Coal pillar burst mechanism and prevention based on local mine stiffness (LMS) criterion
-
摘要:
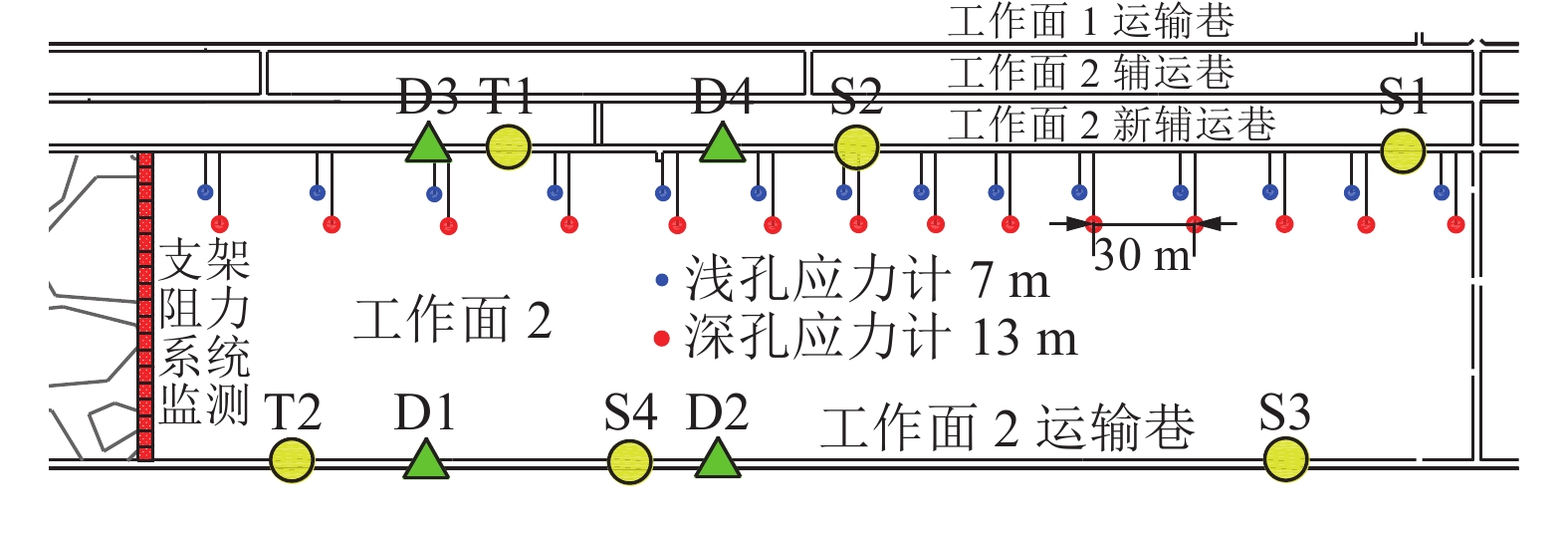
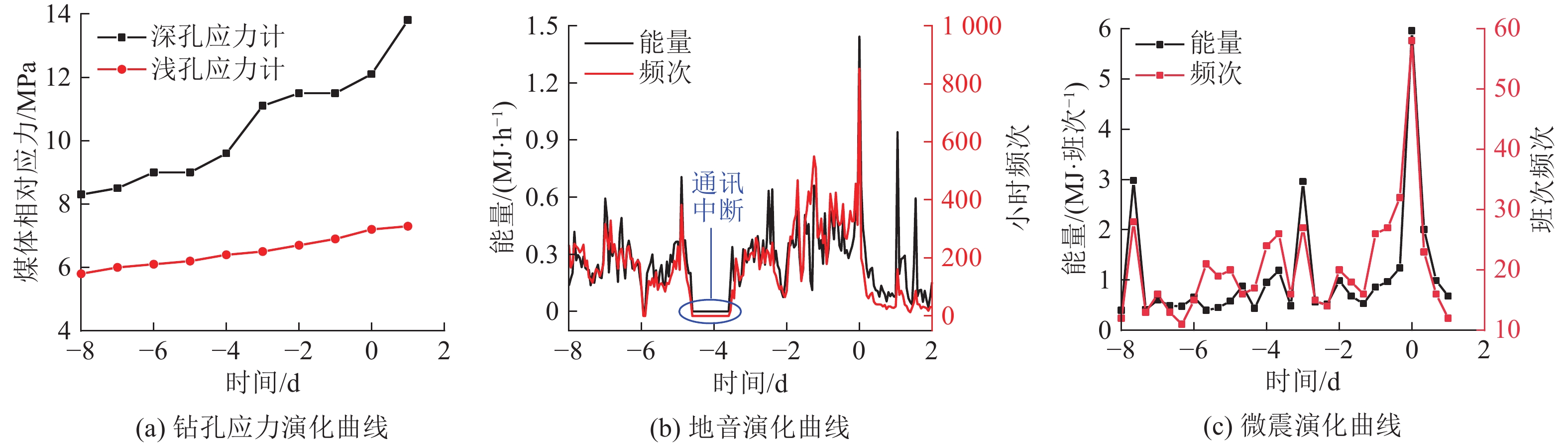
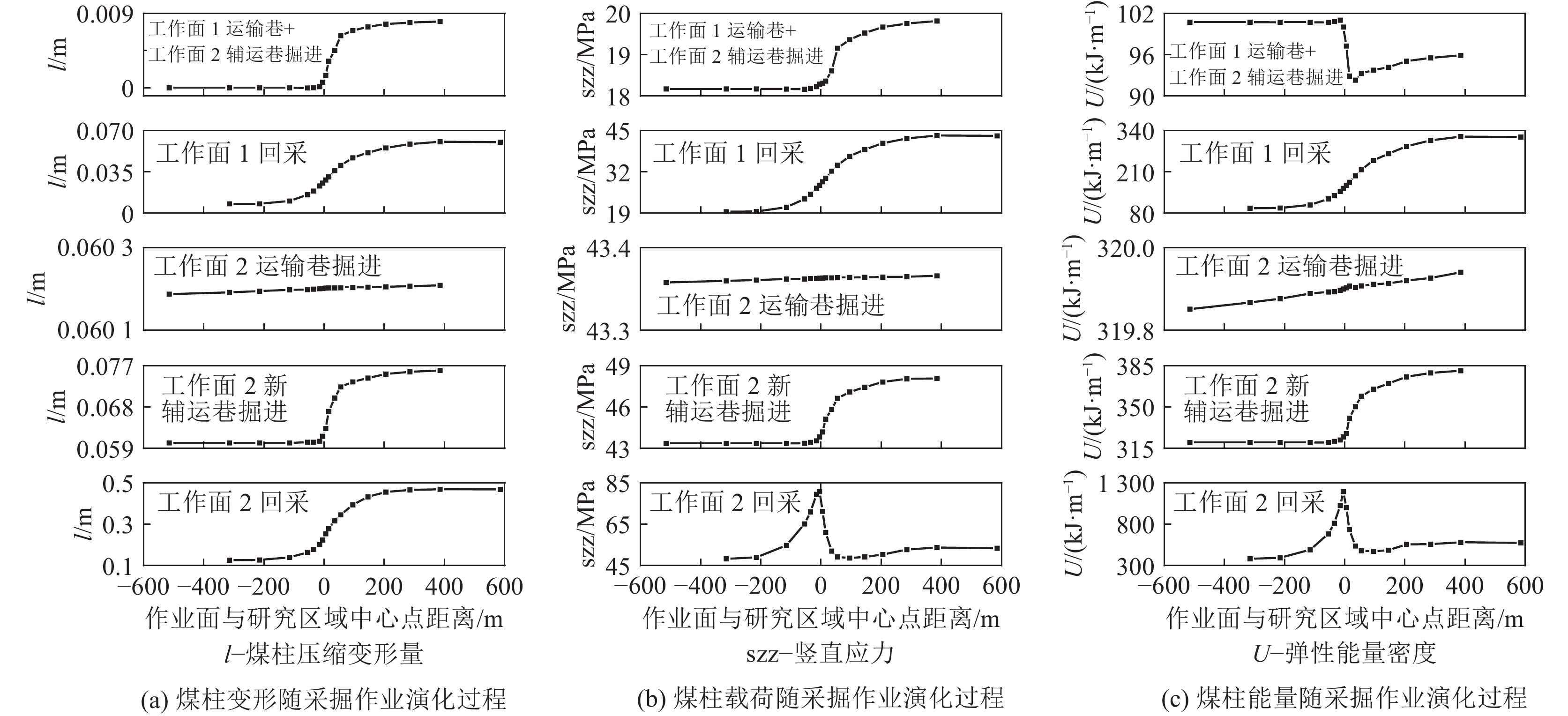
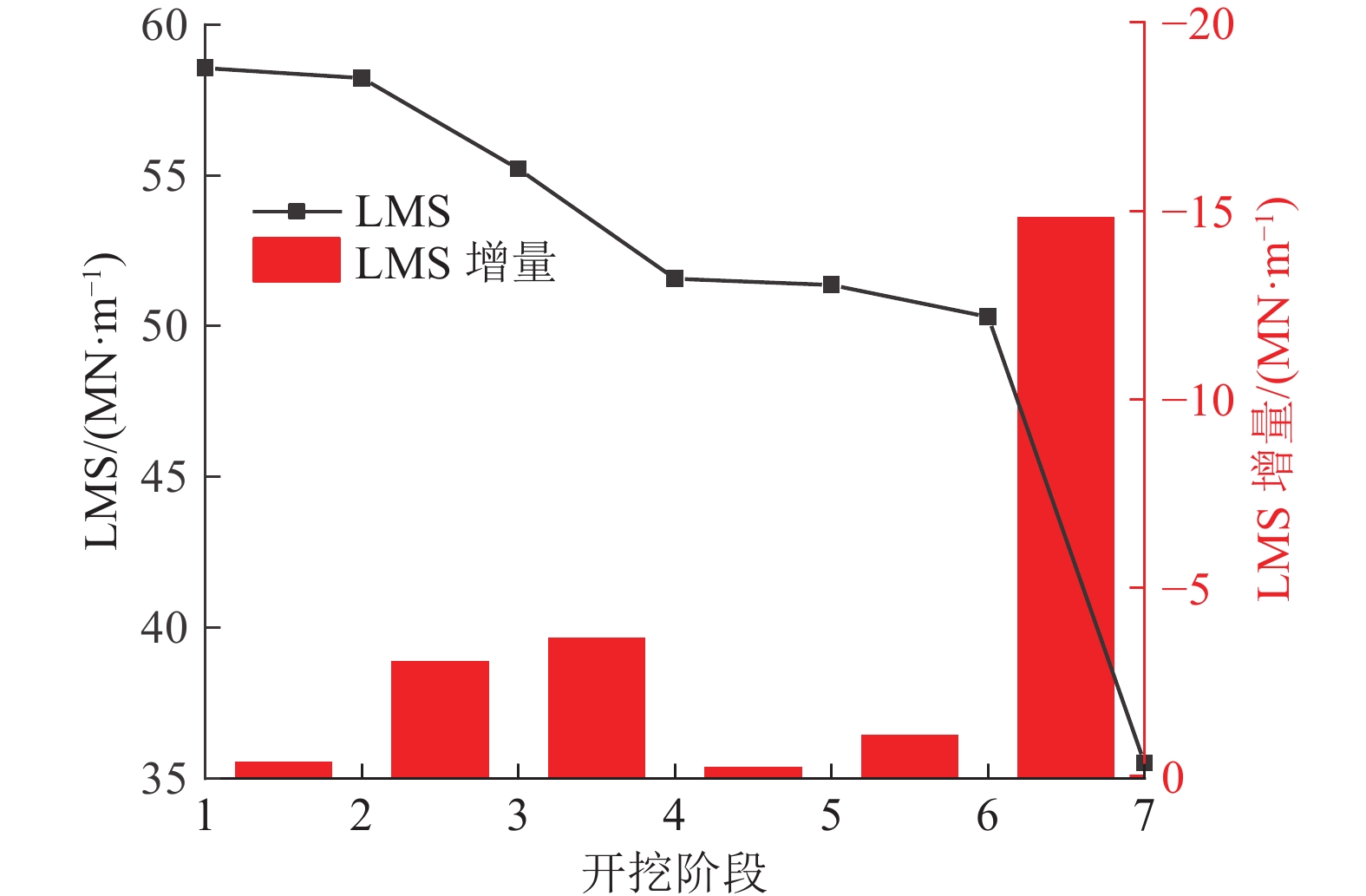
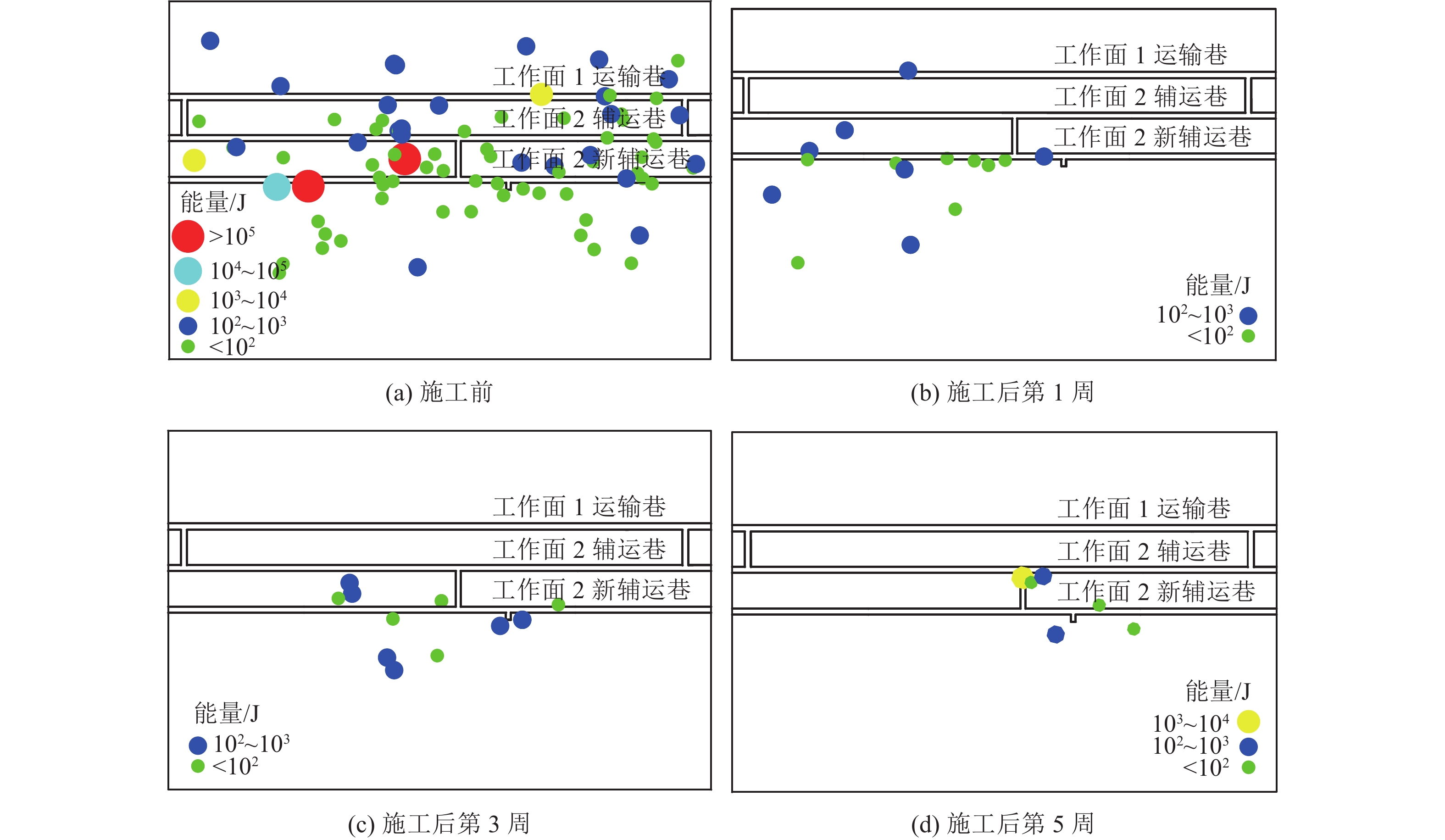
冲击地压频发严重威胁煤炭资源安全高效回收,冲击地压机理研究是预测预警和灾害防治的基础。针对某矿井应力环境稳定且未受到动载影响的条件下发生的冲击事件,引入局部矿井刚度(LMS)概念,并以该矿井冲击事件高发区域为工程背景,综合运用数值分析和现场实测等方法,分析复杂采掘布置条件下大空间尺度采掘作业过程中煤柱力学响应规律,并考察该过程中局部矿井刚度演化。指出采掘作业导致局部矿井刚度降低,煤层及其顶底板系统中能量快速积累,超过煤柱破坏所需能量,在失稳瞬间迅速释放造成煤柱冲击破坏,并对比分析随工作面推进局部矿井刚度演化与现场地音及微震实测数据。基于煤柱冲击破坏机理,结合该矿生产实际,采用大直径钻孔弱化煤体,降低冲击危险性,并以实测微震数据验证防冲效果。研究表明:①煤柱变形、载荷及弹性能量积累随采掘作业整体呈增长趋势,但LMS呈降低趋势,采出空间尺寸及其与研究区域间距离是主要影响因素,LMS对工作面回采响应程度显著大于巷道掘进,工作面回采对LMS降低显著影响范围是巷道掘进的3.67倍,单位推进距离下LMS降幅是巷道掘进的6.41倍。②随工作面推进LMS演化与现场地音及微震数据的良好对应关系,表明煤层回采导致LMS降低直接影响煤柱破坏方式,煤层及其顶底板系统中能量随LMS降低而快速积累,在煤柱承载能力降低时迅速释放,致使煤柱发生冲击破坏。③采用大直径钻孔弱化煤体后,微震能量及频次均显著降低,表明大直径钻孔破坏该区域煤体,降低煤柱峰后刚度,冲击危险性降低。
Abstract:The frequent occurrence of coal burst seriously threatens the safe and efficient recovery of coal resources. The research on the mechanism of coal burst is the basis of prediction and disaster prevention. Aiming at the coal burst event under the condition that the stress environment is stable and not affected by dynamic load, the concept of local mine stiffness (LMS) is introduced. Taking the mining area with complex mining layout of the mine as the engineering background, the mechanical response of coal pillar in the process of large-scale mining is analyzed by comprehensively using numerical analysis and field measurement, The evolution of LMS in this process is investigated. It is pointed out that the mining leads to the reduction of LMS, the rapid accumulation of energy in the coal seam and its roof and floor system, and the rapid release of energy when the coal pillar is unstable, resulting in impact damage. The engineering verification is carried out by comparing the evolution of LMS with the mining and the field measured ground sound and microseismic data. The research shows that:①the deformation, load and elastic energy accumulation of coal pillar increase with the overall mining operation, but the LMS decreases. The mining space size and the distance between the mining space and the research area are the main influencing factors. The response degree of the two to the mining of the working face is significantly greater than that of the roadway excavation. The significant influence range of the mining of the working face on the LMS reduction is 3.67 times that of the roadway excavation, and the LMS reduction under the unit advancing distance is 6.41 times that of the roadway excavation.②The good correspondence between the evolution of local mine stiffness with the advancement of the working face and the on-site ground sound and microseismic data indicates that the reduction of local mine stiffness caused by coal mining directly affects the failure mode of coal pillars. The energy in the coal seams and their roof and floor systems accumulates rapidly with the reduction of local mine stiffness and is released rapidly when the bearing capacity of coal pillars decreases, resulting in impact damage. ③After using large-diameter drilling to weaken the coal body, the microseismic energy and frequency are significantly reduced, indicating that large-diameter drilling destroys the coal body in this area, reduces its post peak stiffness, and effectively realizes the impact prevention effect.
-
-
表 1 数值模型岩层参数
Table 1 Numerical model rock parameters
层位 厚度/m 体积模量/
GPa剪切模量/
GPa黏聚力/
MPa抗拉强
度/MPa底板 30 2.2 0.8 1.6 1.0 煤层 5 2.1 0.7 1.5 0.8 直接顶 10 2.6 0.9 1.9 1.2 关键层 40 5.4 4.8 6.2 1.8 覆岩 150 2.5 0.8 1.6 1.0 -
[1] 鞠文君,卢志国,高富强,等. 煤岩冲击倾向性研究进展及综合定量评价指标探讨[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2021,40(9):1839−1856. JU Wenjun,LU Zhiguo,GAO Fuqiang,et al. Research progress and comprehensive quantitative evaluation index of coal rock bursting liability[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2021,40(9):1839−1856.
[2] 康红普. 煤炭开采与岩层控制的空间尺度分析[J]. 采矿与岩层控制工程学报,2020,2(2):1−26. KANG Hongpu. Spatial scale analysis on coal mining and strata control technologies[J]. Journal of Mining and Strata Control Engineering,2020,2(2):1−26.
[3] 窦林名,王永忠,卢方舟,等. 急倾斜特厚煤层冲击地压防治探索与总结[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2024,52(1):84−94. doi: 10.12438/cst.2023-1700 DOU Linming,WANG Yongzhong,LU Fangzhou,et al. Exploration and summary of prevention and control of rock burst in steeply inclined and ultra-thick coal seam[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2024,52(1):84−94. doi: 10.12438/cst.2023-1700
[4] 陆 闯,王元杰,陈法兵,等. 基于地音监测技术的多类型冲击地压前兆特征研究[J]. 采矿与岩层控制工程学报,2023(1):85−93. LU Chuang,WANG Yuanjie,CHEN Fabing,et al. Study on the precursor characteristics of rockbursts based on acoustic emission monitoring technology[J]. Journal of Mining and Strata Control Engineering,2023(1):85−93.
[5] 曹安业,王常彬,杨 旭,等. 微震定位精度影响下采场裂隙表征与冲击地压预警[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2024,52(2):1−9. doi: 10.12438/cst.2023-1968 CAO Anye,WANG Changbin,YANG Xu,et al. Fractures characterization in mining field considering seismic location accuracy and its application on pre-warning coal burst hazards[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2024,52(2):1−9. doi: 10.12438/cst.2023-1968
[6] 朱小景,潘一山,齐庆新,等. 矿震诱发巷道冲击地压力学机制及判别准则研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2024,41(3):493−503. ZHU Xiaojing,PAN Yishan,QI Qingxin,et al. Study on mechanical mechanism and criterion of roadway rockburst induced by mine earthquake[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2024,41(3):493−503.
[7] 潘俊锋,闫耀东,马宏源,等. 一次成孔300 mm煤层大直径钻孔防冲效能试验[J]. 采矿与岩层控制工程学报,2022(5):1−11. PAN Junfeng,YAN Yaodong,MA Hongyuan,et al. Using 300 mm diameter boreholes for coal burst prevention a case study[J]. Journal of Mining and Strata Control Engineering,2022(5):1−11.
[8] 齐庆新,潘一山,李海涛,等. 煤矿深部开采煤岩动力灾害防控理论基础与关键技术[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(5):1567−1584. QI Qingxin,PAN Yishan,LI Haitao,et al. Theoretical basis and key technology of prevention and control of coal-rock dynamic disasters in deep coal mining[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2020,45(5):1567−1584.
[9] 王爱文,范德威,潘一山,等. 基于能量计算的冲击地压巷道三级吸能支护参数确定[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2021,49(6):72−81. WANG Aiwen,FAN Dewei,PAN Yishan,et al. Determination of three-level energy absorbing support parameters in rock burst roadway based on energy calculation[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2021,49(6):72−81.
[10] COOK N G W. The failure of rock[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics & Mining ences & Geomechanics Abstracts,1965,2(4):389−403.
[11] XU Y H,CAI M. Influence of strain energy released from a test machine on rock failure process[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2018,55(6):777−791. doi: 10.1139/cgj-2017-0256
[12] 李东辉,何学秋,陈建强,等. 乌东煤矿近直立煤层冲击地压机制研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2020,49(5):835−843. LI Donghui,HE Xueqiu,CHEN Jianqiang,et al. Inducing mechanism of rockburst occurring in steeply-inclined coal seam of Wudong coal mine[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,2020,49(5):835−843.
[13] 卢志国,鞠文君,高富强,等. 基于非线性储能与释放特征的煤冲击倾向性指标[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2021,40(8):1559−1569. LU Zhiguo,JU Wenjun,GAO Fuqiang,et al. Bursting liability index of coal based on nonlinear storage and release characteristics of elastic energy[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2021,40(8):1559−1569.
[14] 李玉生. 冲击地压机理及其初步应用[J]. 中国矿业学院学报,1985,14(3):42−48. LI Yusheng. Rock burst mechanism and its preliminary application[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,1985,14(3):37−43.
[15] 齐庆新. 层状煤岩体结构破坏的冲击矿压理论与实践研究[D]. 北京:煤炭科学研究总院,1996. QI Qingxin. The theory and practice of rockburst led by structure failure of bedded coal-rock mass[D].Beijing:China Coal Research Institute,1996.
[16] 章梦涛. 冲击地压机理的探讨[J]. 阜新矿业学院学报,1985,4(S1):65−72. ZHANG Mengtao. Discussion on the mechanism of coal burst[J]. Journal of Fuxin Mining Institute,1985,4(S1):65−72.
[17] 潘一山. 煤矿冲击地压扰动响应失稳理论及应用[J]. 煤炭学报,2018,43(8):2091−2098. PAN Yishan. Disturbance reponse instability theory of rockburst incoal mine[J]. Journal of China Coal Socety,2018,43(8):2091−2098.
[18] 潘俊锋,宁宇,毛德兵,等. 煤矿开采冲击地压启动理论[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2012,31(3):586−596. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.03.017 PAN Junfeng,NING Yu,MAO Debing,et al. Theory of rockburst start-up during coal mining[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2012,31(3):586−596. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.03.017
[19] 谭云亮,谭涛,张修峰,等. 正断层两盘动力灾害显现差异性及机制[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2023,51(1):214−223. TAN Yunliang,TAN Tao,ZHANG Xiufeng,et al. Difference and mechanism of dynamic behaviors between two walls of normal fault[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2023,51(1):214−223.
[20] 赵红亮,仇岩,梁海安,等. 地应力环境对深埋硐室岩爆特性影响的数值模拟研究[J]. 采矿与岩层控制工程学报,2023,5(6):063071. ZHAO Hongliang,QIU Yan,LIANG Haian,et al. Numerical study on the influence of in-situ stress environment on rock-burst characteristics in deep-buried chambers[J]. Journal of Mining and Strata Control Engineering,2023,5(6):063071.
[21] 窦林名,陆菜平,牟宗龙,等. 冲击矿压的强度弱化减冲理论及其应用[J]. 煤炭学报,2005,30(6):690−694. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2005.06.003 DOU Linming,LU Caiping,MOU Zonglong,et al. Intensity weakening theory for rockburst and its application[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2005,30(6):690−694. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2005.06.003
[22] DOU L M,MU Z L,LI Z L,et al. Research progress of monitoring,forecasting,and prevention of rockburst in underground coal mining in China[J]. International Journal of Coal Science & Technology,2014,1(3):278−288.
[23] 齐庆新,雷毅,李宏艳,等. 深孔断顶爆破防治冲击地压的理论与实践[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2007,(S1):3522-3527. QIN Qingxin ,LEI Yi,LI Hongyan,et al. Theory and application of prevention of rock burst by break-tip blast in deep hole[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2007,(S1):3522-3527.
[24] 赵善坤,齐庆新,李云鹏,等. 煤矿深部开采冲击地压应力控制技术理论与实践[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(S2):626−636. ZHAO Shankun,QI Qingxin,LI Yunpeng,et al. Theory and practice of rockburst stress control technology in deep coal mine[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2020,45(S2):626−636.
[25] PETUKHOV I M,LINKOV A M. The theory of post-failure deformations and the problem of stability in rock mechanics[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts,1979,16(2):57−76.
[26] SALAMON M D G. Stability,instability and design of pillar workings[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts,1970,7(6):613−631.
[27] KAISER P K,CAI M. Design of rock support system under rockburst condition[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering,2012,4(3):215−227. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1235.2012.00215
[28] JAISWAL A,SHRIVASTVA B K. Stability analysis of the proposed hybrid method of partial extraction for underground coal mining[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences,2012,52:103−111. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2012.03.002
[29] Jaiswal A,Shrivastva B K. Proposed hybrid method of partial extraction[J]. Journal of Scientific and Industrial Research,2009,68(4):307−311.
[30] ADHIKARY D P,SHEN B,DUNCAN FAMA M E. A study of highwall mining panel stability[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences,2002,39(5):643−659. doi: 10.1016/S1365-1609(02)00062-X
[31] GAO F Q,KANG H P,LOU J F,et al. Evolution of local mine stiffness with mining process:insight from physical and numerical modeling[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering,2019,52(10):3947−3958. doi: 10.1007/s00603-019-01798-5
[32] 高富强,原贵阳,娄金福,等. 基于局部矿井刚度理论的冲击地压试验装置研制及应用[J]. 煤炭学报,2023,48(5):1985−1995. GAO Fuqiang,YUAN Guiyang,LOU Jinfu,et al. Development and application of coal burst experiment system based on local mine stiffness theory[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2023,48(5):1985−1995.
[33] 卢志国. 基于局部矿井刚度理论的应变型冲击地压机理研究[D]. 北京:煤炭科学研究总院,2022. LU Zhiguo Study on strainbursts mechanism based on local mine stiffness theory[D].Beijing:China Coal Research Institute,2022.
[34] ZIPF R K. Using a post failure stability criterion in pillar design[C]. Proceedings of the second international workshop on coal pillar mechanics and design,NIOSH IC. 1999,9448:181-192.
[35] 陆闯. 红庆河煤矿冲击地压地音前兆信息识别及预警模型研究[D]. 北京:煤炭科学研究总院,2019. LU Chuang Study on precursor information recognition and warning model of rock burst earth-sound in hongqinghe coal mine[D].Beijing:China Coal Research Institute,2019.
[36] LU Z G,JU W J,GAO F Q,et al. Numerical analysis on the factors affecting post-peak characteristics of coal under uniaxial compression[J]. International Journal of Coal Science & Technology,2024,11(1):2.




 下载:
下载: