Coal-rock interface image recognition based on MRU-Net++ for extremely thin coal seam fully-mechanized mining face
-
摘要:
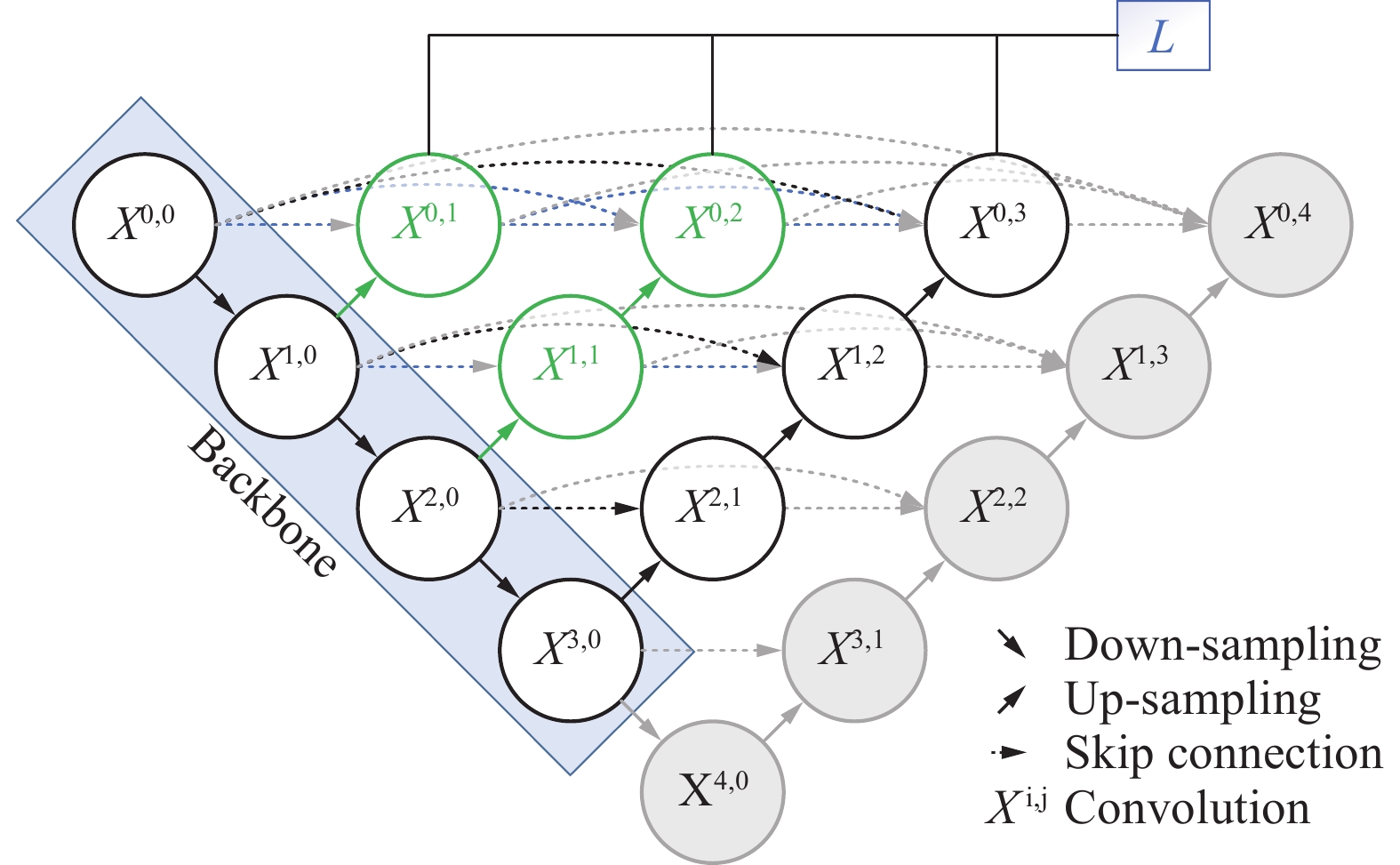
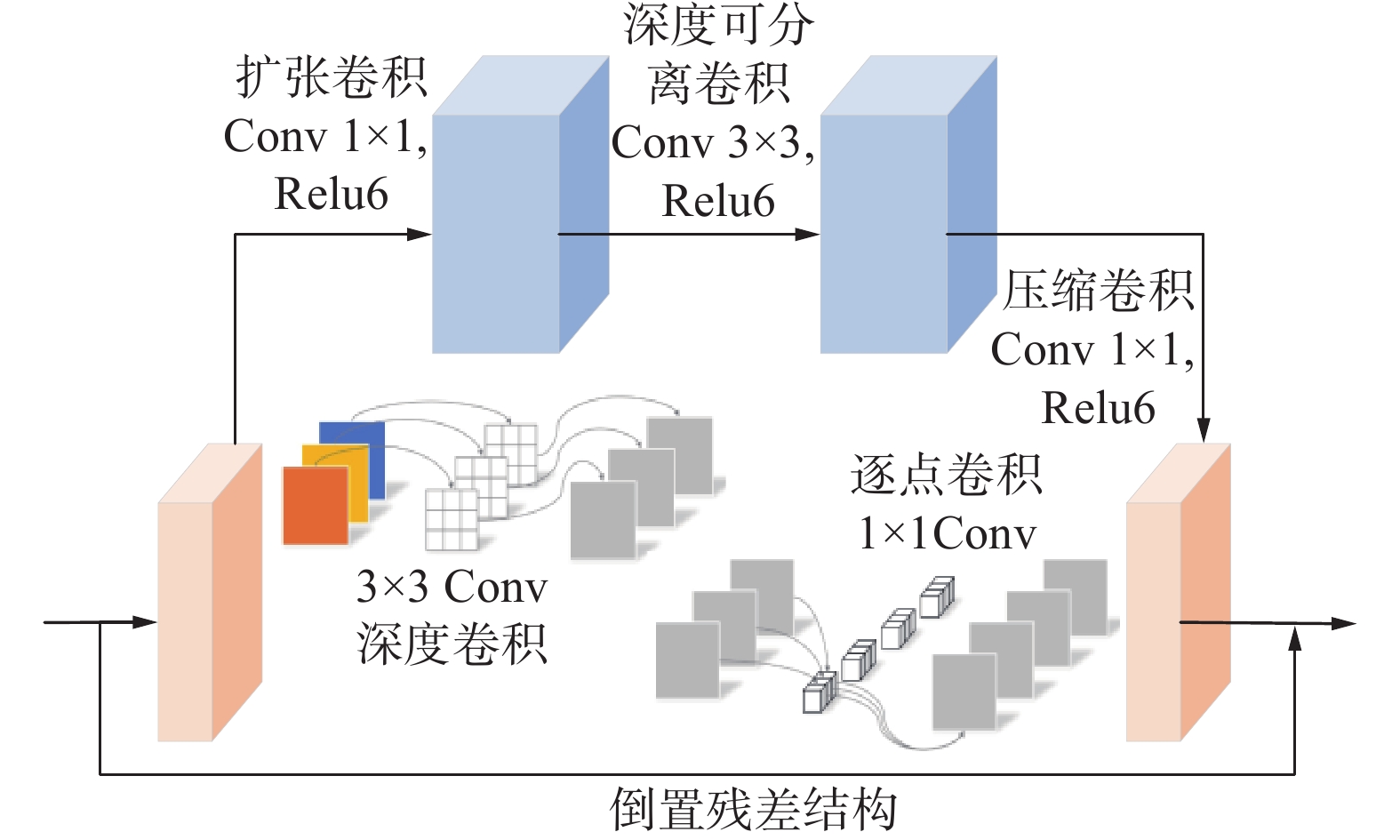
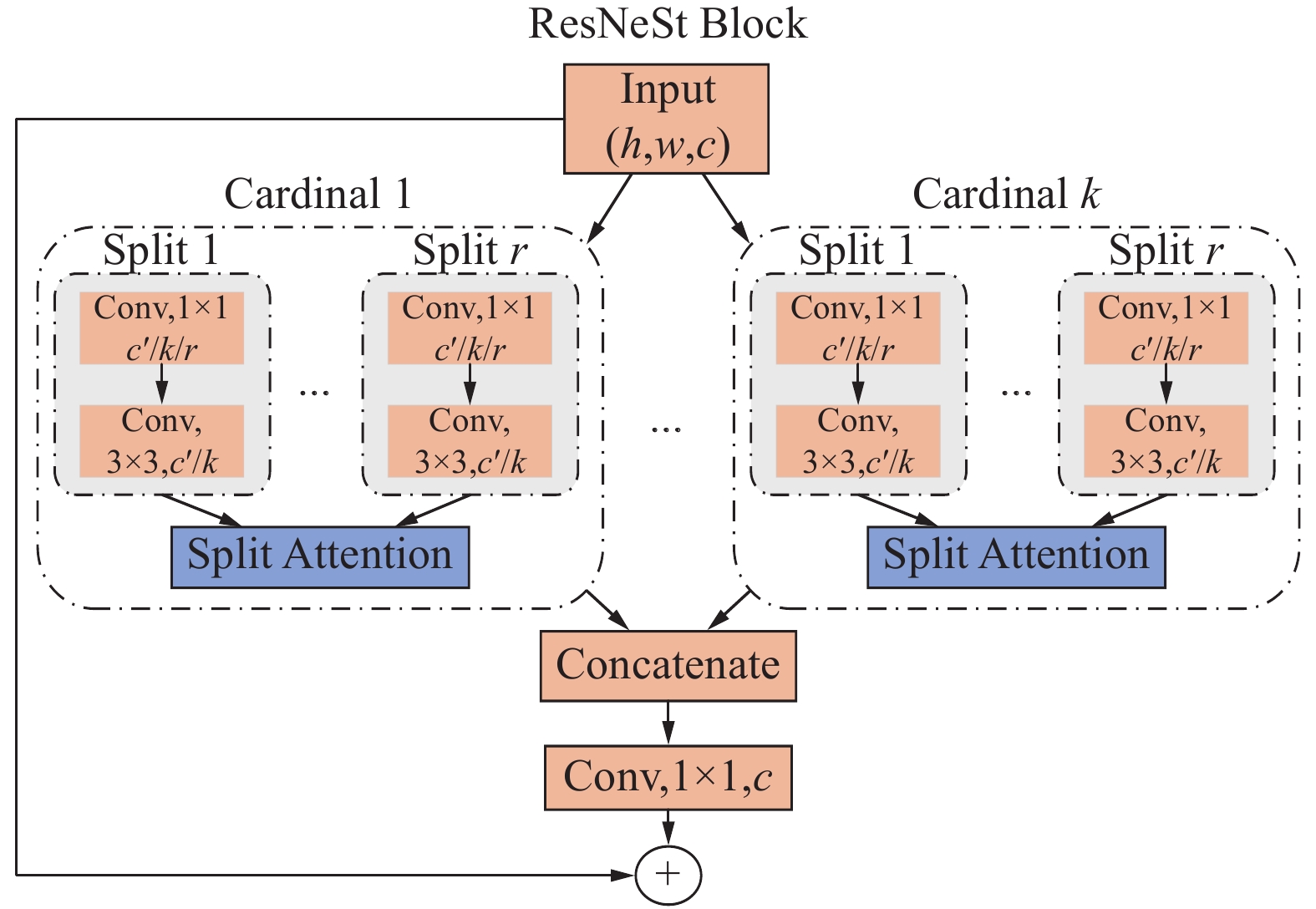
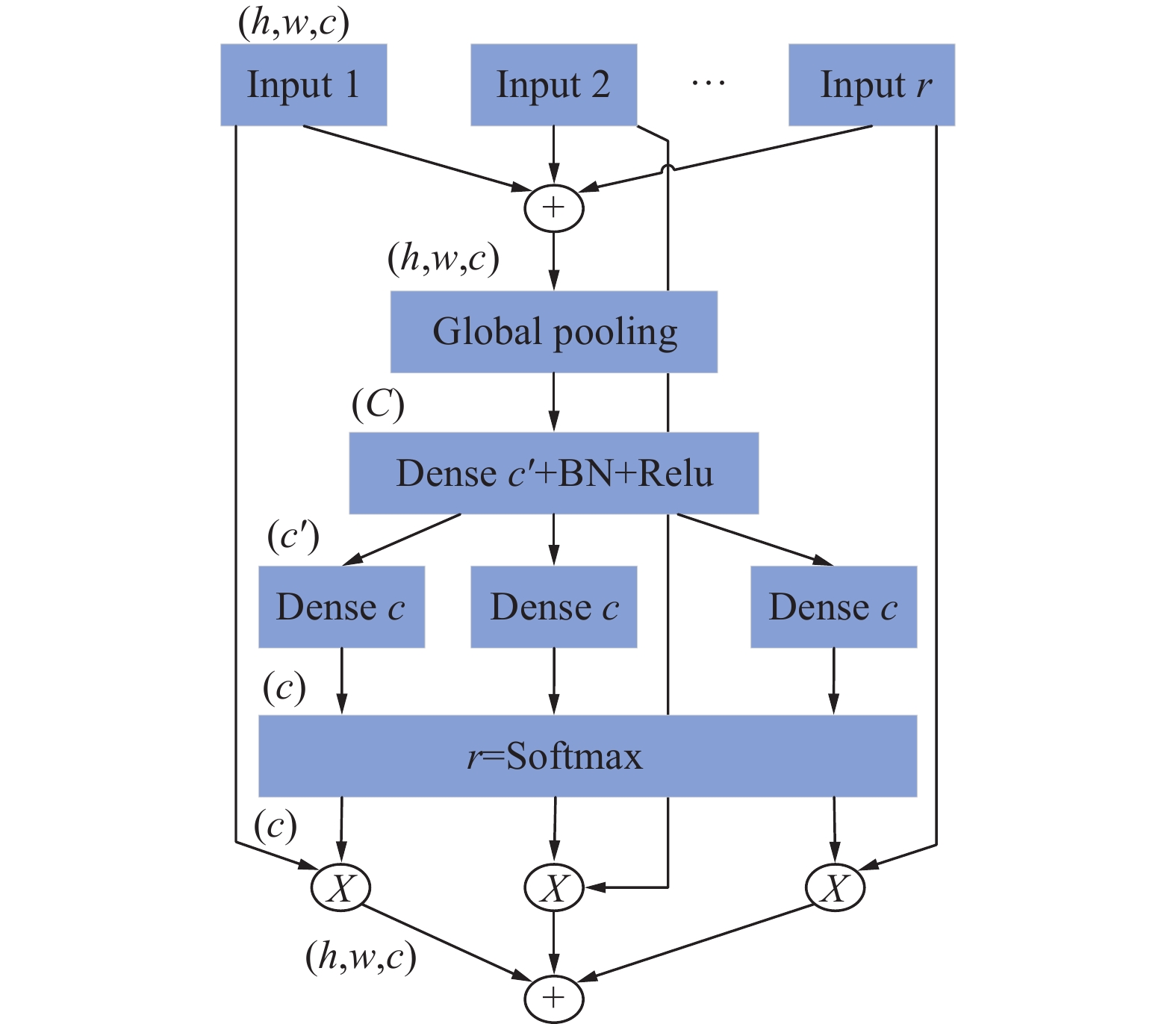
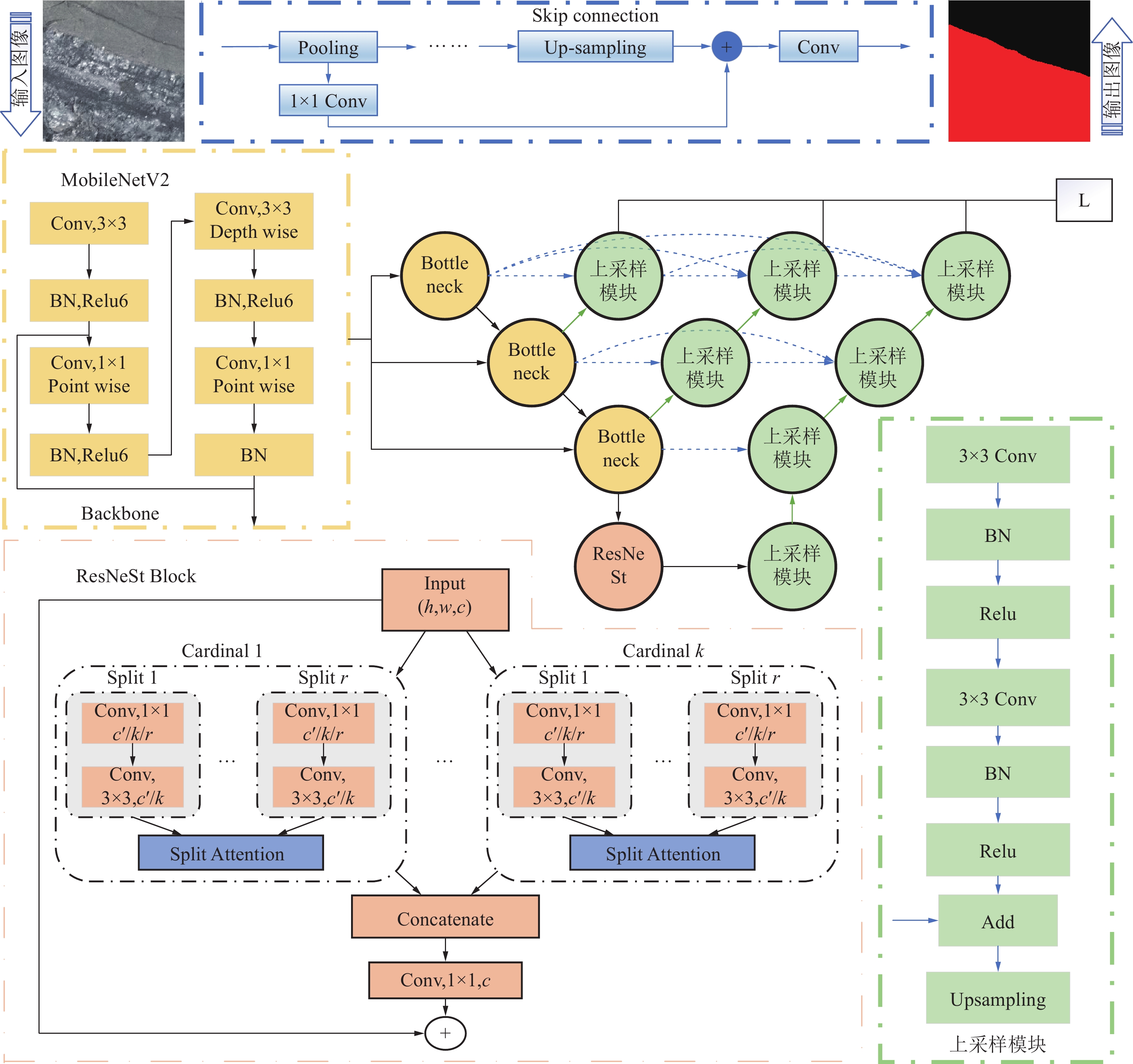
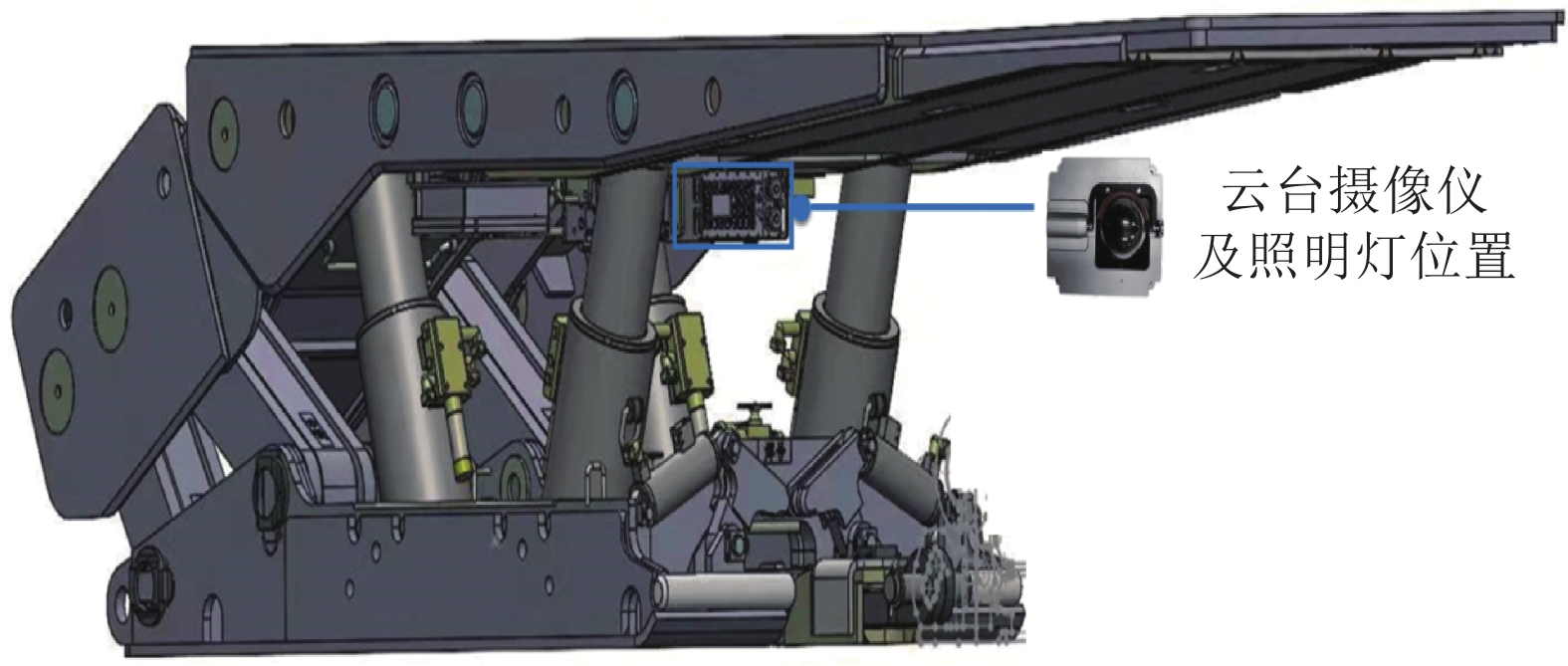
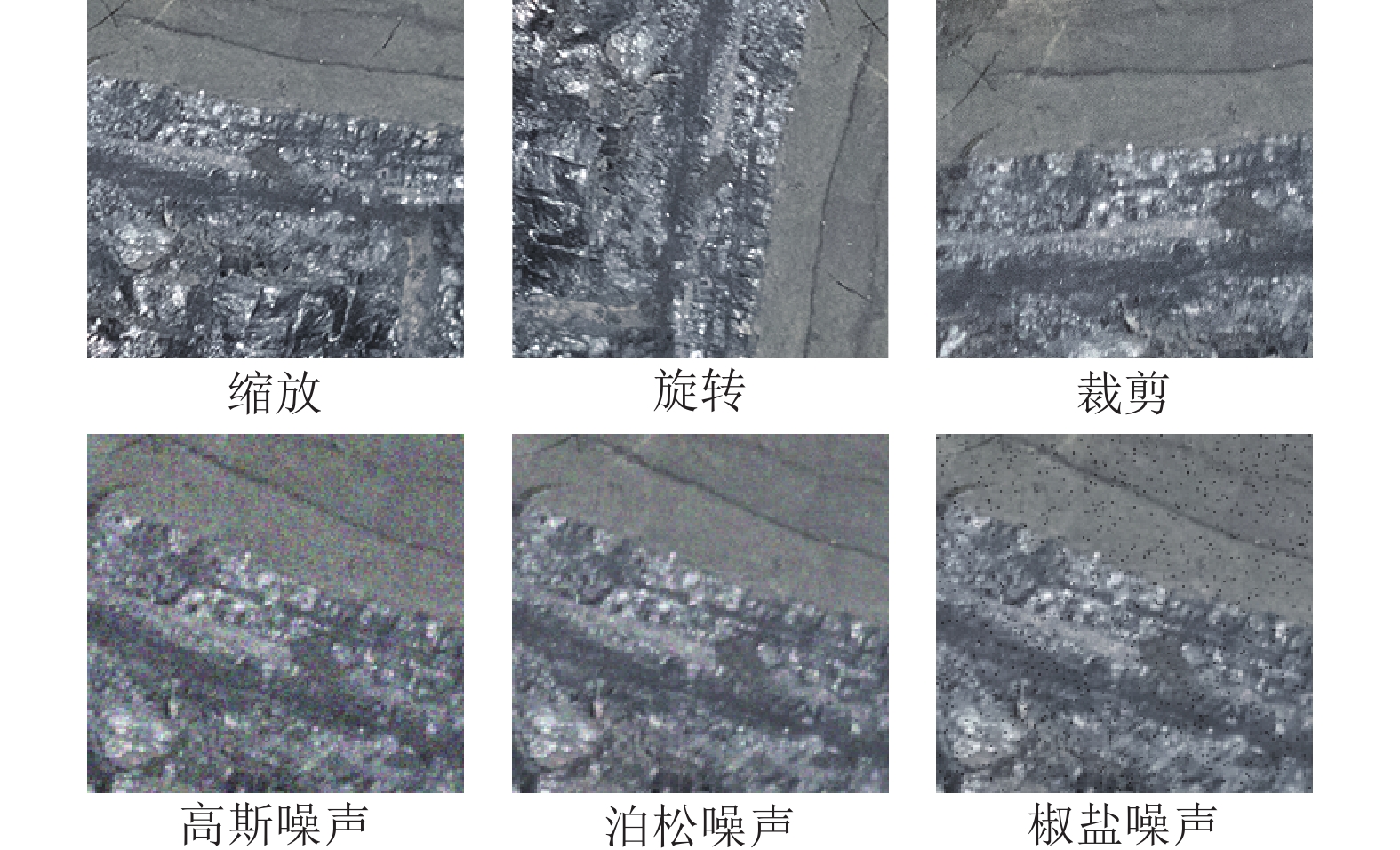
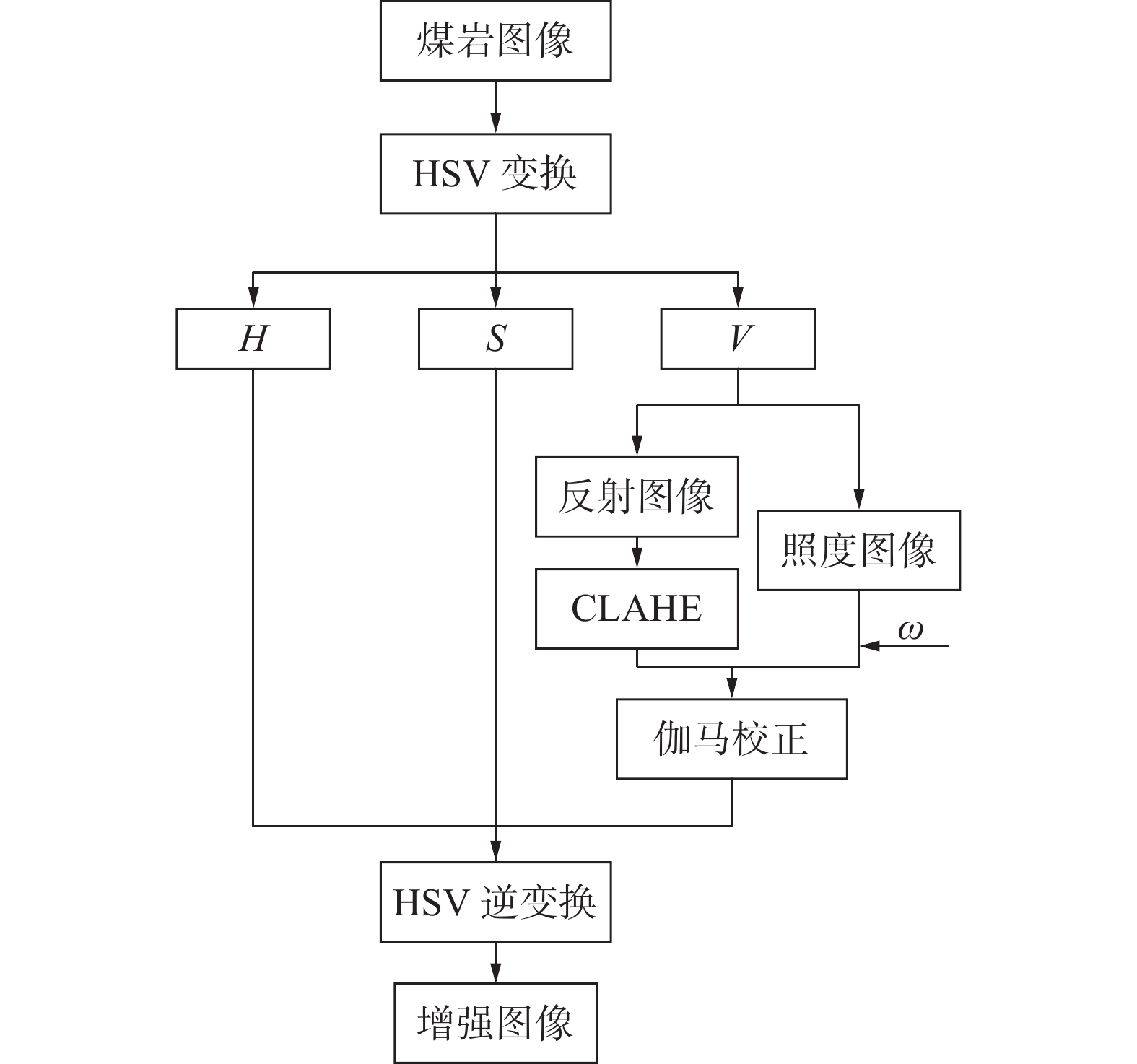
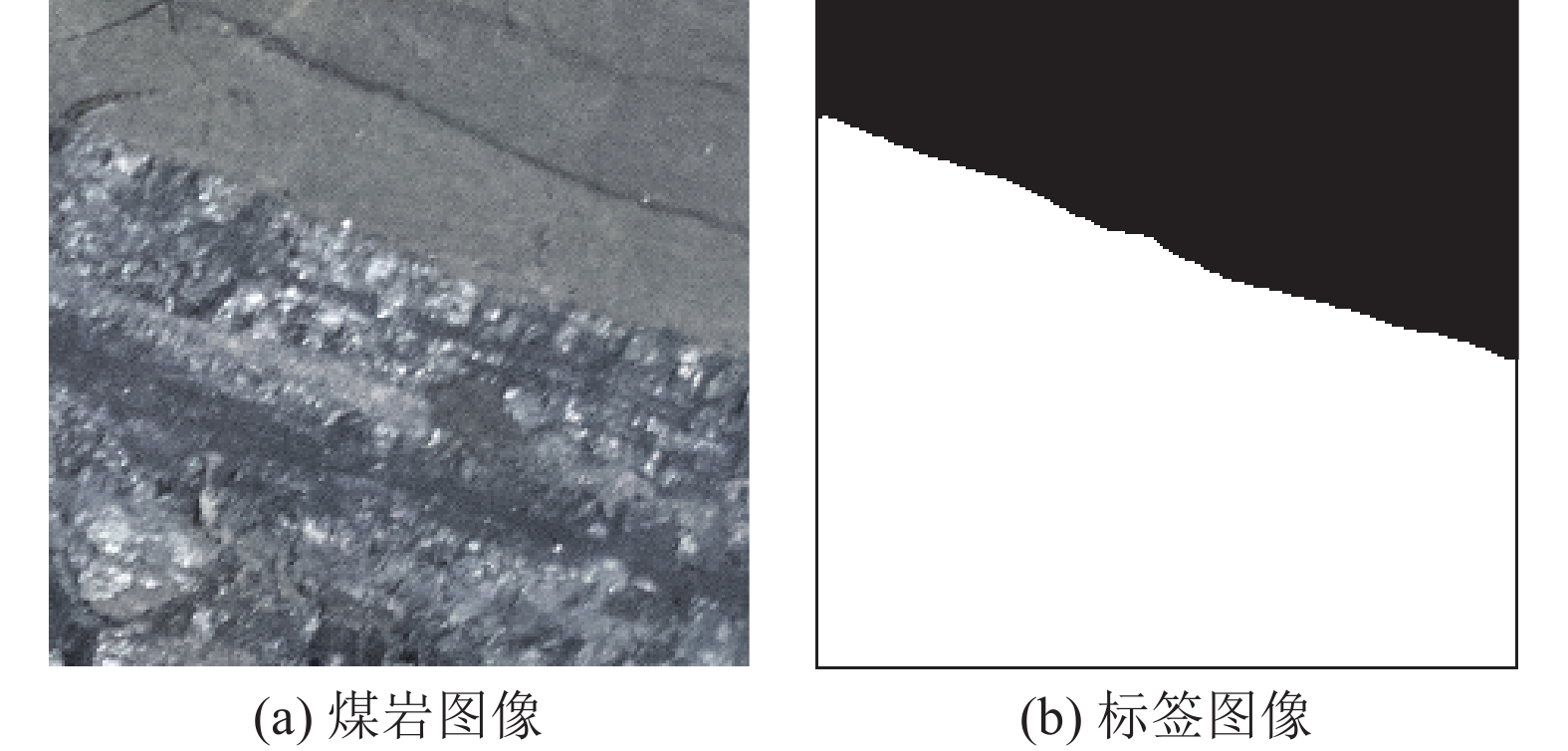
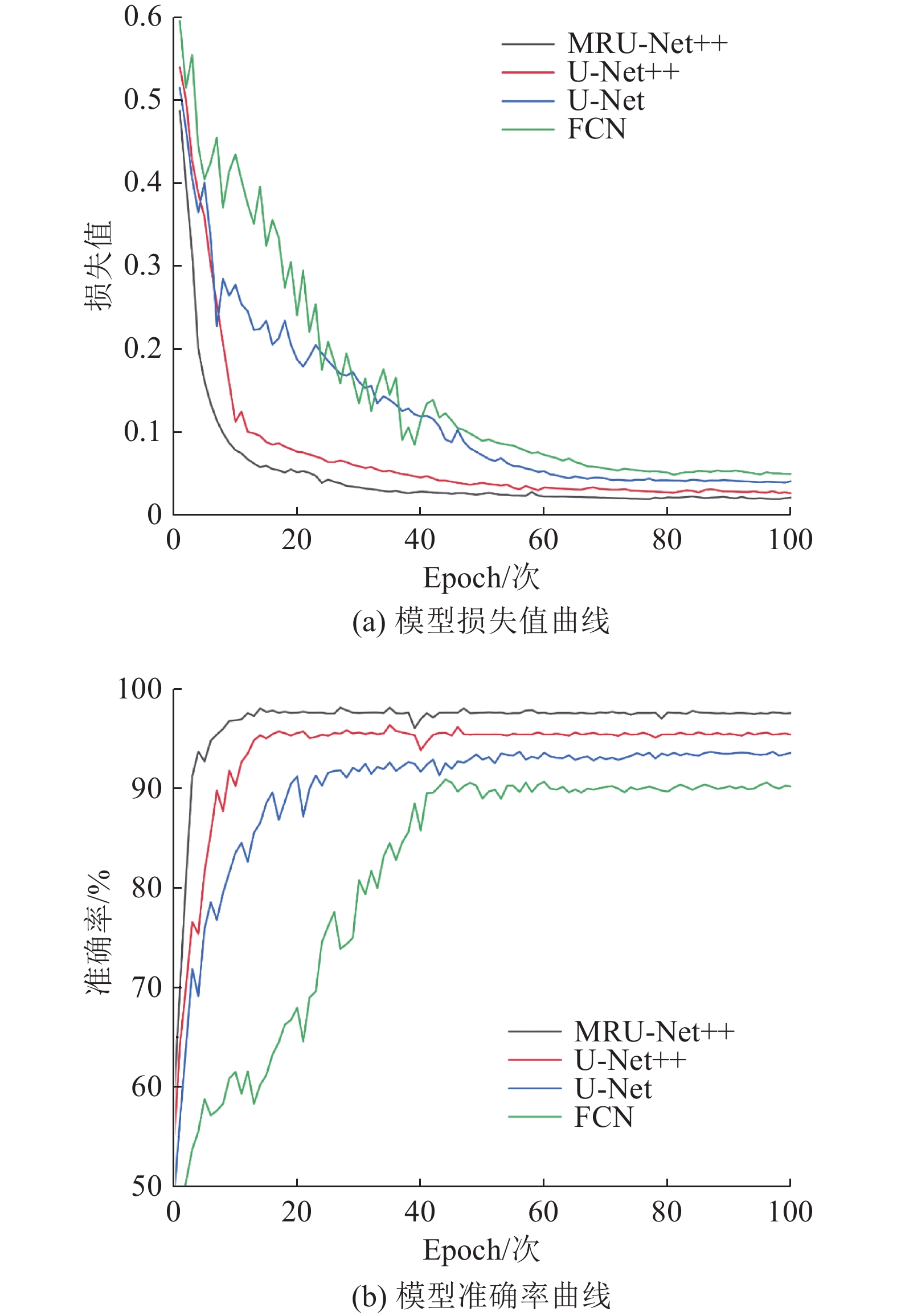
煤岩识别是极薄煤层综采工作面实现智能化开采的核心技术之一。针对极薄煤层开采时煤岩分界线自然裸露在外的特殊情况,提出了一种基于MRU-Net++网络的极薄煤层煤岩图像识别方法。该网络以U-Net++为基础,通过“剪枝”技术对U-Net++结构进行优化,在U-Net++网络性能损失最小的同时减少其复杂度,以提高运算速度;采用MobileNetV2轻量化网络,构建一个基于MobileNetV2的核心骨干网络,替代U-Net++原有的网络架构,显著降低了模型的参数数量,提高了模型分割效率;同时引入含有通道注意力机制的ResNeSt模块来增强对煤岩图像边缘细节特征的提取能力,提高分割精度。利用液压支架上的防爆摄像仪采集极薄煤层综采工作面煤岩图像,获取具有煤岩分布信息的高清煤岩图像并对图像进行预处理,创建含有2 536个样本的极薄煤层综采面煤岩图像数据集。设置消融试验,验证改进部分对网络性能的影响,并将该模型与经典FCN、U-Net、U-Net++网络模型进行对比,利用自适应学习算法训练各网络模型,选择像素准确度(Pixel Accuracy, PA)、交并比(Intersection over Union, IOU)及测试时间等关键指标评估模型分割效果。结果显示,MRU-Net++网络模型的平均像素准确度PAM和交并比IOUM分别为97.15%和94.16%,模型占用内存25.71 M,每张图像的平均测试时间28.61 ms,充分证明了该方法在极薄煤层特殊环境下进行煤岩识别任务的可行性与有效性。
-
关键词:
- 极薄煤层 /
- 煤岩识别 /
- 语义分割 /
- U-Net++网络模型 /
- 深度学习
Abstract:Coal rock recognition is one of the core technologies to realize intelligent mining in the integrated mining face of extremely thin coal seam. Aiming at the special situation that the coal-rock boundary is naturally exposed during the mining of extremely thin coal seams, an image recognition method based on MRU-Net++ network was proposed for coal-rock image recognition of extremely thin coal seams. The network is based on U-Net++, and the structure of U-Net++ was optimized by the method of “pruning”, which reduces the complexity of U-Net++ network while minimizing the loss of its performance in order to improve the computing speed. MobileNetV2 lightweight network was used to construct a core backbone network based on MobileNetV2, replacing the original network architecture of U-Net++, which significantly reduces the number of parameters of the model and improves the efficiency of the model segmentation. At the same time, the ResNeSt module, which contains the channel attention mechanism, was introduced to enhance the ability of extracting the detailed features of the edges of the coal and rock images, and to increase the segmentation accuracy. The explosion-proof camera on the hydraulic support was used to collect the coal rock images of the comprehensive mining face in the extremely thin coal seam, and the high-definition coal rock images with coal rock distribution information were acquired and preprocessed to create a coal rock image dataset of the comprehensive mining face of the extremely thin coal seam containing 2 536 samples. The ablation test was set up to verify the effect of the improved part on the network performance. The model was compared with the classical FCN, U-Net, and U-Net++ network models and the network models were trained using adaptive learning algorithms. Key indexes such as Pixel Accuracy (PA), Intersection over Union (IOU) and test time were selected to evaluate the model segmentation effect. The results show that the Mean Pixel Ascuracy (PAM) and Mean Intersection over Union (IOUM) of the MRU-Net++ network model are 97.15% and 94.16%, respectively, the memory occupied by the model is 25.71 M, and the average test time of each image is 28.61 ms, which fully proves the feasibility and effectiveness of the method for the coal rock recognition task under the special environment of extremely thin coal seam.
-
-
表 1 图像增强前后质量评估指标
Table 1 Quality assessment metrics before and after image enhancement
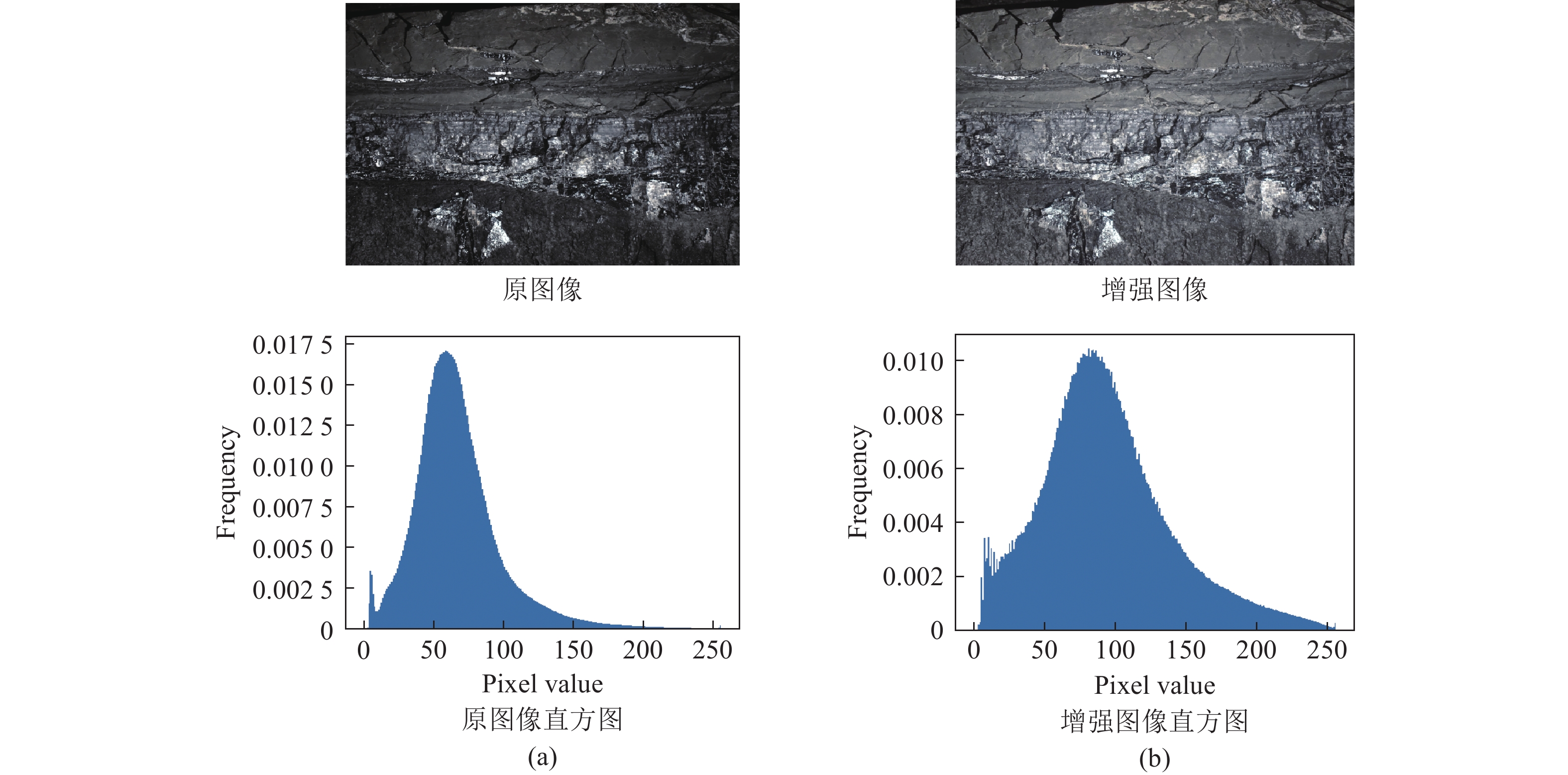
类别 均值 标准差 IE PSNR SSIM 原图像 58.75 37.81 6.98 — — 增强图像 101.64 42.73 7.32 27.38 0.82 表 2 试验环境配置
Table 2 Experimental environment configuration
试验环境 项目 参数 硬件 CPU Intel core i7−12700H 内存 16 G GPU NVIDIA GeForce RTX3060 显存 6 G 软件 操作系统 Windows 10 深度学习框架 PyTorch 2.0.1 CUDA 12.4 编程语言 Python 3.9 表 3 训练参数设置
Table 3 Training parameter settings
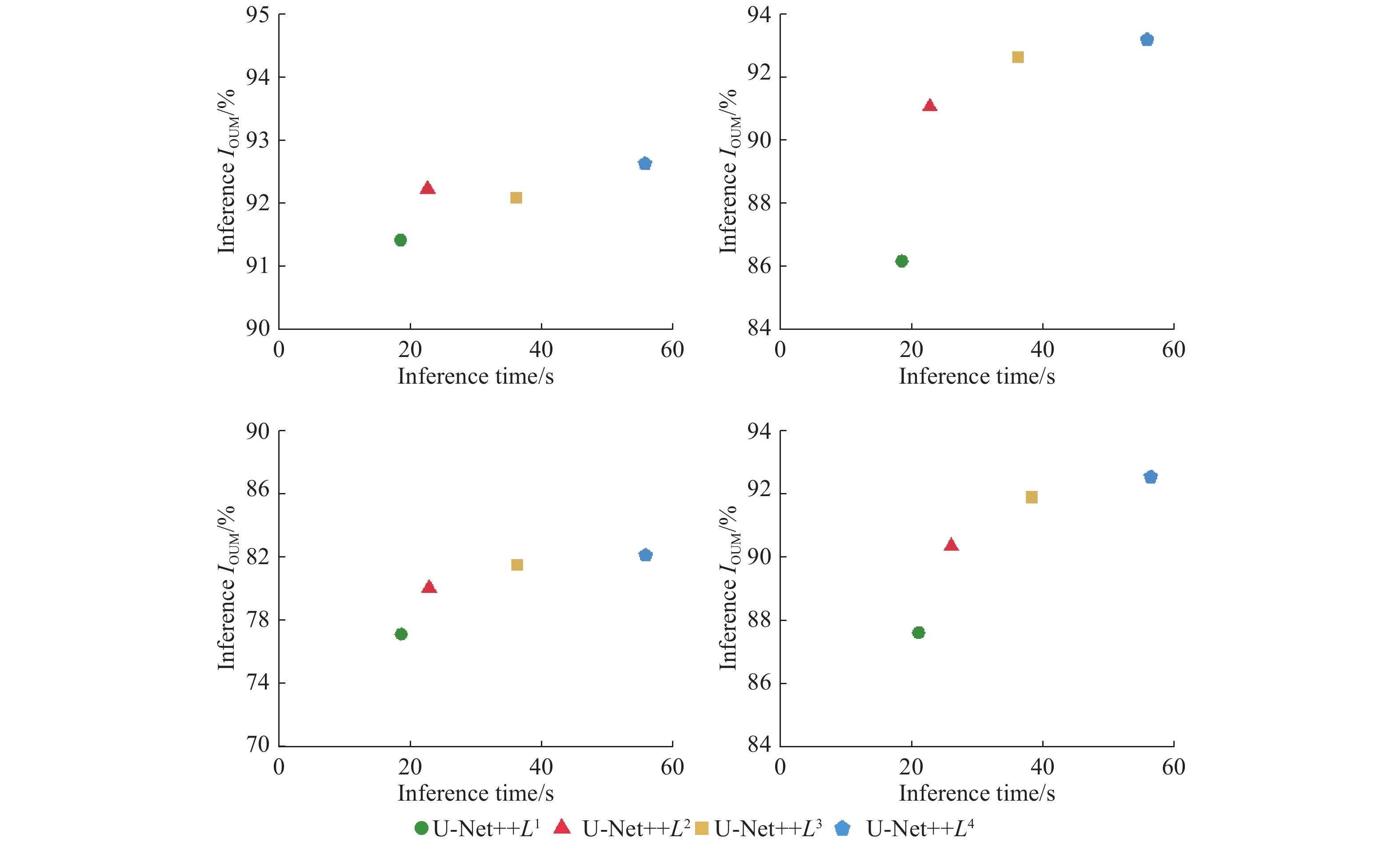
项目 数值 初始学习率 0.0001 BatchSize 8 Epoch 100 损失函数 交叉熵 表 4 “剪枝”方法消融试验对比结果
Table 4 Comparative results of the "pruning" method ablation tests
试验模型 IOUM/% 测试用时/(ms·张−1) 剪枝后的U-Net++L3 91.74 30.68 未剪枝的U-Net++ 92.43 44.36 表 5 骨干网络性能对比结果
Table 5 Backbone network performance comparison results
骨干网络 IOUM/% 测试用时/(ms·张−1) MobileNetV2 91.49 24.53 原U-Net++L3 91.74 30.68 表 6 ResNeSt模块消融试验对比结果
Table 6 Comparative results of the ResNeSt module ablation tests
试验模型 IOUM/% PAM/% 未引入ResNeSt模块 91.49 95.27 MRU-Net++ 94.62 97.38 表 7 各网络模型的内存及测试时间
Table 7 Memory and test time of each network model
网络模型 模型大小/M 测试用时/(ms·张-1) FCN 46.35 56.74 U-Net 31.24 39.43 U-Net++ 34.96 44.59 MRU-Net++ 25.71 28.61 表 8 PA评估得分
Table 8 PA evaluation score
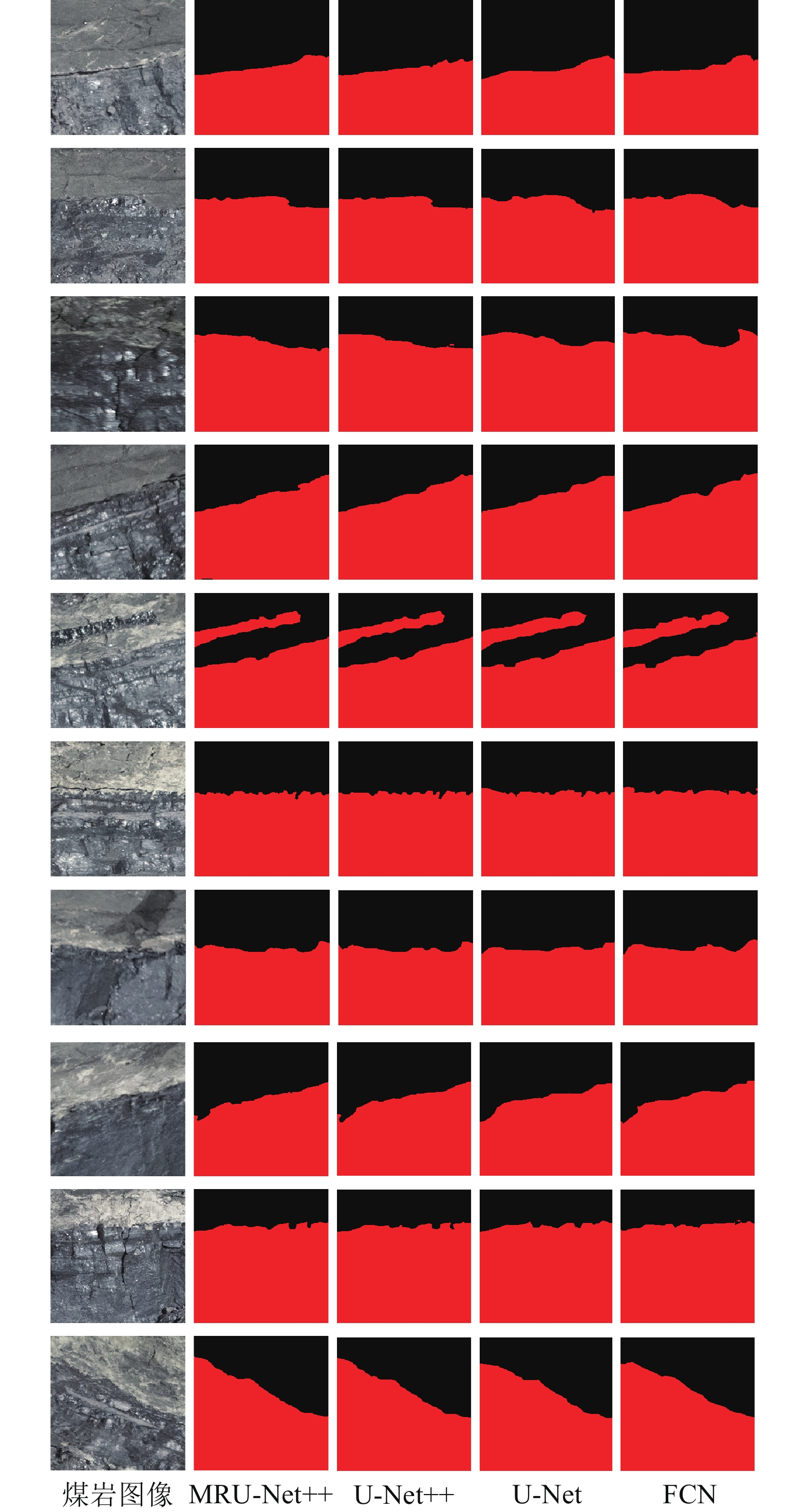
项目 PA/% MRU-Net++ U-Net++ U-Net FCN 1 98.23 96.74 95.87 94.28 2 97.49 96.18 94.65 93.35 3 98.10 95.42 93.92 88.97 4 97.57 94.66 95.43 93.56 5 96.68 95.39 93.10 90.74 6 94.20 93.27 91.71 89.13 7 97.76 96.35 94.38 94.30 8 96.81 95.64 93.25 93.26 9 95.35 94.36 92.46 89.67 10 99.27 97.58 94.84 93.91 平均值 97.15 95.56 93.96 92.12 表 9 IOU评估得分
Table 9 IOU evaluation score
项目 IOU/% MRU-Net++ U-Net++ U-Net FCN 1 95.19 94.34 93.77 93.31 2 94.37 92.96 89.95 87.49 3 93.80 93.47 92.89 85.72 4 94.49 95.16 93.51 91.83 5 92.99 89.75 88.63 89.25 6 91.58 87.54 86.12 85.98 7 95.87 94.21 94.80 93.79 8 94.42 93.82 92.31 92.64 9 92.21 88.43 87.69 86.85 10 96.68 95.46 94.52 95.37 平均值 94.16 92.51 91.42 90.18 -
[1] 汤家轩,刘具,梁跃强,等. “十四五” 时期我国煤炭工业发展思考[J]. 中国煤炭,2021,47(10):6−10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-530X.2021.10.002 TANG Jiaxuan,LIU Ju,LIANG Yueqiang,et al. Thoughts on the development of China’s coal industry during the 14th Five-Year Plan period[J]. China Coal,2021,47(10):6−10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-530X.2021.10.002
[2] 王国法. 煤矿智能化最新技术进展与问题探讨[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(1):1−27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2336.2022.1.mtkxjs202201001 WANG Guofa. New technological progress of coal mine intelligence and its problems[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(1):1−27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2336.2022.1.mtkxjs202201001
[3] 翟雨生,史春祥,吕晓,等. 薄煤层滚筒式采煤机发展现状及关键技术[J]. 煤炭工程,2020,52(7):182−186. ZHAI Yusheng,SHI Chunxiang,LYU Xiao,et al. Development status and key technologies of thin coal seam drum shearer[J]. Coal Engineering,2020,52(7):182−186.
[4] 秦涛,张腾,刘永立. 极薄煤层智能开采关键技术进展分析[J]. 煤炭技术,2023,42(6):45−48. QIN Tao,ZHANG Teng,LIU Yongli. Analysis on key technology progress of intelligent mining in extremely thin coal seam[J]. Coal Technology,2023,42(6):45−48.
[5] 鲍久圣,张可琨,王茂森,等. 矿山数字孪生 MiDT:模型架构、关键技术及研究展望[J]. 绿色矿山,2023,1(1):166−177. BAO Jiusheng,ZHANG Kekun,WANG Maosen,et al. Mine digital twin:Model architecture,key technologies and research prospects[J]. Journal of Green Mine,2023,1(1):166−177.
[6] 王国法,刘峰,庞义辉,等. 煤矿智能化:煤炭工业高质量发展的核心技术支撑[J]. 煤炭学报,2019,44(2):349−357. WANG Guofa,LIU Feng,PANG Yihui,et al. Coal mine intellectualization:The core technology of high quality development[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2019,44(2):349−357.
[7] 张科学,李首滨,何满潮,等. 智能化无人开采系列关键技术之一:综采智能化工作面调斜控制技术研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2018,46(1):139−149. ZHANG Kexue,LI Shoubin,HE Manchao,et al. Study on key technologies of intelligent unmanned coal mining series Ⅰ:Study on diagonal adjustment control technology of intelligent fully-mechanized coal mining face[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2018,46(1):139−149.
[8] 王国法,庞义辉,任怀伟. 智慧矿山技术体系研究与发展路径[J]. 金属矿山,2022(5):1−9. WANG Guofa,PANG Yihui,REN Huaiwei. Research and development path of smart mine technology system[J]. Metal Mine,2022(5):1−9.
[9] 顾清华,江松,李学现,等. 人工智能背景下采矿系统工程发展现状与展望[J]. 金属矿山,2022(5):10−25. GU Qinghua,JIANG Song,LI Xuexian,et al. Development status and prospect of mining system engineering under the background of artificial intelligence[J]. Metal Mine,2022(5):10−25.
[10] 张强,张润鑫,刘峻铭,等. 煤矿智能化开采煤岩识别技术综述[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(2):1−26. ZHANG Qiang,ZHANG Runxin,LIU Junming,et al. Review on coal and rock identification technology for intelligent mining in coal mines[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(2):1−26.
[11] 贺艳军,李海雄,胡淼龙,等. 煤岩识别技术发展综述[J]. 工矿自动化,2023,49(12):1−11. HE Yanjun,LI Haixiong,HU Miaolong,et al. Overview of the development of coal rock recognition technology[J]. Journal of Mine Automation,2023,49(12):1−11.
[12] 王学文,王孝亭,谢嘉成,等. 综采工作面XR技术发展综述:从虚拟3D可视化到数字孪生的演化[J]. 绿色矿山,2024,2(1):76−85. WANG Xuewen,WANG Xiaoting,XIE Jiacheng,et al. Review of XR technology development in fully mechanized mining faces:From 3D visualization to digital twin[J]. Journal of Green Mine,2024,2(1):76−85.
[13] HUILING G,XIN L. Coal-rock interface recognition method based on image recognition[J]. Nature Environment & Pollution Technology,2019,18(5):1627−1633.
[14] MENG H L,LI M. Characteristic analysis and recognition of coal-rock interface based on visual technology[J]. International Journal of Signal Processing,Image Processing and Pattern Recognition,2016,9(4):61−68. doi: 10.14257/ijsip.2016.9.4.06
[15] WANG H J,ZHANG Q. Dynamic identification of coal-rock interface based on adaptive weight optimization and multi-sensor information fusion[J]. Information Fusion,2019,51:114−128. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2018.09.007
[16] 田慧卿,魏忠义. 基于图像识别技术的煤岩识别研究与实现[J]. 西安工程大学学报,2012,26(5):657−660. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-649X.2012.05.023 TIAN Huiqing,WEI Zhongyi. The research and implementation of coal and rock identification based on image recognition technology[J]. Journal of Xi’an Polytechnic University,2012,26(5):657−660. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-649X.2012.05.023
[17] 章华,李振璧,姜媛媛. 基于图像纹理的煤岩识别研究[J]. 煤炭技术,2015,34(7):120−121. ZHANG Hua,LI Zhenbi,JIANG Yuanyuan. Study on coal and rock identification based on image texture[J]. Coal Technology,2015,34(7):120−121.
[18] 伍云霞,田一民. 基于字典学习的煤岩图像特征提取与识别方法[J]. 煤炭学报,2016,41(12):3190−3196. WU Yunxia,TIAN Yimin. Method of coal-rock image feature extraction and recognition based on dictionary learning[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2016,41(12):3190−3196.
[19] 伍云霞,田一民. 基于最大池化稀疏编码的煤岩识别方法[J]. 工程科学学报,2017,39(7):981−987. WU Yunxia,TIAN Yimin. A coal-rock recognition method based on max-pooling sparse coding[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering,2017,39(7):981−987.
[20] 张斌,苏学贵,段振雄,等. YOLOv2在煤岩智能识别与定位中的应用研究[J]. 采矿与岩层控制工程学报,2020,2(2):94−101. ZHANG Bin,SU Xuegui,DUAN Zhenxiong,et al. Application of YOLOv2 in intelligent recognition and location of coal and rock[J]. Journal of Mining and Strata Control Engineering,2020,2(2):94−101.
[21] 司垒,王忠宾,熊祥祥,等. 基于改进U-net网络模型的综采工作面煤岩识别方法[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(S1):578−589. SI Lei,WANG Zhongbin,XIONG Xiangxiang,et al. Identification method of coal and rock in fully mechanized mining face based on improved U-net network model[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2021,46(S1):578−589.
[22] 闫志蕊,王宏伟,耿毅德. 基于改进DeeplabV3+和迁移学习的煤岩界面图像识别方法[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2023,51(S1):429−439. YAN Zhirui,WANG Hongwei,GENG Yide. Coal-rock interface image recognition method based on improved DeeplabV3+ and transfer learning[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2023,51(S1):429−439.
[23] 高峰,殷欣,刘泉声,等. 基于塔式池化架构的采掘工作面煤岩图像识别方法[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(12):4088−4102. GAO Feng,YIN Xin,LIU Quansheng,et al. Coal-rock image recognition method for mining and heading face based on spatial pyramid pooling structure[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2021,46(12):4088−4102.
[24] ZHOU Z,RAHMAN SIDDIQUEE M M,TAJBAKHSH N,et al. Unet++:A nested u-net architecture for medical image segmentation[C]//Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support:4th International Workshop,DLMIA 2018,and 8th International Workshop,ML-CDS 2018,Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2018,Granada,Spain,September 20,2018,Proceedings 4. Springer International Publishing,2018:3−11.
[25] SANDLER M,HOWARD A,ZHU M,et al. Mobilenetv2:Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2018:4510−4520.
[26] ZHANG H,WU C,ZHANG Z,et al. Resnest:Split-attention networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2022:2736−2746.



 下载:
下载: