Study on efficient mineralization method of fly ash based on three-stage division in reaction process
-
摘要:
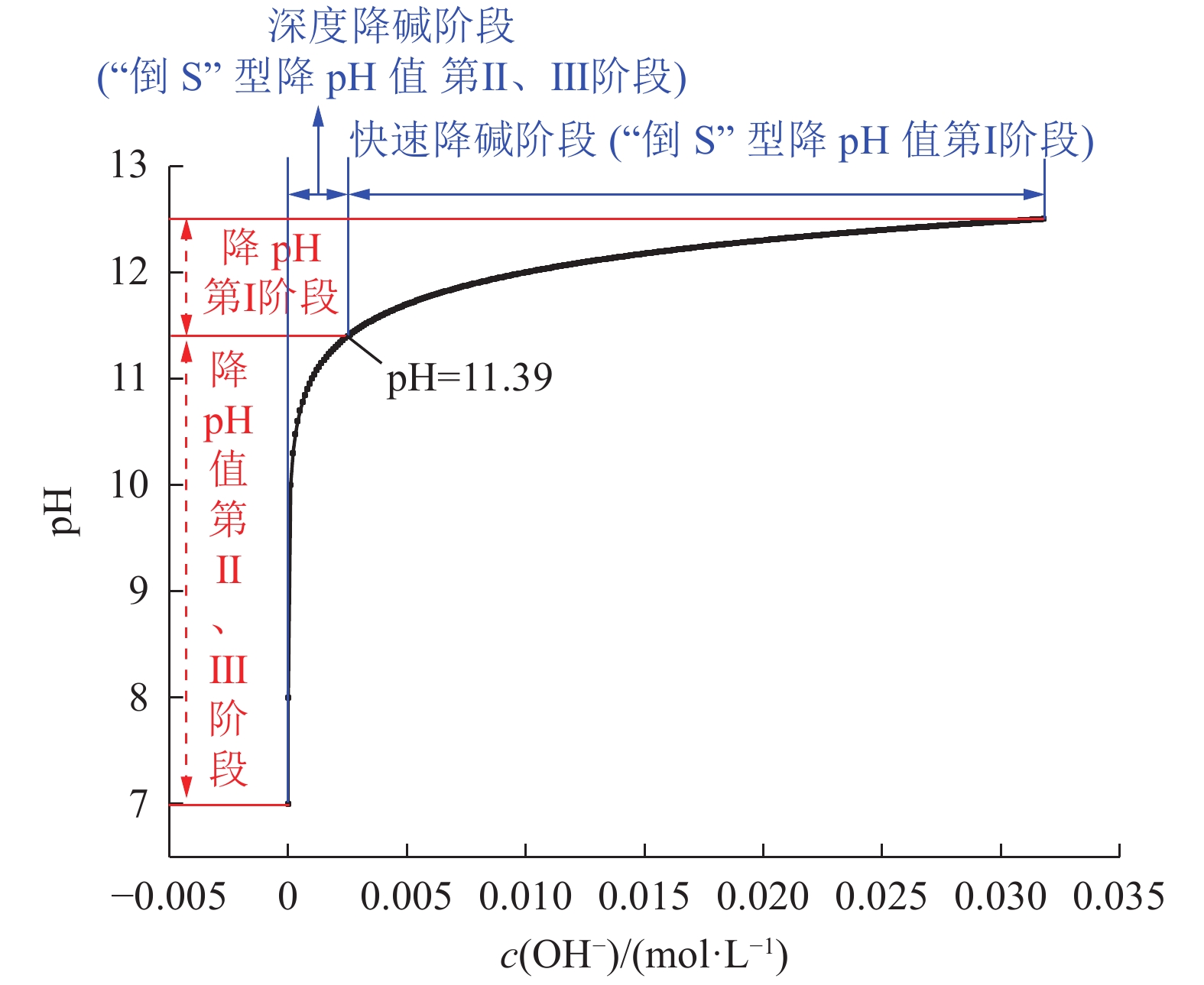
粉煤灰由于含有钙镁等碱土金属氧化物导致其浆液呈碱性,直接充填井下采空区易污染地下水源。利用陕北矿区府谷电厂粉煤灰开展组分测试、浆液pH值特性测试及固碳降碱试验,基于浆液pH值与OH−浓度理论关系对粉煤灰固碳降碱反应过程进行阶段划分并提出两级耦合的粉煤灰高效矿化方法。研究结果表明:①粉煤灰含CaO、MgO、K2O等碱土金属氧化物,溶于水浆液呈高碱特性,浆液pH值随浆液浓度增大而增大,当粉煤灰浆液质量分数≥30%时,浆液pH值不受质量分数影响且粉煤灰碱土金属氧化物与水反应生成OH−速率较快,溶于水20 min,OH−浓度饱和;②粉煤灰与CO2发生矿化反应生成方解石型CaCO3,每1 kg粉煤灰可矿化封存29.57 g CO2;③粉煤灰与CO2发生矿化粉煤灰固碳降碱过程中pH变化曲线呈“倒S”型,按降pH速率分为慢速(I)、快速(II)、慢速(III)3个阶段,3个阶段的pH值分界点分别为11.39、7~8且第I阶段无法消除;④降pH与降碱不是同一概念,降碱指的是降浆液中OH−浓度,降pH第I阶段对应快速降碱阶段,降pH第II、III阶段对应深度降碱阶段;⑤决定粉煤灰固碳量的主要为降pH第I阶段,而非pH下降速率较大的第II阶段,第I阶段CO2利用率约为30.78%,第II、III阶段CO2总利用率约为9.04%;⑥基于粉煤灰固碳降碱过程阶段划分及反应装置降碱速率、容积的差异性,提出两级耦合的粉煤灰高效矿化方法。研究结果对分析粉煤灰固碳降碱机理,提高粉煤灰固碳降碱效率,促进粉煤灰处置工业化应用具有重要意义。
Abstract:Due to alkaline earth metal oxide such as calcium and magnesium being existed in the fly ash, its slurry is alkaline. It’s easy to pollute the underground water when the slurry was filled in the goaf. Thus, some experiments such as composition test, slurry pH characteristic test, carbon and alkali reduction test were carried out by using fly ash selected from Fugu Power Plant in northern Shaanxi Mining area. Based on the theoretical relationship between slurry pH value and OH− concentration, the reaction process of carbon and alkali reduction of fly ash was divided into stages and a two-stage coupling method for high efficiency mineralization was proposed. The results showed that the slurry of fly ash had high alkali for the reason that the alkali metal oxides such as CaO,MgO,K2O,etc being existed and the pH value increased with the slurry concentration. While the pH value was not affected by the concentration when the slurry concentration was more than 30%. At the same time, the OH− concentration was saturated after fly ash being dissolved in water for 20 minutes due to the fast reaction of alkali earth metal oxides with water. And the reaction product is calcium carbonate of calcite type as well as 20 grams of carbon dioxide being mineralized per kilogram of fly ash. In the process of carbon fixation and alkali reduction, pH reduction curve reflected as reverse S type and the pH reduction rate was divided into three stages, referring to slow, fast and slow. The changing points of three stages were that pH values being 11.39 and 7−8 as while as the first stage cannot be eliminated. Simultaneously, the pH value and alkali reduction were not the same concept for alkali reduction referring to the decrease of OH−concentration in the slurry. So the first stage corresponded to the rapid alkali reduction and the second and third stage corresponded to the deep alkali reduction. The carbon fixation amount was mainly determined by the first stage, not the second stage of rapid pH value decrease for the reason thar the CO2 utilization rate of the first stage was about 30.78%, while the total CO2 utilization rate of the second and third stages was about 9.04%. Based on the stage division of reaction as while as the difference of alkali reduction rate and reaction device volume, a two-stage coupling method of high efficiency mineralization was proposed. The research results have great significance for analyzing the mechanism of carbon fixation and alkali reduction of fly ash, improving the efficiency and promoting the industrial application of fly ash disposal.
-
-
表 1 粉煤灰组分XRF分析成果
Table 1 Components of fly ash by XRF spectrometric analysis
组分 SiO2 Al2O3 CaO Fe2O3 K2O MgO Na2O P2O5 SO3 TiO2 其他 质量分数/% 46.9 19.5 17.8 9.4 1.6 1.1 0.9 0.9 0.8 0.8 0.3 表 2 固碳降碱试验方案
Table 2 Carbon fixation and alkali reduction test scheme
方案编号 气量/(m3·h−1) 浆液质量分数/% 试验装置 1 50 17 涡流式 2 134 25 涡流式 3 75 30 涡流式 4 125 30 涡流式 5 125 30 旋桨式 -
[1] 中华人民共和国国家统计局,2022年国民经济和社会发展统计公报[R/OL]. (2023-02-28) [2024-01-04]. https://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2023-02/28/content_5743623.htm. [2] 秦波涛,蒋文婕,史全林,等. 矿井粉煤灰基防灭火技术研究进展[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2023,51(1):329−342. QIN Botao,JIANG Wenjie,SHI Quanlin,et al. Research progress on fly ash foundation technology to prevent and control spontaneous combustion of coal in mines[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2023,51(1):329−342.
[3] 邢静锴,齐德娥,秦身钧,等. 粉煤灰中有价元素的高值化利用研究进展[J]. 现代化工,2023,43(7):39−43,49. XING Jingkai,QI Dee,QIN Shenjun,et al. Research progress on high-value utilization of valuable elements in fly ash[J]. Modern Chemical Industry,2023,43(7):39−43,49.
[4] 甘志超,尹希文,纪龙. 粉煤灰的CO2矿化降碱反应特性研究[J]. 煤炭工程,2023,55(8):154−158. GAN Zhichao,YIN Xiwen,JI Long. Performance of CO2 mineralization and alkaline reduction of coal fly ash[J]. Coal Engineering,2023,55(8):154−158.
[5] 王建新,李晶,赵仕宝,等. 中国粉煤灰的资源化利用研究进展与前景[J]. 硅酸盐通报,2018,37(12):3833−3841. WANG Jianxin,LI Jing,ZHAO Shibao,et al. Research progress and prospect of resource utilization of fly ash in China[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2018,37(12):3833−3841.
[6] 姜龙. 燃煤电厂粉煤灰综合利用现状及发展建议[J]. 洁净煤技术,2020,26(4):31−39. JIANG Long. Comprehensiveutilization situation of fly ash in coal-fired power plants and its development suggestions[J]. Clean Coal Technology,2020,26(4):31−39.
[7] 榆林市生态环境局,榆林市2022年度固体废物污染环境防治信息[R/OL]. (2023-06-25) [2024-01-04]. http://hb.yl.gov.cn/uploads/files/20231106/d33fcac9bad262a148c016a76520102c.pdf. [8] 王晓龙,刘蓉,王琪,等. 电厂烟气低浓度CO2的粉煤灰直接液相矿化技术[J]. 热力发电,2021,50(1):104−109. WANG Xiaolong,LIU Rong,WANG Qi,et al. A new direct aqueous mineralization process to capture low concentration CO2 from power plant flue gas using fly ash[J]. Thermal Power Generation,2021,50(1):104−109.
[9] 马立强,翟江涛,NGO Ichhuy. CO2矿化煤基固废制备保水开采负碳充填材料试验研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(12):4228−4236. MA Liqiang,ZHAI Jiangtao,ICHHUY N. Experimental study on preparation of negative carbon filling material forwater protection mining by CO2 mineralization of coal-based solid waste[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(12):4228−4236.
[10] HE L L,YU D X,LV W Z,et al. A novel method for CO2 sequestration via indirect carbonation of coal fly ash[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2013,52(43):15138−15145.
[11] BACIOCCHI R,COSTA G,POLETTINI A,et al. Comparison of different reaction routes for carbonation of APC residues[J]. Energy Procedia,2009,1(1):4851−4858. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2009.02.313
[12] 蔡洁莹,李向东,李海红,等. 电厂粉煤灰固定二氧化碳实验研究[J]. 煤炭转化,2019,42(1):87−94. CAI Jieying,LI Xiangdong,LI Haihong,et al. Experimental study on solidification of carbon dioxide by coal fly ash in power plant[J]. Coal Conversion,2019,42(1):87−94.
[13] 王晓龙,刘蓉,纪龙,等. 利用粉煤灰与可循环碳酸盐直接捕集固定电厂烟气中二氧化碳的液相矿化法[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2018,38(19):5787−5794,5935. WANG Xiaolong,LIU Rong,JI Long,et al. A new direct aqueous mineralization process using fly ash and recyclable carbonate salts to capture and storage CO2 from flue-gas[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE,2018,38(19):5787−5794,5935.
[14] 尹希文,于秋鸽,甘志超,等. 高钙粉煤灰固碳降碱反应特性及煤矿井下规模化利用新途径[J]. 煤炭学报,2023,48(7):2717−2727. YIN Xiwen,YU Qiuge,GAN Zhichao,et al. Reaction characteristics of carbon fixation and alkali reduction in high calcium fly ash and new way of large-scale utilization in coal mine[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2023,48(7):2717−2727.
[15] 王晓钧,陈悦,周洪庆,等. 粉煤灰机械研磨过程中硅氧四面体结构的变化趋向[J]. 硅酸盐学报,2001,29(4):389−391. WANG Xiaojun,CHEN Yue,ZHOU Hongqing,et al. Changes of silicate tetrahedron of fly ash in mechanical grinding[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2001,29(4):389−391.
[16] 刘音,刘洋,周煜明,等. 机械研磨时间对粗粉煤灰基充填胶凝材料性能的影响[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2017,45(6):221−225. LIU Yin,LIU Yang,ZHOU Yuming,et al. Mechanical grinding time affected to performances of reject fly ash-based backfill binding material[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2017,45(6):221−225.
[17] 国家能源局. 燃煤电厂粉煤灰资源化利用分类规范:DL/T 2297—2021[S]. 北京:中国电力出版社,2021. [18] 纪 龙. 利用粉煤灰矿化封存二氧化碳的研究[D]. 北京:中国矿业大学(北京),2018. JI Long. Carbon dioxide sequestration by mineralisation of coal fly ash[D]. Beijing:China University of Mining & Technology,Beijing,2018.
[19] HOSSEINI T,SELOMULYA C,HAQUE N,et al. Indirect carbonation of Victorian brown coal fly ash for CO2 sequestration:multiple-cycle leaching-carbonation and magnesium leaching kinetic modeling[J]. Energy & Fuels,2014,28(10):6481−6493.
[20] 中华人民共和国生态环境部,国家市场监督管理总局. 一般工业固体废物贮存和填埋污染控制标准:GB 18599—2020[S]. 北京:中国环境科学出版社,2021. [21] 北京师范大学无机化学教研室,华中师范大学无机化学教研室,南京师范大学无机化学教研室. 无机化学(上册)[M]. 北京:高等教育出版社,1981. [22] 翁伯琦. 酸碱理论与溶液pH值计算[J]. 福建农业科技,1985(3):51−52. WENG Boqi. Acid-base theory and solution pH calculation[J]. Fujian Agricrltural Science and Technology,1985(3):51−52.




 下载:
下载: