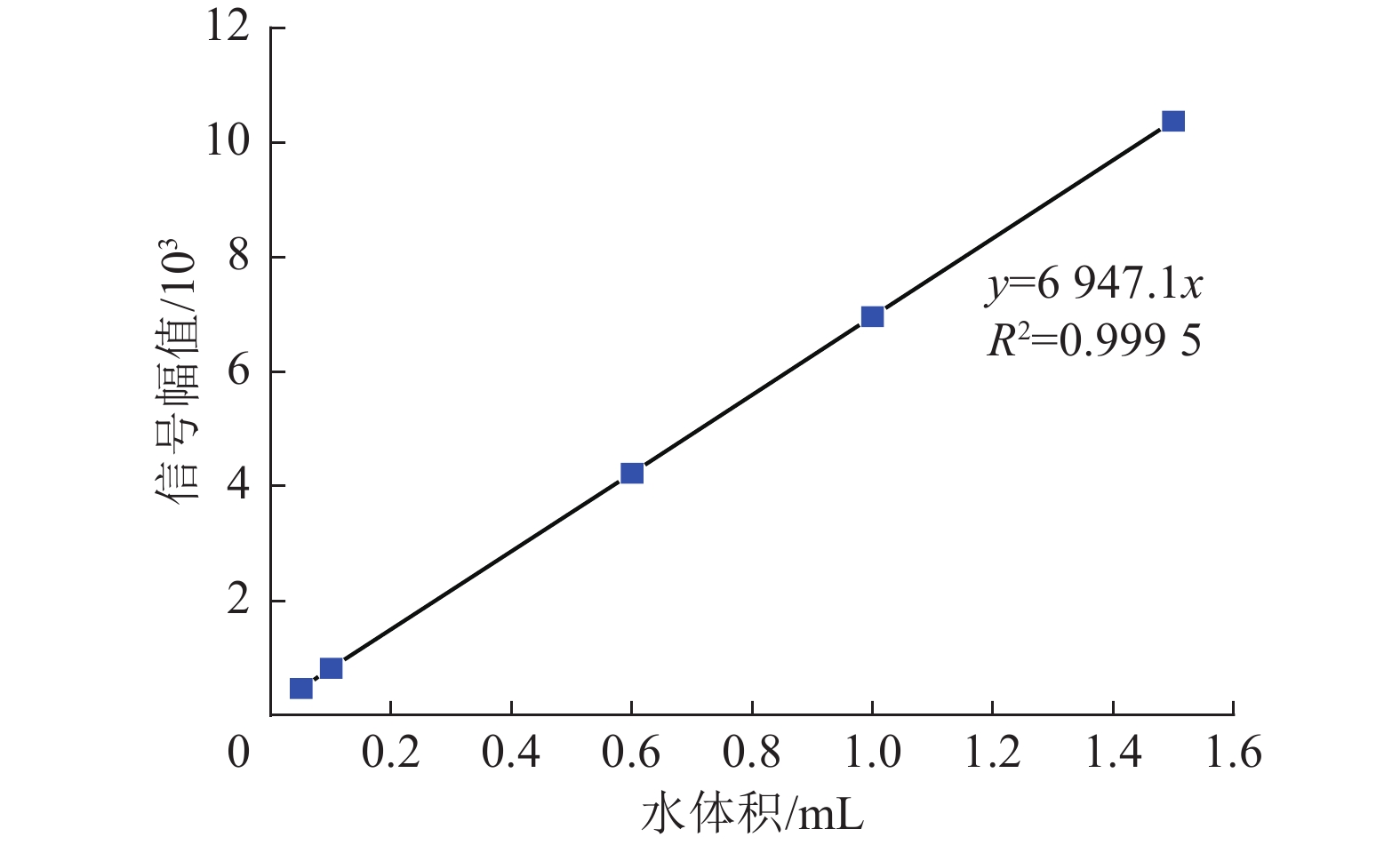
Comprehensive characterization of pore structure in coal seams with abnormal gas emission in deep close range coal seam clusters
-
摘要:
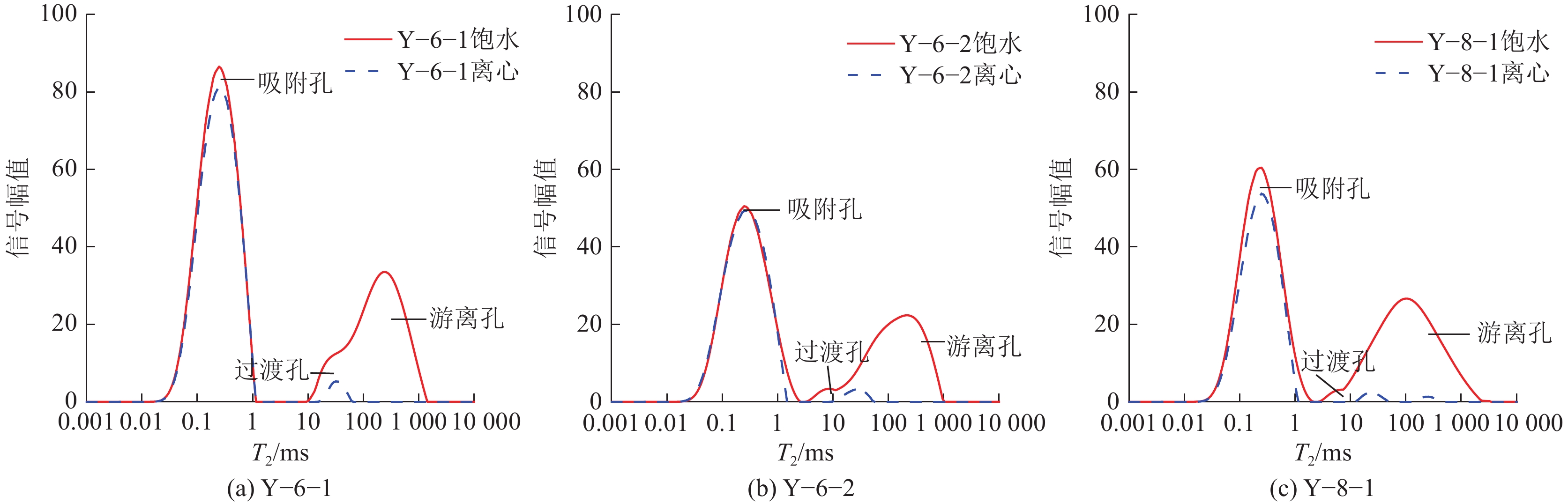
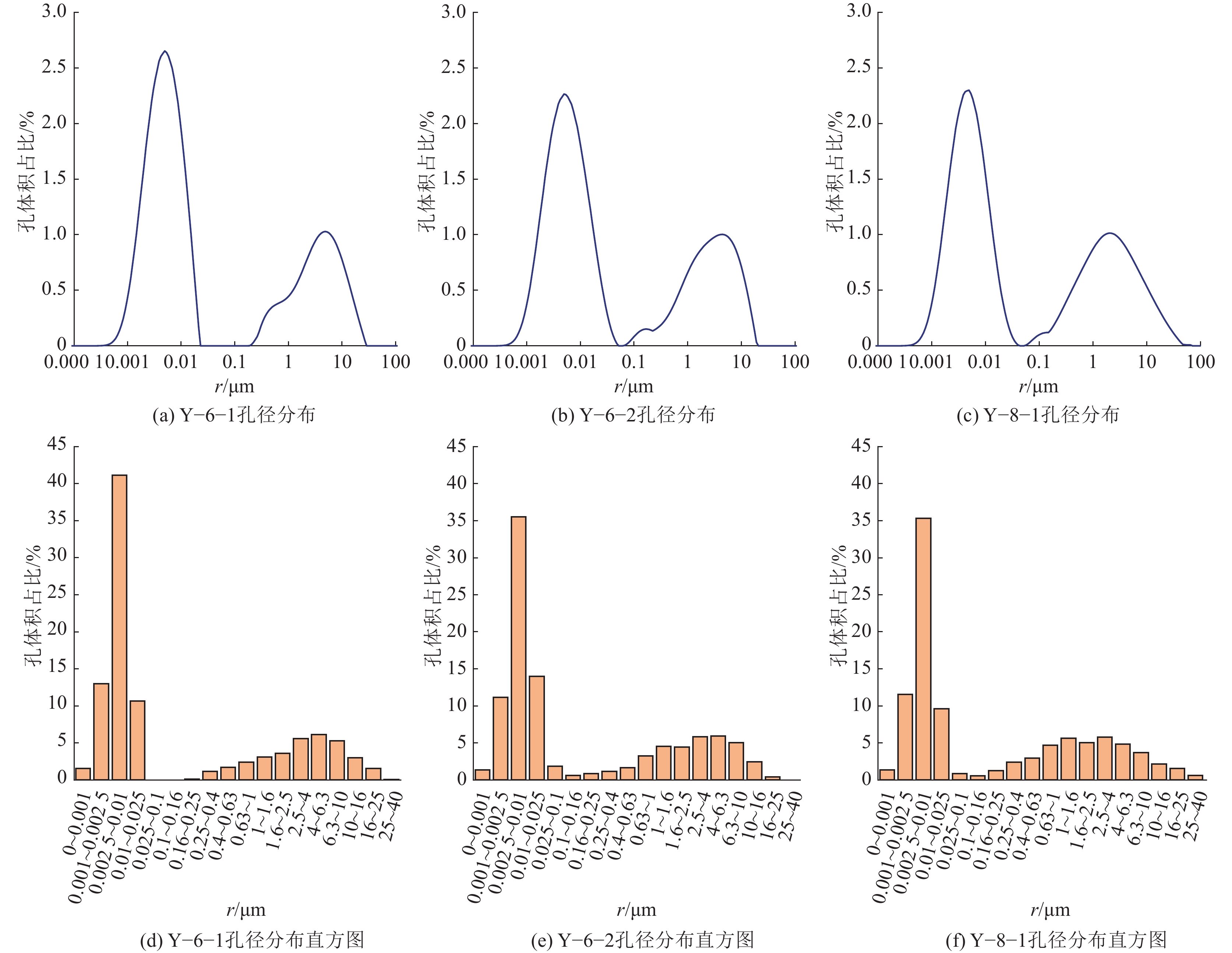
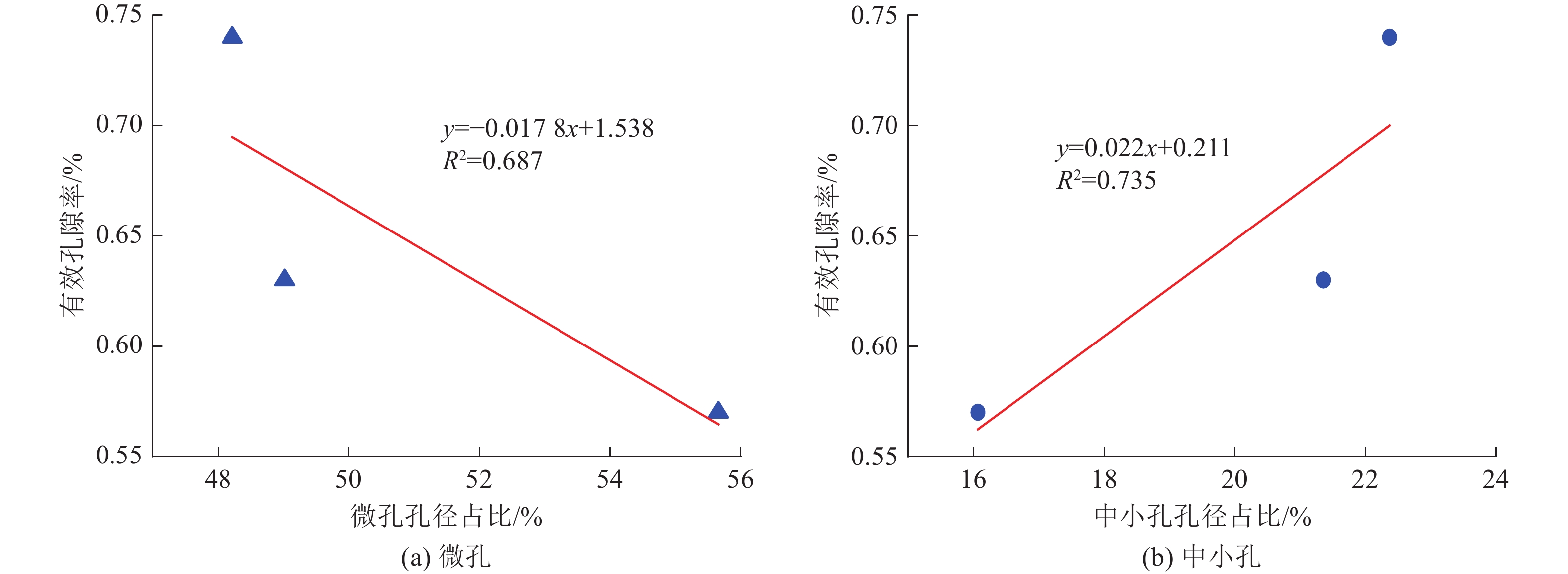
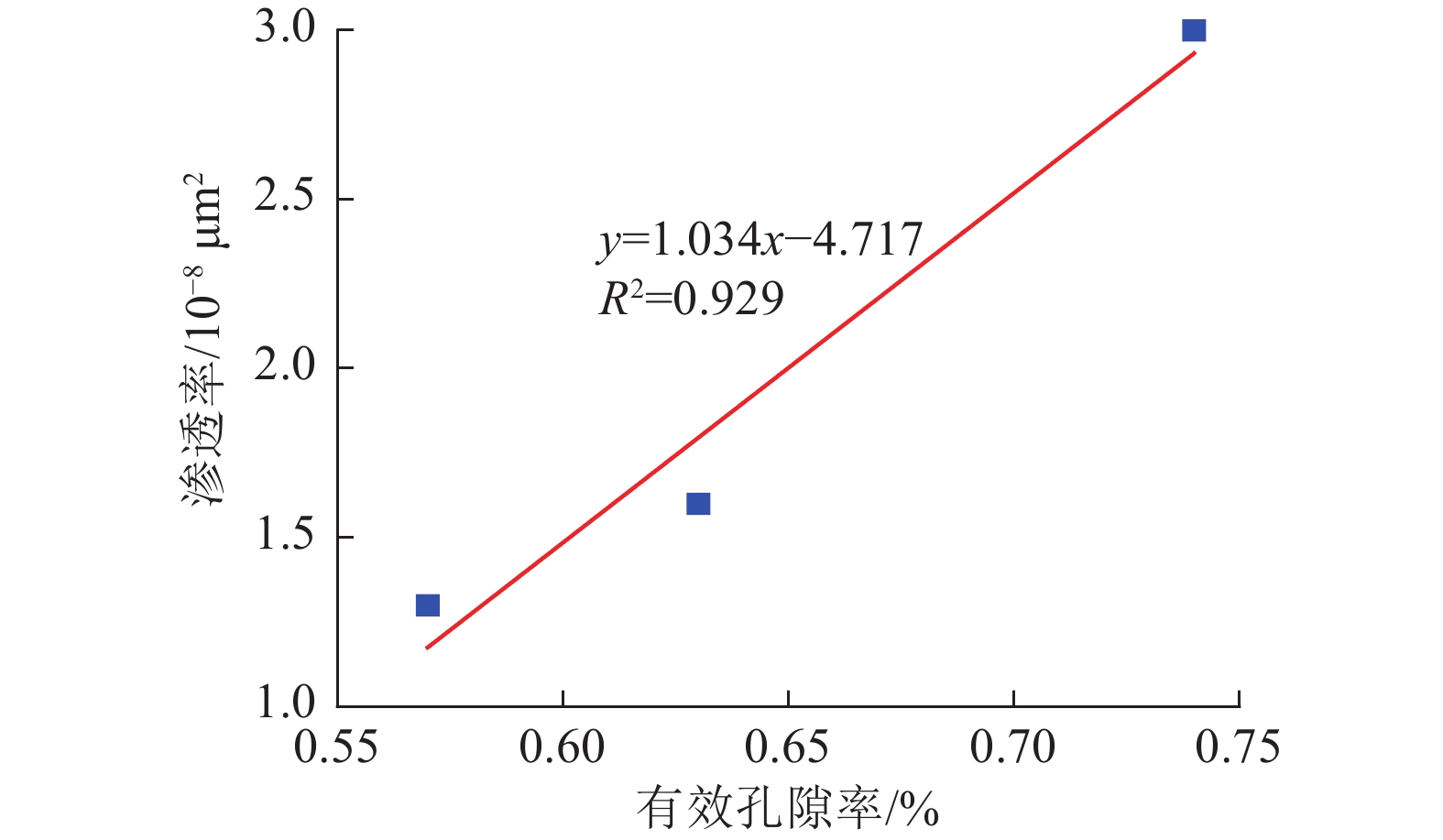
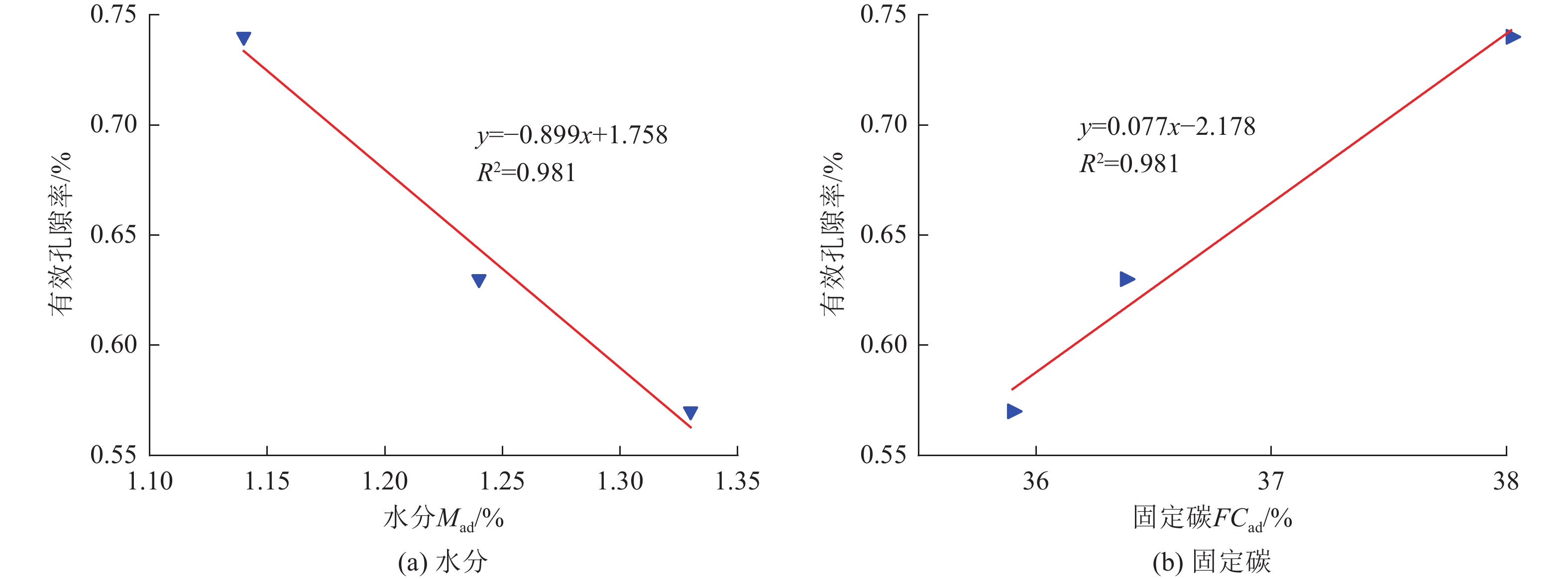
煤与瓦斯突出事故一直是煤矿安全生产中的重大问题,煤体中孔裂隙是瓦斯吸附与运移的主要场所,研究孔裂隙结构特征对瓦斯灾害的防控治理具有重大意义。以淮南矿区谢桥矿瓦斯异常涌出煤层煤体为研究对象,对比未发生事故区域及邻近煤层煤体,开展扫描电镜(SEM)、低场核磁共振(NMR)等试验研究,对煤体孔裂隙类型、孔隙连通性、孔径分布、有效孔隙率及渗透率等参数进行研究,探讨煤体孔隙结构对瓦斯吸附及运移的影响。结果表明:煤体孔隙结构必将影响其渗透性,煤体内部碎粒孔大量发育及矿物充填情况严重时不利于流体运移;异常煤层与邻近煤层饱和水煤样核磁共振时间T2谱均发育3个峰,主要以短弛豫时间为主,但各煤体孔径分布及孔隙连通性具有一定差异,异常煤体微孔异常发育,中小孔相对不发育、吸附孔与过渡孔之间连通性差,说明瓦斯运移的差异性与孔径分布和孔隙连通性有关;异常煤体有利于瓦斯吸附不利于瓦斯扩散,且瓦斯放散初速度更大,在受到采动影响时更易发生瓦斯异常涌出或突出事故;煤体微孔占比与有效孔隙率呈负相关关系,中小孔占比与有效孔隙率呈正相关关系,而有效孔隙率与煤体渗透率呈显著线性关系,说明煤体孔径分布是通过影响煤体有效孔隙率,进而影响煤体渗透率;有效孔隙率直接影响煤层渗透率大小,也与煤质参数存在一定关系,在一定程度上可作为评价煤层性质的指标之一。
Abstract:Coal and gas outburst accidents have always been a major problem in coal mine safety production. Pores and fissures in coal are the main places for gas adsorption and migration. It is of great significance to study the structural characteristics of pores and fissures for the prevention and control of gas disasters. Taking the abnormal gas emission coal seam of Xieqiao Coal Mine in Huainan Mining Area as the research object, Compares the areas without accidents and adjacent coal seams conducting experimental studies such as scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and low field nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) to study the parameters of coal pore and fracture types, pore connectivity, pore size distribution, effective porosity, and permeability, and explores the influence of coal pore structure on gas adsorption and migration. The results show that the internal pore structure of coal body will affect its permeability, and the development of a large number of granular pores in coal body and the serious filling of minerals are not conducive to fluid migration. The T2 spectrum of saturated water coal samples in three regions shows three peaks in nuclear magnetic resonance time, mainly with short relaxation time. However, there are certain differences in the pore size distribution and connectivity of each coal body. The abnormal areas have abnormally developed micropores in the coal body, relatively undeveloped small and medium-sized pores, and poor connectivity between adsorption pores and transition pores, indicating that the differences in gas migration are related to pore size distribution and pore connectivity; The abnormal coal body in the area is conducive to gas adsorption but not conducive to gas diffusion, and the initial velocity of gas release is higher, making it more prone to gas abnormal outburst or outburst accidents when affected by mining; The proportion of micropores in coal is negatively correlated with effective porosity, while the proportion of small and medium-sized pores is positively correlated with effective porosity. The effective porosity is significantly linearly related to coal permeability, indicating that the pore size distribution of coal affects the effective porosity of coal, thereby affecting the permeability of coal; The effective porosity directly affects the permeability of coal seams and is also related to coal quality parameters, which can be used as one of the indicators to evaluate the properties of coal seams to a certain extent .
-
-
表 1 试验煤样工业分析
Table 1 Proximate analysis data of experimental coal samples
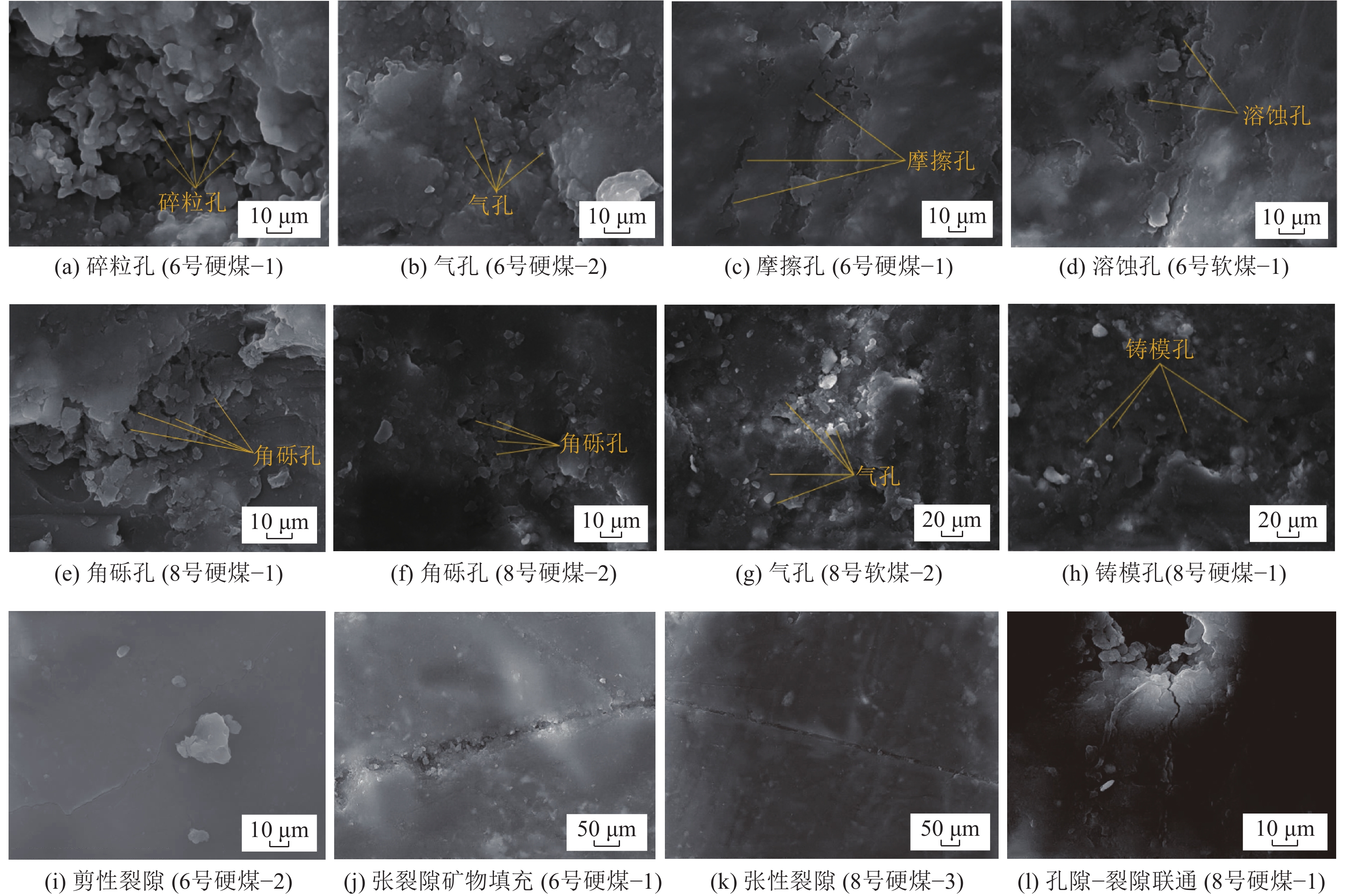
煤样 Mad/% Aad/% Vdaf/% FCad/% 6号硬煤−1 1.33 5.85 35.90 35.90 6号硬煤−2 1.24 5.56 32.95 36.38 6号硬煤−3 1.24 5.56 32.95 36.38 6号软煤−1 1.58 13.14 31.52 31.52 6号软煤−2 1.43 18.15 28.75 32.73 8号硬煤−1 1.14 6.04 38.02 38.02 8号硬煤−2 1.08 7.34 36.98 38.88 8号硬煤−3 0.92 6.92 38.67 39.42 8号软煤−1 1.39 39.76 23.93 23.93 8号软煤−2 1.34 38.66 20.14 19.54 表 2 煤层孔裂隙类型及成因
Table 2 Types and genesis of coal seam pore fractures
煤层 发育孔裂隙类型 成因简述 连通性 6号煤 碎粒孔
摩擦孔受构造应力破坏形成碎粒间孔隙
受构造应力破坏形成碎粒间孔隙差
差气孔
溶蚀孔矿物质在水、汽作用下溶蚀形成
受压应力作用面与面摩擦形成一般
差张性裂隙
剪性裂隙受张应力作用产生
受剪应力作用产生好
好8号煤 角砾孔
气孔
铸模孔受构造应力破坏形成角砾间孔隙
成煤过程中生气、聚气作用形成
矿物质因硬度差异形成印坑好
一般
差张性裂隙
剪性裂隙受张应力作用产生
受剪应力作用产生好
好表 3 各类孔径尺寸对应比例
Table 3 Corresponding proportions of various aperture sizes
煤样 孔径区间占比/% 微孔(0~0.01 μm ) 小孔(>0.01~0.10 μm) 中孔(>0.1~1.0 μm) 大孔(>1 μm) Y−6−1 55.6585 10.6522 5.4142 28.2765 Y−6−2 49.0186 13.8105 7.5423 29.6287 Y−8−1 48.2199 10.4826 11.8853 29.4122 表 4 基于NMR-T2C法煤样孔隙率及渗透率
Table 4 Porosity and permeability of coal samples based on NMR T2C method
煤样 核磁
孔隙率φ/%可动流体
孔隙率φF/%束缚流体
孔隙率φB/%T2
截止值/ms自由流体
饱和度IFF/%束缚流体
饱和度IBV/%核磁渗透率
K/10−3μm 2Y−6−1 1.60 0.57 1.03 0.77 35.81 64.19 0.013 Y−6−2 1.45 0.63 0.82 0.70 43.73 56.27 0.016 Y−8−1 1.51 0.74 0.77 0.55 49.05 50.95 0.030 -
[1] 王恩元,张国锐,张超林,等. 我国煤与瓦斯突出防治理论技术研究进展与展望[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(1):297−322. WANG Enyuan,ZHANG Guorui,ZHANG Chaolin,et al. Research progress and prospect on theory and technology for coal and gas outburst control and protection in China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(1):297−322.
[2] 谢和平. 深部岩体力学与开采理论研究进展[J]. 煤炭学报,2019,44(5):1283−1305. XIE Heping. Research review of the state key research development program of China:deep rock mechanics and mining theory[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2019,44(5):1283−1305.
[3] 袁亮. 深部采动响应与灾害防控研究进展[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(3):716−725. YUAN Liang. Research progress of mining response and disaster prevention and control in deep coal mines[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2021,46(3):716−725.
[4] 张超林,蒲静轩,宋世豪,等. 煤与瓦斯突出两相流运移规律研究进展[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2023,51(8):129−139. ZHANG Chaolin,PU Jingxuan,SONG Shihao,et al. Research progress on the two-phase flow migration law of coal and gas outburst[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2023,51(8):129−139.
[5] 翟成,丛钰洲,陈爱坤,等. 中国煤矿瓦斯突出灾害治理的若干思考及展望[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2023,52(6):1146−1161. ZHAI Cheng,CONG Yuzhou,CHEN Aikun,et al. Reflection and prospect on the prevention of gas outburst disasters in China’s coal mines[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,2023,52(6):1146−1161.
[6] 赵洪宝,秦逢缘,李作泉,等. 煤层纳米孔隙结构对瓦斯运移特性的影响研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2022,39(6):1256−1264,1271. ZHAO Hongbao,QIN Fengyuan,LI Zuoquan,et al. The influence of coal seam nano-pore structure on gas migration characteristics[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2022,39(6):1256−1264,1271.
[7] 张开仲,程远平,王亮,等. 基于煤中瓦斯赋存和运移方式的孔隙网络结构特征表征[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(10):3680−3694. ZHANG Kaizhong,CHENG Yuanping,WANG Liang,et al. Pore network structure characterization based on gas occurrence and migration in coal[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(10):3680−3694.
[8] 王亮,李子威,郑思文,等. 颗粒煤基质尺度计算新方法及应用[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2024,52(2):115−125. doi: 10.12438/cst.2023-0886 WANG Liang,LI Ziwei,ZHENG Siwen,et al. A new method for calculating particle coal matrix scale and its application[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2024,52(2):115−125. doi: 10.12438/cst.2023-0886
[9] 刘怀谦,王磊,谢广祥,等. 煤体孔隙结构综合表征及全孔径分形特征[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2022,39(3):458−469,479. LIU Huaiqian,WANG Lei,XIE Guangxiang,et al. Comprehensive characterization and full pore size fractal characteristics of coal pore structure[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2022,39(3):458−469,479.
[10] MOORE T. Coalbed methane:A review[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,2012,101:36−81. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2012.05.011
[11] 李阳,张玉贵,张浪,等. 基于压汞、低温N2吸附和CO2吸附的构造煤孔隙结构表征[J]. 煤炭学报,2019,44(4):1188−1196. LI Yang,ZHANG Yugui,ZHANG Lang,et al. Characterization on pore structure of tectonic coals based on the method of mercury intrusion,carbon dioxide adsorption and nitrogen adsorption[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2019,44(4):1188−1196.
[12] 程远平,胡彪. 基于煤中甲烷赋存和运移特性的新孔隙分类方法[J]. 煤炭学报,2023,48(1):212−225. CHENG Yuanping,HU Biao. A new pore classification method based on the methane occurrence and migration characteristics in coal[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2023,48(1):212−225.
[13] 杨昌永,常会珍,邵显华,等. 扫描电镜下不同煤体结构煤微孔隙特征研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2019,47(12):194−200. YANG Changyong,CHANG Huizhen,SHAO Xianhua,et al. Study on micro-pore characteristics of structural coal in different coal bodies under scanning electron microscopy[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2019,47(12):194−200.
[14] 李祥春,李忠备,张良,等. 不同煤阶煤样孔隙结构表征及其对瓦斯解吸扩散的影响[J]. 煤炭学报,2019,44(S1):142−156. LI Xiangchun,LI Zhongbei,ZHANG Liang,et al. Pore structure characterization of various rank coals and its effect on gas desorption and diffusion[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2019,44(S1):142−156.
[15] 蒋静宇,程远平,张硕. 低阶煤孔隙结构定量表征及瓦斯吸附放散特性[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(10):3221−3233. JIANG Jingyu,CHENG Yuanping,ZHANG Shuo. Quantitative characterization of pore structure and gas adsorption and diffusion properties of low-rank coal[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2021,46(10):3221−3233.
[16] 杨明,柳磊,刘佳佳,等. 中阶煤孔隙结构的氮吸附−压汞−核磁共振联合表征研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2021,49(5):67−74. YANG Ming,LIU Lei,LIU Jiajia,et al. Study on joint characterization of pore structure of middle-rank coal by nitrogen adsorption-mercury intrusion-NMR[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2021,49(5):67−74.
[17] 张文政,王经玺. 基于显微CT的不同煤种微观孔隙结构综合表征[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2021,49(S2):85−92. ZHANG Wenzheng,WANG Jingxi. Characterization of microscopic pore structure of different coal types based on micro CT[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2021,49(S2):85−92.
[18] 刘纪坤,任棒,王翠霞. 中低阶煤孔隙结构特征及其对瓦斯解吸特性影响[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(12):153−161. LIU Jikun,REN Bang,WANG Cuixia. Pore structure characteristics of middle and low rank coals and their influence on gas desorption characteristics[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(12):153−161.
[19] 赵健光,王猛,马如英,等. 基于压汞法对黔西青龙矿构造煤孔隙结构特征的研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(10):159−168. ZHAO Jianguang,WANG Meng,MA Ruying,et al. Study on pore structure characteristics of tectonic coal in Qinglong Coal Mine in Western Guizhou based on mercury injection[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(10):159−168.
[20] 孙四清,杨帆,郑玉岐,等. 煤层瓦斯含量测定技术及装备研究进展[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2024,52(4):164−176. SUN Siqing,YANG Fan,ZHENG Yuqi,et al. Research progress of coal seam gas content determination technology and equipment[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2024,52(4):164−176.
[21] 程庆迎,黄炳香,李增华. 煤的孔隙和裂隙研究现状[J]. 煤炭工程,2011,43(12):91−93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0959.2011.12.035 CHENG Qingying,HUANG Bingxiang,LI Zenghua. Research status of pore and crack in coal[J]. Coal Engineering,2011,43(12):91−93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0959.2011.12.035
[22] YAO Y B,LIU D M,CHE Y,et al. Petrophysical characterization of coals by low-field nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)[J]. Fuel,2010,89(7):1371−1380. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2009.11.005
[23] 翟成,孙勇,范宜仁,等. 低场核磁共振技术在煤孔隙结构精准表征中的应用与展望[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(2):828−848. ZHAI Cheng,SUN Yong,FAN Yiren,et al. Application and prospect of low-field nuclear magnetic resonance technology in accurate characterization of coal pore structure[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(2):828−848.
[24] 霍多特. 煤与瓦斯突出[M]. 北京:中国工业出版社,1966. [25] 安丰华,贾宏福,刘军. 煤孔隙特征对瓦斯放散初速度影响研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2021,49(9):82−87. AN Fenghua,JIA Hongfu,LIU Jun. Study on influence of coal pore characteristics on initial velocity of gas emission[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2021,49(9):82−87.
[26] ZHANG Y R,XU S X,FANG Z F,et al. Permeability of concrete and correlation with microstructure parameters determined by 1H NMR[J]. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering,2020,2020(1):1−11.
[27] 任会康,王安民,李昌峰,等. 基于核磁共振技术的低阶煤储层孔隙特征研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2017,45(4):143−148. REN Huikang,WANG Anmin,LI Changfeng,et al. Study on porosity characteristics of low-rank coal reservoirs based on nuclear magnetic resonance technology[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2017,45(4):143−148.
[28] QIN L,ZHAI C,LIU S M,et al. Changes in the petrophysical properties of coal subjected to liquid nitrogen freeze-thaw–a nuclear magnetic resonance investigation[J]. Fuel,2017,194:102−114. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.01.005



 下载:
下载: