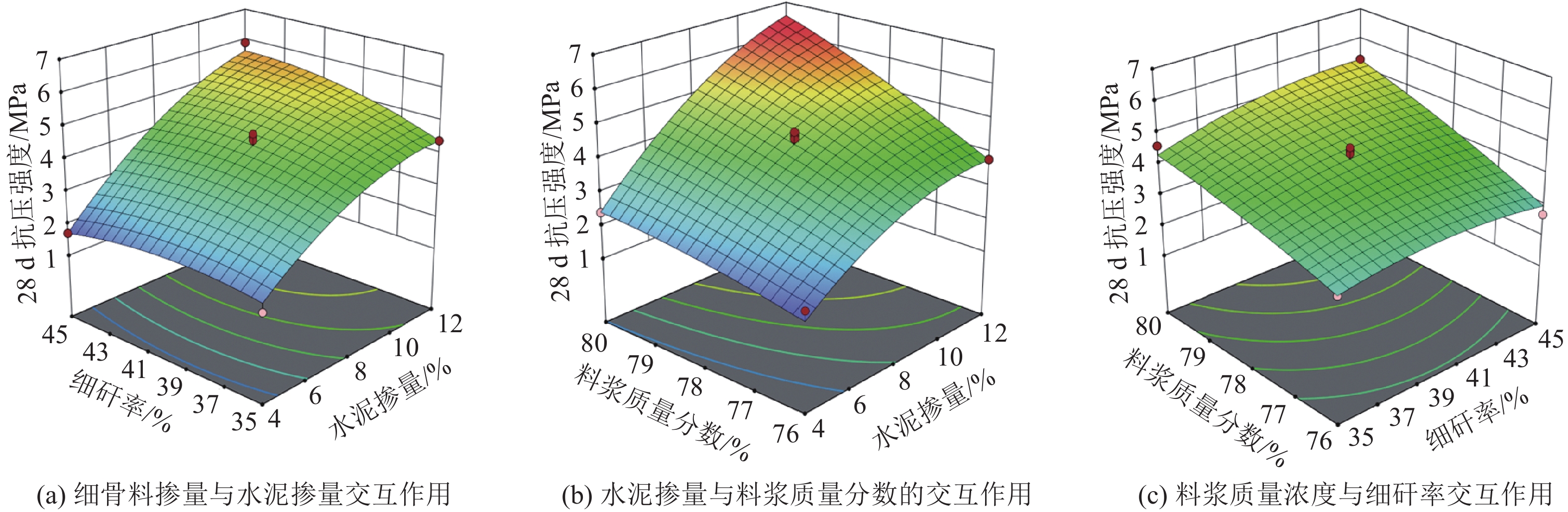
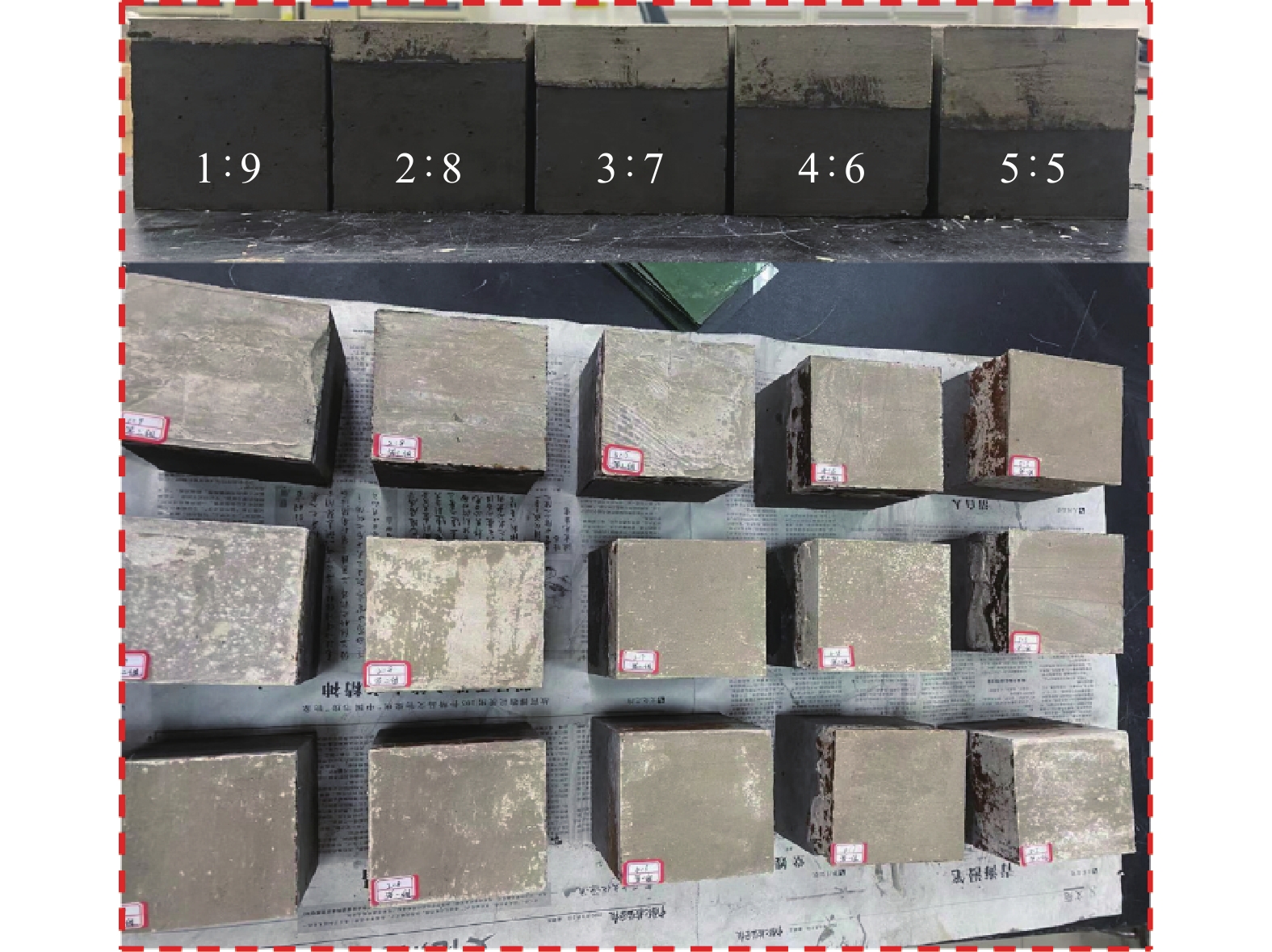
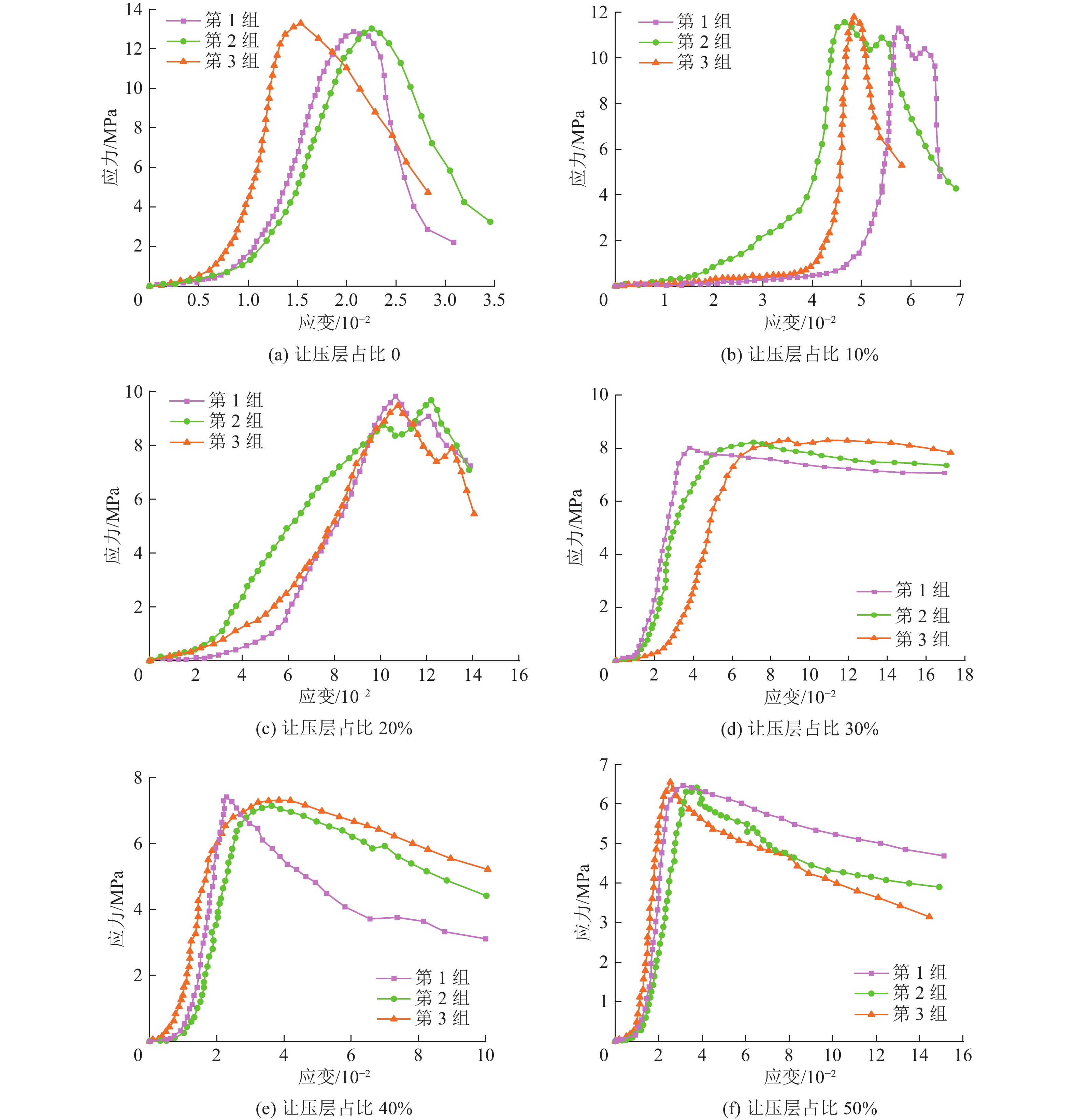
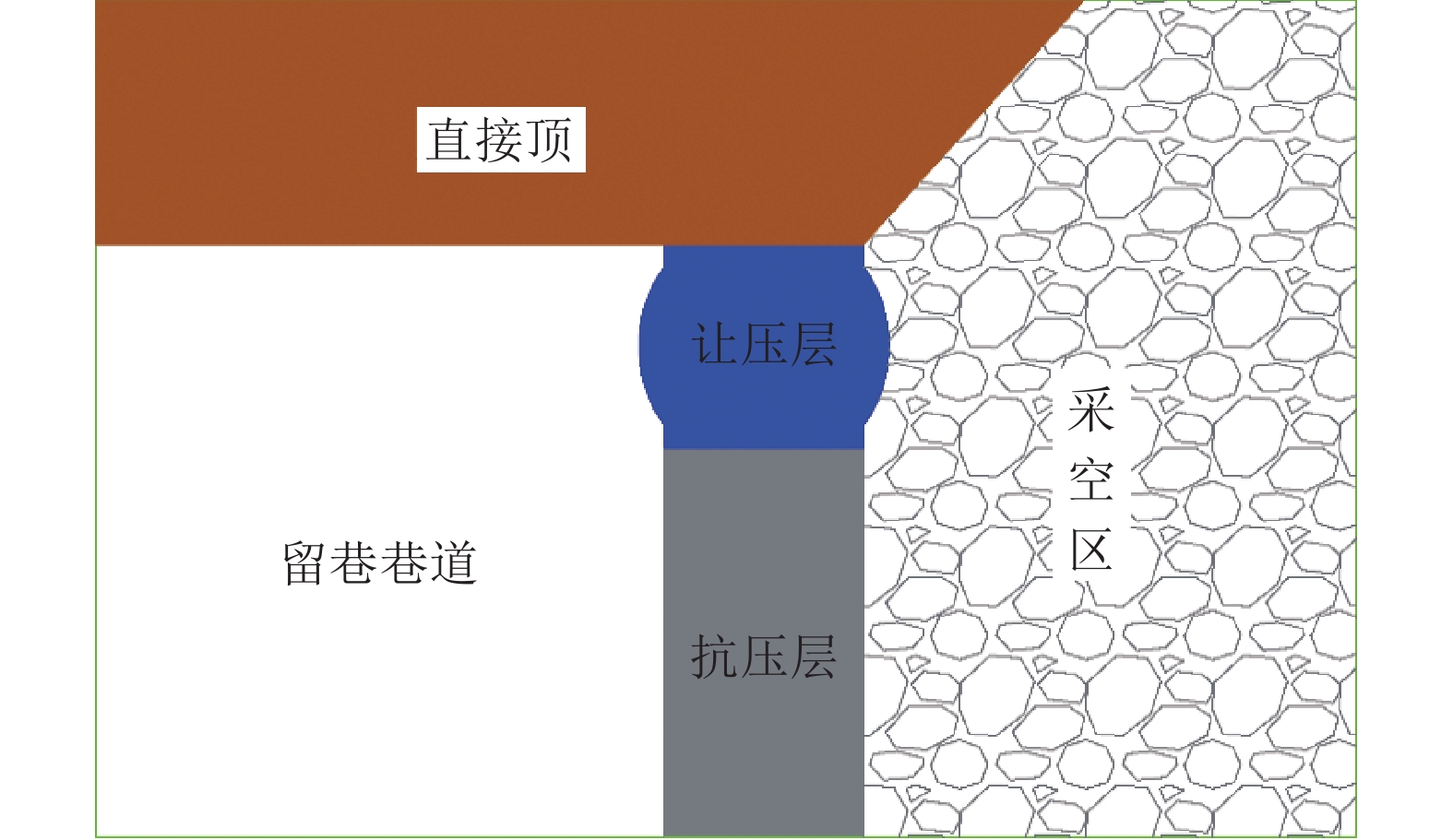
沿空留巷巷旁充填体分为让压层和抗压层,让压层材料应具有大变形的特性,减缓基本顶岩梁的剧烈活动;抗压层材料应具有强度高、刚性大等特点,柔性让压之后实现对上覆岩梁的有效控制。因此对让压层和抗压层材料的不同配比进行力学特性分析,并通过电镜扫描(SEM)对让压层和抗压层的对照组和优化组进行微观结构分析,最后对让压层和抗压层的最优配比进行组合试验。研究结果表明:让压层材料的最优配比为水灰质量比1.5∶1,发泡剂掺量0.06%,纤维掺量0.2%;优化组28 d时抗压强度达到了8.84 MPa;不同期龄下的应变力,优化组为对照组的1.8~2.6倍。抗压层材料配比中细矸率为40%,料浆质量分数78%,水泥掺量为20%时为最优,其平均抗压强度为13.21 MPa,抗拉强度为0.97 MPa,弹性模量为0.75 GPa,内摩擦角为26°,黏聚力为2.85 MPa;该配比下的充填体随着水泥掺量的增加后期强度逐渐增大。组合试件中让压层占比10%~20%时,具有较好的让压能力,也具有一定的关键承载能力。研究结果为沿空留巷巷旁充填体材料配比提供了参考。
Abstract:Along the hollow stay lane roadside filling body is divided into letting pressure layer and compression layer, letting pressure layer material should have the characteristics of large deformation, slow down the violent activities of the basic roof rock beam. The compressive layer material should be characterised by high strength and rigidity, and effective control of the overlying rock beams should be achieved after flexible letting pressure. Therefore, this paper analyzes the mechanical properties of different ratios of yield layer and compressive layer materials, and analyzes the microstructure of the control group and optimization group of yield layer and compressive layer by scanning electron microscope ( SEM ). Finally, the optimal ratio of yield layer and compressive layer is tested. The results of the study showed that the optimum ratio of the material for letting the compaction layer was 1.5:1 for the water-cement ratio, 0.06% for the blowing agent dosage and 0.2% for the fibre dosage. The compressive strength of the optimised group reached 8.84 MPa at 28 d. Strain at different ages was 1.8 to 2.6 times higher in the optimised group than in the control group. The compressive layer material ratio of 40% fine gangue rate, slurry mass concentration of 78%, cement dosage of 20% is optimal, the average compressive strength of 13.21 MPa, tensile strength of 0.97 MPa, modulus of elasticity of 0.75 GPa, the angle of internal friction of 26°, cohesion of 2.85 MPa. The filler at this ratio showed a gradual increase in strength with the increase in cement dosage in the later stages. When the yield layer accounts for 10%−20% of the composite specimen, it has good yield capacity and certain key bearing capacity. The research results provide a reference for the material ratio of roadside filling body in gob-side entry retaining.
-
-
表 1 让压层正交试验结果
Table 1 Orthogonal test results
序号 水灰质量比X1 发泡剂掺量X2/% 聚丙烯纤维掺量X3/% 抗压强度Y1/MPa 膨胀率Y2/% 1 1.00 0.03 0.20 14.18 5.54 2 1.00 0.06 0.60 13.75 7.91 3 1.00 0.09 0.40 13.63 8.34 4 1.25 0.03 0.60 12.92 5.99 5 1.25 0.06 0.40 12.38 9.71 6 1.25 0.09 0.20 10.41 9.80 7 1.50 0.03 0.40 9.08 9.10 8 1.50 0.06 0.20 8.97 10.31 9 1.50 0.09 0.60 7.64 11.71 表 2 单轴抗压强度各主控因素极差分析
Table 2 Uniaxial compressive strength of main control factors range analysis
项目 X1 X2 X3 K1 40.64 38.28 34.13 K2 35.31 35.09 37.34 K3 28.79 31.37 33.27 $\overline{K}_1 $ 13.55 12.76 11.38 $\overline{K}_2 $ 11.77 11.70 12.45 $\overline{K}_3 $ 9.60 10.46 11.09 R 3.95 2.30 1.36 表 3 膨胀率各主控因素极差分析
Table 3 Range analysis of main controlling factors of expansion rate
项目 X1 X2 X3 K1 21.79 20.63 27.65 K2 25.5 29.93 27.15 K3 33.12 29.85 25.61 $\overline{K}_1 $ 7.26 6.88 9.22 $\overline{K}_2 $ 8.50 9.98 9.05 $\overline{K}_3 $ 11.04 9.95 8.54 R 3.78 3.10 0.68 表 4 对照组与优化组力学测试结果
Table 4 Mechanical test results of control group and optimization group
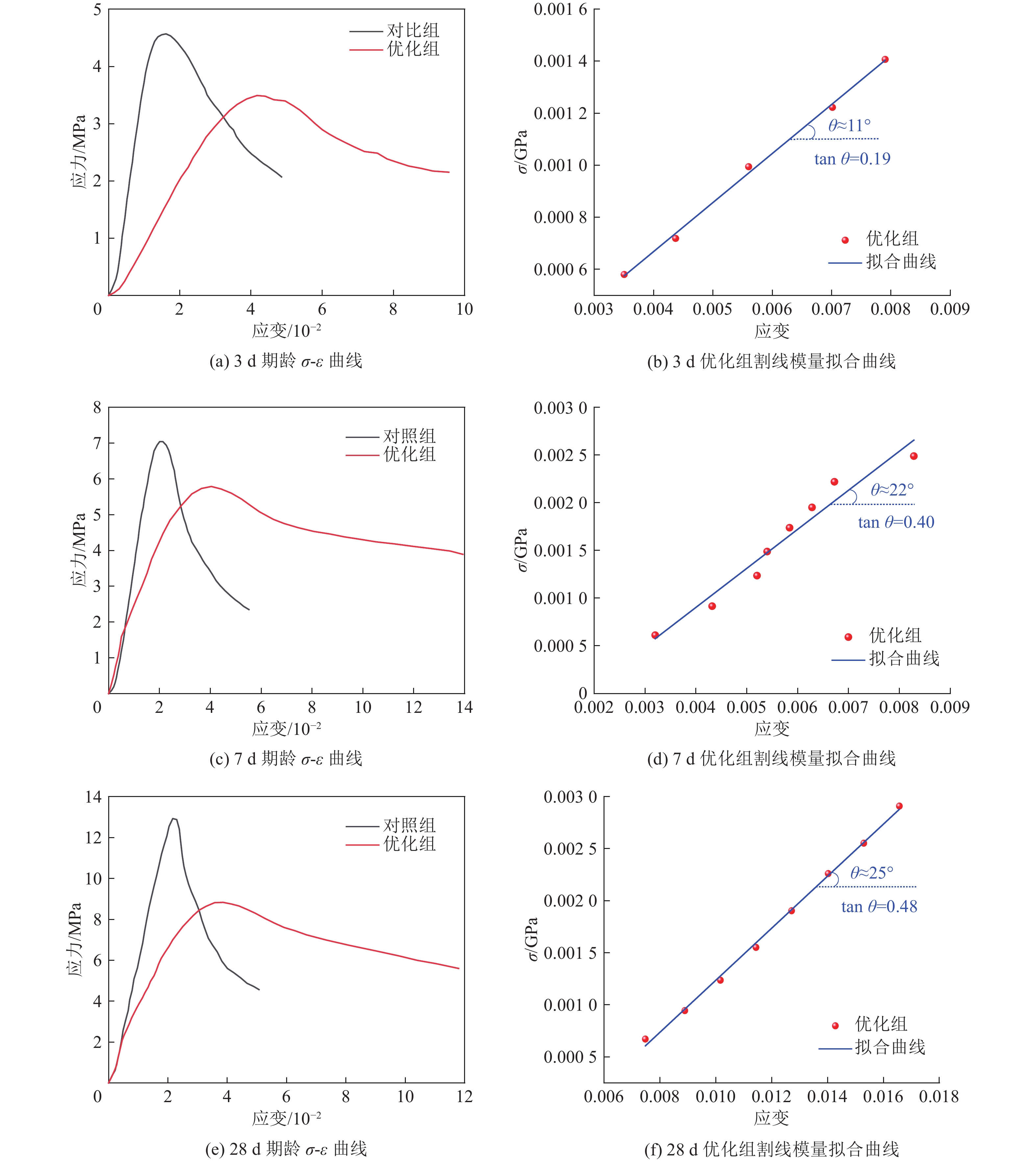
期龄/d 组别 峰值强度/MPa 峰值应变/10−2 弹性模量/GPa 黏聚力/MPa 内摩擦角/(°) 抗拉强度/MPa 3 对照组 4.57 1.60 0.62 — — — 优化组 3.49 4.17 0.19 — — — 7 对照组 6.44 2.05 0.65 — — — 优化组 5.79 4.03 0.40 — — — 28 对照组 12.94 2.16 0.77 1.50 17 1.3 优化组 8.84 3.86 0.48 1.05 15 1.6 -
[1] 冯友良. 考虑采空区压实效应的沿空掘巷煤柱设计方法研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术,2021,17(11):53−59. FENG Youliang. Study on coal pillar design method of gob-side entry driving considering gob compaction effect[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology,2021,17(11):53−59.
[2] 何满潮,高玉兵,盖秋凯,等. 无煤柱自成巷力学原理及其工法[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2023,51(1):19−30. HE Manchao,GAO Yubing,GAI Qiukai,et al. Mechanical principle and mining methods of automagical entry formation without coal Pillars[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2023,51(1):19−30.
[3] ZHANG J,HE Y F,YANG T,et al. Coevolution mechanism and branch of pillar-overburden fissures in shallow coal seam mining[J]. Energy Science & Engineering,2023,11(5):1630−1642.
[4] 李胜,李军文,范超军,等. 综放沿空留巷顶板下沉规律与控制[J]. 煤炭学报,2015,40(9):1989−1994. LI Sheng,LI Junwen,FAN Chaojun,et al. Roof subsidence laws and control technology for gob-side entry retaining in fully-mechanized top-coal caving face[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2015,40(9):1989−1994.
[5] 郑西贵,安铁梁,郭玉,等. 原位煤柱沿空留巷围岩控制机理及工程应用[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2018,35(6):1091−1098. ZHENG Xigui,AN Tieliang,GUO Yu,et al. Surrounding rock control mechanism and engineering application of in situ coal pillar in gob-side entry retaining[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2018,35(6):1091−1098.
[6] 李鹏,朱永建,王平,等. 大倾角厚层坚固顶板巷旁支护体合理宽度及让压尺度研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2022,53(11):4494−4503. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2022.11.028 LI Peng,ZHU Yongjian,WANG Ping,et al. Study on reasonable width and yield scale of roadway side support with strong roof and thick seam with large dip angle[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology),2022,53(11):4494−4503. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2022.11.028
[7] PANG D D,NIU X G,HE K,et al. Study on the deformation mechanism of the bottom plate along the empty lane of deep mining and the control technology of the bottom drum[J]. Geofluids,2022,2022(1):1−16.
[8] 冯国瑞,任玉琦,王朋飞,等. 厚煤层综放沿空留巷巷旁充填体应力分布及变形特征研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2019,36(6):1109−1119. FENG Guorui,REN Yuqi,WANG Pengfei,et al. Stress distribution and deformation characteristics of roadside backfill body for gob-side entry of fully-mechanized caving in thick coal seam[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2019,36(6):1109−1119.
[9] 华心祝,李琛,刘啸,等. 再论我国沿空留巷技术发展现状及改进建议[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2023,51(1):128−145. HUA Xinzhu,LI Chen,LIU Xiao,et al. Current situation of gob-side entry retaining and suggestions for its improvement in China[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2023,51(1):128−145.
[10] 王凯,杨宝贵,王鹏宇,等. 软弱厚煤层沿空留巷变形破坏特征及控制研究[J]. 岩土力学,2022,43(7):1913−1924,1960. WANG Kai,YANG Baogui,WANG Pengyu,et al. Deformation and failure characteristics of gob-side entry retaining in soft and thick coal seam and the control technology[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2022,43(7):1913−1924,1960.
[11] 华心祝,李志华,李迎富,等. 深井大断面沿空留巷分阶段底鼓特征分析[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2016,44(9):26−30. HUA Xinzhu, LI Zhihua, LI Yingfu,et al. Analysis on floor heave features of large cross section gob-side entry retaining in deep mine[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2016,44(9):26−30.
[12] BIAN W H,YANG J,HE M C,et al. Research and application of mechanical models for the whole process of 110 mining method roof structural movement[J]. Journal of Central South University,2022,29(9):3106−3124. doi: 10.1007/s11771-022-5148-9
[13] 王家臣. 我国综放开采40年及展望[J]. 煤炭学报,2023,48(1):83−99. WANG Jiachen. 40 years development and prospect of longwall top coal caving in China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2023,48(1):83−99.
[14] 康红普,张晓,王东攀,等. 无煤柱开采围岩控制技术及应用[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(1):16−44. KANG Hongpu,ZHANG Xiao,WANG Dongpan,et al. Strata control technology and applications of non-pillar coal mining[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(1):16−44.
[15] 朱珍,张科学,袁红平. 切顶卸压沿空留巷碎石巷帮控制技术及应用[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2018,46(3):25−32. ZHU Zhen,ZHANG Kexue,YUAN Hongping. Control technology and its application of roadway side wall formed by gangue in gob-side entry retaining formed by roof cutting and pressure releasing[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2018,46(3):25−32.
[16] LIU Yufei,WU Xinhua,ZHU Tao,et al. Influence of mechanical properties of filling paste on overlying strata movement and surface settlement[J]. Shock and Vibration,2022,2022(1):4687200.
[17] 柏建彪,张自政,王襄禹,等. 高水材料充填沿空留巷应力控制与围岩强化机理及应用[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(6):16−28. BAI Jianbiao,ZHANG Zizheng,WANG Xiangyu,et al. Stress control and surrounding rock strengthening mechanism of gob-side entry retaining with high-water content material filling and its application[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(6):16−28.
[18] 候朝炯,易安伟,柏建彪,等. 高水灰渣速凝材料巷旁充填沿空留巷的试验研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,1995,23(2):2−5,34,63. HOU Chaojiong,YI Anwei,BAI Jianbiao,et al. Experimental study on gob-side entry retaining with roadside filling of high water-cement slag quick-setting material[J]. Coal Science and Technology,1995,23(2):2−5,34,63.
[19] 李西凡,熊祖强,张耀辉,等. 沿空留巷高水充填材料改性试验及工程应用[J]. 重庆大学学报,2020,43(4):94−106. doi: 10.11835/j.issn.1000-582X.2019.252 LI Xifan,XIONG Zuqiang,ZHANG Yaohui,et al. Modification test and engineering application of high-water filling material in gob-side entry retaining[J]. Journal of Chongqing University,2020,43(4):94−106. doi: 10.11835/j.issn.1000-582X.2019.252
[20] 李舒霞,姜福兴,朱权洁. 复合墙体支护技术在沿空留巷中的应用研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2014,42(12):32−36. LI Shuxia,JIANG Fuxing,ZHU Quanjie. Study on composite wall support technology applied to gob-side entry retaining[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2014,42(12):32−36.
[21] 叶根喜,朱权洁,李舒霞,等. 千米深井沿空留巷复合充填体研制与应用[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2016,33(5):787−794. YE Genxi,ZHU Quanjie,LI Shuxia,et al. Development and application of composite filling body in gob-side entry retaining with 1000m-plus deep coal mine[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2016,33(5):787−794.
[22] 孙恒虎,赵炳利. 沿空留巷的理论与实践[M]. 北京:煤炭工业出版社,1993. [23] 王平,曾梓龙,孙广京,等. 深井矸石充填工作面沿空留巷围岩控制原理与技术[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(6):68−76. WANG Ping,ZENG Zilong,SUN Guangjing,et al. Principle and technology of surrounding rock control for gob-side entry retaining in deep mine gangue backfilling face[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(6):68−76.
[24] 谭云亮,于凤海,宁建国,等. 沿空巷旁支护适应性原理与支护方法[J]. 煤炭学报,2016,41(2):376−382. TAN Yunliang,YU Fenghai,NING Jianguo,et al. Adaptability theory of roadside support in gob-side entry retaining and its supporting design[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2016,41(2):376−382.
[25] 宁建国,马鹏飞,刘学生,等. 坚硬顶板沿空留巷巷旁“让-抗” 支护机理[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2013,30(3):369−374. NING Jianguo,MA Pengfei,LIU Xuesheng,et al. Supporting mechanism of “yielding-supporting” beside roadway maintained along the goaf under hard rocks[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2013,30(3):369−374.
[26] 曹悦. 综放工作面沿空留巷组合充填体失稳机理及围岩控制技术研究[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2022. CAO Yue. Study on instability mechanism and surrounding rock control technology of gob-side entry retaining combined backfill in fully mechanized caving face[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2022.



 下载:
下载: