Based on Box-Behnken method superfine cement grouting material ratio andperformance optimization model
-
摘要:
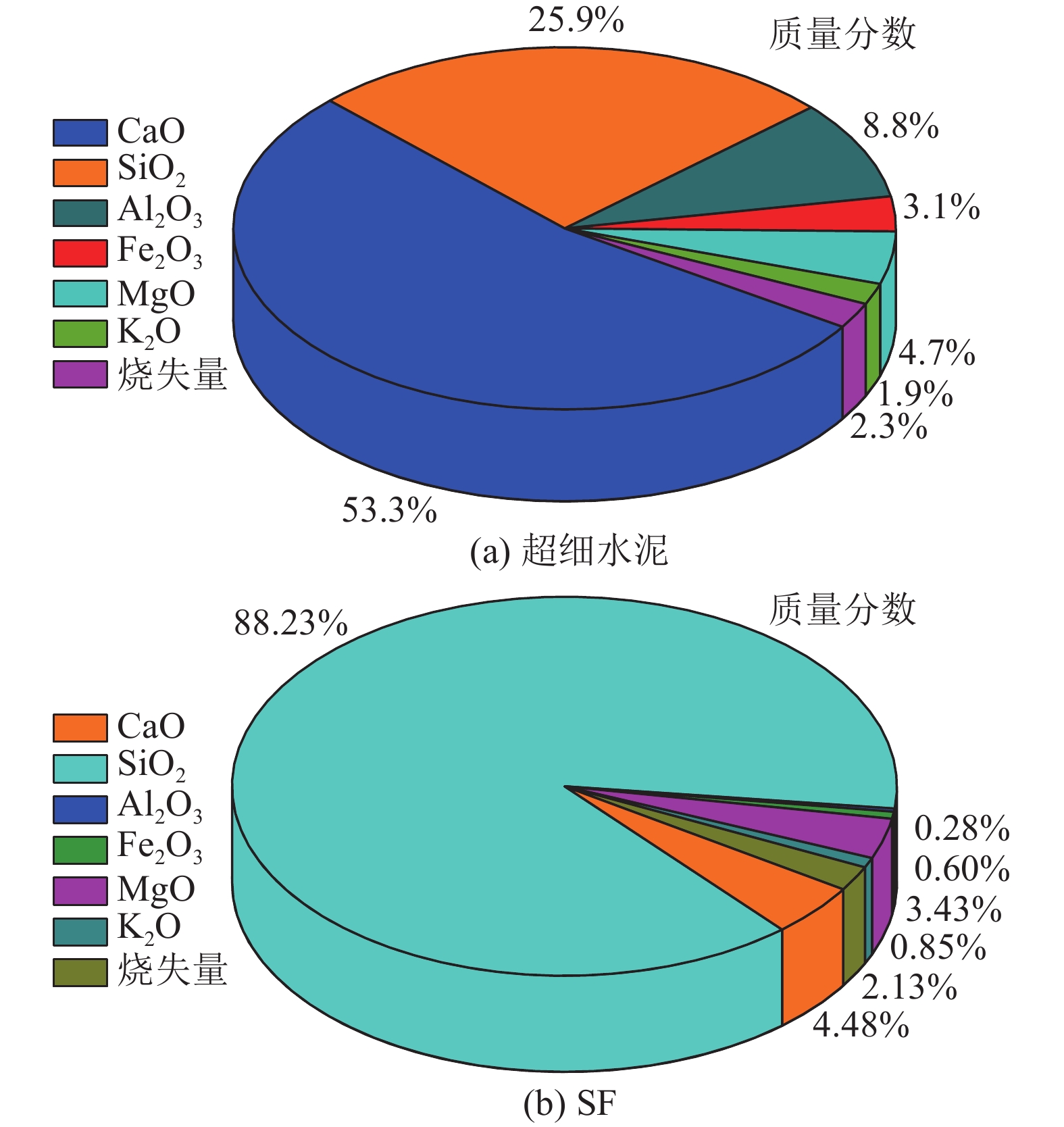
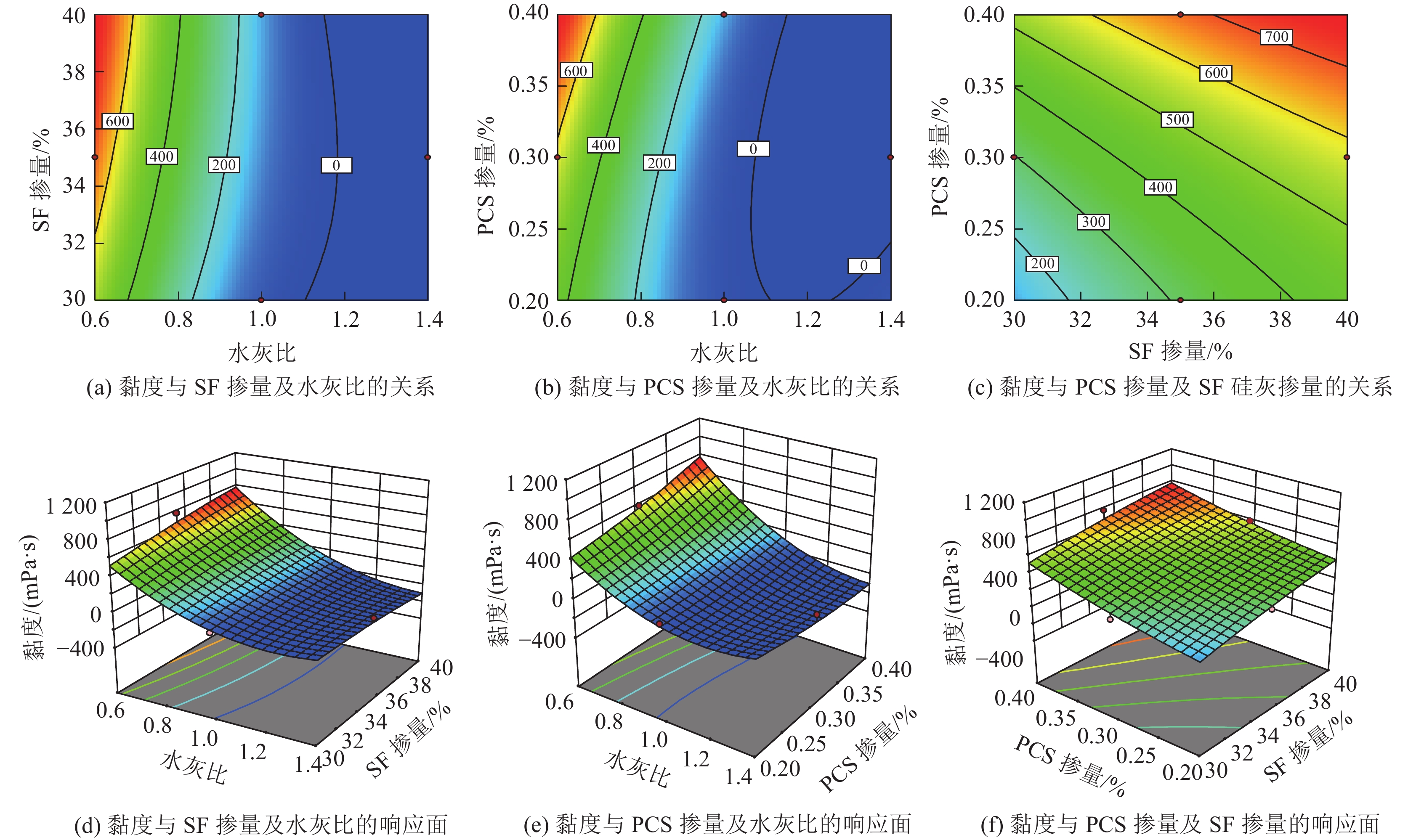
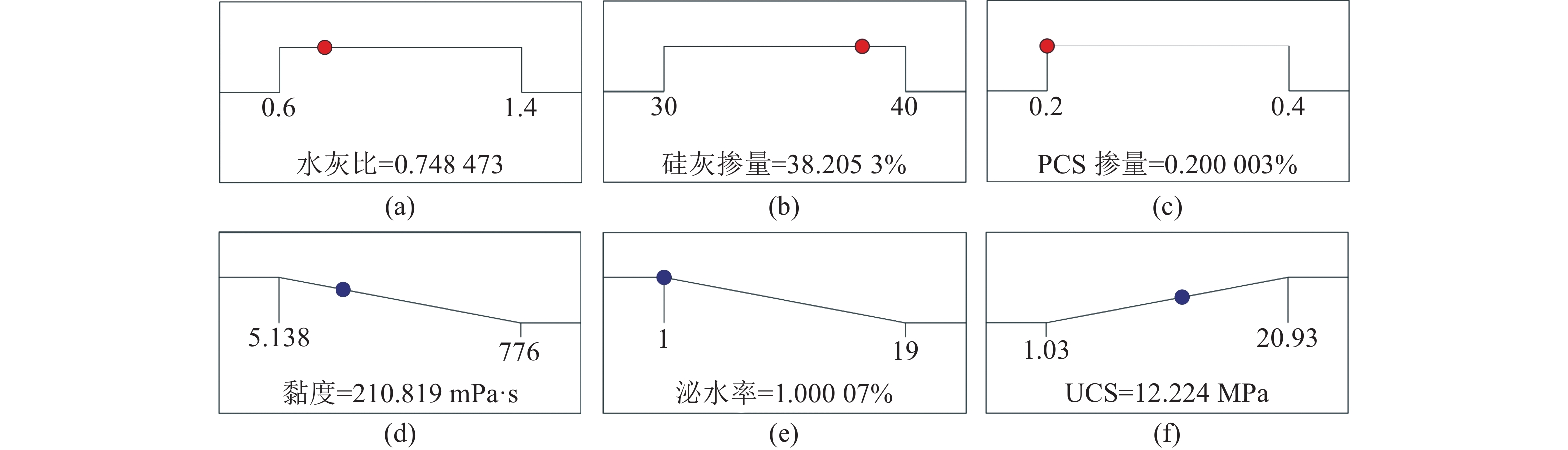
注浆堵水技术已成为水害措施防范向工程治理不可缺少的技术之一,超细材料的研究也成为了目前注浆材料发展的新方向。为了解决矿井水害注浆治理工程中注浆材料优选和配比优化问题,采用单因素试验与响应曲面法(RSM)相结合的方法进行超细水泥注浆材料优化配比研究。首先通过单因素试验对不同水灰比、硅灰(SF)掺量及高效聚羧酸减水剂(PCS)掺量条件下浆液黏度、泌水率及7 d单轴抗压强度进行分析,以确定RSM最佳基准水平,其次构建以浆液黏度、泌水率及7 d单轴抗压强度为响应目标的二次多项式预测模型,结合方差、残差及响应曲面分析各响应变量对响应目标的影响规律,确定注浆材料最优配比。通过单因素试验结果对比分析,发现最优水灰比、SF掺量及PCS掺量分别为1∶1、35%及0.3%。通过RSM研究发现,浆液黏度、泌水率及7 d单轴抗压强度不仅受单一因素影响,且存在多因素交互作用。根据建立的二次多项式响应面回归预测模型可知,当水灰比、SF掺量及PCS掺量分别为0.7∶1、38%及0.2%时,注浆材料性能最优,其回归模拟预测浆液黏度、泌水率及7 d单轴抗压强度分别为210.82 mPa·s、1.0%及12.22 MPa。通过室内试验,其结果与预测模型结果吻合度较高,进一步验证了模型的可靠性,证明了该模型能够用于注浆材料优化配比设计研究。
Abstract:Grouting water plugging technology has become one of the indispensable technologies for water damage prevention to engineering treatment, and research on ultrafine materials have has also become a new direction for the development of grouting materials. In order to solve the problem of optimal selection and ratio optimization of grouting materials in mine water damage grouting treatment project, the method of single factor test combined with response surface method (RSM) was used to study the optimal ratio of superfine cement grouting materials. The slurry viscosity, bleeding rate and 7-day uniaxial compressive strength of slurry with different water-cement ratio, silica fume (SF) content and highly efficient polycarboxylate water reducer (PCS) content were analyzed through single factor test, and the optimal reference level of RSM was determined. Secondly, a quadratic polynomial prediction model with slurry viscosity, bleeding rate and 7-day uniaxial compressive strength as the response target was constructed, combination with variance, residual and response surface analyzed the influence of each response variable on the response target, and the optimal ratio of grouting materials was determined. Through comparative analyze of single factor test results, the optimal water-cement ratio, SF content and PCS content were 1∶1, 35% and 0.3%, respectively. Through RSM study, it was found that slurry viscosity, bleeding rate and 7-day uniaxial compressive strength were not only affected by a single factor, but also by multi-factor interaction. According to the established quadratic polynomial response surface regression prediction model, the optimal grouting material properties were achieved when the water-cement ratio, SF content and PCS content were 0.7∶1, 38% and 0.2%, respectively. The regression simulated prediction of slurry viscosity, bleeding rate and 7-day uniaxial compressive strength was 210.82 MPa·s, 1.0% and 12.22 MPa, respectively. The laboratory verification test results showed a high degree of consistency with the predicted model results, which further verifying the reliability of the model, and the model can be used to optimize the proportion of grouting materials.
-
-
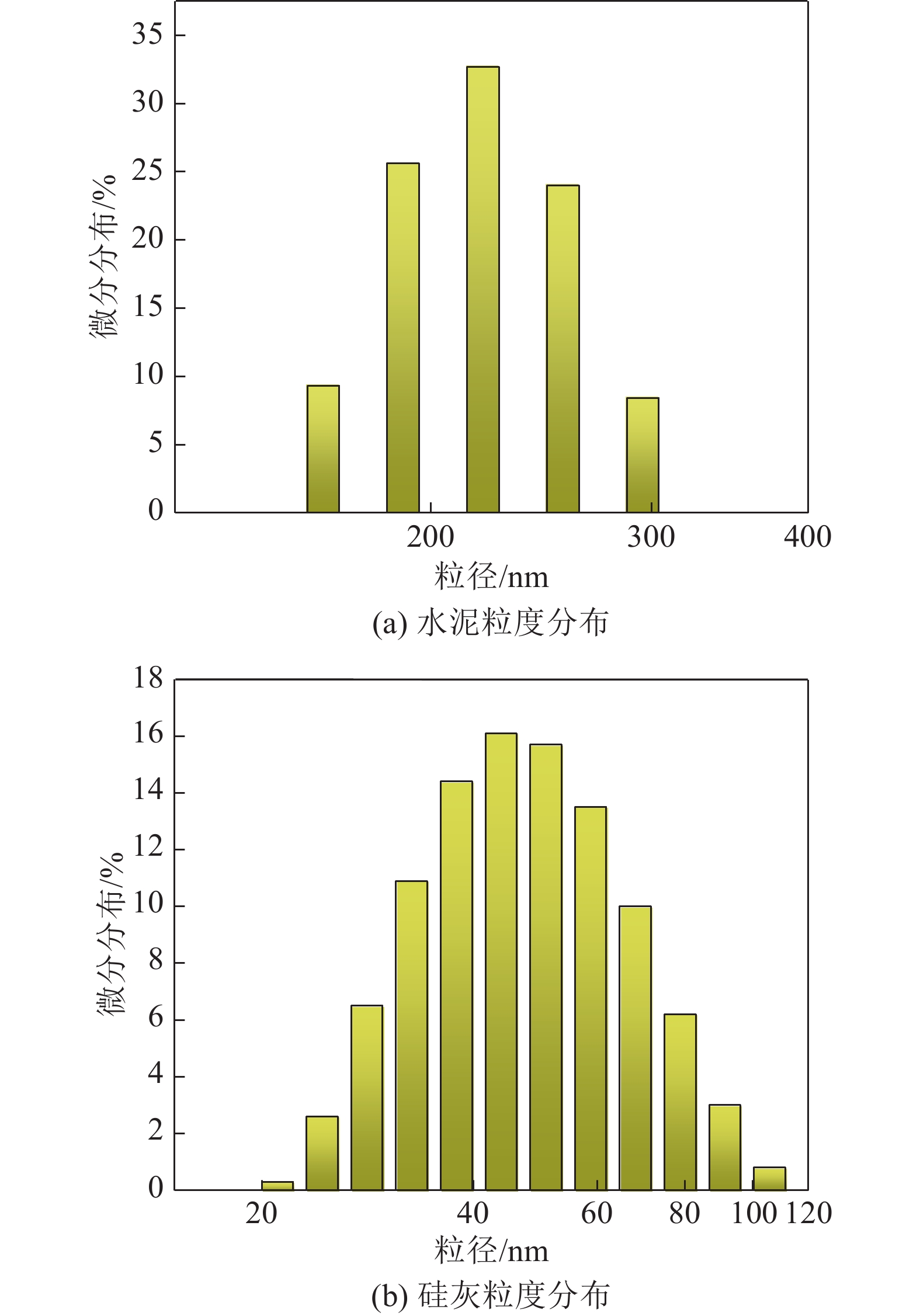
表 1 单因素试验设计
Table 1 Single-factor experimental design table
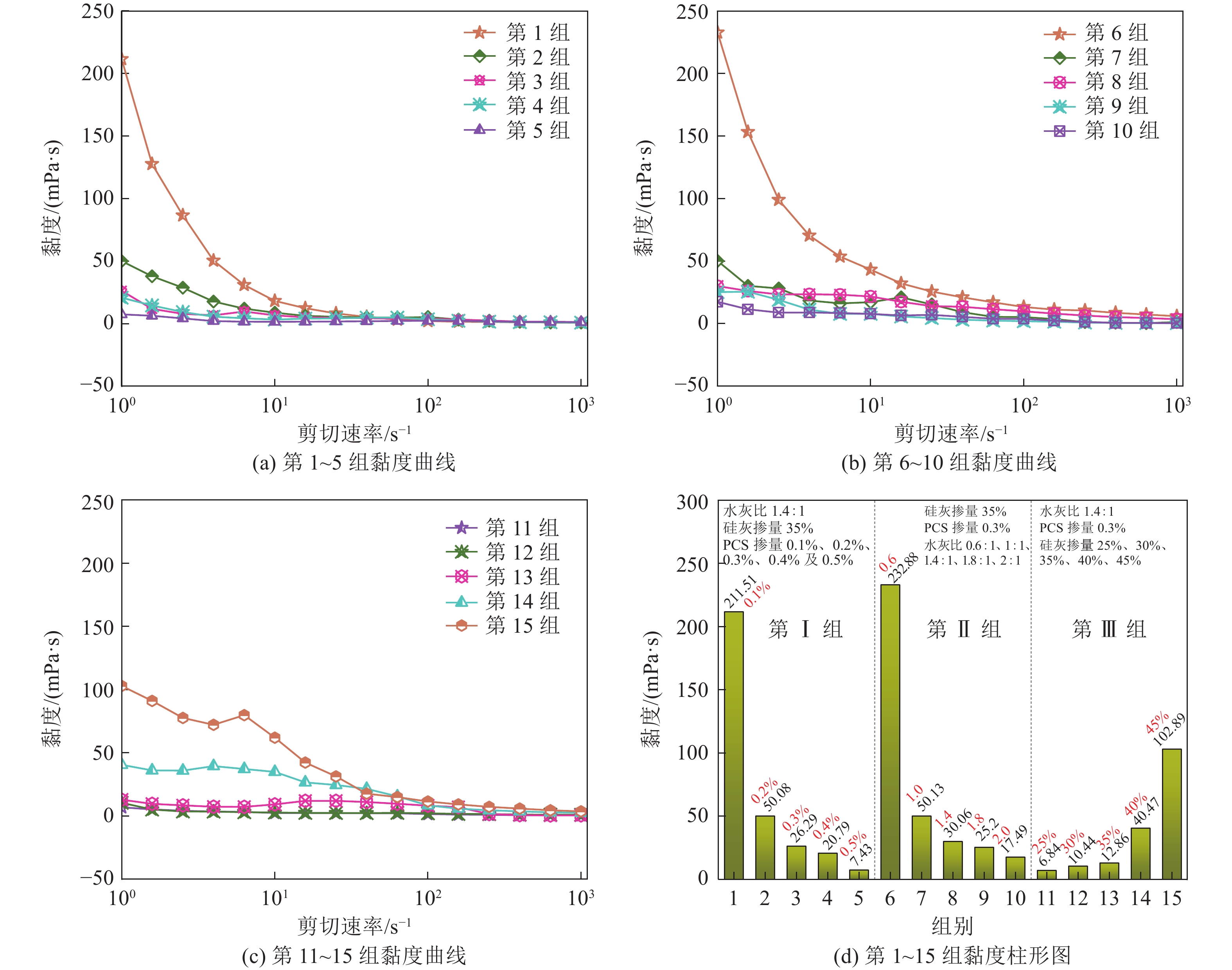
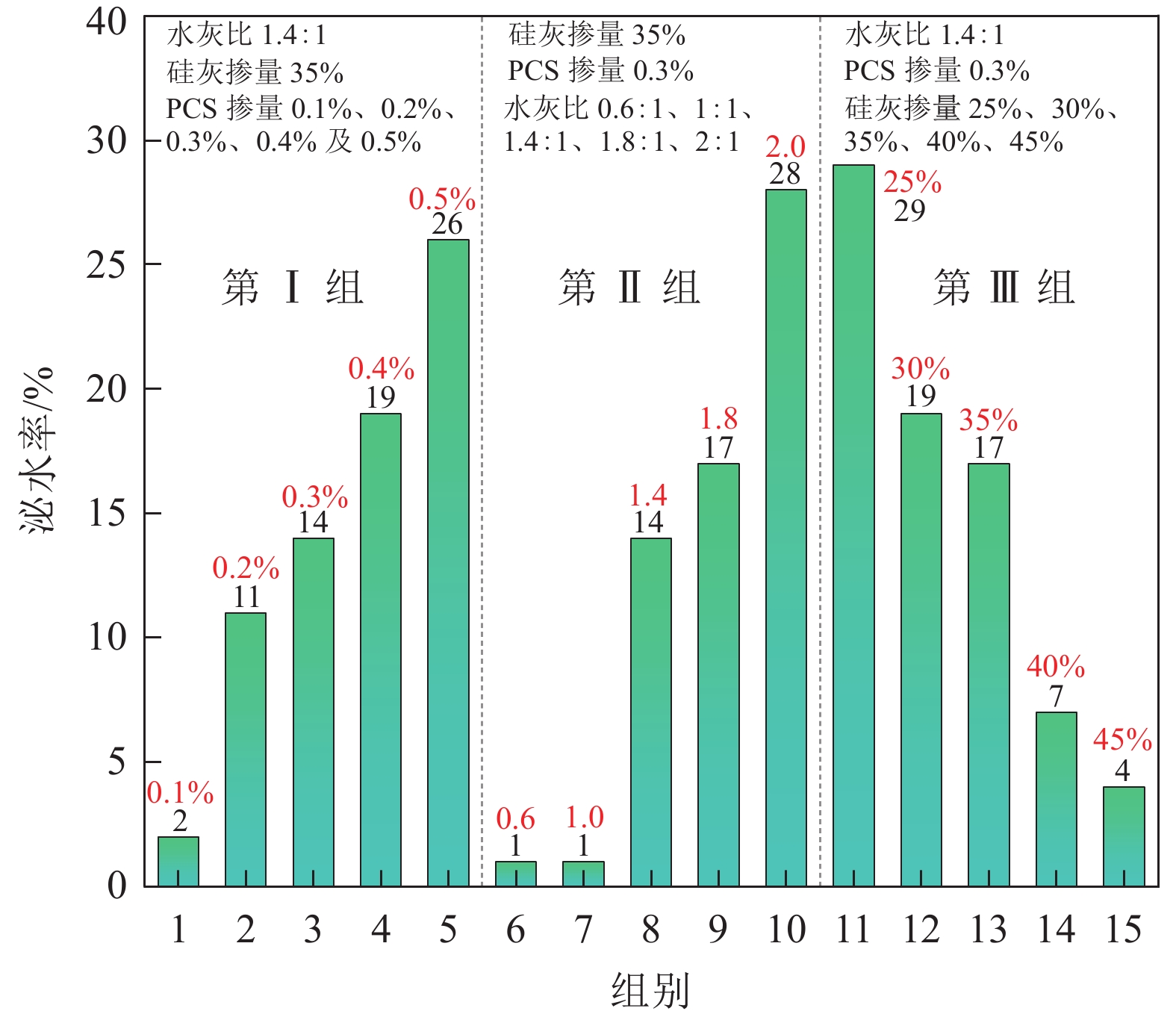
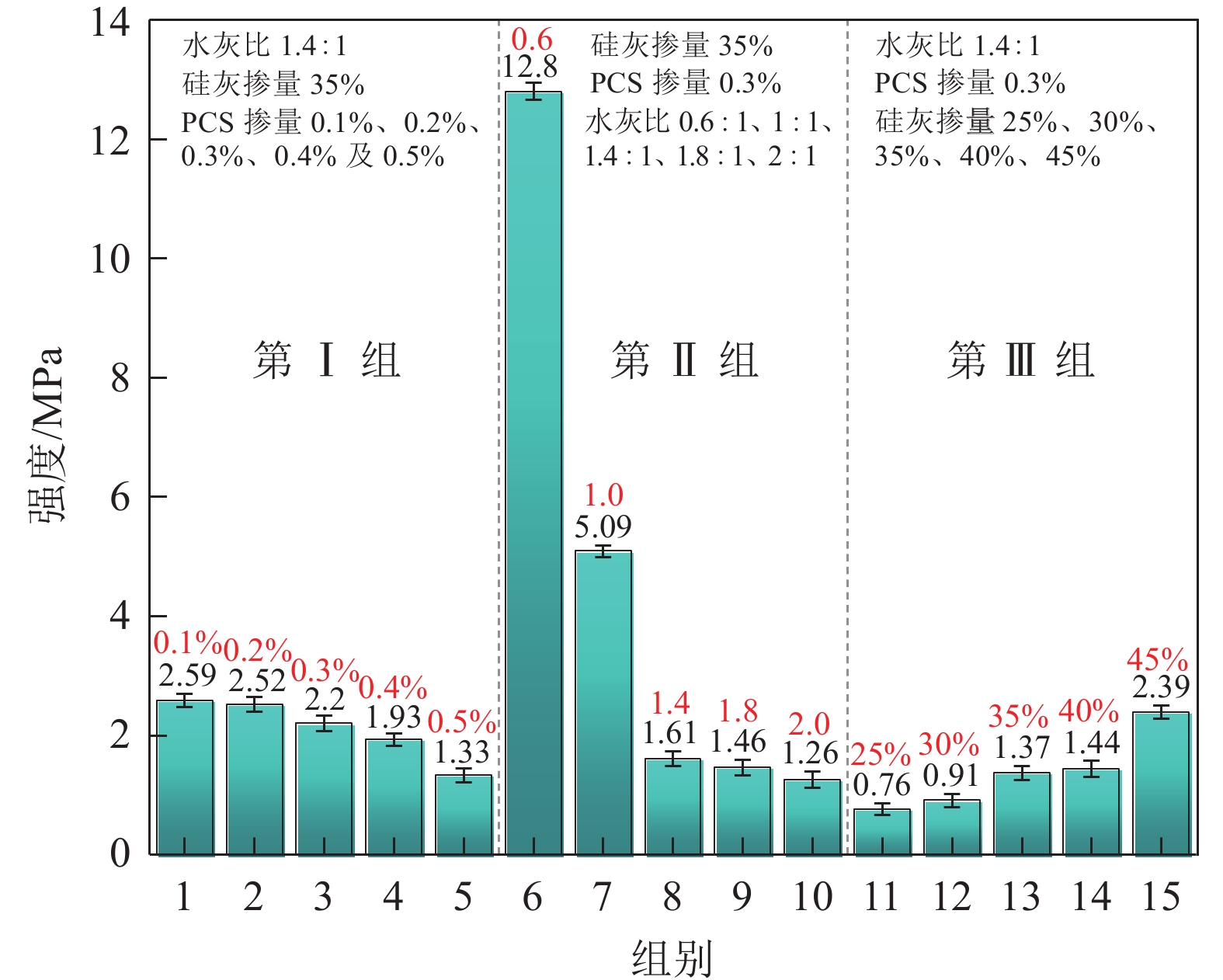
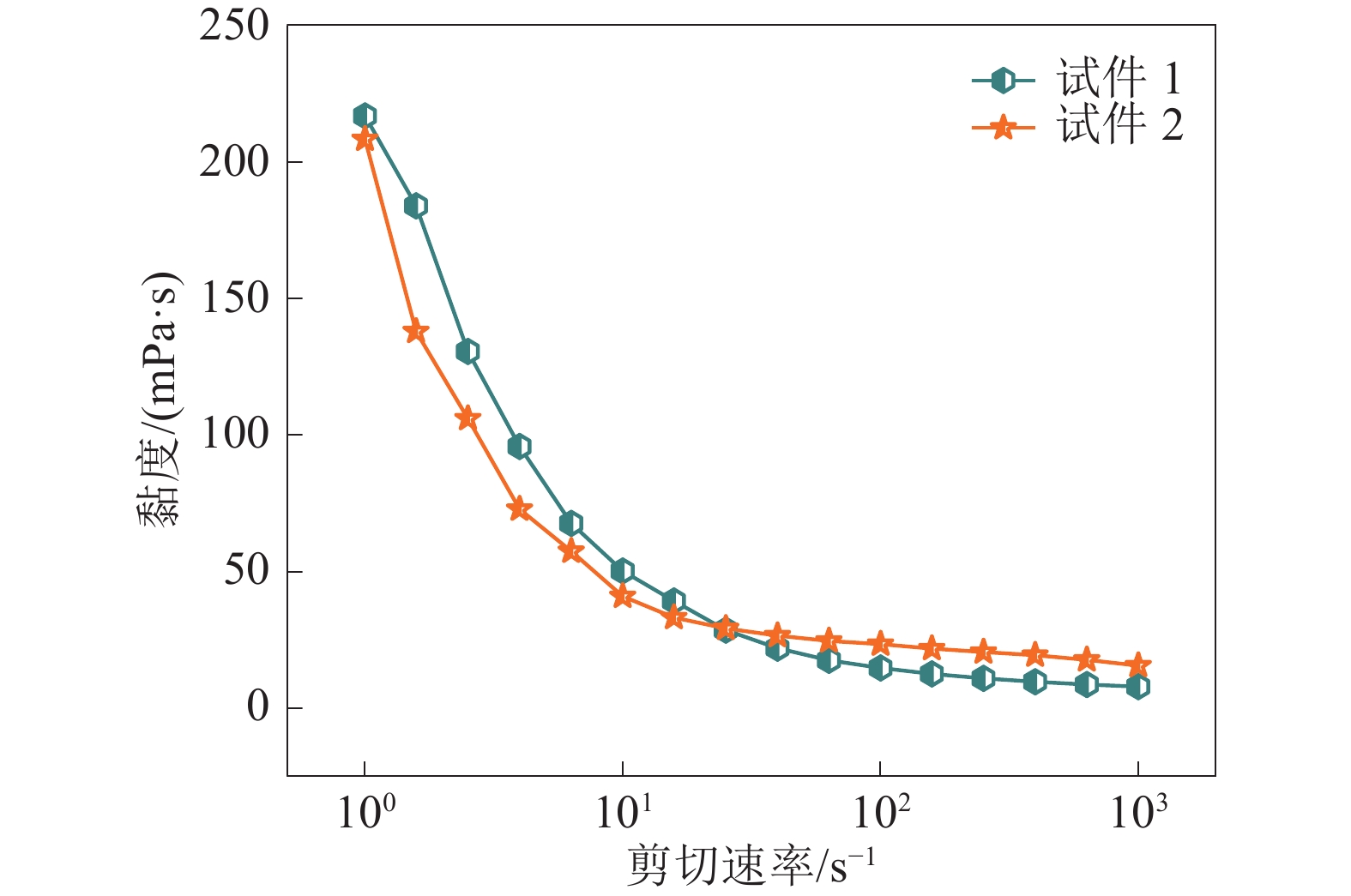
序号 水灰比 SF掺量/% PCS掺量/% 1 1.4∶1.0 35% 0.1% 2 1.4∶1.0 35% 0.2% 3 1.4∶1.0 35% 0.3% 4 1.4∶1.0 35% 0.4% 5 1.4∶1.0 35% 0.5% 6 0.6∶1.0 35% 0.3% 7 1.0∶1.0 35% 0.3% 8 1.4∶1.0 35% 0.3% 9 1.8∶1.0 35% 0.3% 10 2.0∶1.0 35% 0.3% 11 1.4∶1.0 25% 0.3% 12 1.4∶1.0 30% 0.3% 13 1.4∶1.0 35% 0.3% 14 1.4∶1.0 40% 0.3% 15 1.4∶1.0 45% 0.3% 注:SF掺量及PCS掺量为水泥质量分数。 表 2 综合性能汇总
Table 2 Comprehensive performance summary table
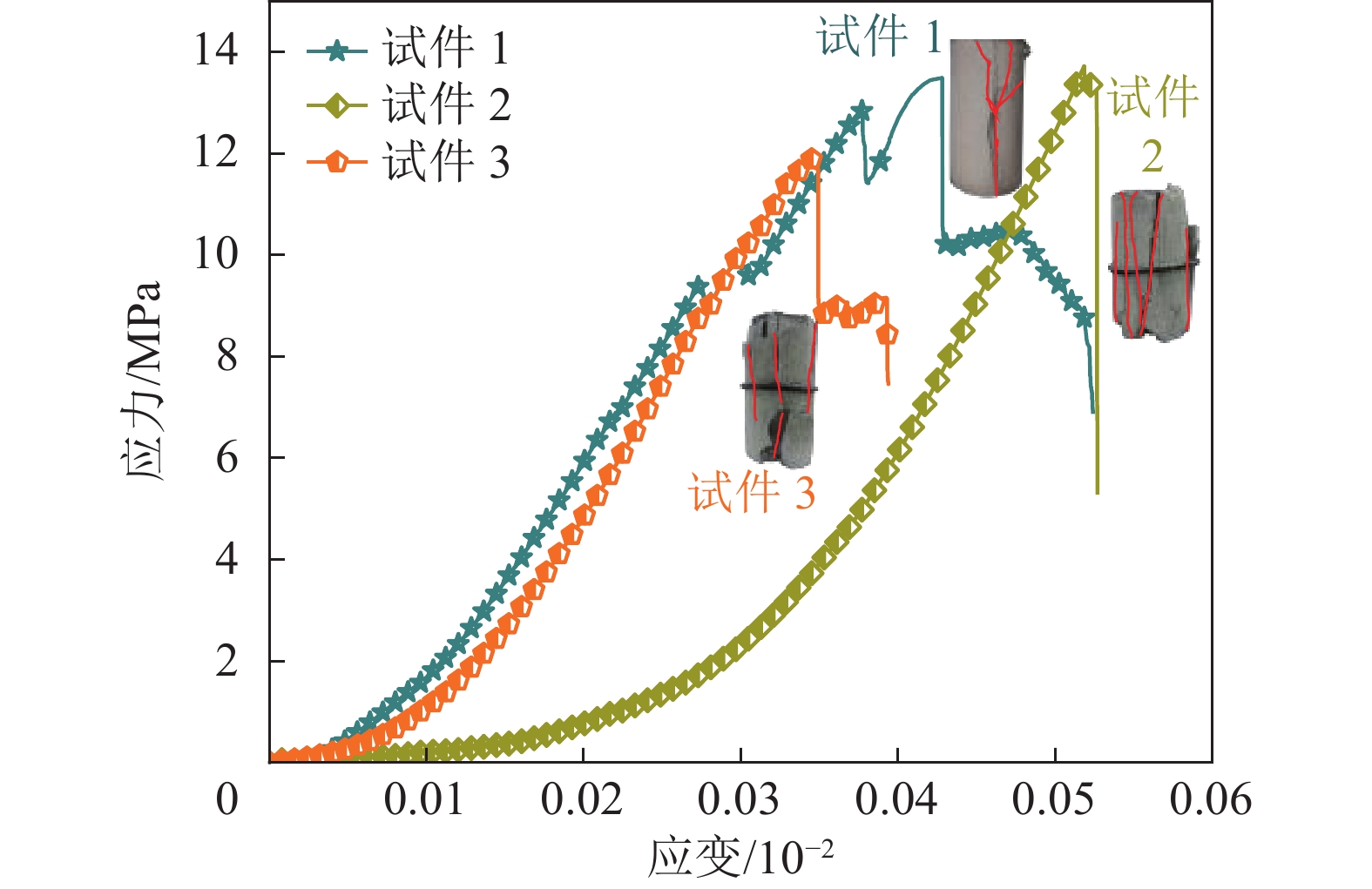
组别 材料配比 黏度/(mPa·s) 泌水率/% 抗压强度/MPa 水灰比 SF掺量/% PCS掺量/% 1 1.4∶1.0 35 0.1 211.51 2 2.59 6 0.6∶1.0 35 0.3 232.88 1 12.8 7 1.0∶1.0 35 0.3 50.13 1 5.09 15 1.4∶1.0 45 0.3 102.89 4 2.39 表 3 RSM设计试验因素与水平
Table 3 Design test factors and levels of RSM
水平 因素 水灰比(A) SF掺量/%(B) PCS掺量/%(C) −1 0.6∶1.0 30 0.2 0 1∶1 35 0.3 +1 1.4∶1.0 40 0.4 表 4 RSM设计方案与试验结果
Table 4 Design scheme and test results of RSM
组号 材料用量 泌水率/% 黏度/(mPa·s) 抗压强度/ MPa 水灰比(A) SF掺量/%(B) PCS掺量/%(C) 1 1.4∶1.0 35 0.2 6 5.283 1.03 2 1.0∶1.0 35 0.3 1 20.872 4.21 3 1.4∶1.0 35 0.4 19 16.721 1.67 4 1.0∶1.0 40 0.2 1 64.220 8.81 5 1.0∶1.0 40 0.4 1 19.294 3.79 6 0.6∶1.0 30 0.3 1 223.120 8.47 7 1.0∶1.0 35 0.3 1 24.125 4.03 8 1.0∶1.0 35 0.3 1 24.087 5.13 9 1.0∶1.0 30 0.2 1 39.169 4.61 10 1.0∶1.0 35 0.3 1 23.396 5.09 11 0.6∶1.0 35 0.4 1 776.000 20.93 12 0.6∶1.0 35 0.2 1 265.810 11.89 13 1.0∶1.0 35 0.3 1 23.034 5.03 14 0.6∶1.0 40 0.3 1 590.970 19.04 15 1.0∶1.0 30 0.4 15 27.298 4.38 16 1.4∶1.0 40 0.3 10 16.638 1.55 17 1.4∶1.0 30 0.3 19 5.138 1.33 表 5 黏度方差分析
Table 5 Analysis of variance of viscosity
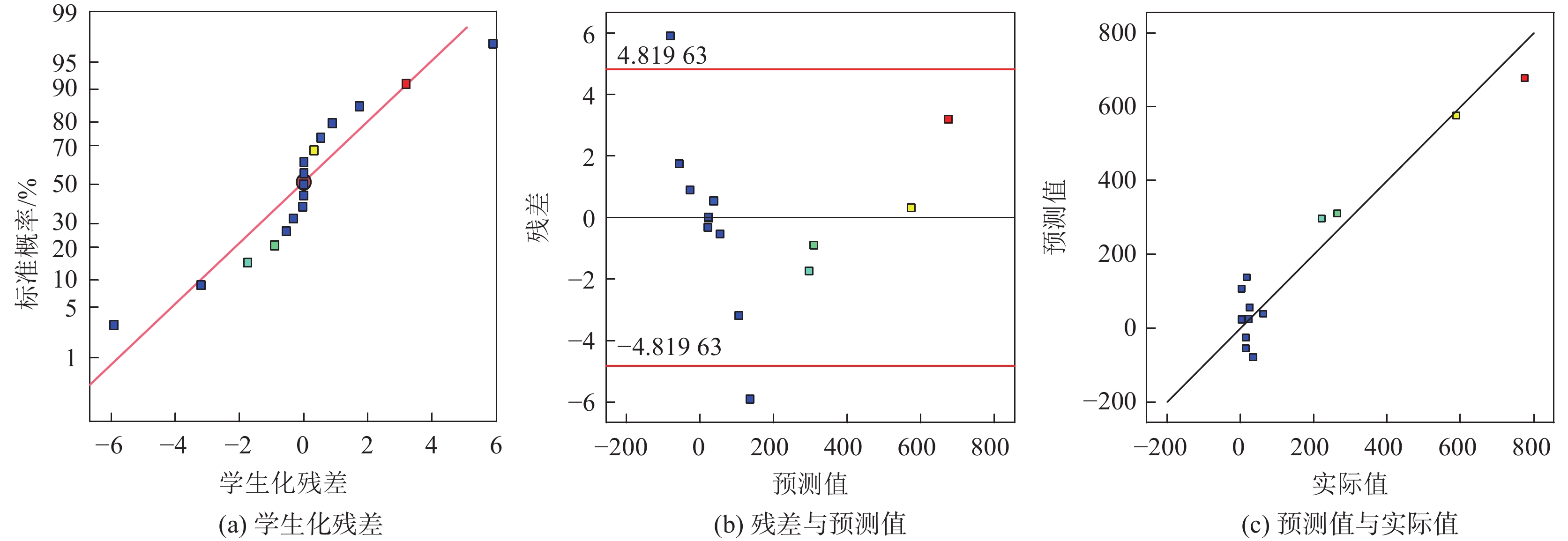
方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方差 F值 P值 显著性 模型 74 1451.67 9 82 383.51 8.91 0.004 4 ** A 410 472.36 1 410472.36 44.41 0.000 3 ** B 19 641.32 1 19 641.32 2.12 0.188 3 C 27 008.48 1 27 008.48 2.92 0.131 1 AB 31 746.33 1 31 746.33 3.43 0.106 3 AC 62 188.38 1 62 188.38 6.73 0.035 7 ** BC 273.16 1 273.16 0.029 6 0.868 4 A2 180 697.55 1 180697.55 19.55 0.003 1 ** B2 1 909.78 1 1 909.78 0.206 6 0.663 2 C2 5 363.19 1 5 363.19 0.580 2 0.471 1 残差 64 706.02 7 9 243.71 失拟项 64 698.94 3 21 566.31 12 183.14 纯误差 7.08 4 1.77 所有项 806 157.69 16 R2 0.919 7 注:*为显著,P<0.05;**为高度显著,P<0.01;***为极完全显著,P<0.001。 表 6 泌水率方差分析
Table 6 Analysis of variance of bleeding rate
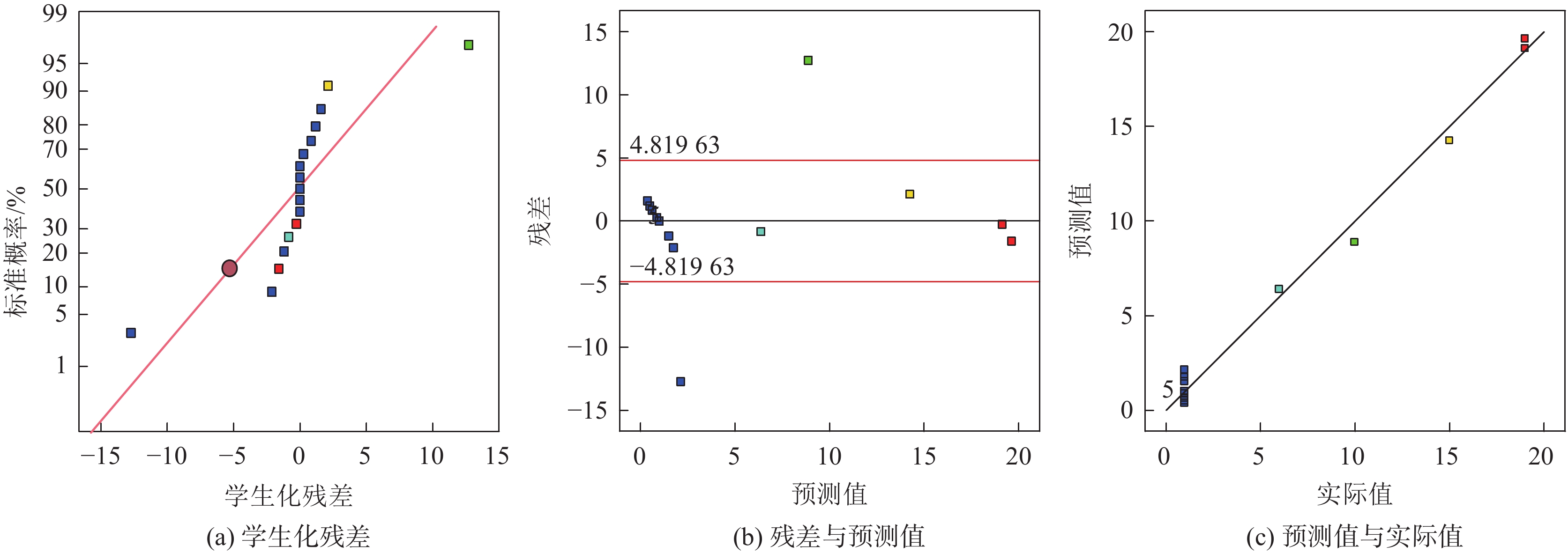
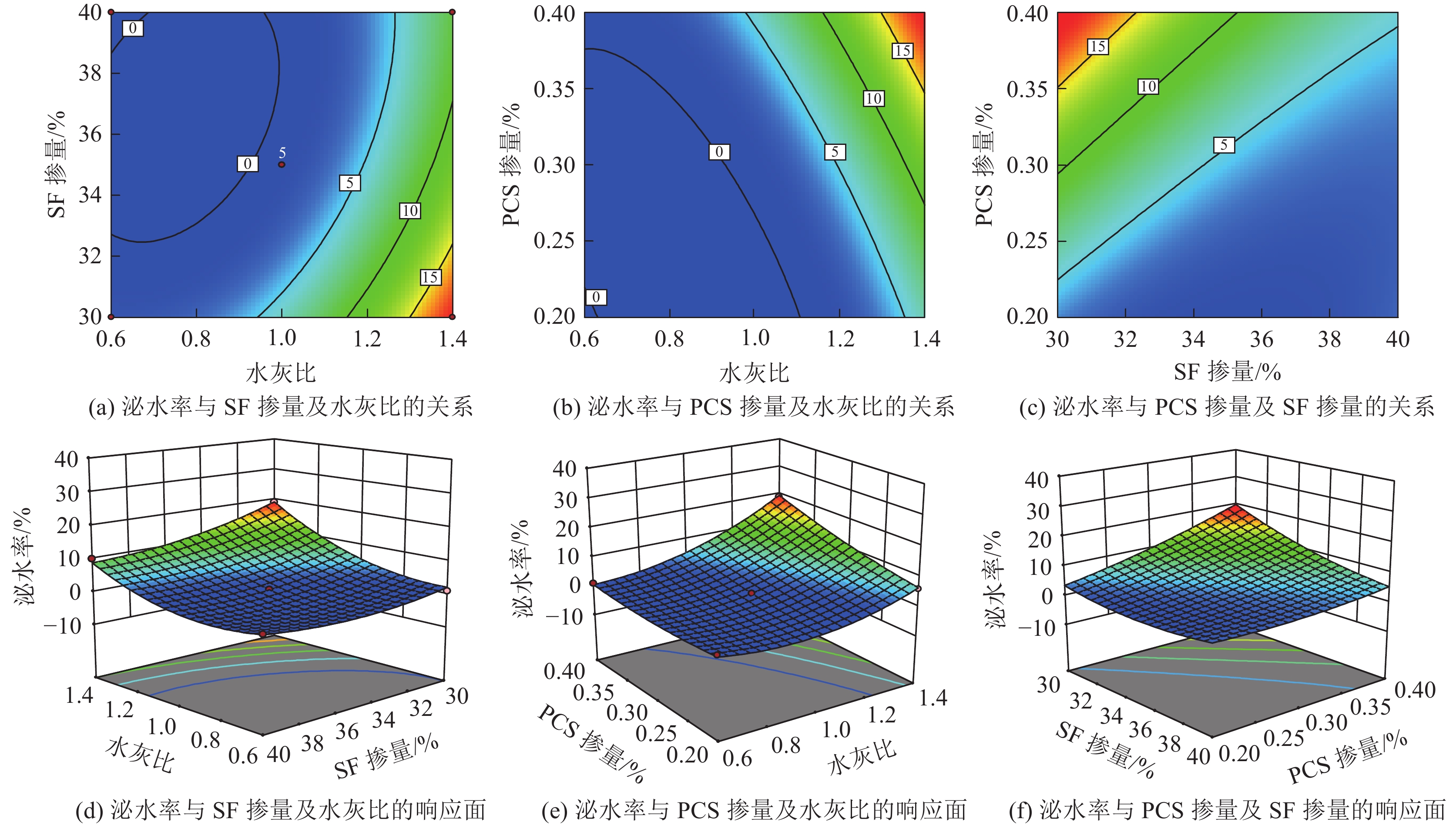
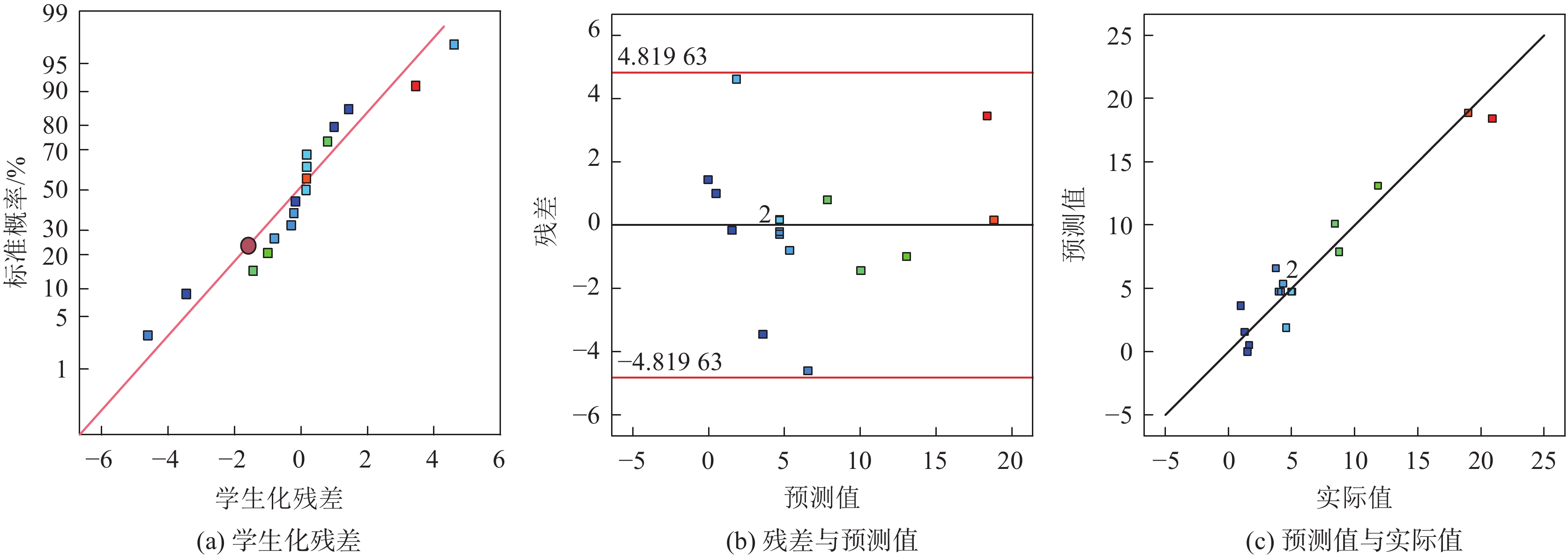
方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方差 F值 P值 显著性 模型 703.81 9 78.20 104.27 <0.000 1 *** A 312.50 1 312.50 416.67 <0.000 1 *** B 66.12 1 66.12 88.17 <0.000 1 *** C 91.13 1 91.13 121.50 <0.000 1 *** AB 20.25 1 20.25 27.00 0.001 3 ** AC 42.25 1 42.25 56.33 0.000 1 ** BC 49.00 1 49.00 65.33 <0.000 1 *** A2 85.26 1 85.26 113.68 <0.000 1 *** B2 21.32 1 21.32 28.42 0.001 1 ** C2 6.58 1 6.58 8.77 0.021 1 * 残差 5.25 7 0.750 失拟项 5.25 3 1.75 12 183.14 纯误差 0 4 0 所有项 708.06 16 R2 0.992 6 注:*为显著,P<0.05;**为高度显著,P<0.01;***为极完全显著,P<0.001。 表 7 UCS方差分析
Table 7 UCS analysis of variance
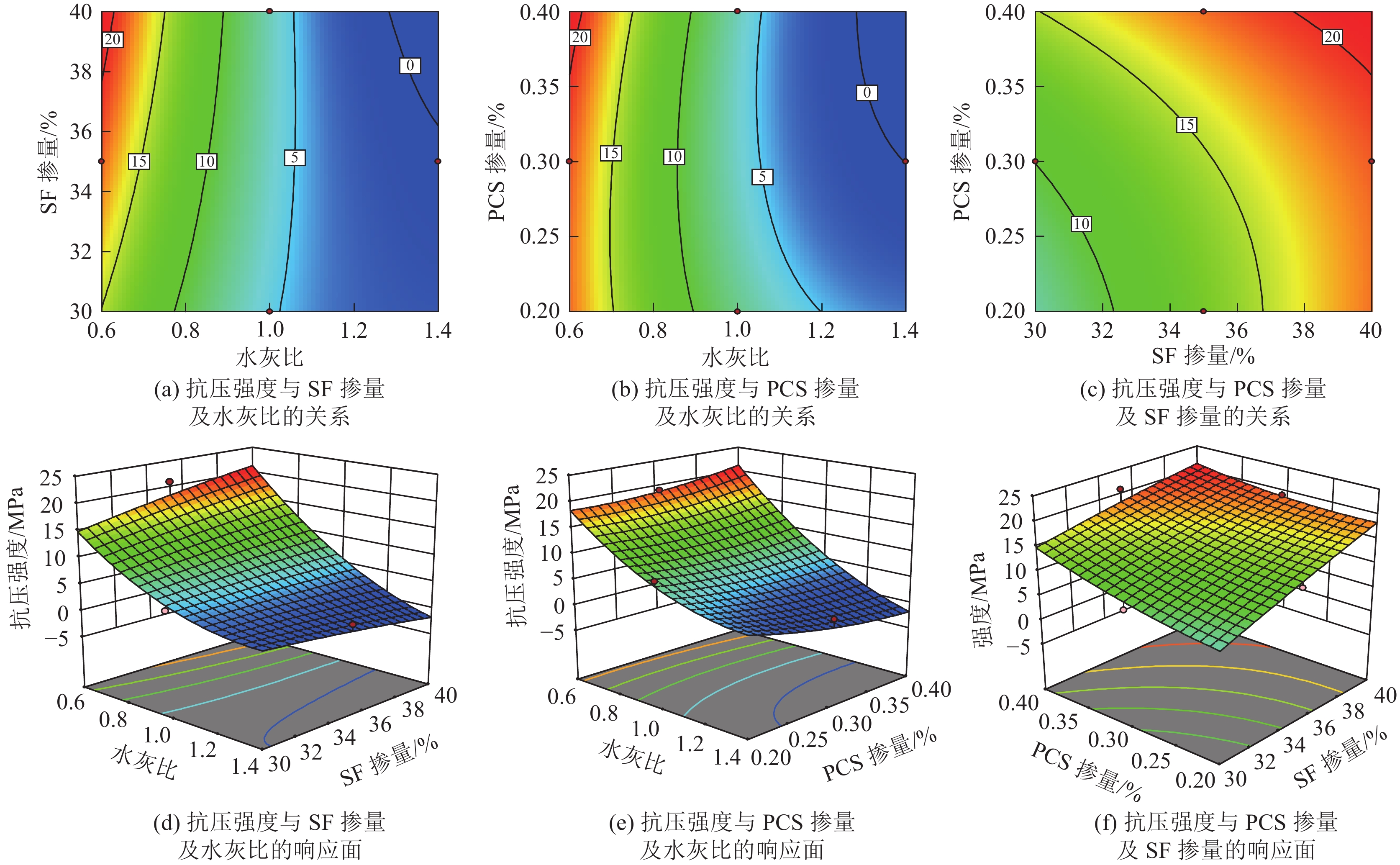
方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方差 F值 P值 显著性 模型 501.93 9 55.77 9.96 0.0031 ** A 374.7 1 374.70 66.95 <0.000 1 *** B 25.92 1 25.92 4.63 0.068 4 C 2.45 1 2.45 0.438 3 0.529 1 AB 26.78 1 26.78 4.79 0.064 9 AC 17.64 1 17.64 3.15 0.119 1 BC 5.74 1 5.74 1.02 0.345 1 A2 42.98 1 42.98 7.68 0.027 6 B2 0.348 0 1 0.348 0 0.062 2 0.810 2 C2 4.17 1 4.17 0.748 8 0.416 7 残差 39.18 7 5.60 失拟项 38.07 3 12.69 46.08 纯误差 1.10 4 0.275 4 所有项 541.11 16 R2 0.927 5 注:*为显著,P<0.05;**为高度显著,P<0.01;***为极完全显著,P<0.001。 -
[1] 张党育. 深部开采矿井水害区域治理关键技术研究及发展[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2017,45(8):8−12. ZHANG Dangyu. Research and development on key technology of mine water disaster regional control in deep mine[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2017,45(8):8−12.
[2] 郭文兵,白二虎,张璞,等. 新近系含水层下厚煤层综放安全绿色开采及水资源清洁利用[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(5):30−37. GUO Wenbing,BAI Erhu,ZHANG Pu,et al. Safe and green mining of thick coal seam under Neogene aquifer and clean utilization of water resources[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(5):30−37.
[3] 尹尚先,徐斌,尹慧超,等. 矿井水防治学科基本架构及内涵[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2023,51(7):24−35. YIN Shangxian,XU Bin,YIN Huichao,et al. Basic structure and connotation of mine water prevention and control discipline[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2023,51(7):24−35.
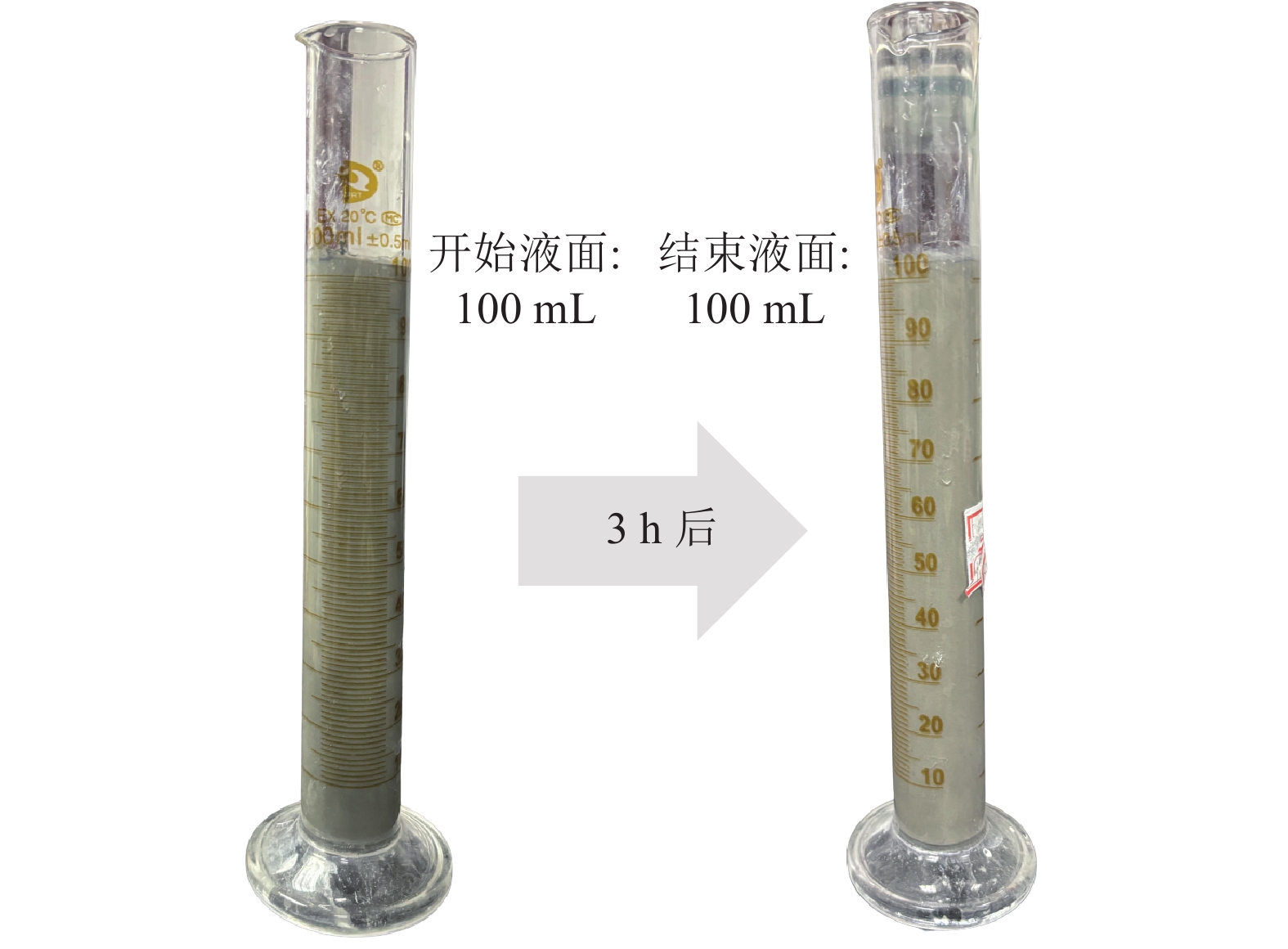
[4] 杨宏飞,王文贞. 开切眼爆破掘进隐伏陷落柱滞后突水灾变规律研究[J]. 矿业安全与环保,2023,50(2):88−92. YANG Hongfei,WANG Wenzhen. Research on catastrophic law of delayed gushing water from subsided karst collapse column in the open−off cut blasting excavation[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection,2023,50(2):88−92.
[5] 曾一凡,武强,杜鑫,等. 再论含水层富水性评价的“富水性指数法”[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(7):2423−2431. ZENG Yifan,WU Qiang,DU Xin,et al. Further research on “water-richness index method” for evaluation of aquifer water abundance[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2020,45(7):2423−2431.
[6] 李术才,李利平,孙子正,等. 超长定向钻注装备关键技术分析及发展趋势[J]. 岩土力学,2023,44(1):1−30. LI Shucai,LI Liping,SUN Zizheng,et al. Key technology analysis and development trend of the equipment for ultra-long directional drilling and grouting[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2023,44(1):1−30.
[7] ZENG Y F,MENG S H,WU Q,et al. Ecological water security impact of large coal base development and its protection[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2023,619:129319. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2023.129319
[8] 曾一凡,刘晓秀,武强,等. 双碳背景下“煤−水−热”正效协同共采理论与技术构想[J]. 煤炭学报,2023,48(2):538−550. ZENG Yifan,LIU Xiaoxiu,WU Qiang,et al. Theory and technical conception of coal-water-thermal positive syner-gistic co-extraction under the dual carbon background[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2023,48(2):538−550.
[9] 黄选明,张雁,王明星,等. 我国露天煤矿截水帷幕关键技术进展[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2022,50(7):1−9. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.21.12.0766 HUANG Xuanming,ZHANG Yan,WANG Mingxing,et al. Key technical progress of water cutoff curtain technology in open-pit coal mines in China[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2022,50(7):1−9. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.21.12.0766
[10] 国家煤矿安全监察局. 煤矿防治水细则[M]. 北京:煤炭工业出版社,2018:1−2. [11] 陈军涛,李昊,贾东秀,等. 流固耦合作用下含不同长度裂隙灰岩注浆加固特性试验研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2024,52(3):189−199. CHEN Juntao,LI Hao,JIA Dongxiu,et al. Experimental study on grouting reinforcement characteristics of limestone with different length cracks under fluid solid coupling[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2024,52(3):189−199.
[12] 席恺. 纳米硅溶胶−超细水泥基浆液的性能研究[D]. 青岛:山东科技大学,2019:1−2. XI Kai. Study on the grouting performance of nanometer silica sol-ultrafine cement based slurry[D]. Qingdao:Shandong University of Science and Technology,2019:1−2.
[13] YU W J,ZHOU M J,WAN X, et al. Experimental study on physical properties of superfine cement grouting material[J]. Frontiers in Materials,2023:1056135.
[14] 刘江峰,王锐,孟庆彬,等. 超细水泥生产工艺、性能及工程应用研究进展[J]. 硅酸盐通报,2023,42(5):1519−1528. LIU Jiangfeng,WANG Rui,MENG Qingbin,et al. Research progress on production technology,properties and engineering application of superfine cement[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2023,42(5):1519−1528.
[15] 万幸. 超细水泥注浆材料性能特征及加固效应[D]. 湘潭:湖南科技大学,2022:57−58. WAN Xing. Performance characteristics and reinforcement effect of ultra-fine cement grouting material[D]. Xiangtan:Hunan University of Science and Technology,2022:57−58.
[16] 廖国胜,徐路,廖宜顺. 硅灰对硫铝酸盐水泥水化行为的影响机理[J]. 建筑材料学报,2017,20(6):840−845. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2017.06.003 LIAO Guosheng,XU Lu,LIAO Yishun. Influence of silica fume on the hydration behavior of calcium sulphoaluminate cement[J]. Journal of Building Materials,2017,20(6):840−845. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2017.06.003
[17] JUN Y B,KIM J,KIM T. Hydration of calcium sulfoaluminate-based binder incorporating red mud and silica fume[J]. Applied Sciences,2019,9(11):2270. doi: 10.3390/app9112270
[18] HAKEEM I Y,AMIN M,ZEYAD A M,et al. Properties and durability of self-compacting concrete incorporated with nanosilica,fly ash,and limestone powder[J]. Structural Concrete,2023,24(5):6738−6760. doi: 10.1002/suco.202300121
[19] 李标,马芹永,张发. 超细矿渣粉与硅灰对水泥基注浆材料性能影响机理分析[J]. 硅酸盐通报,2022,41(12):4343−4352. LI Biao,MA Qinyong,ZHANG Fa. Influence mechanism analysis of ultrafine ground granulated blast furnace slag and silica fume on properties of cement-based grouting material[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2022,41(12):4343−4352.
[20] AVCI E. Silica fume effect on engineering properties of superfine cement-grouted sands[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering,2019,31(11):04019269. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0002928
[21] 张晋霞,牛福生. 响应曲面法优化赤铁矿絮凝体浮选行为研究[J]. 矿产综合利用,2021(3):22−26,38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.03.004 ZHANG Jinxia,NIU Fusheng. Optimization of hematite floc flotation behavior by response surface method[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources,2021(3):22−26,38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.03.004
[22] 郑伯坤. 基于响应面分析法的全尾砂絮凝沉降试验及参数优化研究[J]. 矿业研究与开发,2022,42(7):30−34. ZHENG Bokun. Study on flocculation settling test and parameter optimization of total tailings based on response surface analysis[J]. Mining Research and Development,2022,42(7):30−34.
[23] 周华强,侯朝炯,孙希奎,等. 固体废物膏体充填不迁村采煤[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2004,33(2):154−158,177. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1964.2004.02.007 ZHOU Huaqiang,HOU Chaojiong,SUN Xikui,et al. Solid waste paste filling for none-village-relocation coal mining[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,2004,33(2):154−158,177. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1964.2004.02.007
[24] 王域骁. 改性超细水泥注浆材料的性能试验研究[D]. 重庆:重庆交通大学,2019:14−15. WANG Yuxiao. Experimental study on properties of modified microfine cement grouting materials[D]. Chongqing:Chongqing Jiaotong University,2019:14−15.
[25] 李相辉,张庆松,张霄,等. 水泥浆析水性能试验研究[J]. 建筑材料学报,2018,21(1):8−14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2018.01.002 LI Xianghui,ZHANG Qingsong,ZHANG Xiao,et al. Research on water-bleeding property of cement slurry[J]. Journal of Building Materials,2018,21(1):8−14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2018.01.002
[26] 王凯. 深井微裂隙软岩高压注浆渗流特性及应用研究[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2020:15−16. WANG Kai. Study on the seepage characteristics and application of high pressure grouting in micro-fractured soft rock under deep mine[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2020:15−16.
[27] 赵建强. 基于响应面法的高强混凝土配比试验研究[J]. 铁道建筑技术,2023(5):35−40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4539.2023.05.009 ZHAO Jianqiang. Experimental study on mixture ratio of high-strength concrete based on response surface method[J]. Railway Construction Technology,2023(5):35−40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4539.2023.05.009
[28] JUENGER M,SIDDIQUE R. Recent advances in understanding the role of supplementary cementitious materials in concrete[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,2015,78:71−80. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2015.03.018
[29] LIN R,WANG X,ZHANG G. Effects of quartz powder on the microstructure and key properties of cement paste[J]. Sustainability,2018,10(10):1−16.
[30] 李新宇,方坤河. 硅粉对硬化水泥浆体微结构的影响的研究进展[J]. 硅酸盐通报,2003(1):54−58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1625.2003.01.012 LI Xinyu,FANG Kunhe. Research progress on the effect of silica powder on the microstructure of hardened cement slurry[J]. Silicate Bulletin,2003(1):54−58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1625.2003.01.012
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(4)




 下载:
下载: