System and engineering practice of coal mining technology under buildings, water bodies and railways in China
-
摘要:
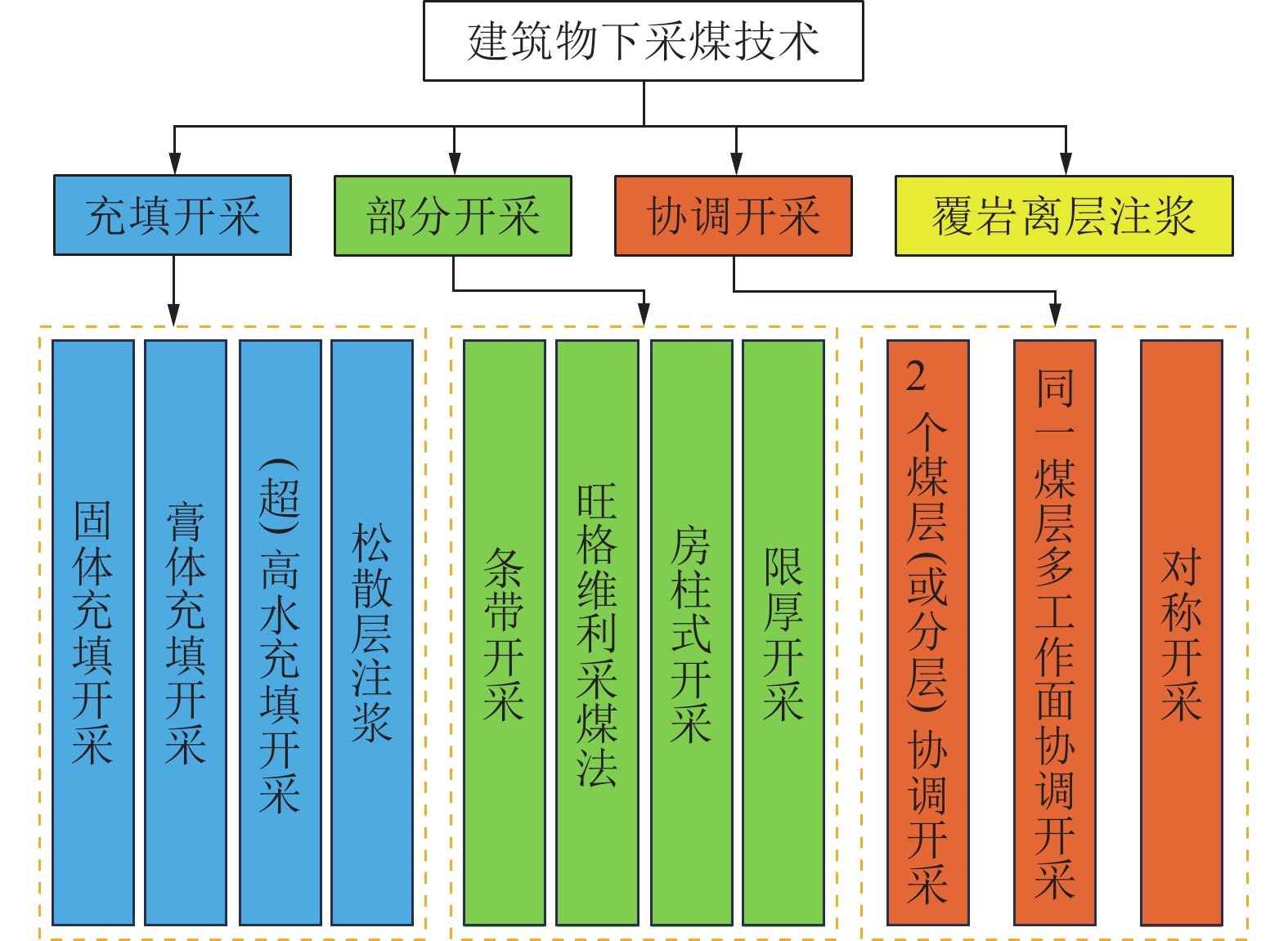
我国“三下”(建筑物、水体、铁路等线性构筑物下)煤炭资源丰富,开展“三下”采煤技术研究、解放“三下”压煤对提高煤炭资源采出率、优化井下采掘布局、延长矿井服务年限等具有重要意义。总结了我国“三下”压煤开采技术以及建(构)筑物保护技术,包括部分开采、充填开采、协调开采、覆岩离层注浆技术以及地面保护、维修加固技术,并分析了各种“三下”采煤技术的优缺点和适用条件等。提出“三下”压煤开采造成建(构)筑物损害的源头是煤炭地下开采引起的覆岩破坏与地表移动,控制地表沉陷、研究地表移动变形规律是建(构)筑物下采煤的关键,减少覆岩破坏、准确预测覆岩破坏高度是水体(覆岩含水层)下安全采煤技术的关键。从经验公式、理论计算、现场实测等方面综合分析了“三下”采煤覆岩破坏与地表移动规律、地表移动变形预测、地面建筑物保护技术等。研究认为高效率、低成本、全固废、智能化覆岩离层注浆和充填开采、地下水原位保护等源头减沉控损技术将是我国未来“三下”开采技术的发展方向,并建立覆岩与地表移动变形的“天−空−地−井”一体化监测、预警机制,加强“三下”采煤工艺、全固废材料、技术与装备水平的提升,科学构建并不断完善绿色低碳、智能、安全高效的“三下”采煤技术体系。
Abstract:There is a large amount of coal resources that are difficult to mine due to buildings, water bodies and railways in China. Conducting research on coal mining technology and liberating pressed coal under building, water body and railways are significant for improving the recovery rate of coal resources, optimizing the layout of mining and extending the service years of mines. The paper summarized the coal mining technology under buildings, water bodies and railways and buildings and structures protection technologies in China, including partial mining, filling mining, coordinated mining, overburden bed separation grouting technology and ground protection, repair and reinforcement techniques, the advantages, disadvantages and applicable conditions of each technique are also analyzed. It is proposed that the source of damage to buildings and structures caused by coal mining under buildings, water bodies and railways is the overburden destruction and surface movement. Controlling surface subsidence and studying the law of surface movement and deformation are the key to coal mining under buildings and structures. Reducing overburden failure and accurately predicting overburden failure height are the key to safe coal mining technology under water bodies (overburden aquifers). Comprehensively analyzed the law of over-burden destruction and surface movement, the prediction of surface movement and deformation, and the protection technology of ground buildings under buildings, water bodies and railways from the experience formula, theoretical calculations, and on-site measurements. Research considers that high efficiency, low cost, all solid waste, intelligent overburden grout injection and filling mining, groundwater in-situ protection and other sources of subsidence reduction technology will be the development direction of coal mining technology under building, water body and railways in the future, and establish the “space-air-ground-well” integrated monitoring and early warning mechanism of overburden and surface movement and deformation, strengthen the improvement of coal mining technology under buildings, water bodies and railways, all solid waste materials, technology and equipment level, scientifically construct and continuously improve the green low-carbon, intelligent, safe and efficient mining technology system under buildings, water bodies and railways.
-
-
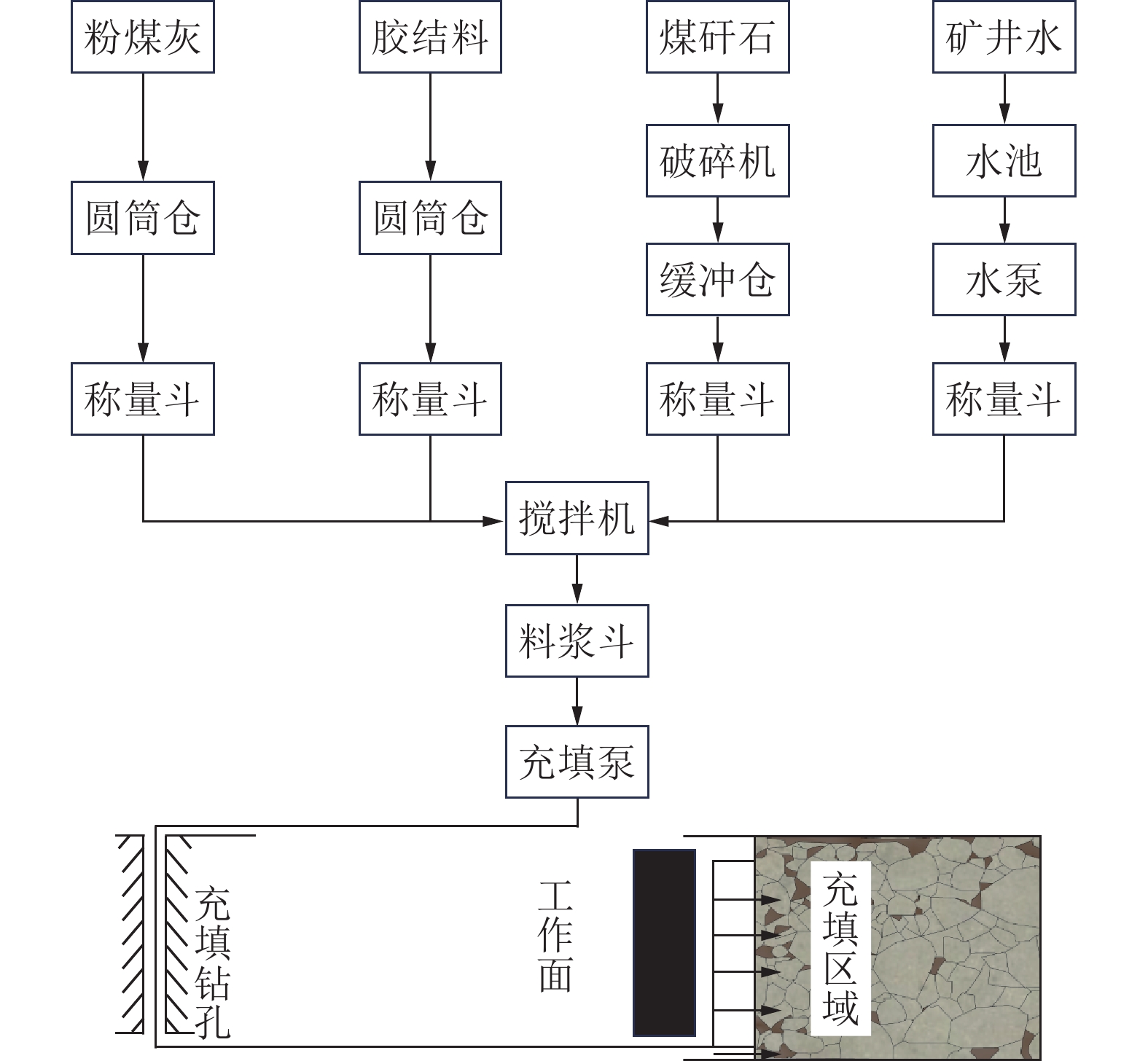
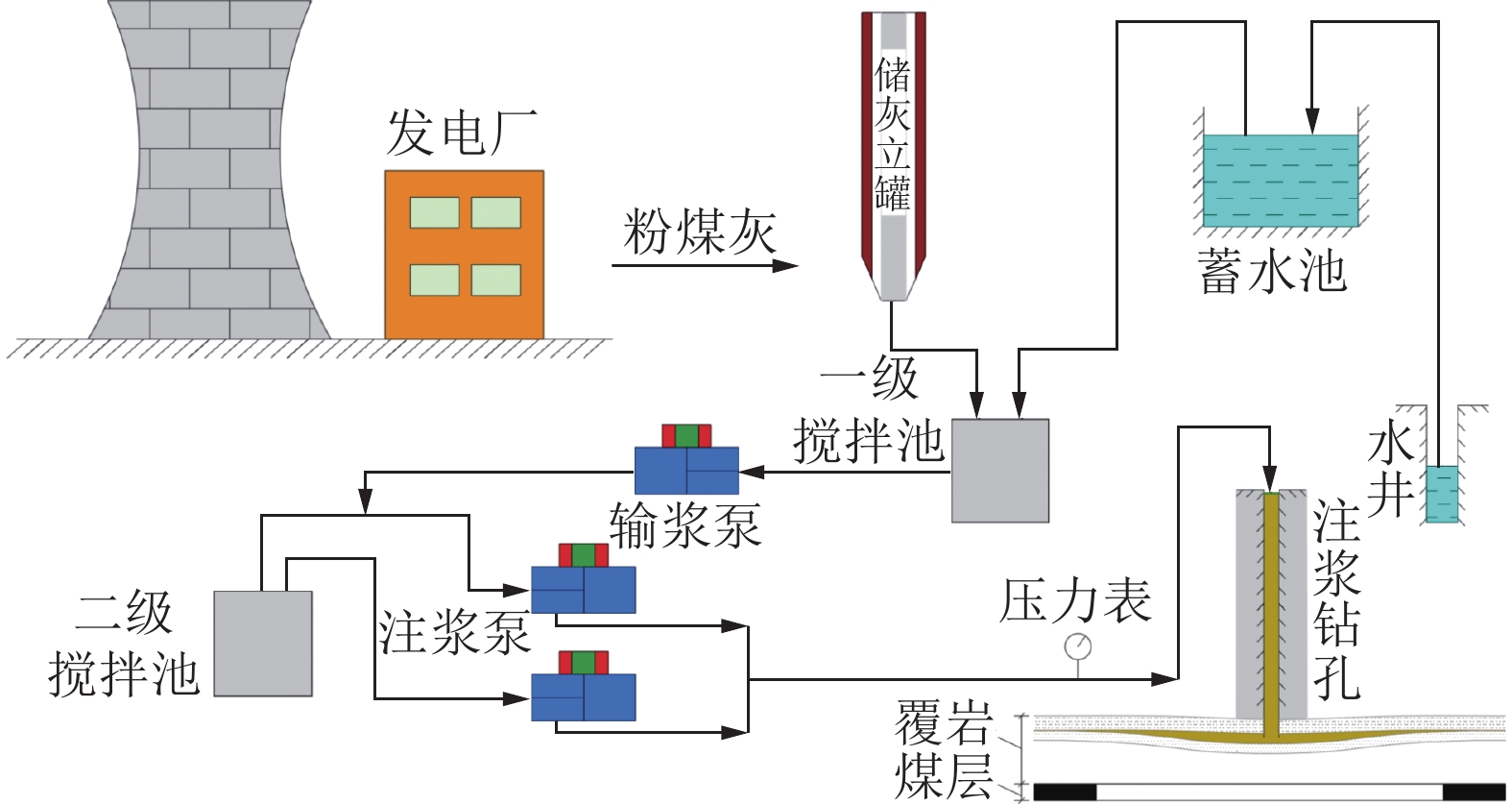
图 3 煤矿膏体充填工艺流程[12]
Figure 3. Technological process of paste backfilling mining
表 1 各项技术的优缺点
Table 1 Advantages and disadvantages of each technology
技术 充填开采 部分开采 覆岩离层注浆 优点 煤炭资源采出率高
矸石等固废资源化利用
覆岩与地表减沉效果好地表减沉效果较好
地质条件适应性强
开采成本相对较低地表减沉控制效果较好
粉煤灰等固废资源化利用
注浆作业对井下不干扰
煤炭资源采出率高缺点 回采充填工艺复杂
开采及充填相互干扰
生产效率低、成本高采出率低掘进率高
采煤工艺比较复杂
生产效率相对较低开采成本相对较高
注浆时空关系难以把握
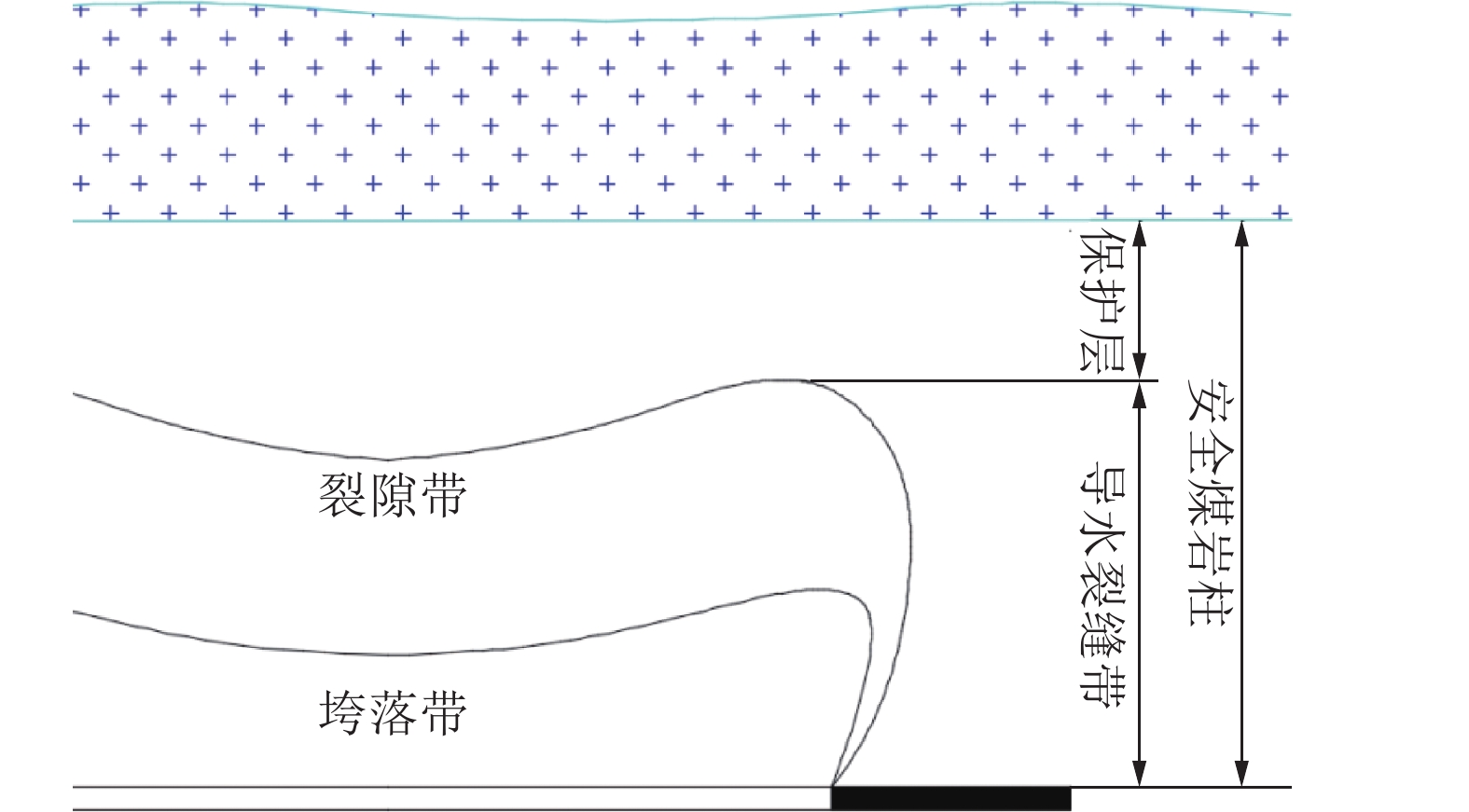
地面冒浆或井下溃浆风险表 2 综放顶煤开采导水裂隙带高度计算公式
Table 2 Formula of the height of fracture zone height in fully mechanized caving mining
岩性 计算公式之一 计算公式之二 坚硬 $H_{\mathrm{li}}=\dfrac{100M}{0.15M+3.12}\pm 11.18$ $H_{\mathrm{li}}=30M+10$ 中硬 $H_{\mathrm{li}}=\dfrac{100M}{0.23M+6.10}\pm 10.42$ $H_{\mathrm{li}}=20M+10$ 软弱 $H_{\mathrm{li}}=\dfrac{100M}{0.31M+8.81}\pm 8.21$ $H_{\mathrm{li}}=10M+10$ 表 3 覆岩破坏高度观测技术
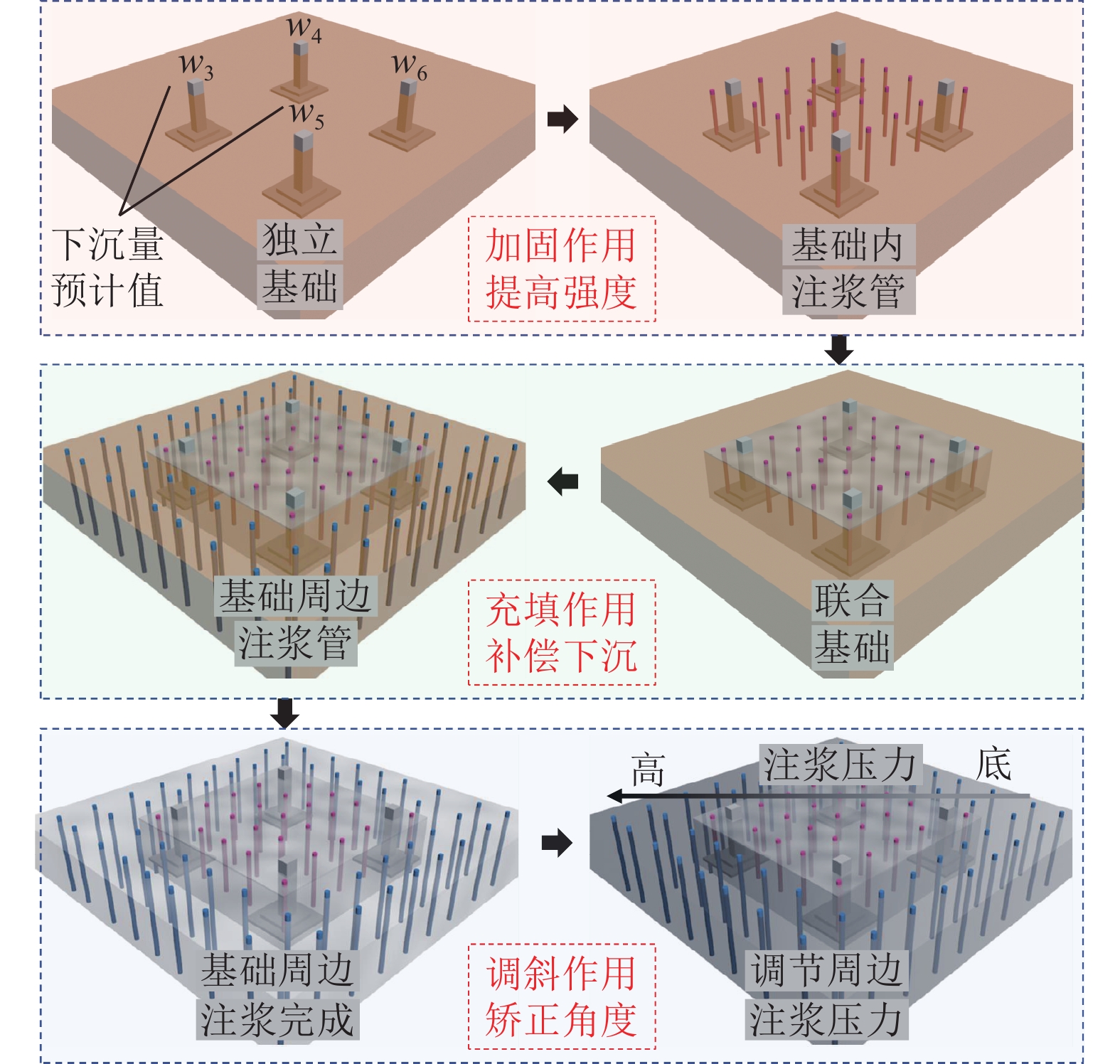
Table 3 Overburden damage height observation technology
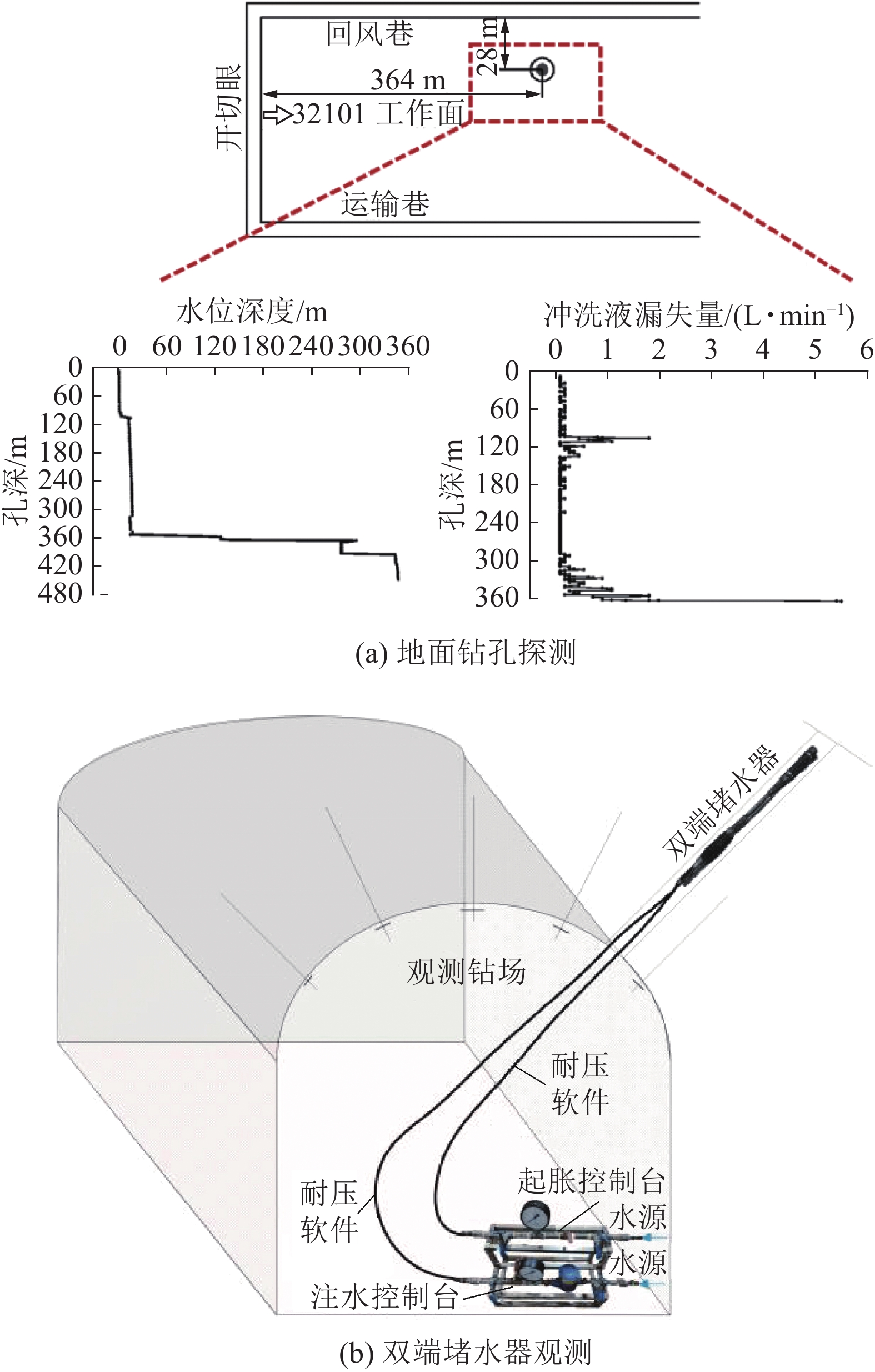
观测方法 观测内容 地面钻孔探测法 通过地面钻孔,观测冲洗液漏失量、水位变化等,判断导水裂隙带高度 岩心观察技术 取样,观察岩心裂隙情况,通过裂隙密度、规模判断导水裂隙带高度 双端堵水器观测法 向采空区上方打仰斜钻孔,使用钻孔双端封堵测漏装置向钻孔进行分段封堵注水,对钻孔各段水的漏失流量进行测定 钻孔电视观测法 在钻孔中放入摄像探头,实时观测孔壁裂隙,分析图像确定导水裂隙带高度 地球物理测井 选用三侧向电阻率、密度(长短源距伽马)、声波时差等参数,分析数据判断裂隙发育情况 表 4 保水开采技术研究内容
Table 4 Water prodection mining technology research content
保水开采
技术方向保水开采关键技术 研究内容 地质条件探测识别 采煤对含水层扰动评价技术 地层结构探测技术
水煤空间关系分析
地质条件分类分区保水开采地质条件分区技术 岩层移动控制技术 导水裂隙带发育高度预测技术 顶板结构分析建模
载荷传递规律分析保水开采技术方法 限高保水开采技术 顶板含水层结构保护
底板含水层结构保护壁式条带充填保水开采技术 连采连充保水开采技术 注浆保水开采技术 固体充填保水开采技术 -
[1] 郭文兵,马志宝,白二虎. 我国煤矿“三下一上” 采煤技术现状与展望[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2020,48(9):16−26. GUO Wenbing,MA Zhibao,BAI Erhu. Current status and prospect of coal mining technology under buildings,water bodies and railways,and above confined water in China[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2020,48(9):16−26.
[2] 吴涛,方向清,宁树正,等. 华北型煤田“三下一上” 煤炭资源现状及开发利用研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2021,49(9):129−135. WU Tao,FANG Xiangqing,NING Shuzheng,et al. Study on status quo and development as well as utilization of coal resources “under buildings,water bodies,railways and above confined water” in North China Coalfields[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2021,49(9):129−135.
[3] 孙希奎. “三下” 采煤膏体充填开采技术研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2021,49(1):218−224. SUN Xikui. Research on paste backfilling mining technology of coal mining under buildings,water bodies and railways[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2021,49(1):218−224.
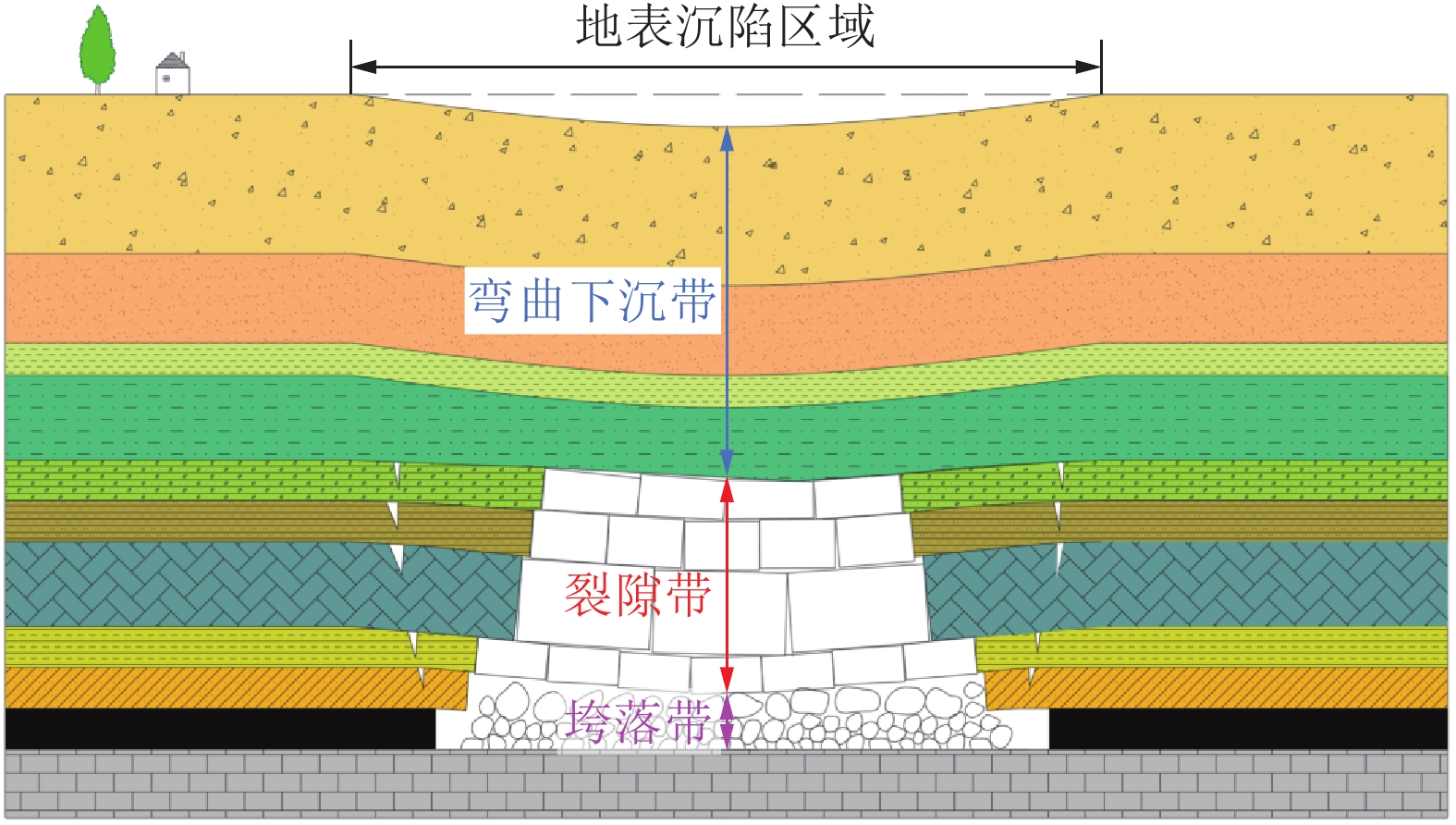
[4] 张吉雄,屠世浩,曹亦俊,等. 深部煤矿井下智能化分选及就地充填技术研究进展[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2020,37(1):1−10,22. ZHANG Jixiong,TU Shihao,CAO Yijun,et al. Research progress of technologies for intelligent separation and in situ backfill in deep coal mines in China[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2020,37(1):1−10,22.
[5] 卞正富,于昊辰,雷少刚,等. 黄河流域煤炭资源开发战略研判与生态修复策略思考[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(5):1378−1391. BIAN Zhengfu,YU Haochen,LEI Shaogang,et al. Strategic consideration of exploitation on coal resources and its ecological restoration in the Yellow River Basin,China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2021,46(5):1378−1391.
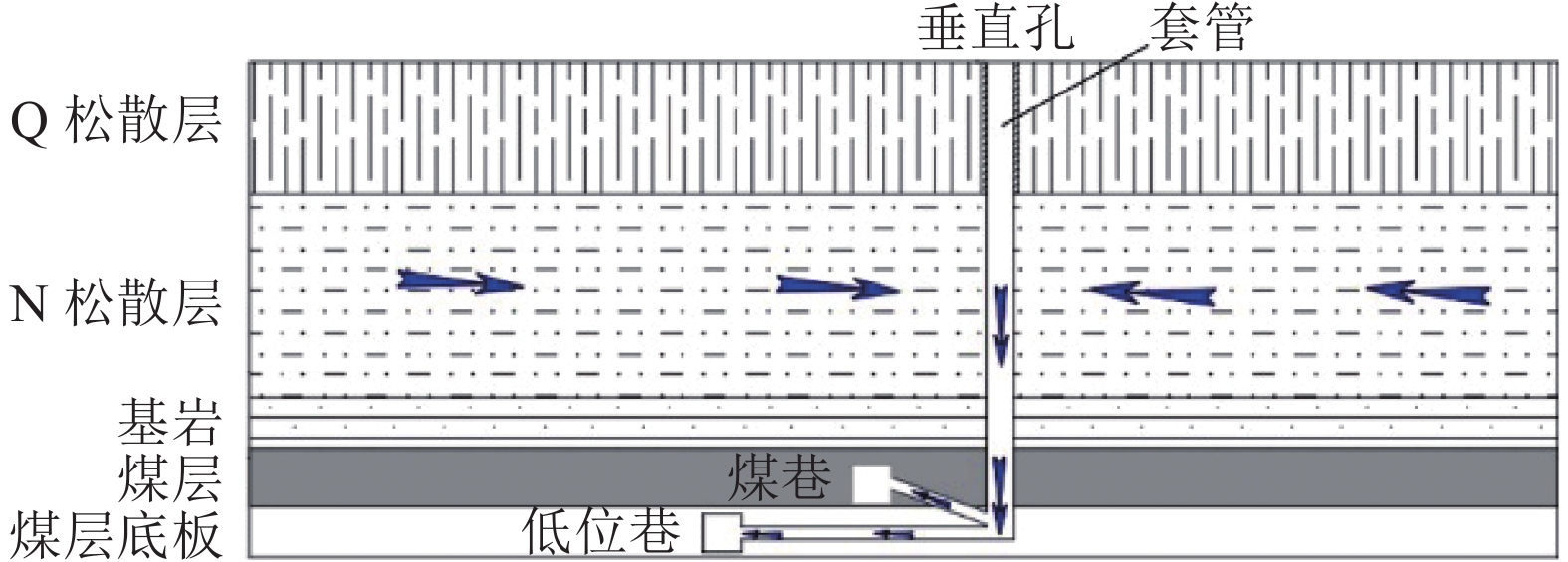
[6] PENG S S, KOHLI K K, CHENG S L. Surface subsidence and structural damages due to underground longwall coal mining: A case study[C]//Proceedings of the 21st U. S. Symposium on Rock Mechanics. Rolla, Missouri: ARMA US Rock Mechanics/Geomechanics Symposium, 1980: ARMA-80-0275. PENG S S,KOHLI K K,CHENG S L. Surface subsidence and structural damages due to underground longwall coal mining: A case study[C]//Proceedings of the 21st U. S. Symposium on Rock Mechanics. Rolla,Missouri:ARMA US Rock Mechanics/Geomechanics Symposium,1980:ARMA-80-0275.
[7] 张吉雄,张强,巨峰,等. 煤矿“采选充+X” 绿色化开采技术体系与工程实践[J]. 煤炭学报,2019,44(1):64−73. ZHANG Jixiong,ZHANG Qiang,JU Feng,et al. Practice and technique of green mining with integration of mining,dressing,backfilling and X in coal resources[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2019,44(1):64−73.
[8] 黄艳利,张吉雄,杜杰. 综合机械化固体充填采煤的充填体时间相关特性研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2012,41(5):697−701. HUANG Yanli,ZHANG Jixiong,DU Jie. Time-dependence of backfilling body in fully mechanized backfilling mining face[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,2012,41(5):697−701.
[9] 刘建功,李新旺,何团. 我国煤矿充填开采应用现状与发展[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(1):141−150. LIU Jiangong,LI Xinwang,HE Tuan. Application status and prospect of backfill mining in Chinese coal mines[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2020,45(1):141−150.
[10] 孙希奎,赵庆民,施现院. 条带残留煤柱膏体充填综采技术研究与应用[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2017,34(4):650−654. SUN Xikui,ZHAO Qingmin,SHI Xianyuan. Research and application on the technology of paste backfilling fully mechanized in residual strip pillar[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2017,34(4):650−654.
[11] 徐斌,杨仁树,李永亮,等. 煤矿胶结充填开采覆岩移动三量关系及其控制原则[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(S1):49−60. XU Bin,YANG Renshu,LI Yongliang,et al. Three measurement relationship and control principle of overburden movement in cemented filling[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(S1):49−60.
[12] 周华强,侯朝炯,孙希奎,等. 固体废物膏体充填不迁村采煤[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2004,33(2):154−158. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1964.2004.02.007 ZHOU Huaqiang,HOU Chaojiong,SUN Xikui,et al. Solid waste paste filling for none-village-relocation coal mining[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,2004,33(2):154−158. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1964.2004.02.007
[13] 冯光明,贾凯军,尚宝宝. 超高水充填材料在采矿工程中的应用与展望[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2015,43(1):5−9. FENG Guangming,JIA Kaijun,SHANG Baobao. Application and prospect of super-high-water packing material in mining engineering[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2015,43(1):5−9.
[14] 王方田,刘超,郝文华,等. 超高水材料充填减灾减损绿色开采理论与技术进展及展望[J]. 金属矿山,2023(5):14−30. WANG Fangtian,LIU Chao,HAO Wenhua,et al. Progress and prospect for disater mitigtion and damage reduction green mining theory and technology of super-high water material backfill[J]. Metal Mine,2023(5):14−30.
[15] 谢和平,张吉雄,高峰,等. 煤矿负碳高效充填开采理论与技术构想[J]. 煤炭学报,2024,49(1):36−46. XIE Heping,ZHANG Jixiong,GAO Feng,et al. Theory and technical conception of carbon-negative and high-efficient backfill mining in coal mines[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2024,49(1):36−46.
[16] GUO W B,XU F Y. Numerical simulation of overburden and surface movements for Wongawilli strip pillar mining[J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology,2016,26(1):71−76. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmst.2015.11.013
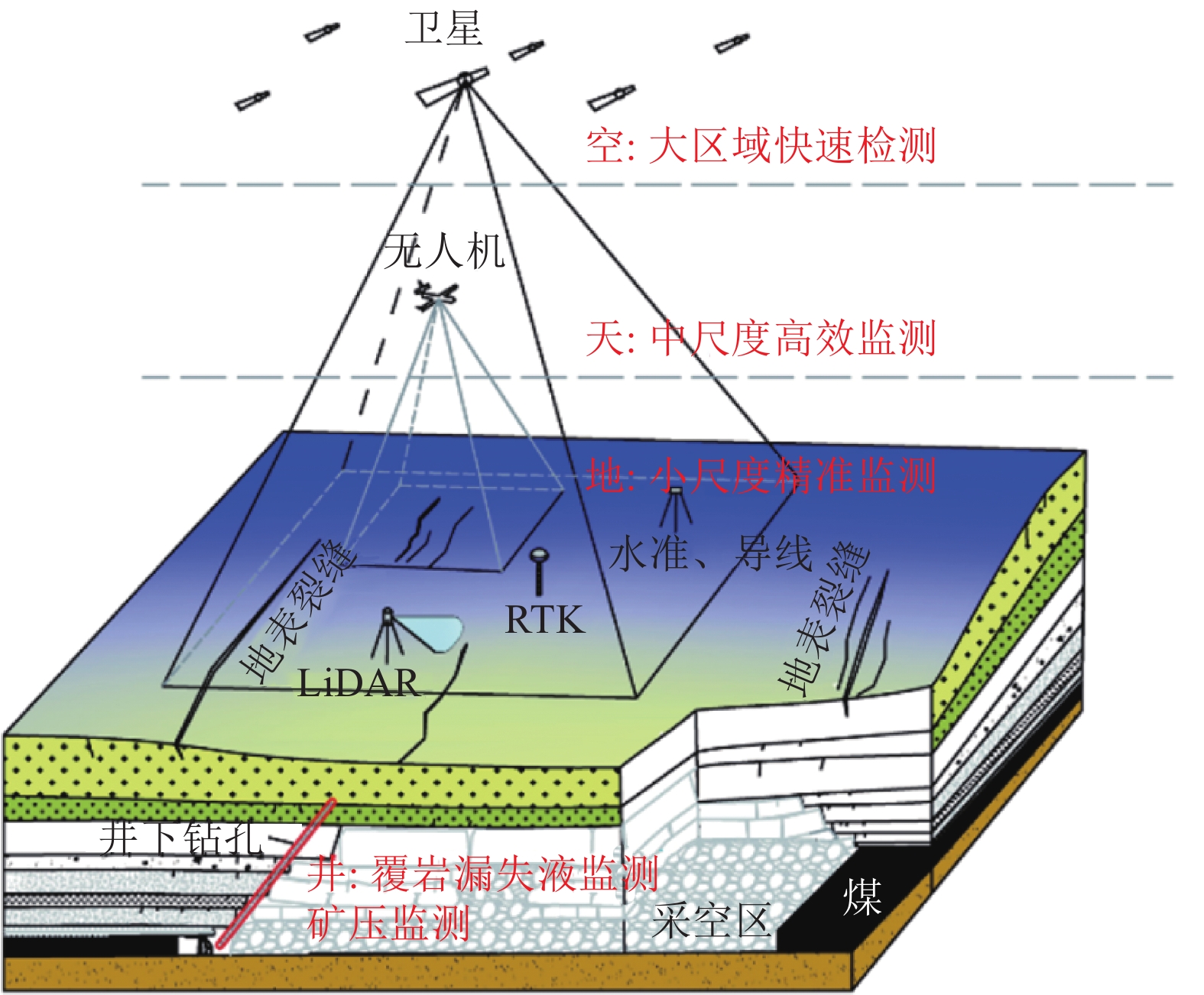
[17] PENG S S, CHENG S L. House damages due to room and piliar mining[C]//Proceedings of the 22nd U. S. Symposium on Rock Mechanics. Cambridge, Massachusetts: ARMA US Rock Mechanics/Geomechanics Symposium, 1981: ARMA-81-0335. PENG S S,CHENG S L. House damages due to room and piliar mining[C]//Proceedings of the 22nd U. S. Symposium on Rock Mechanics. Cambridge,Massachusetts:ARMA US Rock Mechanics/Geomechanics Symposium,1981:ARMA-81-0335.
[18] 刘小平,田延哲,曹晓毅,等. 多煤层开采条件下高陡山体变形控制[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2021,49(11):180−190. LIU Xiaoping,TIAN Yanzhe,CAO Xiaoyi,et al. Deformation control of high and steep mountain under condition of multi-coal mining[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2021,49(11):180−190.
[19] 郭文兵,邵强,石显怡. 水库坝体下厚煤层放顶煤协调开采技术[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2013,41(9):133−137. GUO Wenbing,SHAO Qiang,SHI Xianyi. Coordinated top coal caving mining technology of thick seam under reservoir dam[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2013,41(9):133−137.
[20] 戴华阳,阎跃观,刘存玉,等. 厚煤层协调全采沉陷控制技术及在村庄下采煤中的应用[J]. 煤炭学报,2023,48(12):4352−4364. DAI Huayang,YAN Yueguan,LIU Cunyu,et al. Subsidence control by coordinated full-area mining of thick coal seam and its application in mining under villages[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2023,48(12):4352−4364.
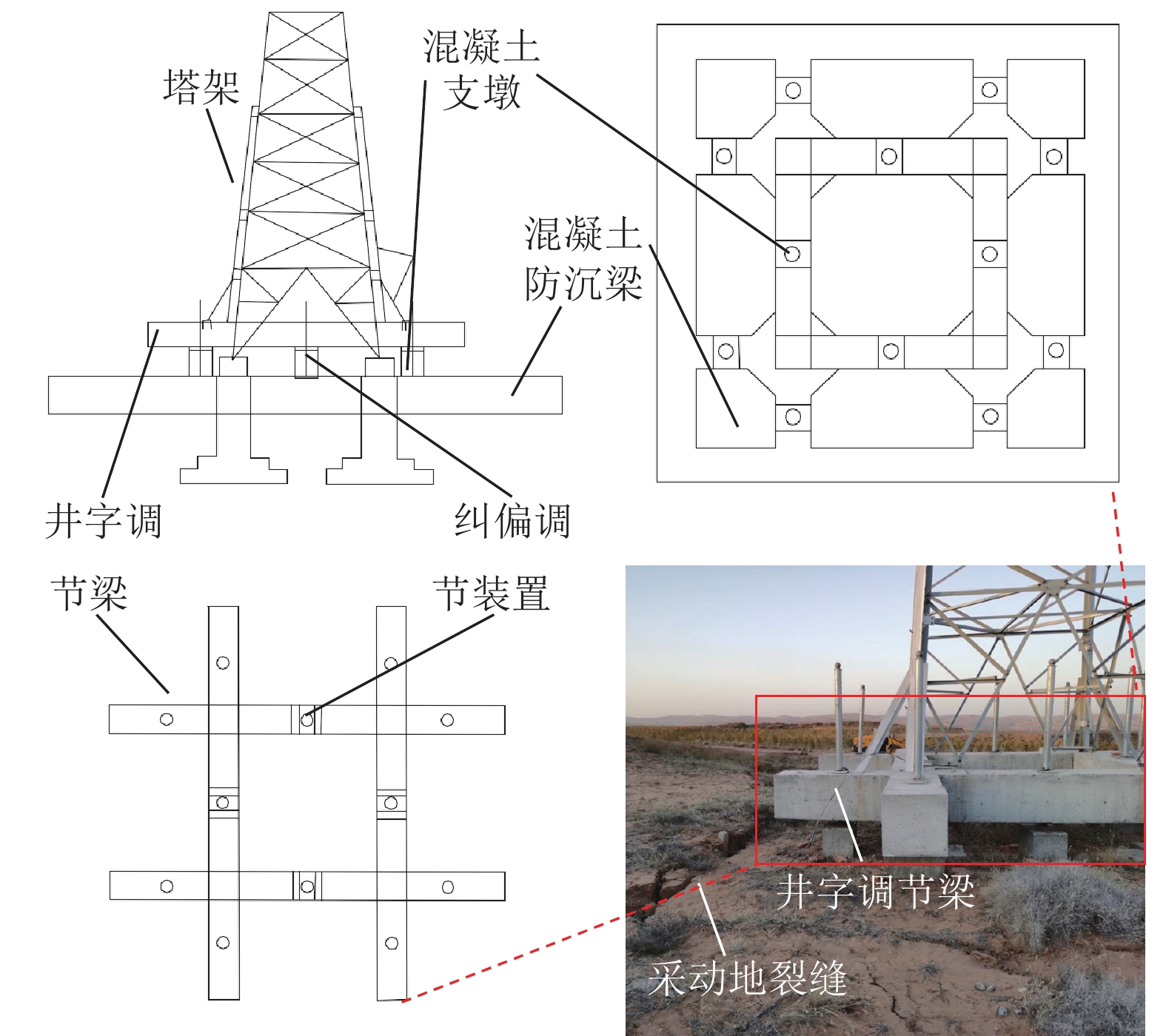
[21] 许家林,秦伟,轩大洋,等. 采动覆岩卸荷膨胀累积效应[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(1):35−43. XU Jialin,QIN Wei,XUAN Dayang,et al. Accumulative effect of overburden strata expansion induced by stress relief[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2020,45(1):35−43.
[22] 王志强,郭晓菲,高运,等. 华丰煤矿覆岩离层注浆减沉技术研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2014,33(S1):3249−3255. WANG Zhiqiang,GUO Xiaofei,GAO Yun,et al. Study of grouting technology of overburden-separation to reduce ground subsidence in Huafeng coal mine[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2014,33(S1):3249−3255.
[23] 郭文兵,吴东涛,郭明杰,等. “三软”厚煤层开采覆岩多层位离层注浆减沉技术及应用[J/OL]. 煤炭科学技术,1−12[2024−06−16]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2402.td.20240715.1210.004.html. GUO Wenbing,WU Dongtao,GUO Mingjie,et al. Multi-bed separation grouting in “three soft” thick coal seams mining and their application[J/OL]. Coal Science and Technology:1−12[2024−06−16]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2402.td.20240715.1210.004.html.
[24] 郭文兵,杨治国,詹鸣. “三软” 煤层开采沉陷规律及其应用[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2013. [25] 国家安全监管总局,国家煤矿安监局,国家能源局等. 建筑物、水体、铁路及主要井巷煤柱留设与压煤开采规范[M]. 北京:煤炭工业出版社,2017:51−52. [26] LI ZHao,LUO Zuijiang,XU Chenghua,et al. 3D fluid-solid full coupling numerical simulation of soil deformation induced by shield tunnelling[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology,2019,90:174−182. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2019.03.020
[27] 郭文兵,赵高博,杨伟强,等. 高耸构筑物采动变形特征与地基精准注浆加固机理[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(5):1908−1920. GUO Wenbing,ZHAO Gaobo,YANG Weiqiang,et al. Deformation characteristics of high-rise structures due to coal mining and their precise grouting reinforcement mechanisms[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(5):1908−1920.
[28] 郭文兵,王比比,杨伟强,等. 河流下多煤层开采安全性及保护技术[J]. 绿色矿山,2024(1):1−10. GUO Wenbing,WANG Bibi,YANG Weiqiang,et al. Safety and protection technology of multi-coal seam mining under river[J]. Journal of Green Mine,2024(1):1−10.
[29] 郭文兵,吴东涛,杨伟强,等. 兴运煤矿河流下厚煤层开采安全性分析和防控技术[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2024,41(2):305−314. GUO Wenbing,WU Dongtao,YANG Weiqiang,et al. Safety analysis and prevention and control technology of thick coal seam mining under river in Xingyun coal mine[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2024,41(2):305−314.
[30] 陈俊杰,郭文兵,邹友峰. 大型水体下顶水安全开采的可行性研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报,2011,21(2):57−62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2011.02.010 CHEN Junjie,GUO Wenbing,ZOU Youfeng. Feasibility study on safe mining under large-scale water bodies[J]. China Safety Science Journal,2011,21(2):57−62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2011.02.010
[31] 邢茂林,郑士田,石志远,等. 注浆改造厚含水砂层提高开采上限技术及应用[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2023,51(5):113−122. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.22.07.0583 XING Maolin,ZHENG Shitian,SHI Zhiyuan,et al. Technology of raising upper limit of mining by grouting reconstruction in thick water-bearing sand layer and its application[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2023,51(5):113−122. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.22.07.0583
[32] 徐智敏,陈天赐,李剑锋,等. 衰老矿区松散含水层下提高残煤资源开采上限研究[J]. 煤炭科技,2022,43(4):93−101. XU Zhimin,CHEN Tianci,LI Jianfeng,et al. Study on increasing mining upper limit of residual coal resources under loose aquifer in exhausted mining area[J]. Coal Science & Technology Magazine,2022,43(4):93−101.
[33] 郭文兵,白二虎,张璞,等. 新近系含水层下厚煤层综放安全绿色开采及水资源清洁利用[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(5):30−37. GUO Wenbing,BAI Erhu,ZHANG Pu,et al. Safe and green mining of thick coal seam under Neogene aquifer and clean utilization of water resources[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(5):30−37.
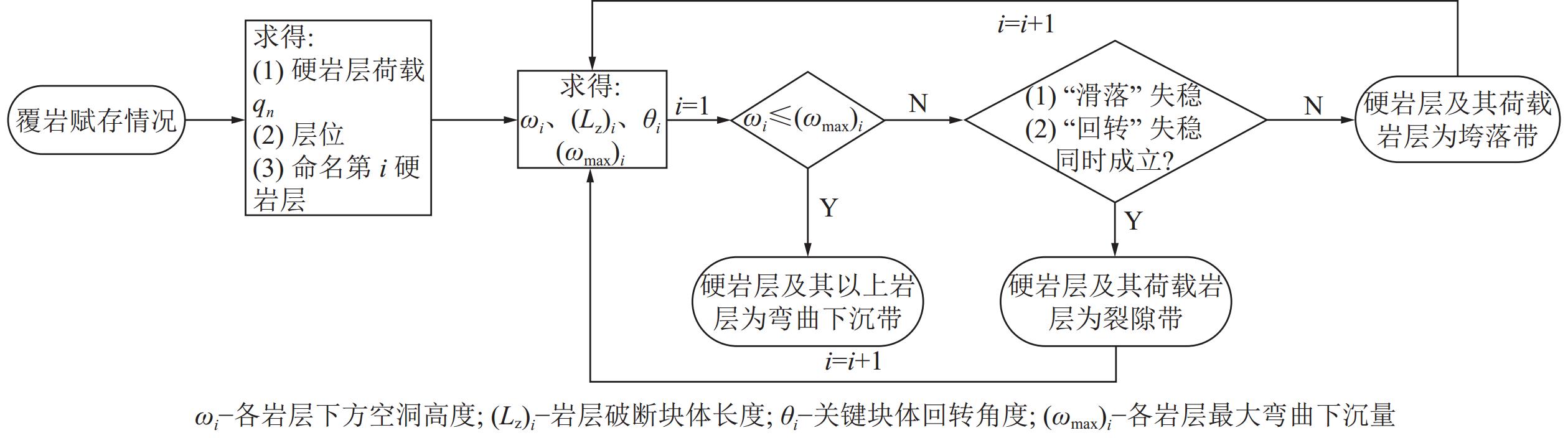
[34] 钱鸣高,石平五,许家林. 矿山压力与岩层控制[M]. 2版. 徐州:中国矿业大学出版社,2010. [35] 赵高博,郭文兵,杨达明,等. 综放开采覆岩破坏模型及导水裂隙带高度研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报,2017,27(11):144−149. ZHAO Gaobo,GUO Wenbing,YANG Daming,et al. Study on overburden failure models and height of water flowing fractured zone in fully mechanized caving mining[J]. China Safety Science Journal,2017,27(11):144−149.
[36] 许家林,朱卫兵,王晓振. 基于关键层位置的导水裂隙带高度预计方法[J]. 煤炭学报,2012,37(5):762−769. XU Jialin,ZHU Weibing,WANG Xiaozhen. New method to predict the height of fractured water-conducting zone by location of key strata[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2012,37(5):762−769.
[37] 张广超,陶广哲,孟祥军,等. 巨厚松散层下软弱覆岩破坏规律[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(11):3998−4010. ZHANG Guangchao,TAO Guangzhe,MENG Xiangjun,et al. Failure law of weak overburden stratum underlying extra-thick alluvium[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(11):3998−4010.
[38] 张玉军,高超. 急倾斜特厚煤层水平分层综放开采覆岩破坏特征[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2016,44(1):126−132. ZHANG Yujun,GAO Chao. Overburden rock failure features of steep thick seam horizontal slicing full- mechanized caving mining[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2016,44(1):126−132.
[39] 杨伟强,郭文兵,赵高博,等. 基于岩层挠曲变形的“竖三带” 理论判别方法及工程应用[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(10):42−50. YANG Weiqiang,GUO Wenbing,ZHAO Gaobo,et al. Theoretical judgement method of overburden “three-zone” based on rock strata deflection deformation and its engineering application[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(10):42−50.
[40] 李博,吴煌,李腾. 基于加权的综采导水裂隙带高度多元非线性回归预测方法研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2022,39(3):536−545. LI Bo,WU Huang,LI Teng. Height prediction of water-conducting fractured zone under fully mechanized mining based on weighted multivariate nonlinear regression[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2022,39(3):536−545.
[41] 范立民,马雄德,蒋泽泉,等. 保水采煤研究30年回顾与展望[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2019,47(7):1−30. FAN Limin,MA Xiongde,JIANG Zequan,et al. Review and thirty years prospect of research on water-preserved coal mining[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2019,47(7):1−30.
[42] 范立民,孙强,马立强,等. 论保水采煤技术体系[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2023,51(1):196−204. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.22.11.0865 FAN Limin,SUN Qiang,MA Liqiang,et al. Technological system of water-conserving coal mining[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2023,51(1):196−204. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.22.11.0865
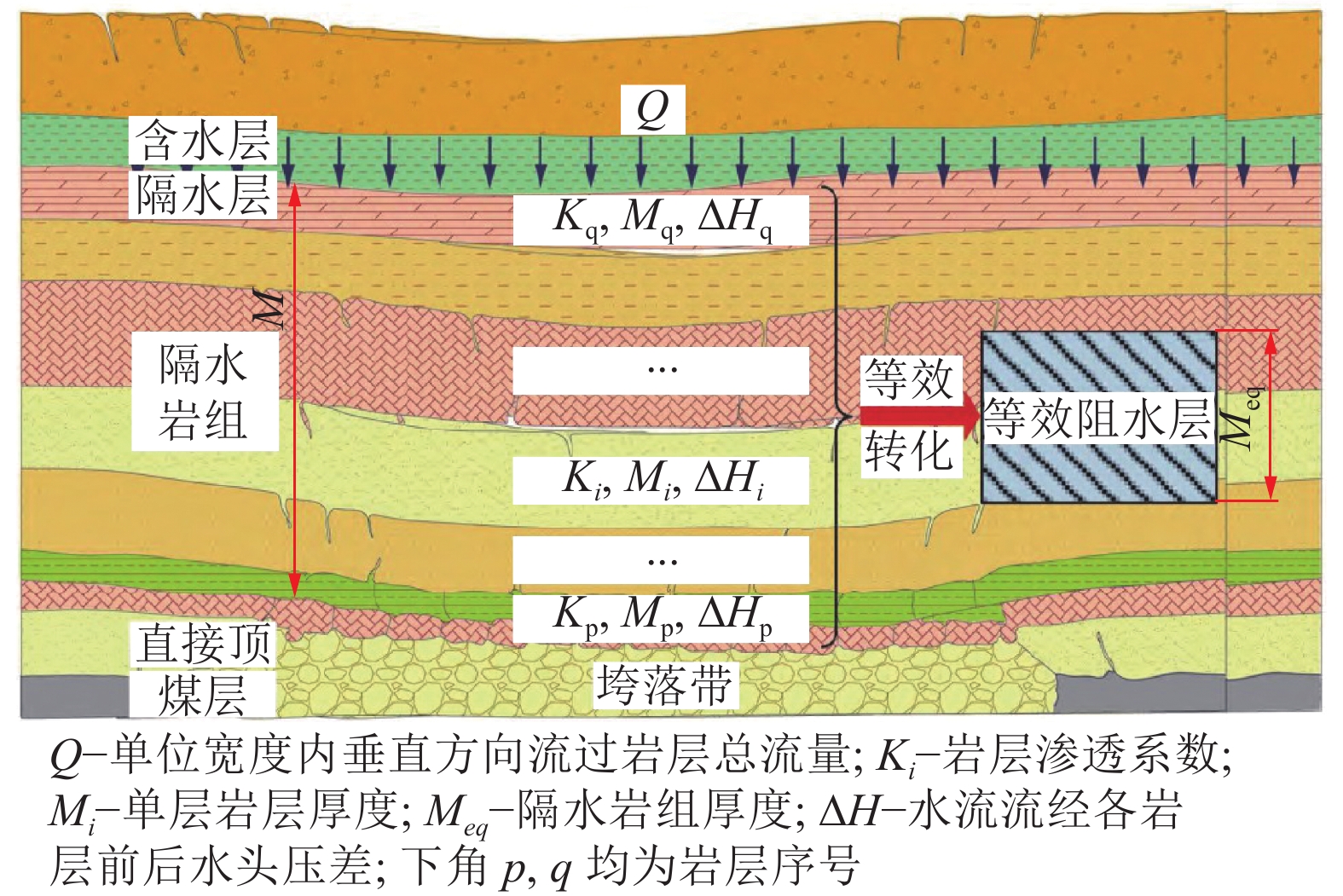
[43] 张东升,范钢伟,张世忠,等. 保水开采覆岩等效阻水厚度的内涵、算法与应用[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(1):128−136. ZHANG Dongsheng,FAN Gangwei,ZHANG Shizhong,et al. Equivalent water-resisting overburden thickness for water-conservation mining:conception,method and application[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(1):128−136.
[44] 刘贵,汪义龙,高超,等. 水库水体及坝体下多煤层开采可行性分析[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2020,48(10):185−191. LIU Gui,WANG Yilong,GAO Chao,et al. Feasibility analysis of multiple coal seams mining under reservoir and dam[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2020,48(10):185−191.
[45] 白二虎,郭文兵,张合兵,等. 黄河流域中上游煤-水协调开采的地下水原位保护技术[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(S2):907−914. BAI Erhu,GUO Wenbing,ZHANG Hebing,et al. In situ groundwater protection technology based on mining-conservation coordination in the middle and upper reaches of Yellow River Basin[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2021,46(S2):907−914.
[46] 邓念东,姚婷,尚慧,等. 铁路专线下综放开采地表沉陷规律[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2019,47(6):121−125,134. DENG Niandong,YAO Ting,SHANG Hui,et al. Surface subsidence law caused by fully mechanized caving mining under railway[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2019,47(6):121−125,134.
[47] 杨嘉威,谭志祥,邓喀中. 基于DS-InSAR的矿区铁路线沉陷监测与规律分析[J]. 煤炭工程,2021,53(9):143−148. YANG Jiawei,TAN Zhixiang,DENG Kazhong. Deformation monitoring and law analysis of railway in mining area based on DS-InSAR[J]. Coal Engineering,2021,53(9):143−148.
[48] 黄旭. 唐山矿铁路煤柱覆岩离层注浆减沉开采方案分析[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2009,37(2):25−28. HUANG Xu. Analysis on ground subsidence control mining plan with grouting in overburden separated strata above coal pillar under railway line in Tangshan Mine[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2009,37(2):25−28.
[49] 邓伟男,李强,王喜会,等. 采煤沉陷影响下高速公路路面损坏特征及应急措施[J]. 煤矿开采,2017(5):57−59,40. DENG Weinan,LI Qiang,WANG Xihui,et al. Study of emergence measure and expressway pavement distress characters under mining subsidence[J]. Coal Mining Technology,2017(5):57−59,40.
[50] 轩大洋,许家林. 铁路隧道下综放面覆岩隔离注浆充填开采试验研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2023,40(5):1102−1110. XUAN Dayang,XU Jialin. Field study of longwall fully-mechanized caving mining by overburden isolated grouting under a surface railway tunnel[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2023,40(5):1102−1110.
[51] 谭志祥,邓喀中. 采动区建筑物附加地基反力变化规律研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2007,32(9):907−911. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2007.09.003 TAN Zhixiang,DENG Kazhong. Study on change laws of additional ground reaction force of buildings in mining area[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2007,32(9):907−911. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2007.09.003
[52] 张凯,李全生,戴华阳,等. 矿区地表移动“空天地” 一体化监测技术研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2020,48(2):207−213. ZHANG Kai,LI Quansheng,DAI Huayang,et al. Research on integrated monitoring technology and practice of“space-sky-ground” on surface movement in mining area[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2020,48(2):207−213.
[53] 刘善军,吴立新,毛亚纯,等. 天−空−地协同的露天矿边坡智能监测技术及典型应用[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(6):2265−2276. LIU Shanjun,WU Lixin,MAO Yachun,et al. Spaceborne-airborne-ground collaborated intelligent monitoring on open-pit slope and its typical applications[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2020,45(6):2265−2276.
[54] 汤伏全,杨倩. 西部黄土高原矿区采煤沉陷多源遥感监测技术进展与展望[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2023,51(12):9−26. doi: 10.12438/cst.2023-1113 TANG Fuquan,YANG Qian. Progress and prospects of multi-source remote sensing monitoring technology for coal mining subsidence in mining areas of the western Loess Plateau[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2023,51(12):9−26. doi: 10.12438/cst.2023-1113
[55] YANG Y X,GAO W G,GUO S R,et al. Introduction to BeiDou-3 navigation satellite system[J]. Navigation,2019,66(1):7−18. doi: 10.1002/navi.291
[56] 郭文兵,赵高博,马志宝,等. 高耸构筑物采动损害与保护技术研究现状与展望[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2023,51(1):403−415. GUO Wenbing,ZHAO Gaobo,MA Zhibao,et al. Research status and prospect on mining damage characteristics and protective technology of high-rise structures[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2023,51(1):403−415.
[57] 徐乃忠,邓增兵,孙万明,等. 平朔矿区380kV高压输电线下特厚煤层开采技术[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2016,44(9):31−35. XU Naizhong,DENG Zengbing,SUN Wanming,et al. Mining technology of ultra thick seam under 380 kV high voltage line in Pingshuo Mining Area[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2016,44(9):31−35.
[58] 冯军,谭志祥,邓喀中. 采动地表倾斜变形对风力发电塔筒的影响研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2015,43(3):130−133,145. FENG Jun,TAN Zhixiang,DENG Kazhong. Study on surface inclined deformation affected to wind turbine tower silo[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2015,43(3):130−133,145.
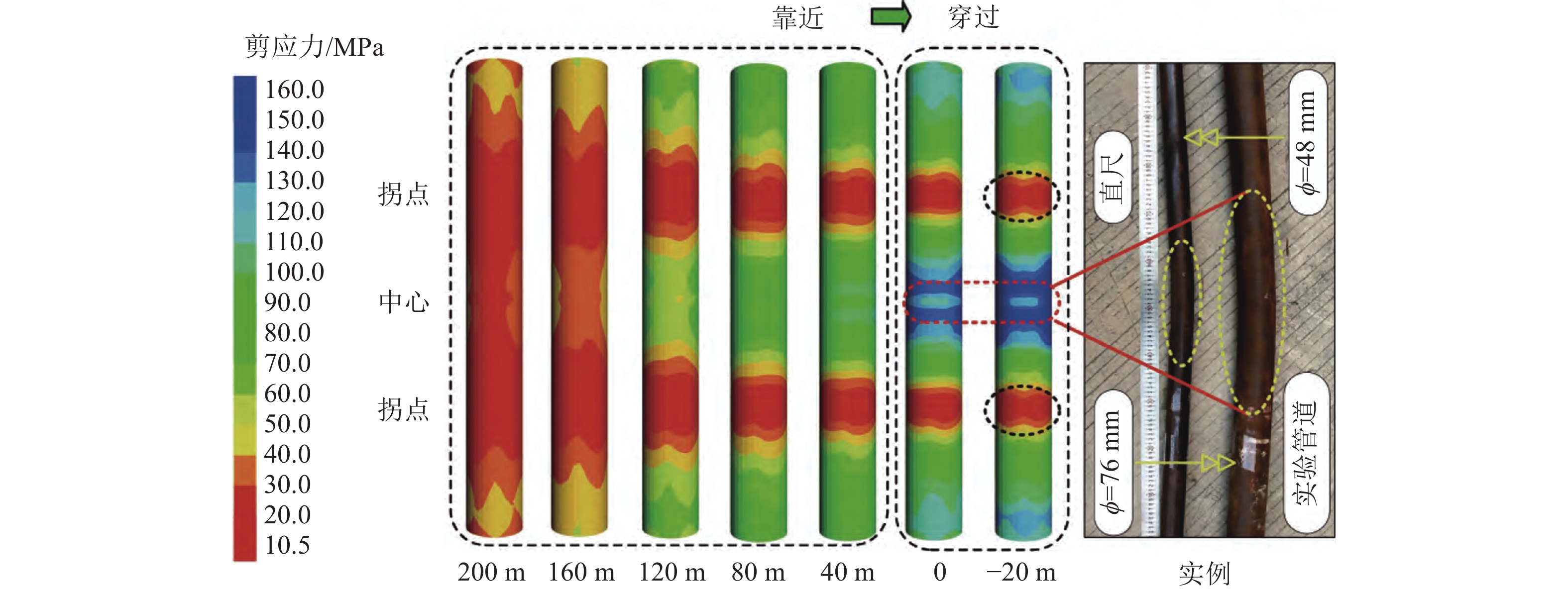
[59] 任建东,赵毅鑫,孙中博,等. 气煤叠置区高强度开采浅埋管道破坏时序规律研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2023,51(S2):152−164. REN Jiandong,ZHAO Yixin,SUN Zhongbo,et al. Study on time series rule of buried pipe failure under high-intensity coal mining in a gas-coal overlapping area[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2023,51(S2):152−164.
[60] 王晓霖,帅健,张建强. 开采沉陷区埋地管道力学反应分析[J]. 岩土力学,2011,32(11):3373−3378,3386. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2011.11.028 WANG Xiaolin,SHUAI Jian,ZHANG Jianqiang. Mechanical response analysis of buried pipeline crossing mining subsidence area[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2011,32(11):3373−3378,3386. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2011.11.028
[61] 张鹏,胡波,李虎,等. 不同穿越角度对采空区埋地管道力学行为的影响[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术,2020,16(5):82−88. ZHANG Peng,HU Bo,LI Hu,et al. Influence of different crossing angles on mechanical behavior of buried pipeline in goaf[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology,2020,16(5):82−88.



 下载:
下载: