Study on the air permeability characteristics of coal gangue dump slope gangue particles
-
摘要:
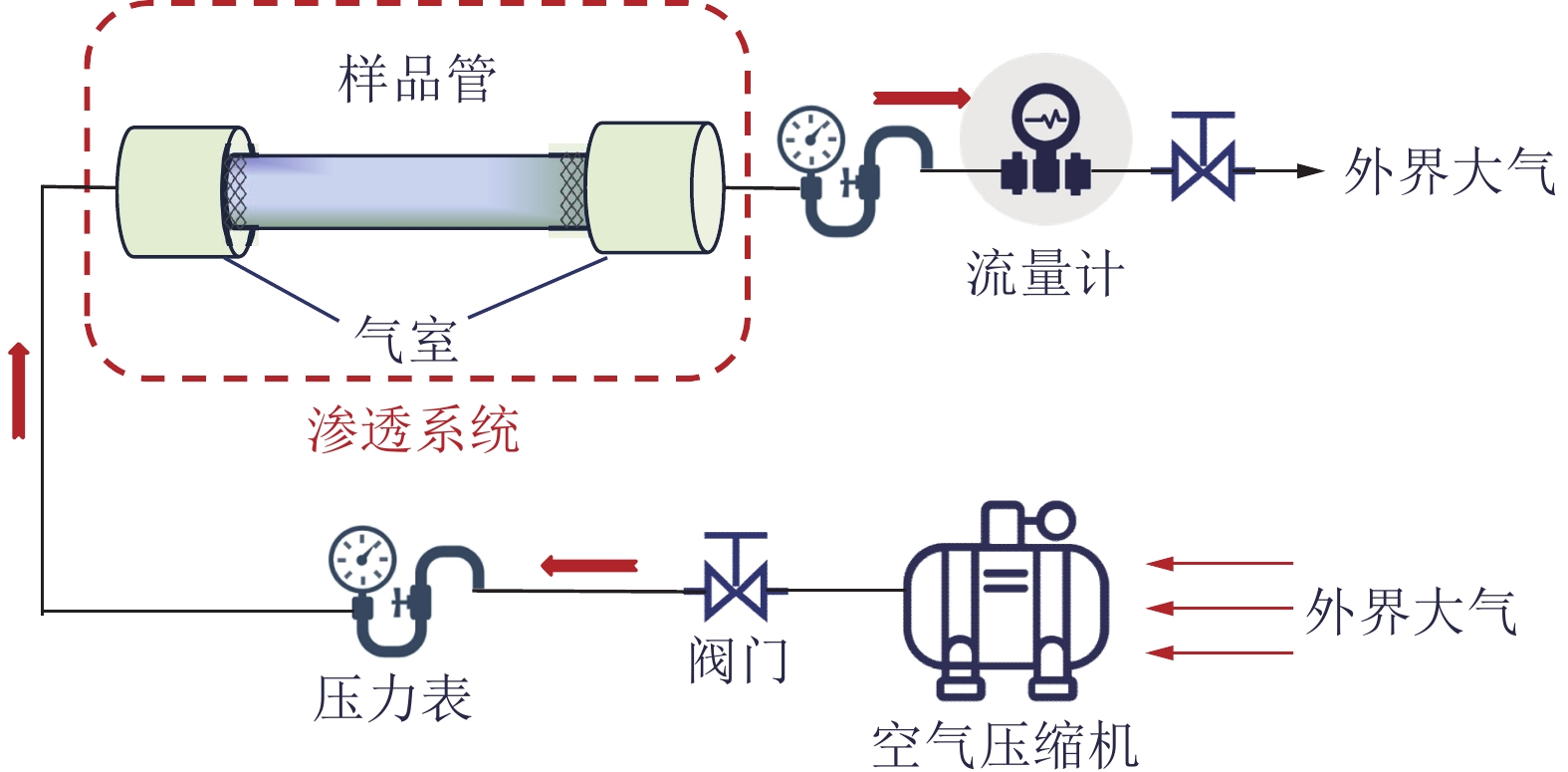
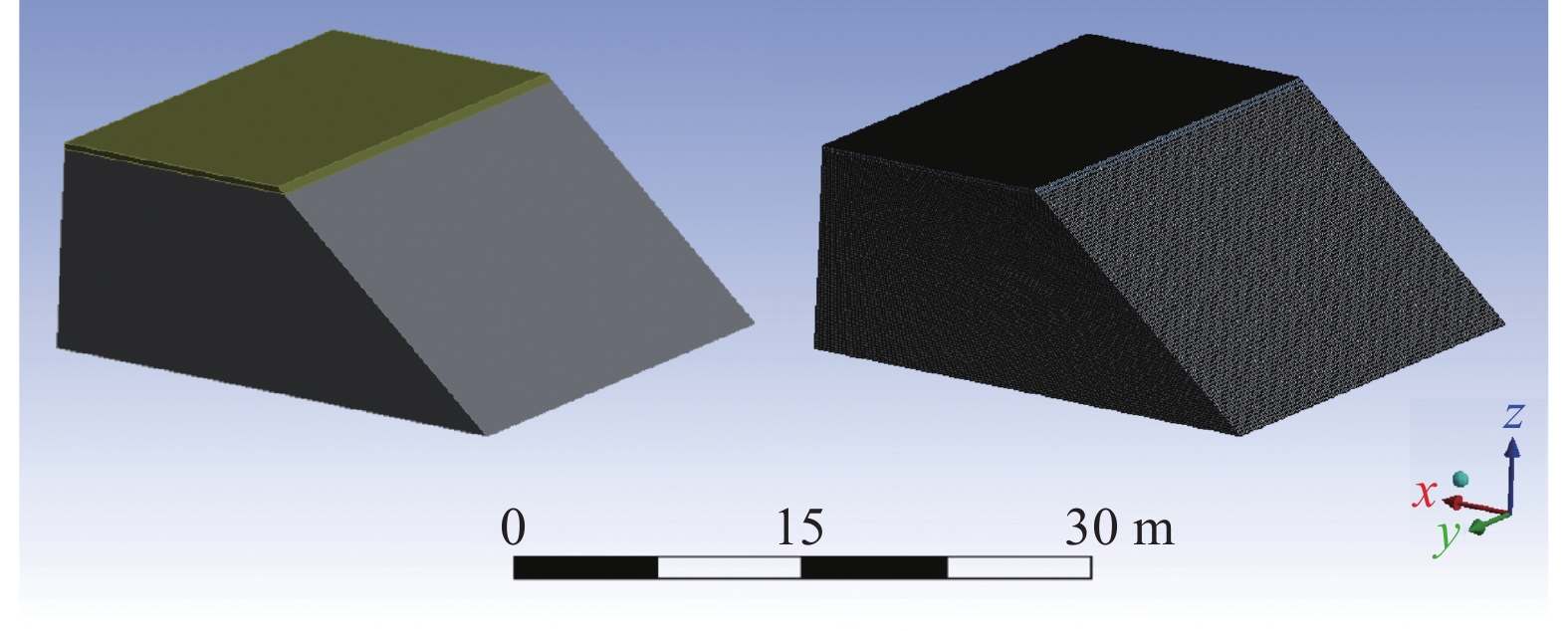
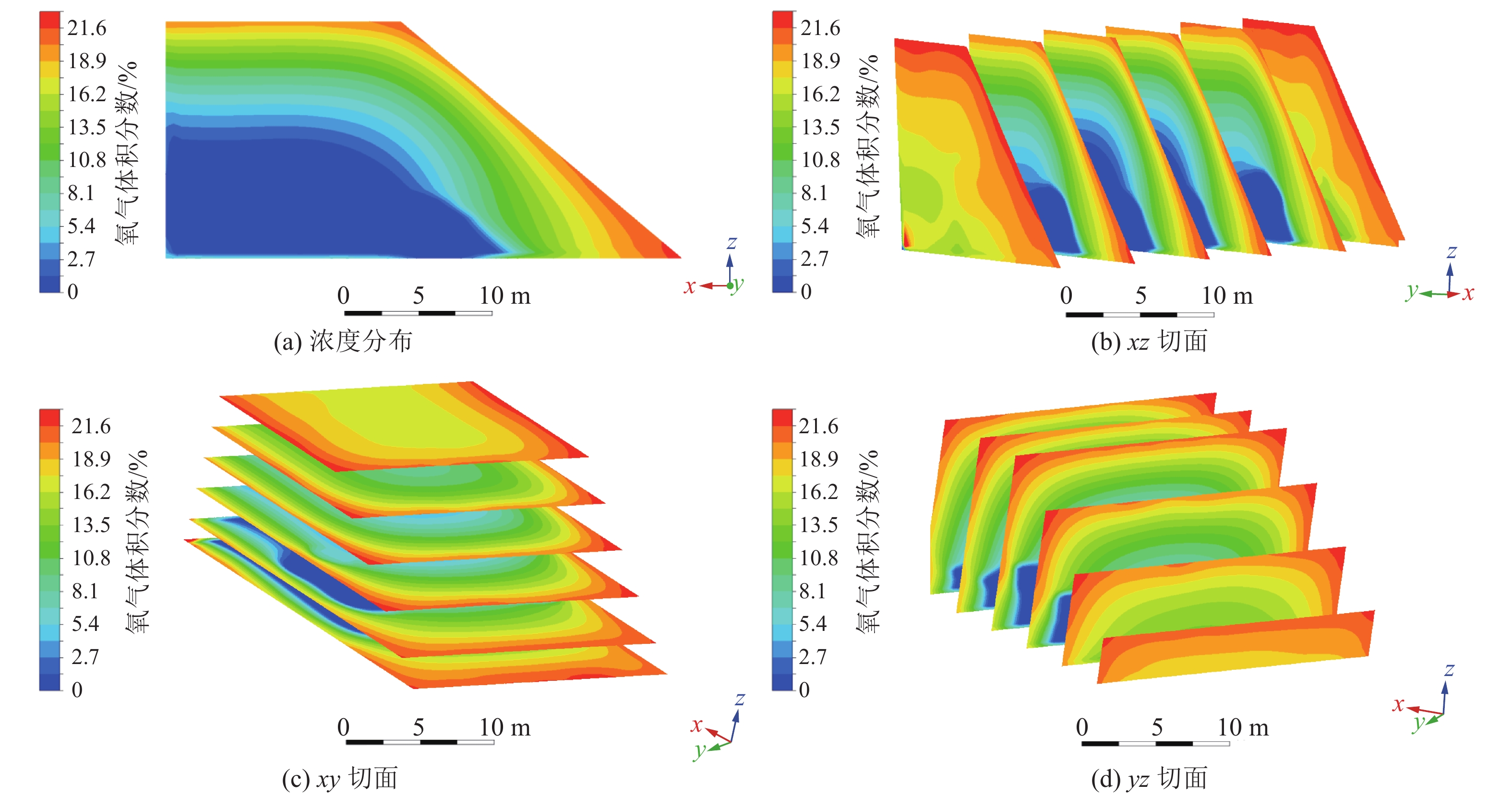
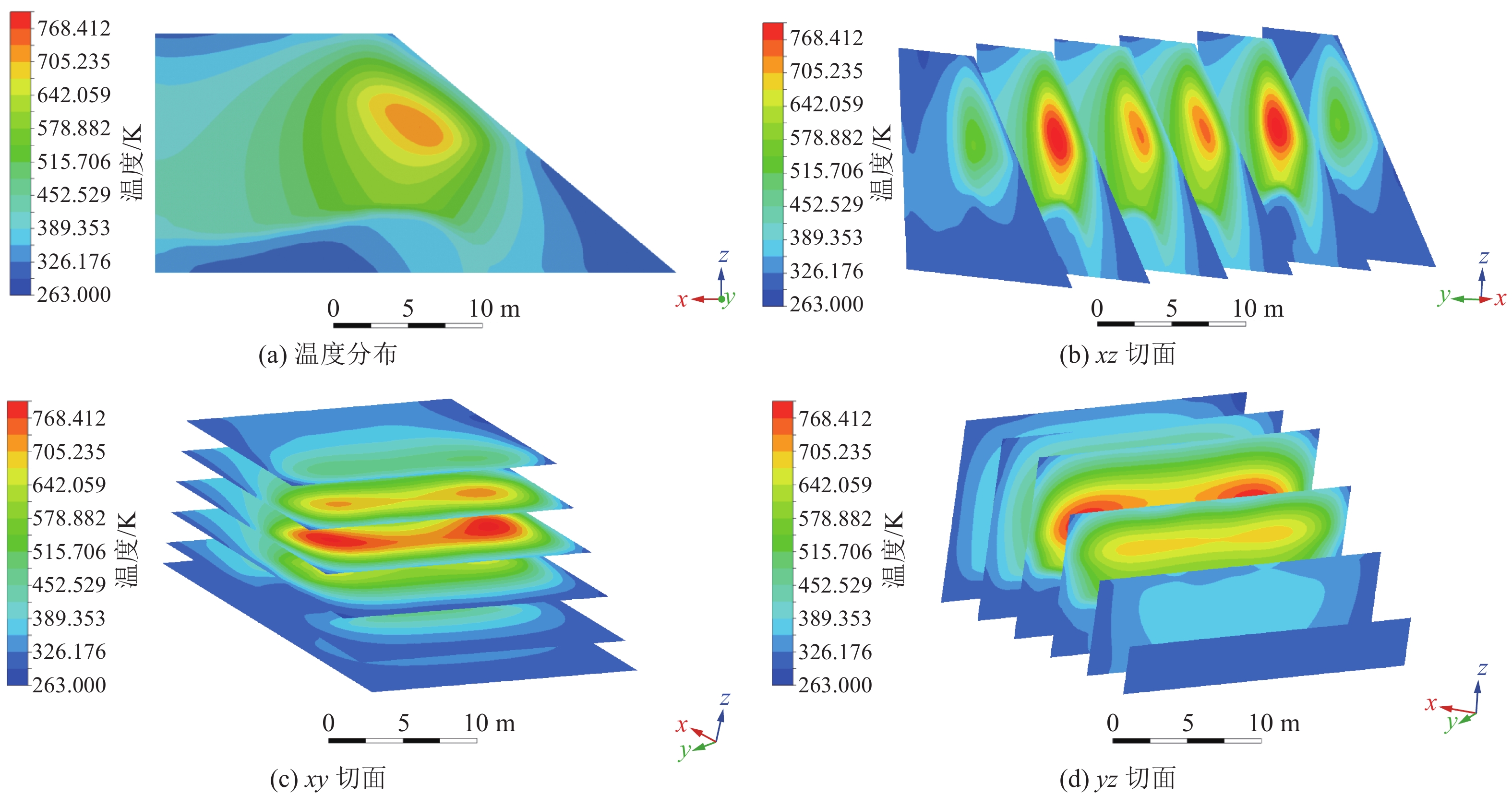
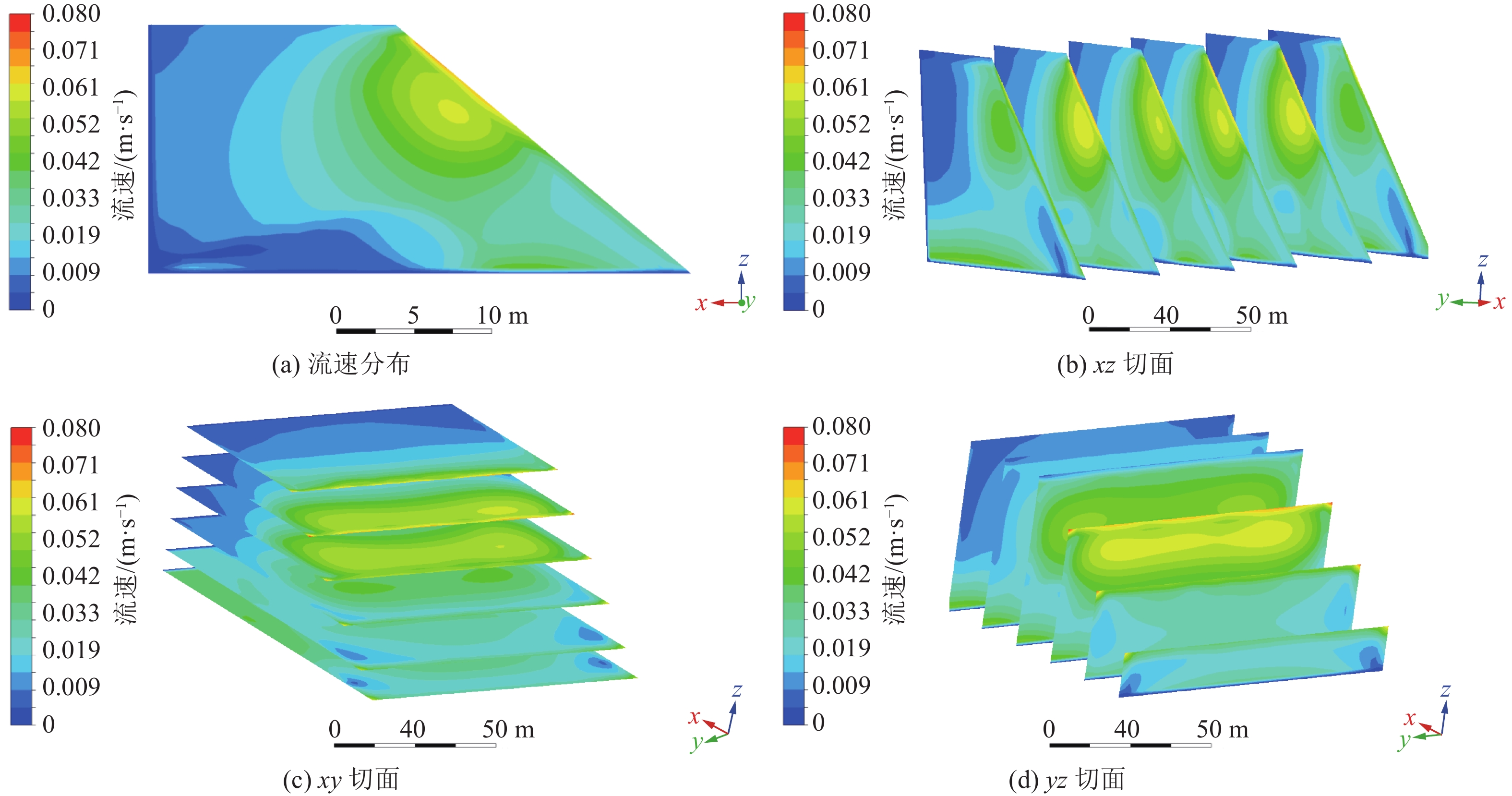
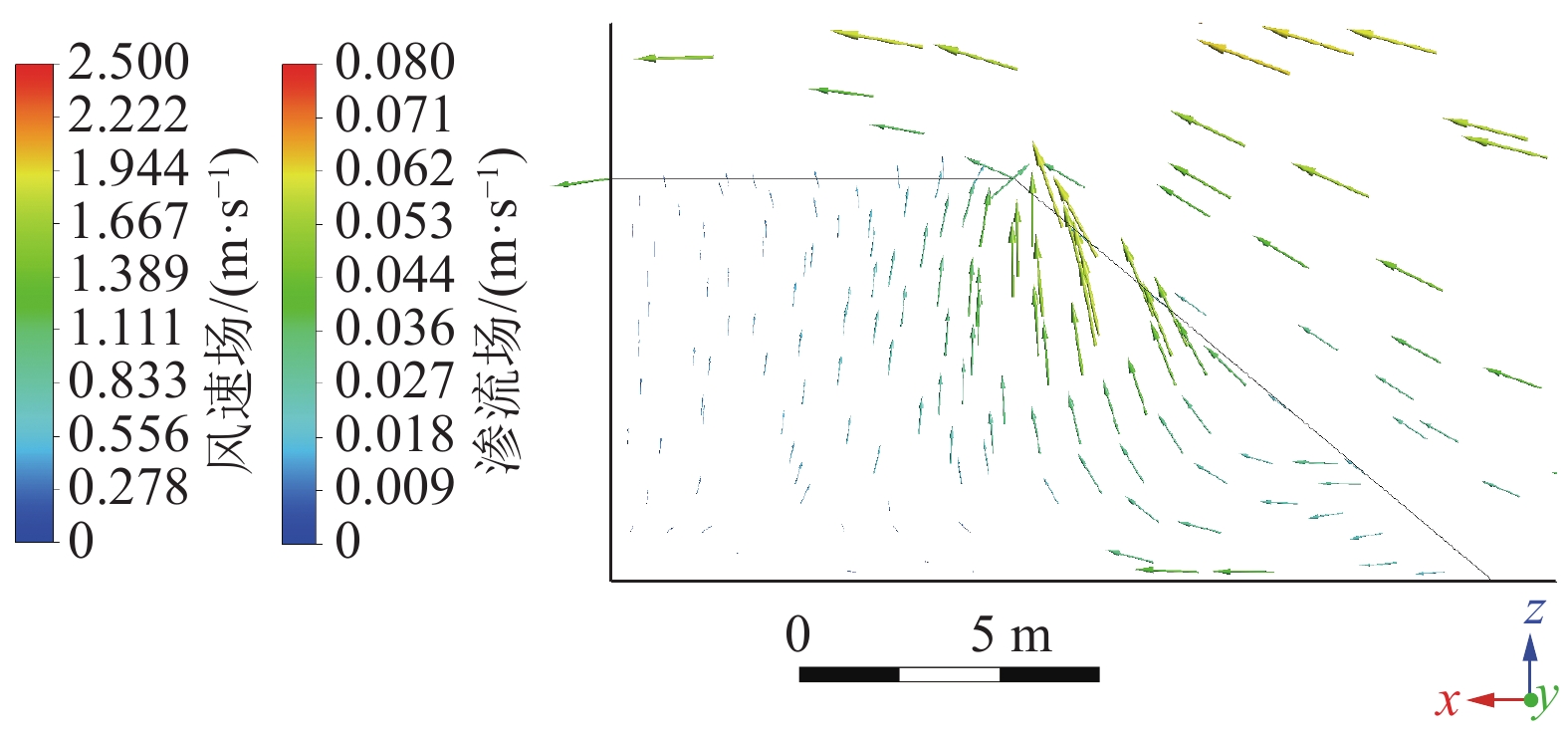
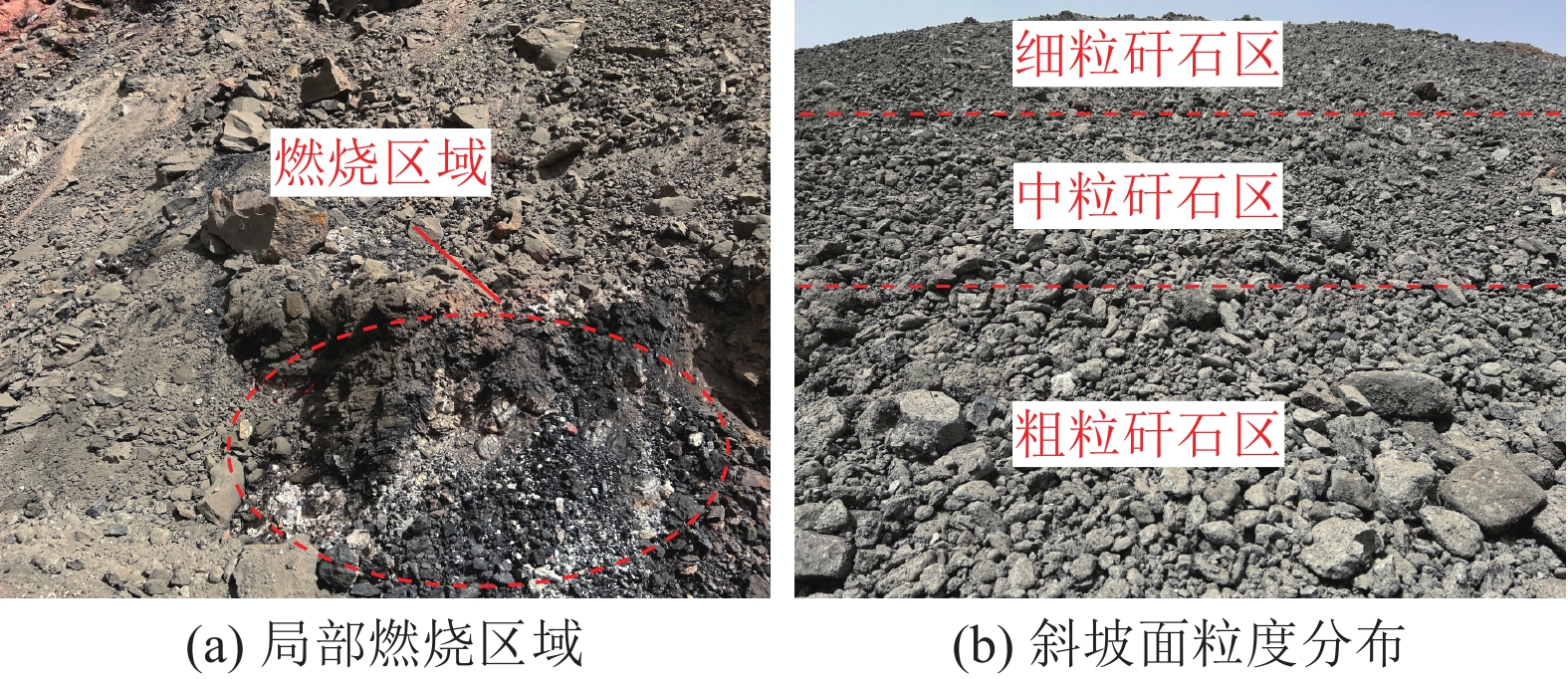
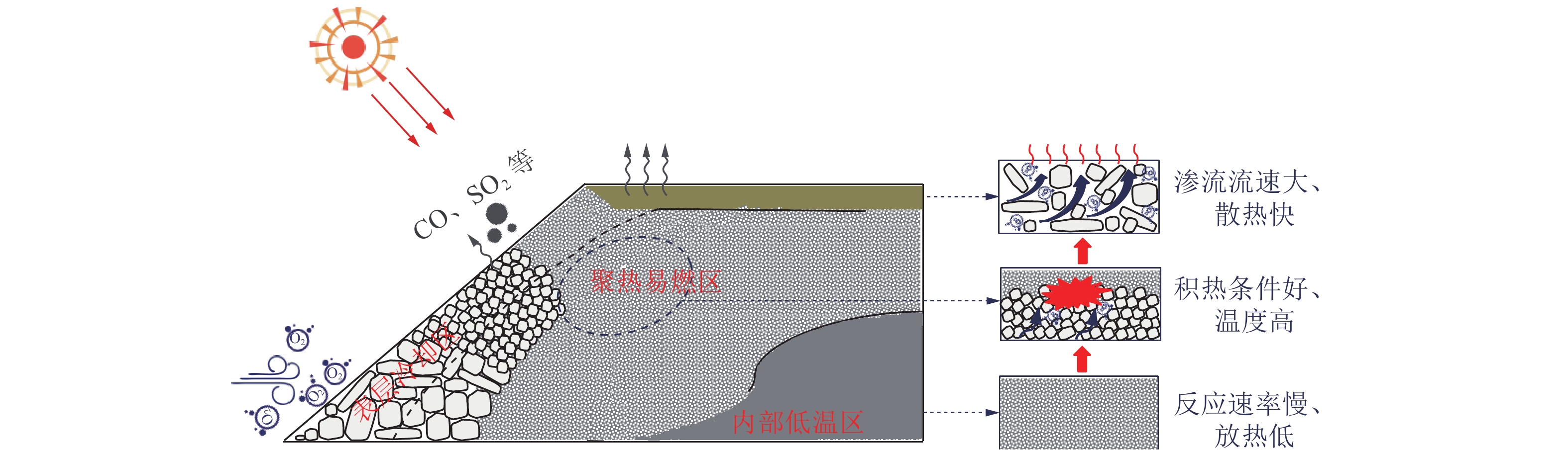
煤矸石山斜坡面矸石散体的颗粒偏析现象对其渗透特性有重要影响。为了研究斜坡面的空气渗流特性,基于自主设计的室内渗透率测定装置,结合散体岩土力学理论、通风理论及FLUENT数值模拟,研究了煤矸石山斜坡面不同高度不同深度处矸石散体孔隙率与渗透率的整体分布规律及空气渗流和温度分布特征,并通过现场实测进行验证。结果表明:在研究预设条件下,矸石山斜坡面浅部的孔隙率和渗透率分布特征受到颗粒偏析现象的显著影响,随着高度与深度增大,呈现出非线性负指数衰减规律;随着斜坡面矸石散体的粒径增大,其孔隙率也呈增大趋势,并且其增速逐渐放缓;矸石山顶部覆盖黄土层,导致渗流速度缓慢,氧气质量浓度较低,不利于氧化放热反应的进行,底部孔隙率较大风速过快,积热条件不佳,因此高温区域位于矸石山中上部距坡面2~3 m处,最高可达780 K;风速场在热风压与外界风压的共同影响下,最高风速位于中上部近坡面处,可达0.06 m/s。此外,沿矸石山X方向和Z方向深入,渗流速度与氧气浓度下降速率逐渐减小;整体而言,矸石山斜坡面孔隙率的分布是影响矸石山内部空气渗流特性的一个极为重要的因素。通过对矸石山风速氧气以及温度场的研究,将矸石山大致划分为表层冷却区、聚热易燃区以及内部低温区。研究成果可为我国干燥多风的中西部矿区煤矸石山自燃火区的准确预测和判定提供基础参考。
Abstract:The phenomenon of particle segregation in the gangue aggregate on the slope surface of the coal gangue mountain significantly influences its permeability characteristics. To investigate the air infiltration characteristics of the slope surface, a self-designed indoor permeability measurement device was utilized. By integrating the theories of granular soil mechanics, ventilation, and FLUENT numerical simulation, the overall distribution patterns of porosity and permeability of the gangue aggregate at different heights and depths on the coal gangue slope surface were studied, as well as the characteristics of air infiltration and temperature distribution. These findings were validated through on-site measurements. The results demonstrate that the distribution characteristics of porosity and permeability in the shallow part of the gangue slope surface are significantly affected by the particle segregation phenomenon, exhibiting a nonlinear negative exponential decay pattern as the height and depth increase. As the particle size of the slope surface gangue aggregate increases, its porosity also shows an increasing trend, but the rate of increase gradually slows down. The presence of a loess layer covering the top of the gangue slope hinders fluid flow and results in lower oxygen content, which is unfavorable for exothermic oxidation reactions. Moreover, at the bottom, where the porosity is larger, the wind speed is excessively high, creating unfavorable heat accumulation conditions. Therefore, the high-temperature region is located in the upper part of the gangue slope, 2~3 meters away from the slope surface, reaching temperatures as high as 780 K. Under the combined influence of thermal wind pressure and external wind pressure, the highest wind speed is found in the upper-middle part near the slope surface, reaching up to 0.06 m/s. Furthermore, as we delve deeper into the gangue slope in the X and Z directions, the flow velocity and the rate of decrease in oxygen concentration gradually decrease. Overall, the distribution of porosity on the gangue slope surface is a crucial factor affecting the air infiltration characteristics within the coal gangue mountain. Through the study of wind speed, oxygen concentration, and temperature fields in the gangue slope, this paper roughly categorizes the gangue slope into a surface cooling zone, a heat-gathering flammable zone, and an internal low-temperature zone. The findings from this research can serve as a fundamental reference for accurately predicting and identifying self-ignition fire zones in the arid and windy mining regions of central and western China.
-
Keywords:
- coal gangue dump /
- seepage /
- permeability /
- porosity /
- hot air pressure
-
-
表 1 煤矸石试样的相似级配
Table 1 Similar grading of coal gangue samples
粒径/mm 相似级配/% >50 24 30~50 18 10~30 15 5~10 11 <5 32 表 2 煤矸石压缩试验结果
Table 2 Compression test results of coal gangue
压力/kPa 孔隙比/% 孔隙率/% 压缩系数/MPa−1 0 56.3 36.0 — 200 54.9 35.4 0.070 400 53.6 34.9 0.064 600 52.4 34.4 0.057 800 51.4 33.9 0.052 1000 50.4 33.5 0.047 1200 49.6 33.2 0.043 1400 48.8 32.8 0.042 1600 48.0 32.5 0.036 1800 47.3 32.1 0.035 2000 46.7 31.8 0.033 表 3 斜坡面不同位置的孔隙率
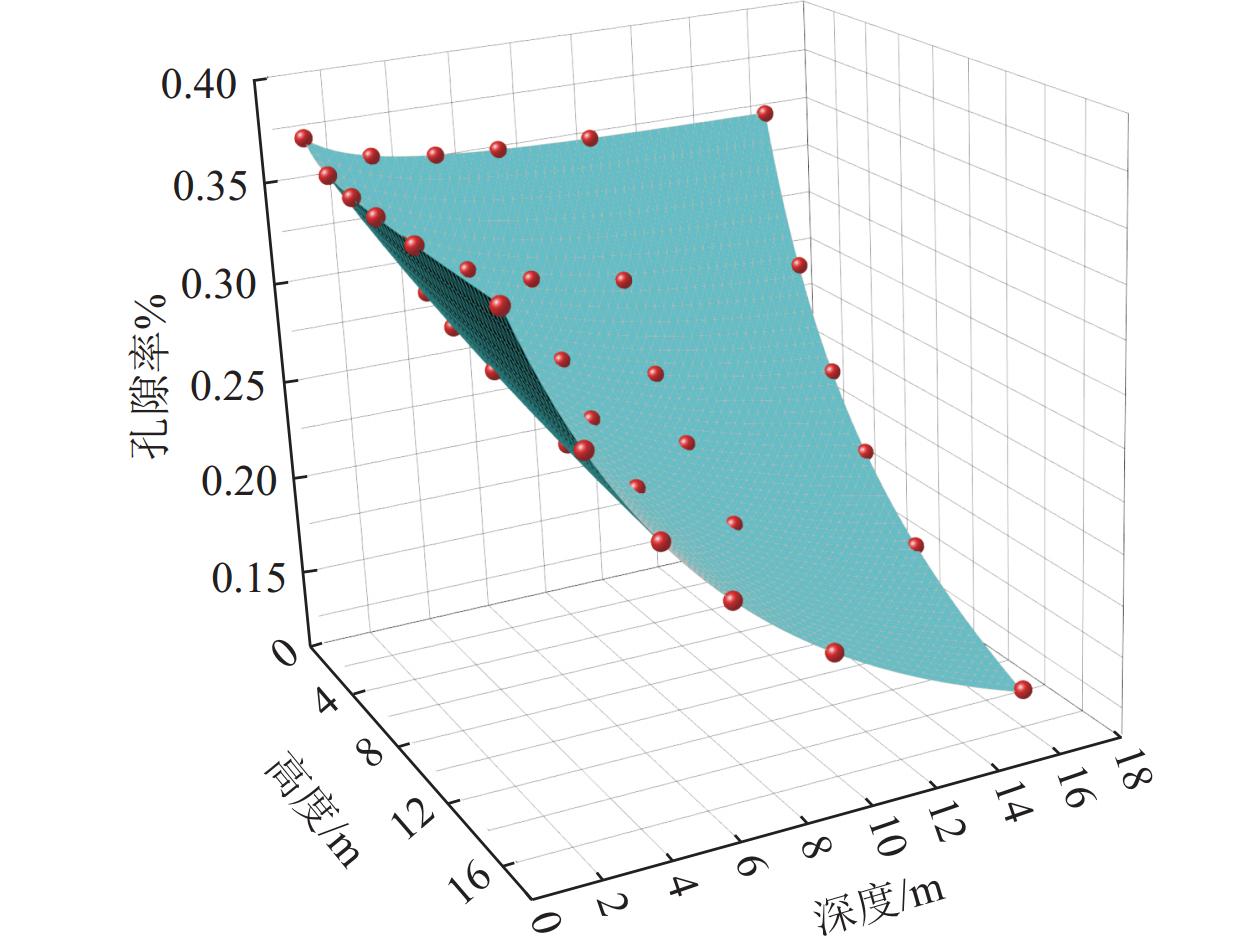
Table 3 Porosity at different heights of sloped surfaces
高度/m 不同深度下煤矸石散体孔隙率/% 1 m 3 m 5 m 7 m 10 m 16 m 1 37.3 36.2 35.9 35.7 35.6 35.5 3 35.9 32.3 39.0 31 29.4 28.8 5 35.5 35.0 28.1 26.6 25.3 24.0 7 35.3 29.5 26.3 24.4 22.5 26.0 10 35.1 28.6 24.7 22.2 19.7 17.0 16 34.9 27.8 23.0 19.8 16.5 12.9 表 4 孔隙率和渗透率的计算结果
Table 4 Calculation results of porosity and permeability
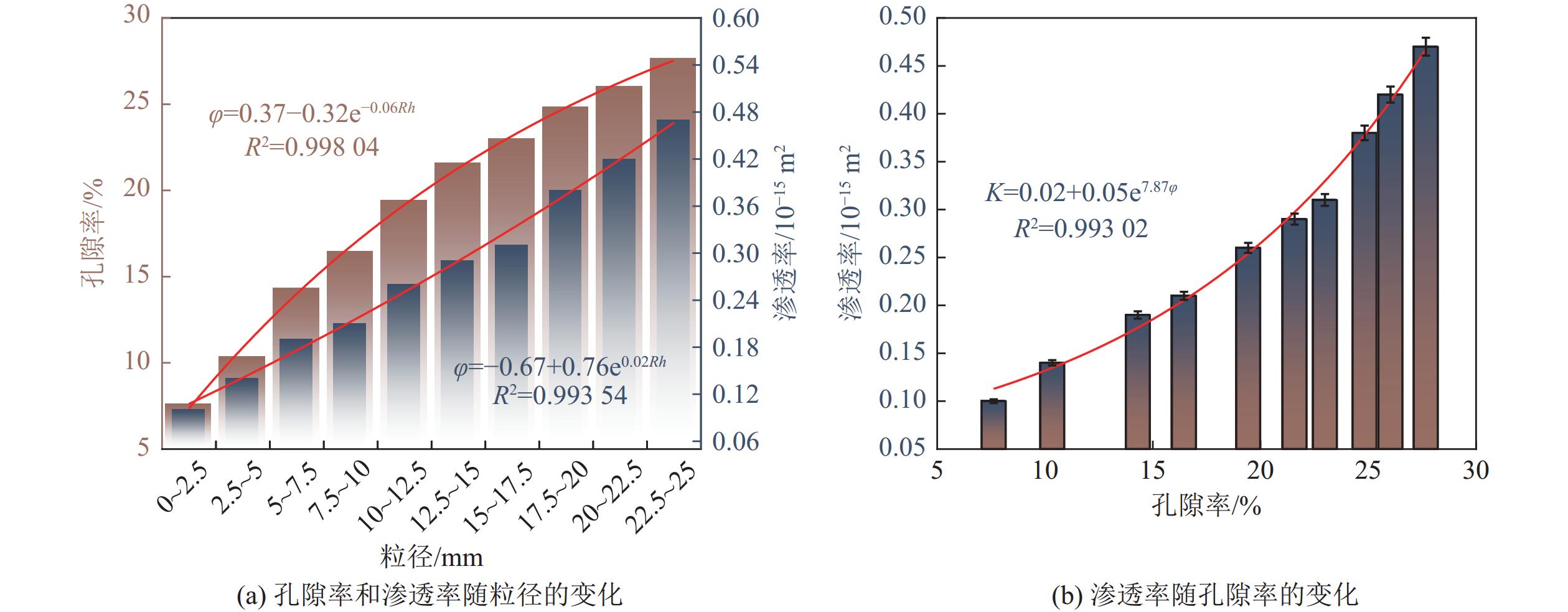
粒径/
mm进口压力/
MPa出口压力/
MPa流量/
(10−5·m3·s−1)孔隙率/
%渗透率/
(10−15 m2)0~2.5 0.60 0.10 27.78 7.62 0.10 2.5~5 0.52 0.10 27.78 10.34 0.14 5~7.5 0.45 0.10 27.78 14.31 0.19 7.5~10 0.43 0.10 27.78 16.45 0.21 10~12.5 0.38 0.10 27.78 19.43 0.26 12.5~15 0.37 0.10 27.78 21.58 0.28 15~17.5 0.35 0.10 27.78 22.99 0.32 17.5~20 0.32 0.10 27.78 24.83 0.39 20~22.5 0.30 0.10 27.78 26.03 0.45 22.5~25 0.29 0.10 27.78 26.67 0.49 表 5 数值模拟参数
Table 5 Numerical simulation parameters
参数 数值 参数 数值 空气密度ρg/(kg·m−3) 1.43 风速v0/(m·s−1) 2 煤矸石密度ρs/(kg·m−3) 2436 氧气体积分数c0/% 21 初始孔隙率e/% 40 大气压Pa/kPa 101.325 初始渗透率k/m2 1.37×10−9 环境温度T/K 293 黄土孔隙率el/% 10 空气动力黏滞系数μ/(kg·m−1·s−1) 1.8×10−5 黄土比热容Cl/(J·kg−1·K−1) 1696 时间步长Δt/s 259200 黄土密度ρl/(kg·m−3) 1600 时步数S 60 表 6 现场渗流试验参数值
Table 6 On site seepage experimental parameter values
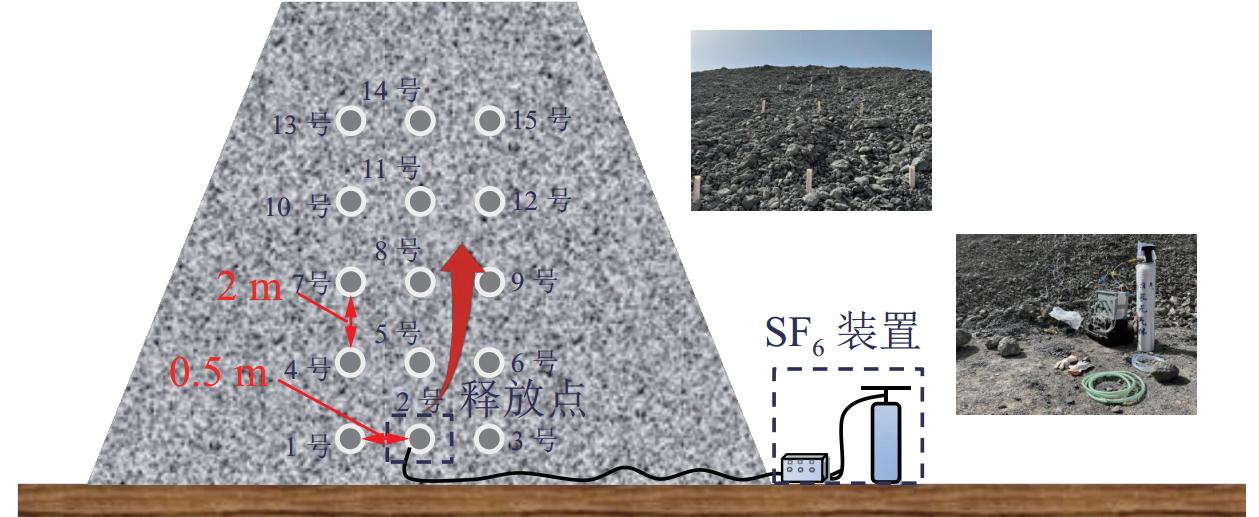
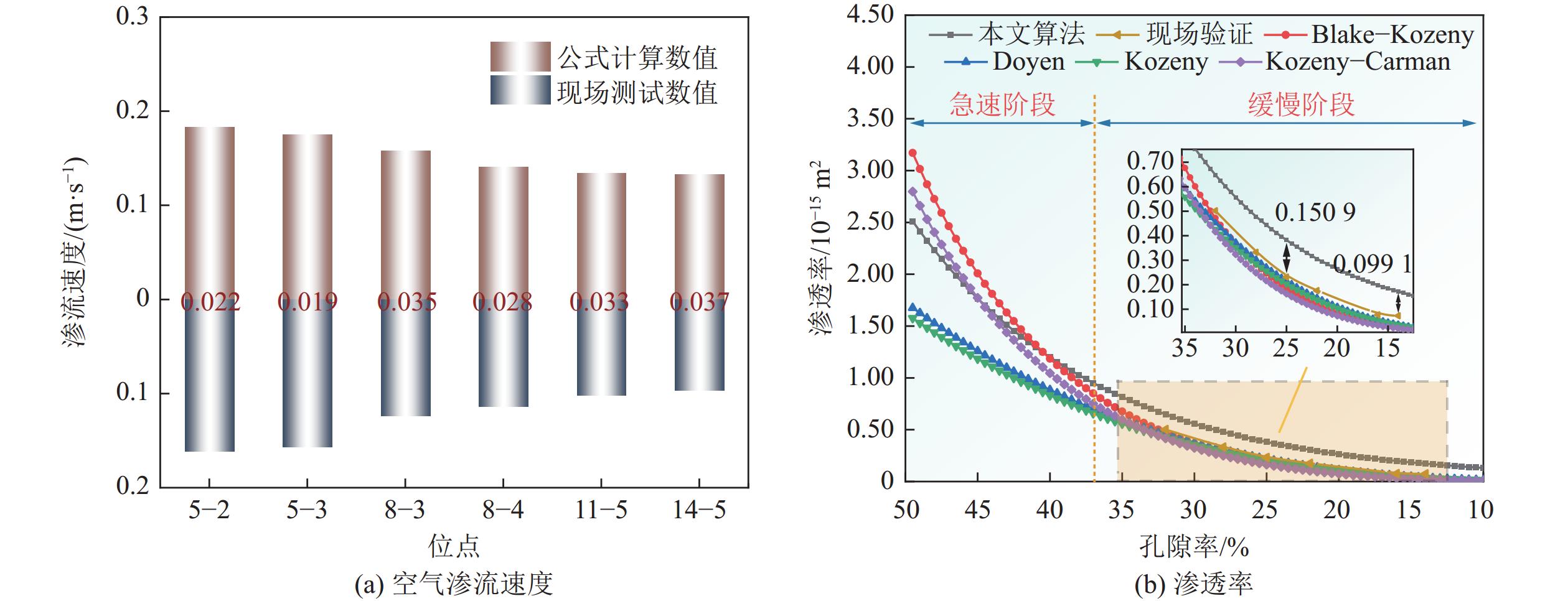
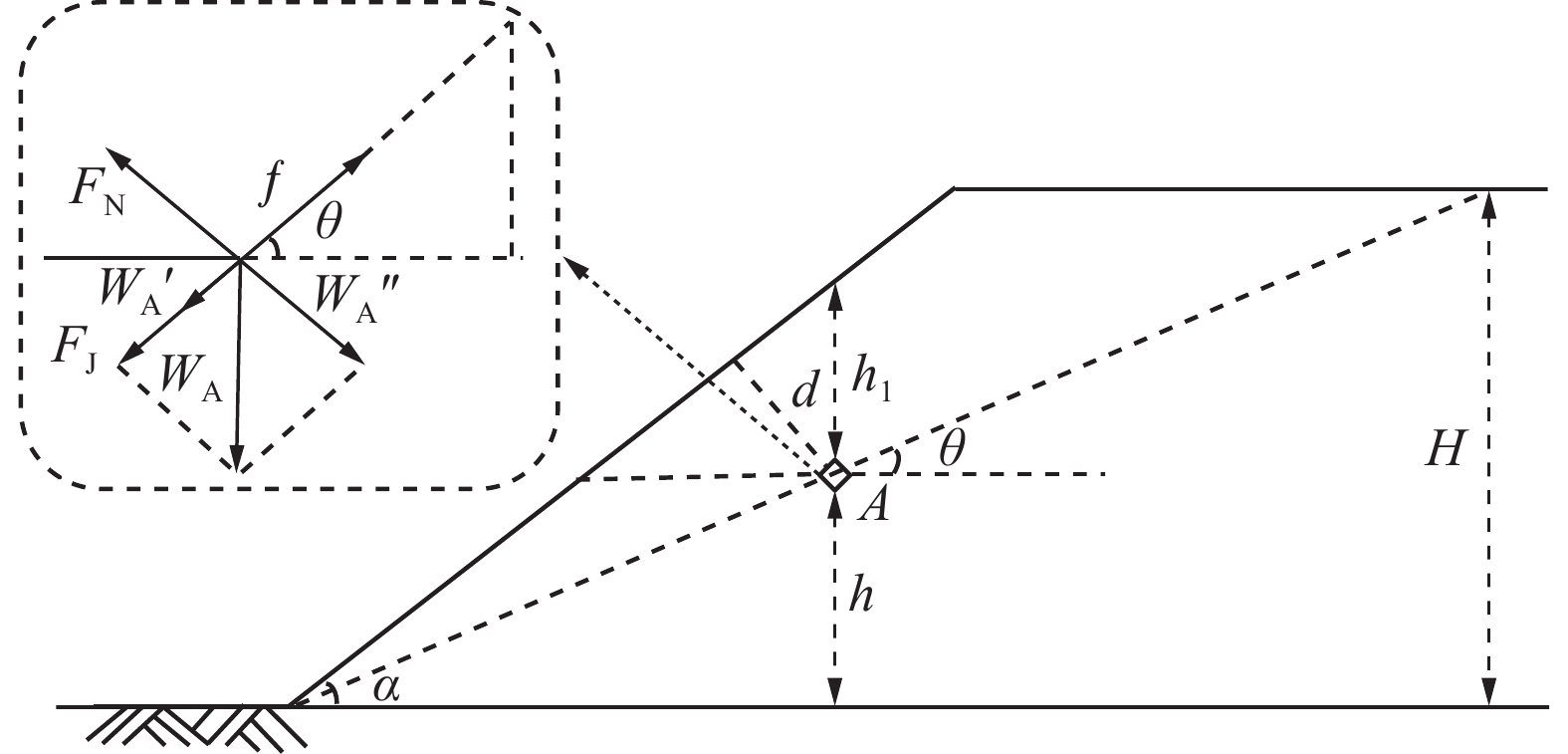
位点 d/m h/m TL/℃ T0/℃ ρ/(kg·m−3) v0/(m·s−1) vm/(m·s−1) θ0/(°) θm/(°) Z/m t/s 5-2 0.8 2.4 29 24.2 1.0260 2.1 3.1 38.9 36.8 15.0 8.2 5-3 1.3 2.0 31.5 24.8 1.0239 1.8 3.1 39.1 37.2 15.0 10.8 8-3 1.3 3.4 35.4 25 1.0232 1.6 3.5 38.7 37.8 14.8 30.4 8-4 1.8 2.9 36.1 25.3 1.0222 1.8 3.5 39 37.9 15.0 39.2 11-5 2.3 4.2 44.8 26.5 1.0215 1.8 3.9 37.9 37.5 15.1 84.5 14-5 2.3 5.8 49.2 28.9 1.0167 1.9 3.7 38.5 37.5 15.0 130.4 -
[1] 肖 武,任 河,赵艳玲,等. 无人机遥感支持下的煤矸石山自燃监测与预警[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2023,51(2):412−421. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2009.04.017 XIAO Wu,REN He,ZHAO Yanling,et al. Monitoring and early warning the spontaneous combustion of coal waste dumps supported by unmanned aerial vehicle remote sensing[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2023,51(2):412−421. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2009.04.017
[2] 边炳鑫,解 强,赵由才,等. 煤系固体废物资源化技术[M]. 北京:化学工业出版社,2005. [3] LIANG Y C,LIANG H D,ZHU S Q. Mercury emission from spontaneously ignited coal gangue hill in Wuda Coalfield,Inner Mongolia,China[J]. Fuel,2016,182:525−530. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.05.092
[4] 薛 刚. 大柳塔煤矿排矸场综合一体化火区治理方法[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(S1):159−167. XUE Gang. Comprehensive integrated fire area treatment method of wastedump in Daliuta Coal Mine[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(S1):159−167.
[5] 李建华,陈 涛,杨木林. 排矸方式对矸石山稳定性的研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(3):308−315. LI Jianhua,CHEN Tao,YANG Mulin. Study on stability of gangue mountain in discharging method[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(3):308−315.
[6] 李舒伶,高建科. 煤矸石山自然发火数学模型在红阳三矿新砰石山自燃防治中的应用[J]. 中国安全科学学报,2003,13(2):31−33,87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2003.02.009 LI Shuling,GAO Jianke. Application of mathematical model for spontaneous combustion of coal gangue dump in new gangue dump site of #3 Hongyang Mine[J]. China Safety Science Journal,2003,13(2):31−33,87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2003.02.009
[7] 贾宝山. 煤矸石山自然发火数学模型及防治技术研究[D]. 阜新:辽宁工程技术大学,2002. JIA Baoshan. Study on mathematical model of spontaneous combustion and its prevention and harness technology of coal gangue dump[D]. Fuxin:Liaoning Technical University,2002.
[8] 郁邦永,潘书才,魏建军,等. 承压饱和破碎岩石颗粒破碎及渗透率演化特征研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2020,37(3):632−638. YU Bangyong,PAN Shucai,WEI Jianjun,et al. Particle crushing and permeability evolution of saturated broken rock under compaction[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2020,37(3):632−638.
[9] 张天军,尚宏波,李树刚,等. 分级加载下破碎砂岩渗透特性试验及其稳定性分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2016,41(5):1129−1136. ZHANG Tianjun,SHANG Hongbo,LI Shugang,et al. Permeability characteristics of broken sandstone and its stability analysis under step loading[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2016,41(5):1129−1136.
[10] 余明高,晁江坤,褚廷湘,等. 承压破碎煤体渗透特性参数演化实验研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2017,42(4):916−922. YU Minggao,CHAO Jiangkun,CHU Tingxiang,et al. Experimental study on permeability parameter evolution of pressure-bear broken coal[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2017,42(4):916−922.
[11] 尚宏波,靳德武,张天军,等. 三轴应力作用下破碎煤体渗透特性演化规律[J]. 煤炭学报,2019,44(4):1066−1075. SHANG Hongbo,JIN Dewu,ZHANG Tianjun,et al. Permeability evolution of broken coal under triaxial stress[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2019,44(4):1066−1075.
[12] 余 为,李 强,黄 伟,等. 破碎岩体中的气体渗流规律研究[J]. 燕山大学学报,2007,31(4):317−321. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-791X.2007.04.009 YU Wei,LI Qiang,HUANG Wei,et al. Study on the laws of gas flow in over-broken rock mass[J]. Journal of Yanshan University,2007,31(4):317−321. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-791X.2007.04.009
[13] 司俊鸿,程根银,朱建芳,等. 采空区非均质多孔介质渗透特性三维建模及应用[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2019,47(5):220−224. SI Junhong,CHENG Genyin,ZHU Jianfang,et al. Three-dimensional modeling and application of permeability characteristics of heterogeneous porous media in goaf[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2019,47(5):220−224.
[14] 苏付义. 围限压力下煤岩孔隙度的变化特征及应用[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,1994,22(3):27−31. SU Fuyi. Variation characteristics and application of coal porosity under confining pressure[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,1994,22(3):27−31.
[15] 李舒伶,高建科. 煤矸石山自然发火数学模型在红阳三矿新矸石山自燃防治中的应用[J]. 中国安全科学学报,2003,13(2):25−27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2003.02.007 LI Shuling,GAO Jianke. Application of mathematical model for spontaneous combustion of coal gangue dump in new gangue dump site of #3 Hongyang Mine[J]. China Safety Science Journal,2003,13(2):25−27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2003.02.007
[16] 裴晓东,张人伟,杜高举,等. 新建煤矿矸石山自然发火的数学模型及其模拟分析[J]. 矿业安全与环保,2009,36(4):11−13,16,91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-4495.2009.04.004 PEI Xiaodong,ZHANG Renwei,DU Gaoju,et al. Mathematical model for spontaneous combustion of waste dump and its simulation analysis in Xinjian coal mine[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection,2009,36(4):11−13,16,91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-4495.2009.04.004
[17] 段玉龙,周心权,余明高,等. 矸石山自燃程度和爆炸的关联分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2009,34(4):514−519. DUAN Yulong,ZHOU Xinquan,YU Minggao,et al. The relations between spontaneous combustion degree and explosions of gangue dump[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2009,34(4):514−519.
[18] 张 凯,郭俊廷,滕 腾. 弱胶结砂质泥岩注水软化与渗流特性试验研究:以神东矿区为例[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(2):195−201. ZHANG Kai,GUO Junting,TENG Teng. Experimental study on water-softening and seepage characteristics of weakly cemented sandy mudstone:taking Shendong Coal Mining Area as an example[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(2):195−201.
[19] 王 刚,李艳青,刘世民,等. 微观等效毛管束下液体初始渗流特性的可视化研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(2):147−153. WANG Gang,LI Yanqing,LIU Shimin,et al. Visualized experimental study on initial seepage characteristics of liquid under micro-equivalent tube bundle[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(2):147−153.
[20] 张培森,侯季群,赵成业,等. 不同应力状态下底板岩体渗流特性分析研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(1):127−133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2336.2022.1.mtkxjs202201011 ZHANG Peisen,HOU Jiqun,ZHAO Chengye,et al. Analysis and study on seepage characteristics of floor rock mass under different stress states[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(1):127−133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2336.2022.1.mtkxjs202201011
[21] PERERA M S A,RANJITH P G,CHOI S K,et al. Numerical simulation of gas flow through porous sandstone and its experimental validation[J]. Fuel,2011,90(2):547−554. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2010.09.029
[22] 李志强,鲜学福,隆晴明. 不同温度应力条件下煤体渗透率实验研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2009,38(4):523−527. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1964.2009.04.012 LI Zhiqiang,XIAN Xuefu,LONG Qingming. Experiment study of coal permeability under different temperature and stress[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,2009,38(4):523−527. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1964.2009.04.012
[23] COLÓN C F J,OELKERS E H,SCHOTT J. Experimental investigation of the effect of dissolution on sandstone permeability,porosity,and reactive surface area[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2004,68(4):805−817. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2003.06.002
[24] 高建良,刘佳佳,张学博. 采空区渗透率对瓦斯运移影响的模拟研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报,2010,20(9):9−14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2010.09.002 GAO Jianliang,LIU Jiajia,ZHANG Xuebo. Simulation study on the influence of permeability on gas migration in gob[J]. China Safety Science Journal (CSSJ),2010,20(9):9−14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2010.09.002
[25] 奥)薛定谔(A. E. Scheidegger)著,王鸿勋译. 多孔介质中的渗流物理[M]. 北京:石油工业出版社,1982.



 下载:
下载: