Study on the impact force evolution law of coal and gas outburst under high ground stress
-
摘要:
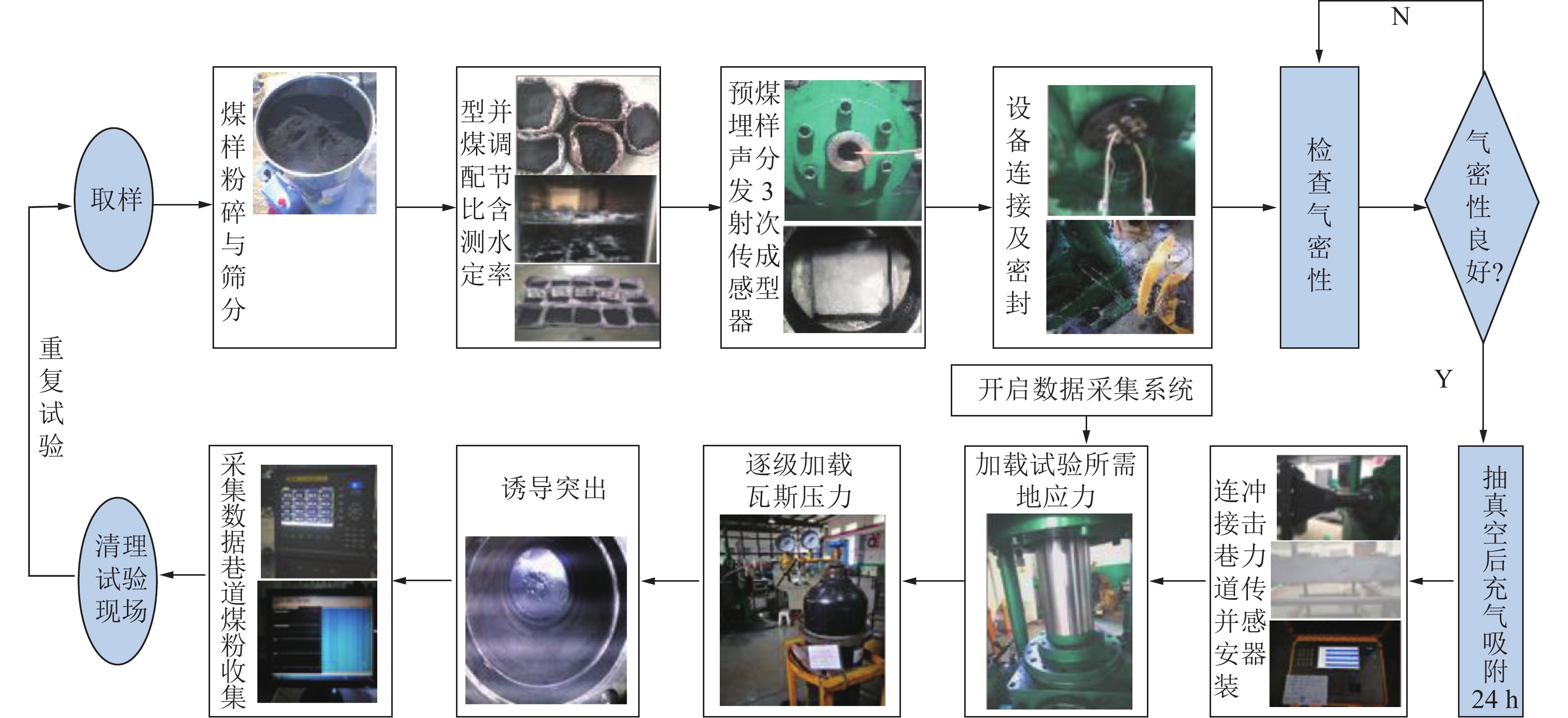
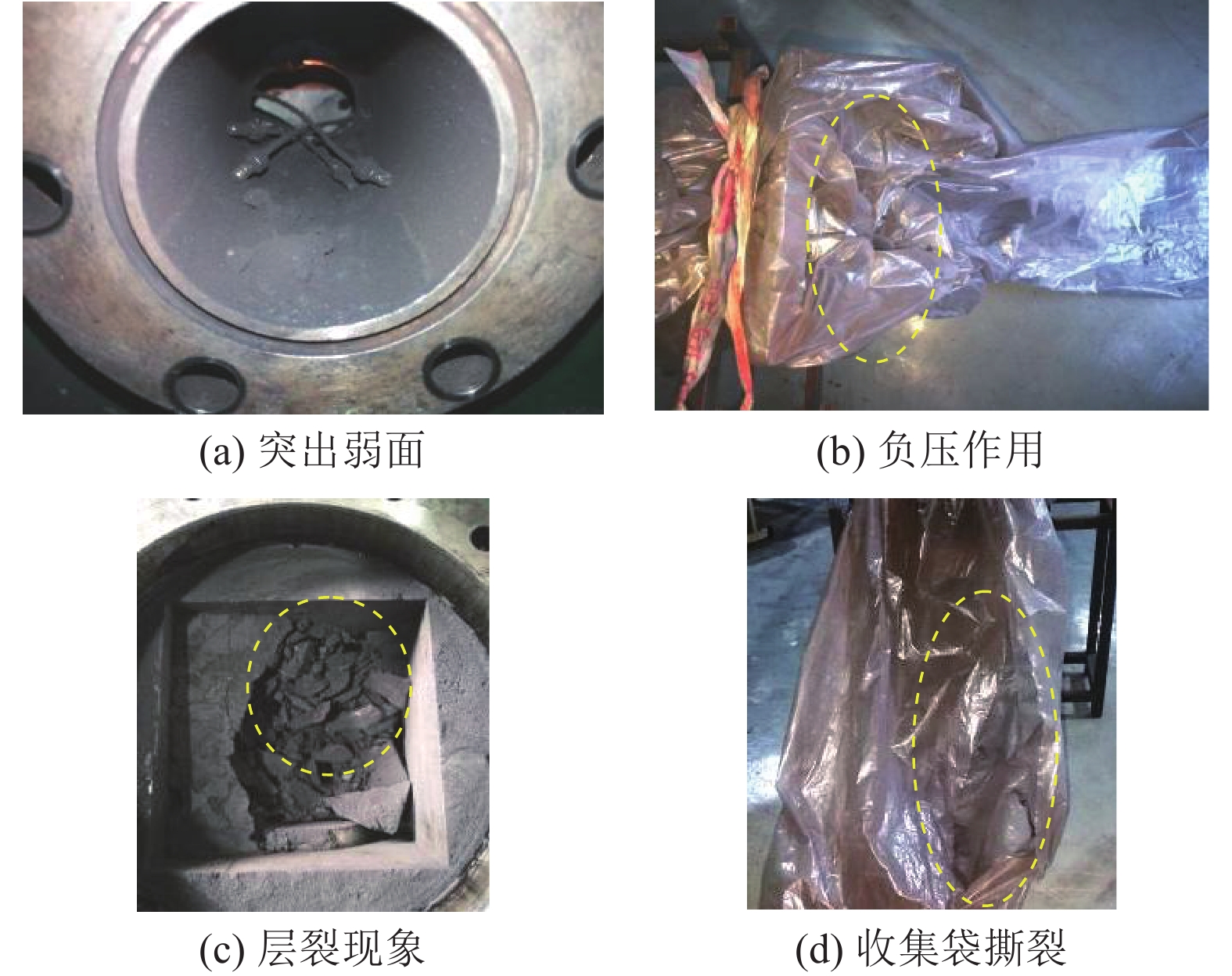
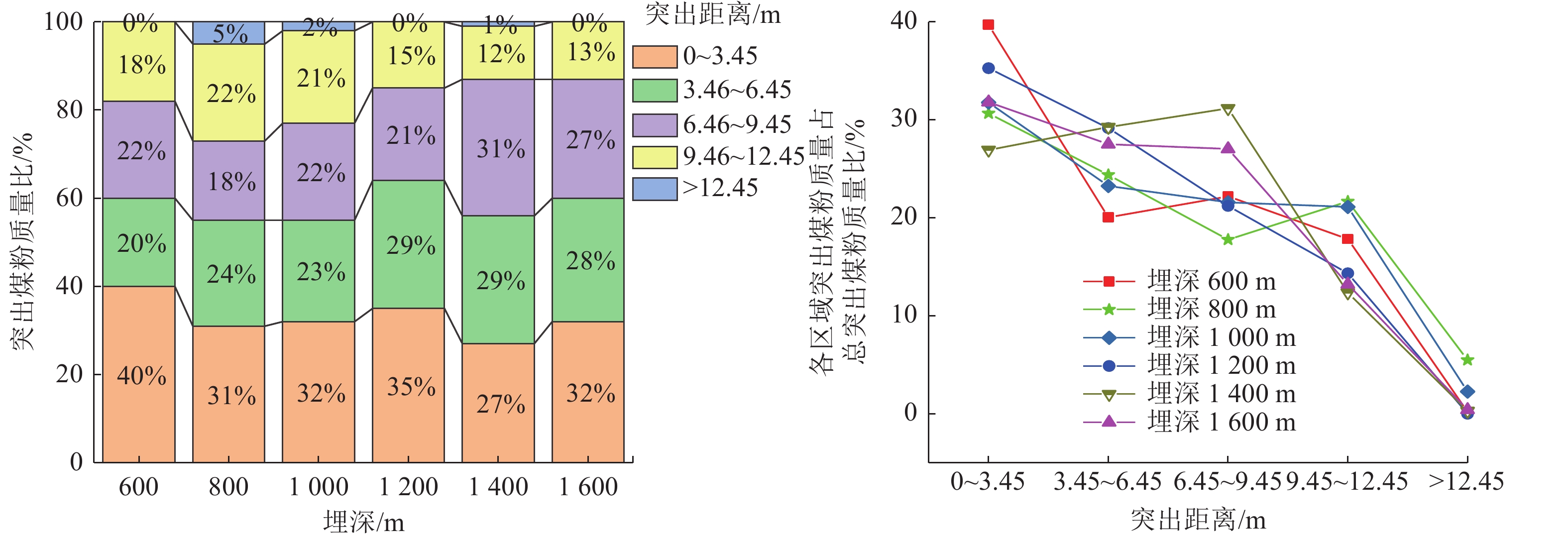
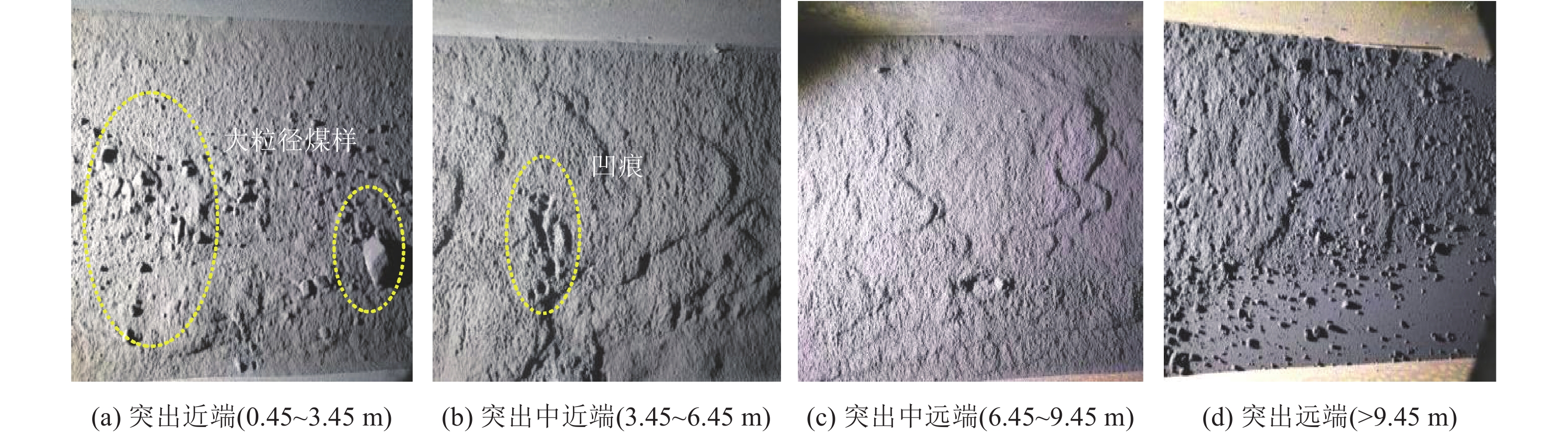
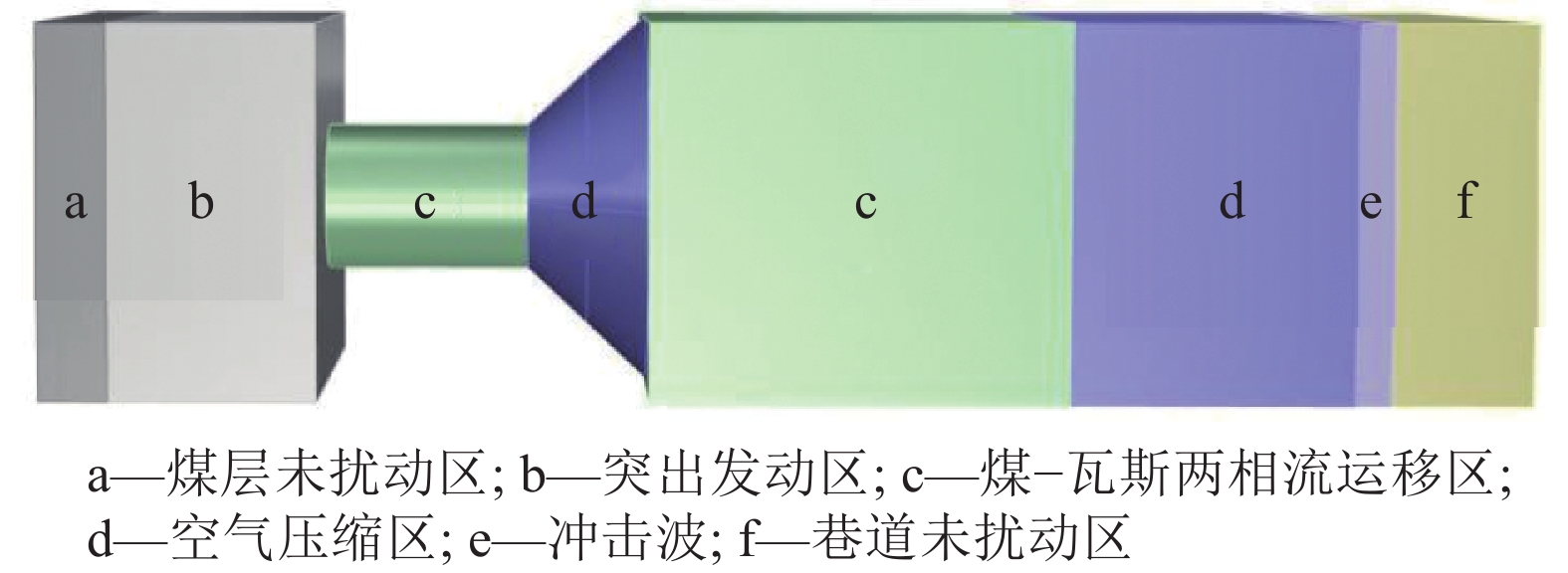
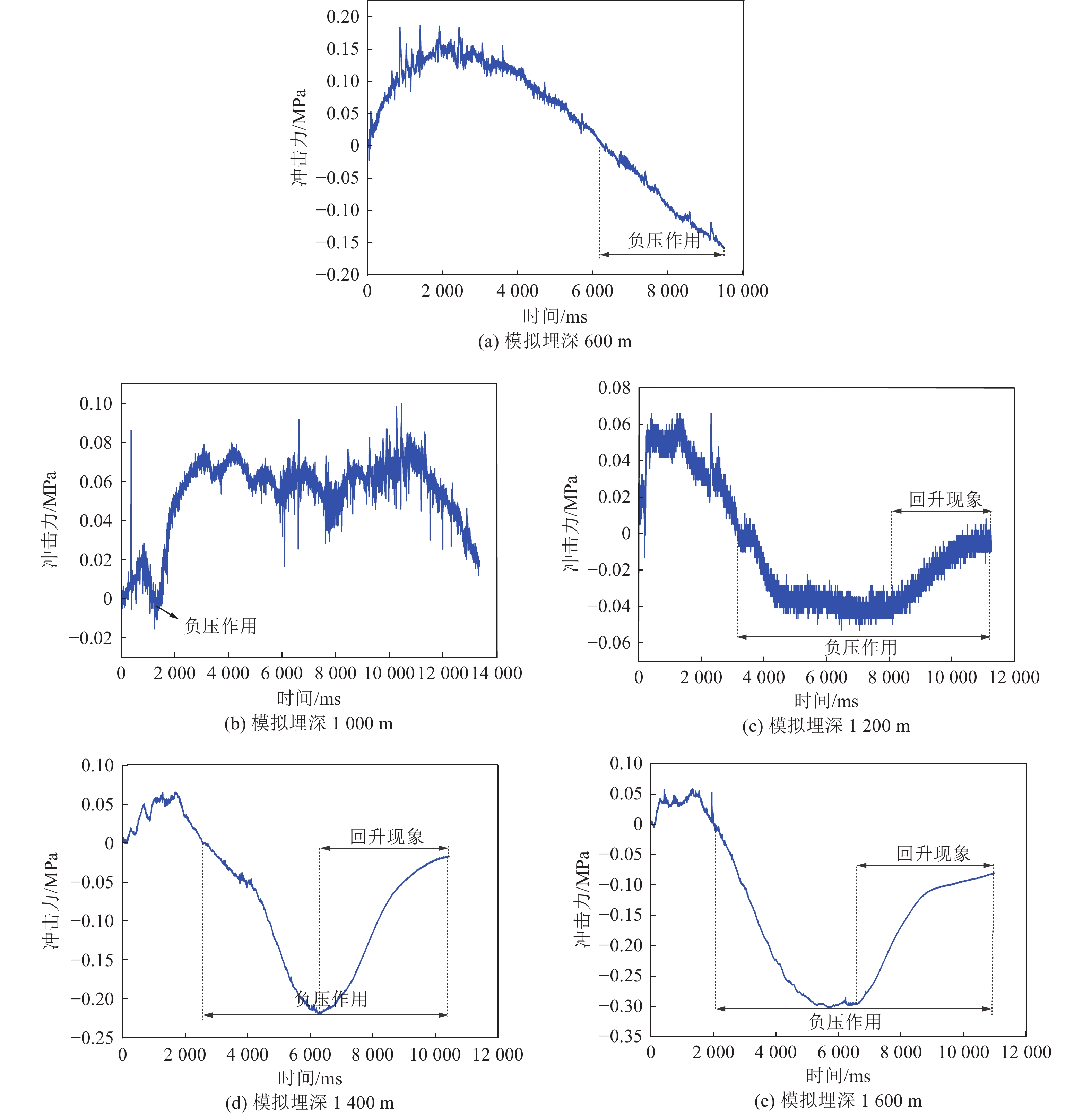
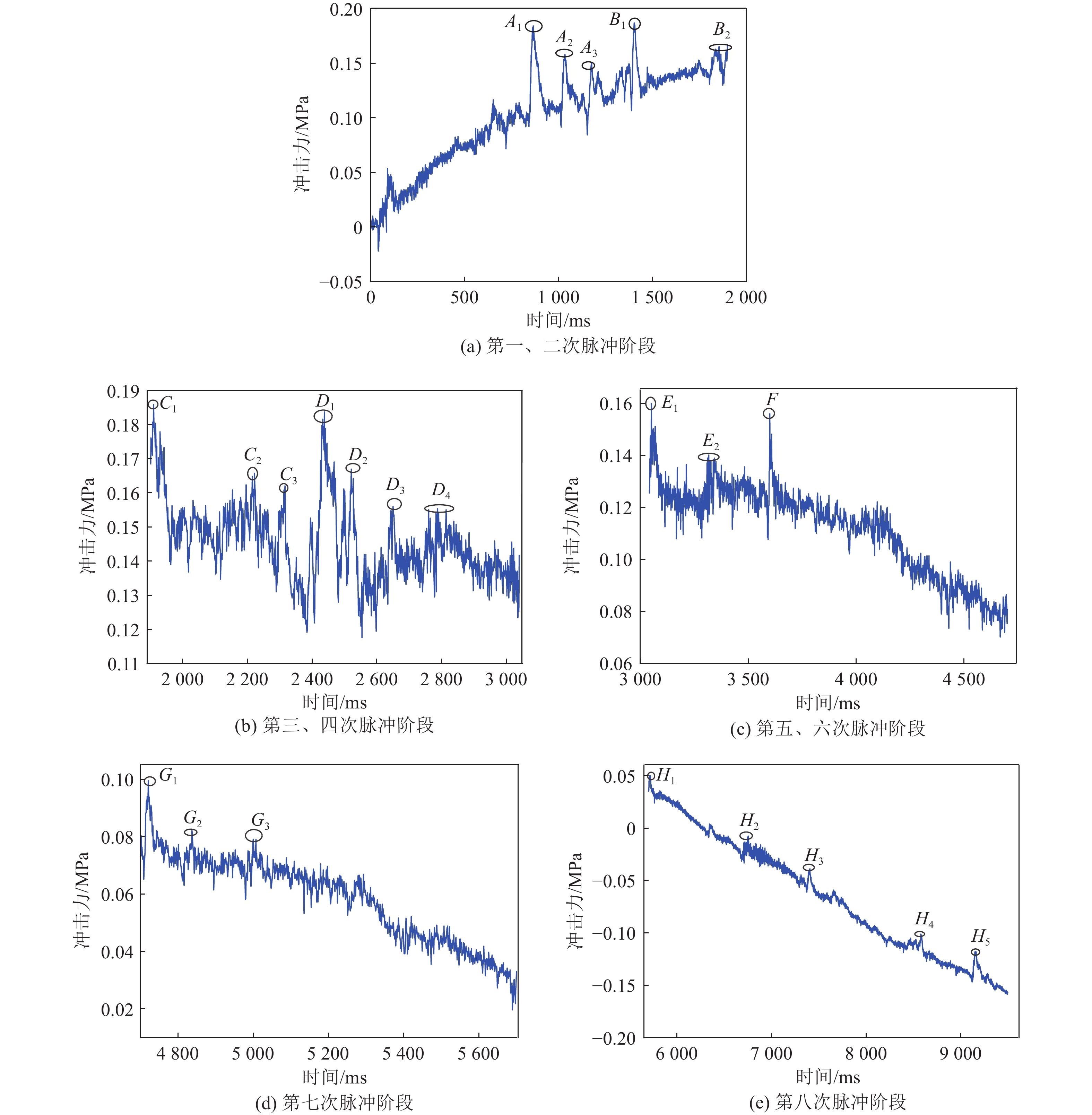
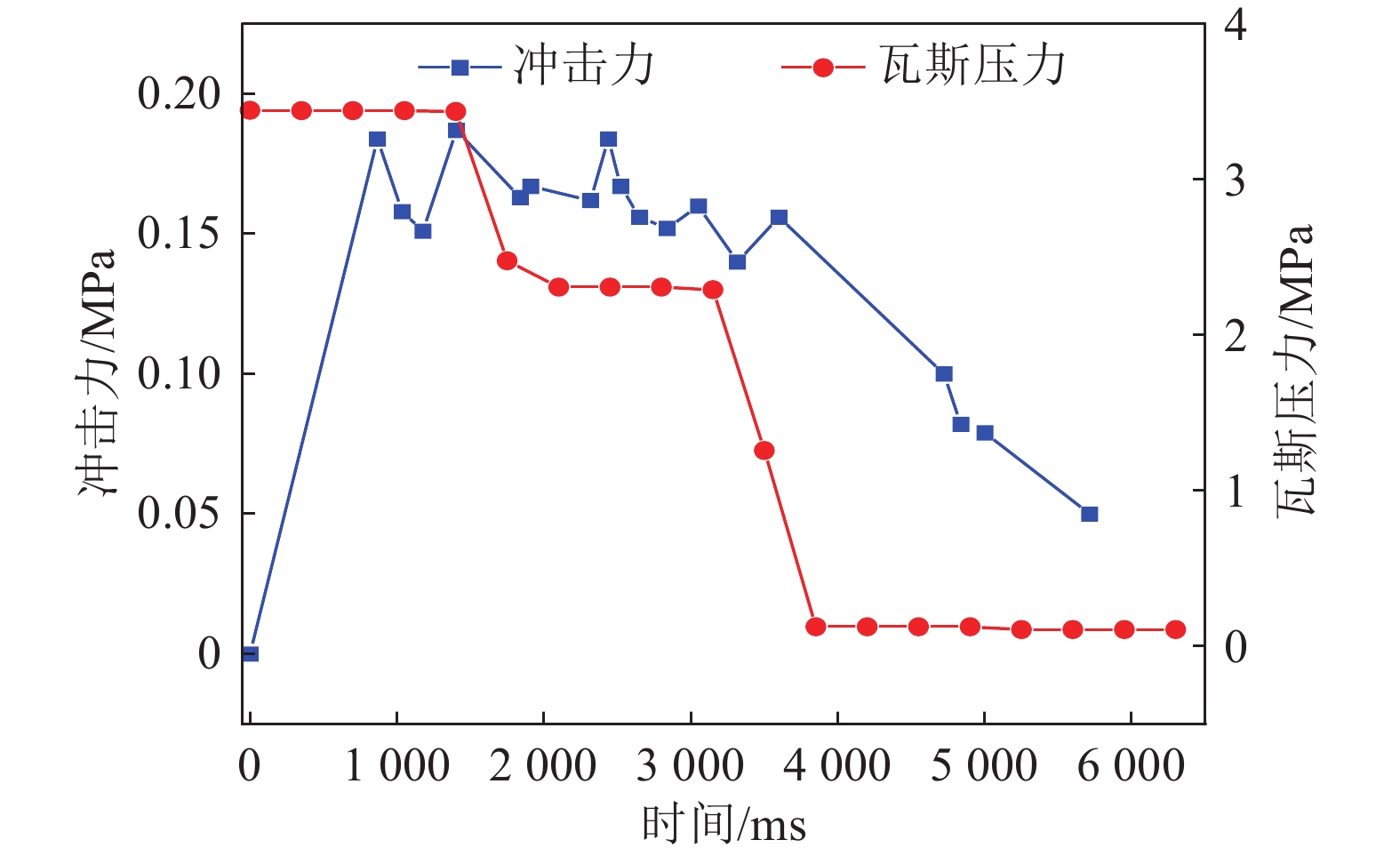
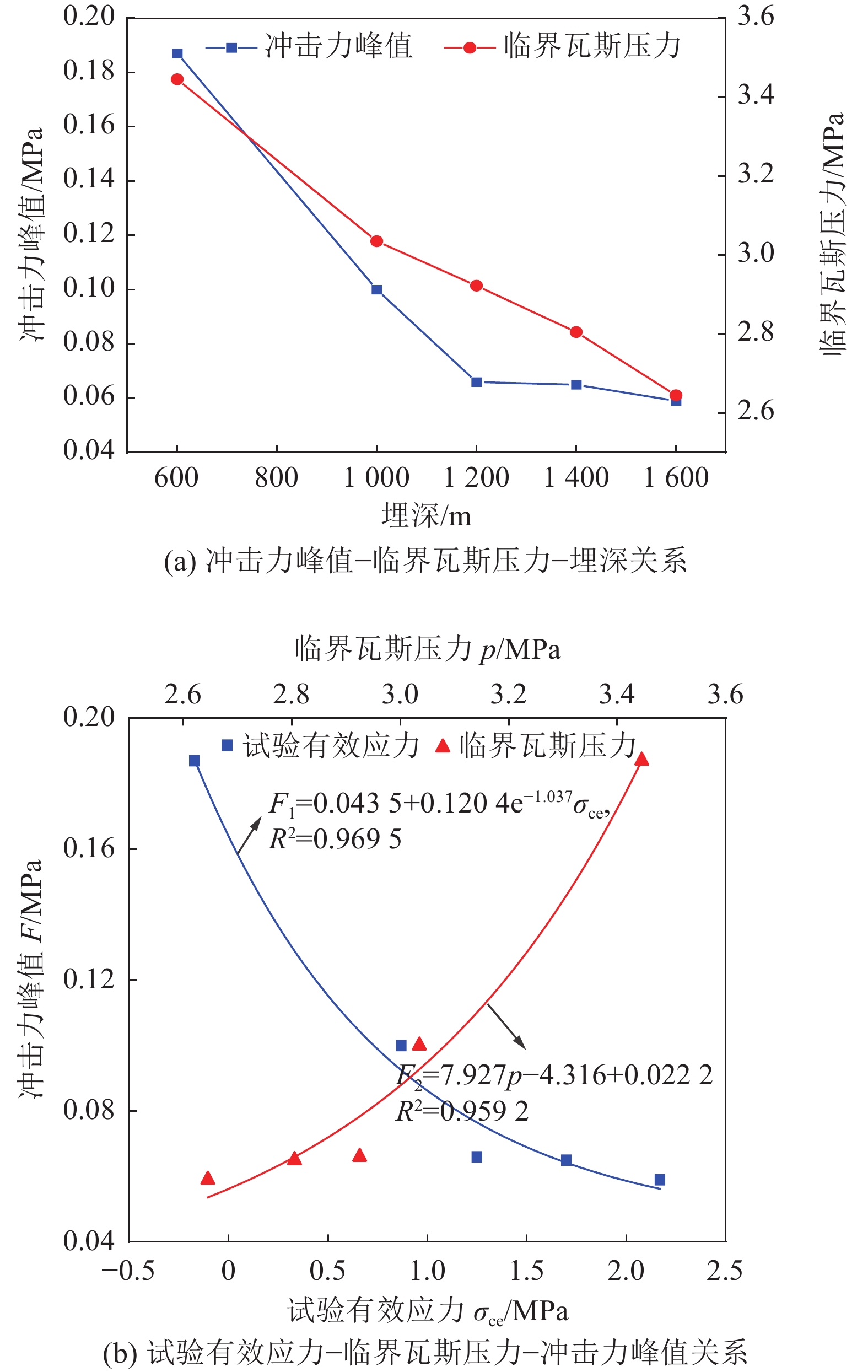
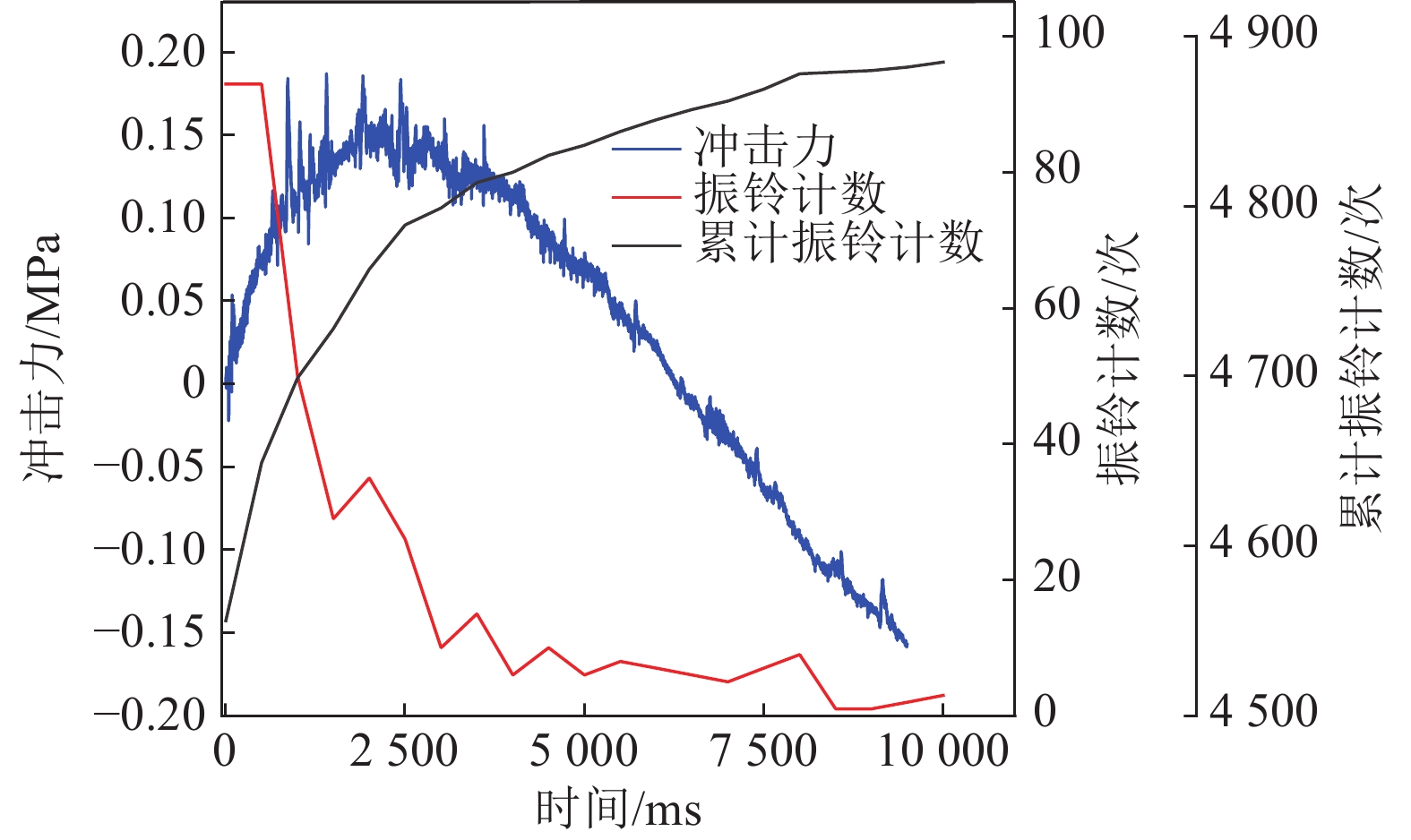
随着开采深度和强度增加,煤与瓦斯突出动力灾害频发,冲击力致灾机制成为目前研究的主要方向。为进一步揭示高地应力条件煤与瓦斯突出冲击力演化规律及破坏机制,采用自主研发的煤与瓦斯突出全过程模拟巷道系统,引入冲击力和声发射监测技术,以45%CO2和55%N2混合气体压力模拟煤层瓦斯压力,以轴压模拟上覆岩层应力作用,围压模拟围岩应力作用,以平煤十一矿突出煤层为研究对象,考虑埋深为600、800、1 000、1 200、1 400和1 600 m的地应力条件,进行了煤与瓦斯突出模拟试验,分析了煤−瓦斯两相流运移过程、煤粉分布及冲击力演化特征,得到了瓦斯压力、临界瓦斯压力、试验有效应力、声发射信号与冲击力之间的影响关系规律,从煤与瓦斯突出能量转化角度分析了瓦斯内能向冲击动能,即瓦斯压力向冲击力转化特征。研究结果表明:①突出孕育阶段受力情况及破坏程度影响突出发生后冲击力在巷道内传播特性,随模拟埋深增加,冲击力演化特征愈发复杂,具有明显脉冲特征,且随脉冲特征出现冲击力升高。②脉冲特征划分为高频阶段和低频阶段,高频阶段煤−瓦斯两相流速度快、强度高、突出危险性强;低频阶段危险性随突出发展进程逐渐减弱。③突出两相流动能主要由瓦斯内能提供,部分瓦斯压力转化成冲击力,冲击力强弱主要由瓦斯压力决定,在高地应力作用下,深部煤体相对浅部更易发生煤与瓦斯突出。④突出开始时,声发射振铃计数峰值点早于冲击力峰值点,声发射信号更早监测到突出危险性,但冲击力更能具象反映煤体破裂情况,声发射振铃计数出现陡增时,伴随脉冲特征出现,但脉冲特征出现不一定对应声发射振铃计数陡增。
Abstract:With the increase of mining depth and intensity, the dynamic disaster of coal and gas outburst was frequent. The disaster-causing mechanism of impact force has become the main direction of current research. In order to further reveal the impact force evolution law and failure mechanism of coal and gas outburst under high ground stress. The self-developed simulation roadway system in the whole process of coal and gas outburst was adopted, and the monitoring technology of impact force and acoustic emission were introduced. The gas pressure in coal seam was simulated by mixture pressure of 45% CO2 and 55% N2. The stress of overlying strata and surrounding rock was simulated by axial and confining stress, respectively. Taking the outburst coal seam of Pingding shan No.11 mine as the research object to conduct the simulation test of coal and gas outburst. The ground stress with buried depths of 600 m, 800 m, 1 000 m, 1 200 m, 1 400 m and 1 600 m were considered. The migration process of coal-gas two-phase flow, distribution of pulverized coal and evolution characteristics of impact force were analyzed. The influence between impact force and gas pressure, critical gas pressure, effective stress of test, acoustic emission signal were obtained, respectively. Transformation characteristics of gas internal energy to impact kinetic energy, i.e., gas pressure to impact force, was analyzed from the viewpoint of energy conversion of coal and gas outburst. The results shown that, (1) The force condition and damage degree in embryonic stage of outburst affected the propagation characteristics of impact force in the roadway after outburst. As the simulated buried depth increased, the impact force evolution became more complex, accompanied by obvious pulse characteristics, and the impact force value increased with the pulse characteristics. (2) The pulse characteristics was divided into the stage of high and low frequency. Coal-gas two-phase flow in high frequency stage had the characteristics of rapid speed, high strength and strong outburst hazard. The outburst hazard in low frequency stage gradually weakened with the development of outburst. (3) The two-phase flow energy of outburst was mainly from gas internal energy. Part of gas pressure was converted into impact force. The strength of impact force was mainly determined by gas pressure. Deep coal, with high ground stress, was more prone to coal and gas outburst than shallow one. (4) At the beginning of outburst, the peak point of acoustic emission ringing count preceded that of impact force, i.e., the acoustic emission signal detected outburst hazard earlier. But the impact force was more specific to coal fracture. A steep increase in acoustic emission ringing count was accompanied by pulse characteristics. However, the appearance of the pulse characteristic did not necessarily correspond to a steep increase in acoustic emission ringing count.
-
-
表 1 煤与瓦斯突出应力加载方案
Table 1 Experimental scheme of coal and gas outburst
试验埋深/m 实际地应力/MPa 试验施加地应力/MPa 瓦斯压力/MPa σH σh σv σH σh σv 600 21.928 11.988 14.675 2.03 1.11 1.36 抽真空3 h,当腔内负压0.1 MPa时,充入气体模拟吸附24 h。试验从0.6 MPa开始,以每级0.2 MPa加载,每次加载稳压2 min,直至突出发生 800 26.688 15.668 18.835 2.47 1.45 1.74 1 000 31.448 19.348 22.995 2.91 1.79 2.13 1 200 36.208 23.028 27.155 3.35 2.13 2.51 1 400 40.968 26.708 31.315 3.79 2.47 2.90 1 600 45.728 30.388 35.475 4.23 2.81 3.28 -
[1] 袁 亮. 我国煤矿安全发展战略研究[J]. 中国煤炭,2021,47(6):1−6. YUAN Liang. China coal mine safety development strategy research[J]. China Coal,2021,47(6):1−6.
[2] 唐巨鹏,任凌冉,潘一山,等. 高地应力条件煤与瓦斯突出模拟试验研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(2):113−121. TANG Jupeng,REN Lingran,PAN Yishan,et al. Simulation test of coal and gas outburst under high ground stress[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(2):113−121.
[3] 许 江,程 亮,彭守建,等. 煤与瓦斯突出冲击气流形成及传播规律[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(1):333−347. XU Jiang,CHENG Liang,PENG Shoujian,et al. The formation and propagation law of impact airflow in coal and gas outburst[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(1):333−347.
[4] 许 江,程 亮,周 斌,等. 突出过程中煤-瓦斯两相流运移的物理模拟研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2019,38(10):1945−1953. XU Jiang,CHENG Liang,ZHOU Bin,et al. Physical simulation of coal-gas two-phase flow migration during outburst[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2019,38(10):1945−1953.
[5] 程五一,刘晓宇,王魁军,等. 煤与瓦斯突出冲击波阵面传播规律的研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2004,29(1):57−60. CHENG Wuyi,LIU Xiaoyu,WANG Kuijun,et al. Study on the propagation law of coal and gas outburst shock wave front[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2004,29(1):57−60.
[6] 吴爱军,蒋承林. 煤与瓦斯突出冲击波传播规律研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2011,40(6):852−857. WU Aijun,JIANG Chenglin. Study on shock wave propagation law of coal and gas outburst[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,2011,40(6):852−857.
[7] 吴爱军,蒋承林,唐 俊. 瓦斯突出作用下煤岩体中冲击波传播规律的研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2010,35(10):1644−1648. WU Aijun,JIANG Chenglin,TANG Jun. Study on the propagation law of shock wave in coal and rock mass under gas outburst[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2010,35(10):1644−1648.
[8] 张建方,王 凯,韦彩平. 煤与瓦斯突出冲击波的形成与传播规律研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2010,27(1):67−71. ZHANG Jianfang,WANG Kai,WEI Caiping. Study on the formation and propagation law of shock wave of coal and gas outburst[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2010,27(1):67−71.
[9] 苗法田,孙东玲,胡千庭. 煤与瓦斯突出冲击波的形成机理[J]. 煤炭学报,2013,38(3):367−372. MIAO Fatian,SUN Dongling,HU Qianting. Formation mechanism of shock wave in coal and gas outburst[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2013,38(3):367−372.
[10] ZHOU Aitao,WANG Kai,WU Zeqi. Propagation law of shock waves and gas flow in cross roadway caused by coal and gas outburst[J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology,2014,24(1):23−29. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmst.2013.12.005
[11] ZHOU Aitao,ZHANG Meng,WANG Kai,et al. Rapid gas desorption and its impact on gas-coal outbursts as two-phase flows[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection,2021,150:478−488. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2021.04.042
[12] ZHOU Aitao, ZHANG Meng, WANG Kai, et al. Quantitative study on gas dynamic characteristics of two-phase gas-solid flow in coal and gas outbursts[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2020, 139.
[13] 刘 义,石必明,张 煜,等. 煤与瓦斯突出冲击气流传播特征研究[J]. 煤炭技术,2021,40(11):94−96. LIU Yi,SHI Biming,ZHANG Yu,et al. Study on the propagation characteristics of coal and gas outburst impact airflow[J]. Coal Technology,2021,40(11):94−96.
[14] 刘 义,石必明,张 煜,等. 煤与瓦斯突出两相流传播特性实验研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术,2021,17(7):91−96. LIU Yi,SHI Biming,ZHANG Yu,et al. Experimental study on two-phase flow propagation characteristics of coal and gas outburst[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology,2021,17(7):91−96.
[15] 曹 偈,孙海涛,戴林超,等. 煤与瓦斯突出动力效应的模拟研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2018,47(1):113−120, 154. CAO Ji,SUN Haitao,DAI Linchao,et al. Simulation study on dynamic effect of coal and gas outburst[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,2018,47(1):113−120, 154.
[16] 孙东玲,曹 偈,苗法田,等. 突出煤-瓦斯在巷道内的运移规律[J]. 煤炭学报,2018,43(10):2773−2779. SUN Dongling,CAO Ji,MIAO Fatian,et al. The migration law of outburst coal-gas in roadway[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2018,43(10):2773−2779.
[17] 许 江,耿加波,彭守建,等. 煤与瓦斯突出脉动式发展过程的试验研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2018,47(1):145−154. XU Jiang,GENG Jabo,PENG Shoujian,et al. Experimental study on pulsating development process of coal and gas outburst[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,2018,47(1):145−154.
[18] 耿加波. 煤与瓦斯突出灾变时空演化及其煤-瓦斯两相流运移特性物理模拟试验研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2018. GENG Jiabo. Physical simulation experiment on spatial-temporal evolution of coal and gas outburst disaster and migration characteristics of coal-gas two-phase flow[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2018.
[19] 程 亮,许 江,周 斌,等. 不同瓦斯压力对煤与瓦斯突出两相流传播规律的影响研究[J]. 岩土力学,2020,41(8):2619−2626. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2019.1811 CHENG Liang,XU Jiang,ZHOU Bin,et al. Study on the influence of different gas pressure on the two-phase flow propagation law of coal and gas outburst[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2020,41(8):2619−2626. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2019.1811
[20] 周 斌,许 江,彭守建,等. 突出过程中煤层及巷道多物理场参数动态响应[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(4):1385−1397. ZHOU Bin,XU Jiang,PENG Shoujian,et al. Dynamic response of multi-physical field parameters of coal seam and roadway during outburst[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2020,45(4):1385−1397.
[21] 唐巨鹏,张 昕,潘一山,等. 深部巷道煤与瓦斯突出及冲击演化特征试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2022,16(5):1−12. TANG Jupeng,ZHANG Xin,PAN Yishan,et al. Experimental study on coal and gas outburst and impact evolution characteristics of deep roadway[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2022,16(5):1−12.
[22] 李 铁,蔡美峰,纪洪广. 抚顺煤田深部开采临界深度的定量判别[J]. 煤炭学报,2010,35(3):363−367. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2010.03.010 LI Tie,CAI Meifeng,JI Hongguang. Quantitative determination of critical depth of deep mining in Fushun coalfield[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2010,35(3):363−367. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2010.03.010
[23] 梁政国. 煤矿山深浅部开采界线划分问题[J]. 辽宁工程技术大学学报(自然科学版),2001,20(4):554−556. LIANG Zhengguo. Division of mining boundary in deep and shallow coal mines[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University(Natural Science),2001,20(4):554−556.
[24] 谢和平,高 峰,鞠 杨,等. 深部开采的定量界定与分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2015,40(1):1−10. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2014.1690 XIE Heping,GAO Feng,JU Yang,et al. Quantitative definition and analysis of deep mining[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2015,40(1):1−10. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2014.1690
[25] 何满潮. 深部的概念体系及工程评价指标[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2005,24(16):2854−2858. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.16.007 HE Manchao. Deep concept system and engineering evaluation index[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2005,24(16):2854−2858. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.16.007
[26] 胡社荣,戚春前,赵胜利,等. 我国深部矿井分类及其临界深度探讨[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2010,38(7):10−13, 43. doi: 10.13199/j.cst.2010.07.18.hushr.018 HU Sherong,QI Chunqian,ZHAO Shengli,et al. Classification and critical depth of deep mines in China[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2010,38(7):10−13, 43. doi: 10.13199/j.cst.2010.07.18.hushr.018
[27] 张庆贺,王汉鹏,李术才,等. 煤与瓦斯突出物理模拟试验中甲烷相似气体的探索[J]. 岩土力学,2017,38(2):479−486. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2017.02.022 ZHANG Qinghe,WANG Hanpeng,LI Shucai,et al. Exploration of methane similar gas in physical simulation test of coal and gas outburst[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2017,38(2):479−486. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2017.02.022
[28] 李新平,汪 斌,周桂龙. 我国大陆实测深部地应力分布规律研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2012,31(S1):2875−2880. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.z1.036 LI Xinping,WANG Bin,ZHOU Guilong. Research on the distribution law of measured deep crustal stress in mainland China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2012,31(S1):2875−2880. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.z1.036
[29] 许 江,叶桂兵,李波波,等. 不同黏结剂配比条件下型煤力学及渗透特性试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2015,36(1):104−110. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2015.01.014 XU Jiang,YE Guibing,LI Bobo,et al. Experimental study on briquette mechanics and permeability characteristics under different binder ratios[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2015,36(1):104−110. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2015.01.014
[30] 唐巨鹏,潘一山,杨森林. 三维应力下煤与瓦斯突出模拟试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2013,32(5):960−965. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2013.05.014 TANG Jupeng,PAN Yishan,YANG Shenlin. Simulation test of coal and gas outburst under three-dimensional stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2013,32(5):960−965. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2013.05.014
[31] 胡祖祥,谢广祥. 煤层瓦斯压力受控于采动应力的“异步-同步”特征研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2015,32(6):1037−1042. doi: 10.13545/j.cnki.jmse.2015.06.027 HU Zuxiang,XIE Guangxiang. A research of asynchronous and synchronous characteristics of coal seam gas pressure controlled by the mining-induced stress[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2015,32(6):1037−1042. doi: 10.13545/j.cnki.jmse.2015.06.027
[32] LIU Hongtao, GUO Linfeng, ZHAO Xidong. Expansionary evolution characteristics of plastic zone in rock and coal mass ahead of excavation face and the mechanism of coal and gas outburst[J]. Energies, 2020, 13(4): 984.
[33] 宋选民,朱德福,王仲伦,等. 我国煤矿综放开采40年: 理论与技术装备研究进展[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2021,49(3):1−29. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2004.01.013 SONG Xuanmin,ZHU Defu,WANG Zhonglun,et al. Advances on longwall fully-mechanized top-coal caving mining technology in China during past 40 years:theory, equipment and approach[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2021,49(3):1−29. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2004.01.013
[34] 熊阳涛,黄 滚,罗甲渊,等. 煤与瓦斯突出能量耗散理论分析与试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2015,34(S2):3694−3702. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2015.0993 XIONG Yangtao,HUANG Gun,LUO Jiayuan,et al. Theoretical analysis and experimental study on energy dissipation of coal and gas outburst[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2015,34(S2):3694−3702. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2015.0993
[35] 王 刚,武猛猛,王海洋,等. 基于能量平衡模型的煤与瓦斯突出影响因素的灵敏度分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2015,34(2):238−248. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2015.02.003 WANG Gang,WU Mengmeng,WANG Hai,et al. Sensitivity analysis of influencing factors of coal and gas outburst based on energy balance model[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2015,34(2):238−248. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2015.02.003
[36] 胡千庭, 文光才. 煤与瓦斯突出的力学作用机理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013. HU Qianting, WEN Guangcai. Mechanical mechanism of coal and gas outburst[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2013.
[37] 鲜学福,许 江. 煤与瓦斯突出潜在区(带)预测[J]. 中国工程科学,2001,3(2):39−46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2001.02.009 XIAN Xuefu,XU Jiang. Prediction of potential coal and gas outburst zones[J]. Strategic Study of CAE,2001,3(2):39−46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2001.02.009
[38] 魏风清,史广山,张铁岗. 基于瓦斯膨胀能的煤与瓦斯突出预测指标研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2010,35(S1):95−99. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2010.s1.030 WEI Fengqing,SHI Guangshan,ZHANG Tiegang,et al. Study on coal and gas outburst prediction indexes base on gas expansion energy[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2010,35(S1):95−99. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2010.s1.030
[39] 李成武,付 帅,解北京,等. 煤与瓦斯突出能量预测模型及其在平煤矿区的应用[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2018,47(2):231−239. doi: 10.13247/j.cnki.jcumt.000832 LI Chengwu,FU Shuai,XIE Beijing,et al. Establishment of the prediction model of coal and gas outburst energy and its application in Pingdingshan coal mining area[J]. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology,2018,47(2):231−239. doi: 10.13247/j.cnki.jcumt.000832
[40] XU L,JIANG C. Initial desorption characterization of methane and carbon dioxide in coal and its influence on coal and gas outburst risk[J]. Fuel,2017,203:700−706. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.05.001
[41] 王 伟,王汉鹏,张 冰,等. 煤与瓦斯突出多因素影响规律与能量判据实验研究[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版),2022,43(4):582−590. doi: 10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2022.04.017 WANG Wei,WANG Hanpeng,ZHANG Bing,et al. Experimental study on multi–factor influence law and energy criterion of coal and gas outburst[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science),2022,43(4):582−590. doi: 10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2022.04.017
[42] 徐小荷, 余 静. 岩石破碎学[M]. 北京: 煤炭工业出版社, 1984. XU Xiaohe, XU Jing. Rock fragmentation[M]. Beijing: China Coal Industry Publishing House, 1984.
[43] 罗甲渊. 煤与瓦斯突出的能量源及能量耗散机理研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2016. LUO Jiayuan. Energy source and energy dissipation mechanism of coal and gas outburst[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2016.
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 郭文兵,胡玉杭,胡超群,李龙翔,吴东涛,葛志博. 我国“三下”采煤技术体系与工程实践. 煤炭科学技术. 2025(01): 19-38 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 章海兵,刘勤志,孔德中,张鹏飞,李利. 喀斯特山区重复采动下地表沉陷预测研究. 矿业研究与开发. 2024(03): 65-72 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张金贵,姬中奎,呼少平,王海,胡俭,韩强,杨帆. 近距离多煤层下行重复采动覆岩变形与裂隙演化特征研究. 中国矿业. 2024(05): 152-163 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 陈璐,余茜,罗容,周子龙,曾铃,郭一鹏. 柱式采空区矿柱失稳诱导边坡滑塌机制研究. 采矿与岩层控制工程学报. 2024(05): 148-163 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 郭文兵,杨伟强,吴东涛. 我国煤矿开采沉陷控制技术研究现状与进展. 采矿与岩层控制工程学报. 2024(06): 5-20 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 田延哲. 高陡山体下多煤层重复开采沉陷对矿区环境影响的累积效应分析. 中国煤炭地质. 2023(01): 57-63 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 田延哲,孟庄涵,刘小平,王玉涛. 基于高陡山体变形控制目标的多煤层协调开采技术. 煤炭科技. 2023(02): 109-113 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: